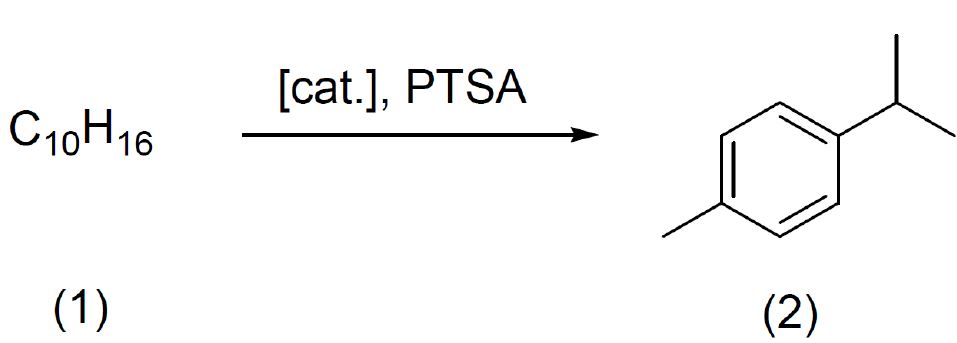
Universidad de Burgos
Technology Transfer Office
Hospital del Rey, s/n, 09001 Burgos, Spain · Spain | PlugAndTransfer
About Universidad de Burgos
0 followers
Research areas
Organization Website |
Organization Type
Technology Transfer Office
|
Founded
1994
|
Headquarters
Hospital del Rey, s/n, 09001 Burgos, Spain
|
Portfolio of Technology Offers (150)
(4)
Summary of the technology
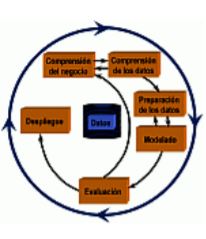
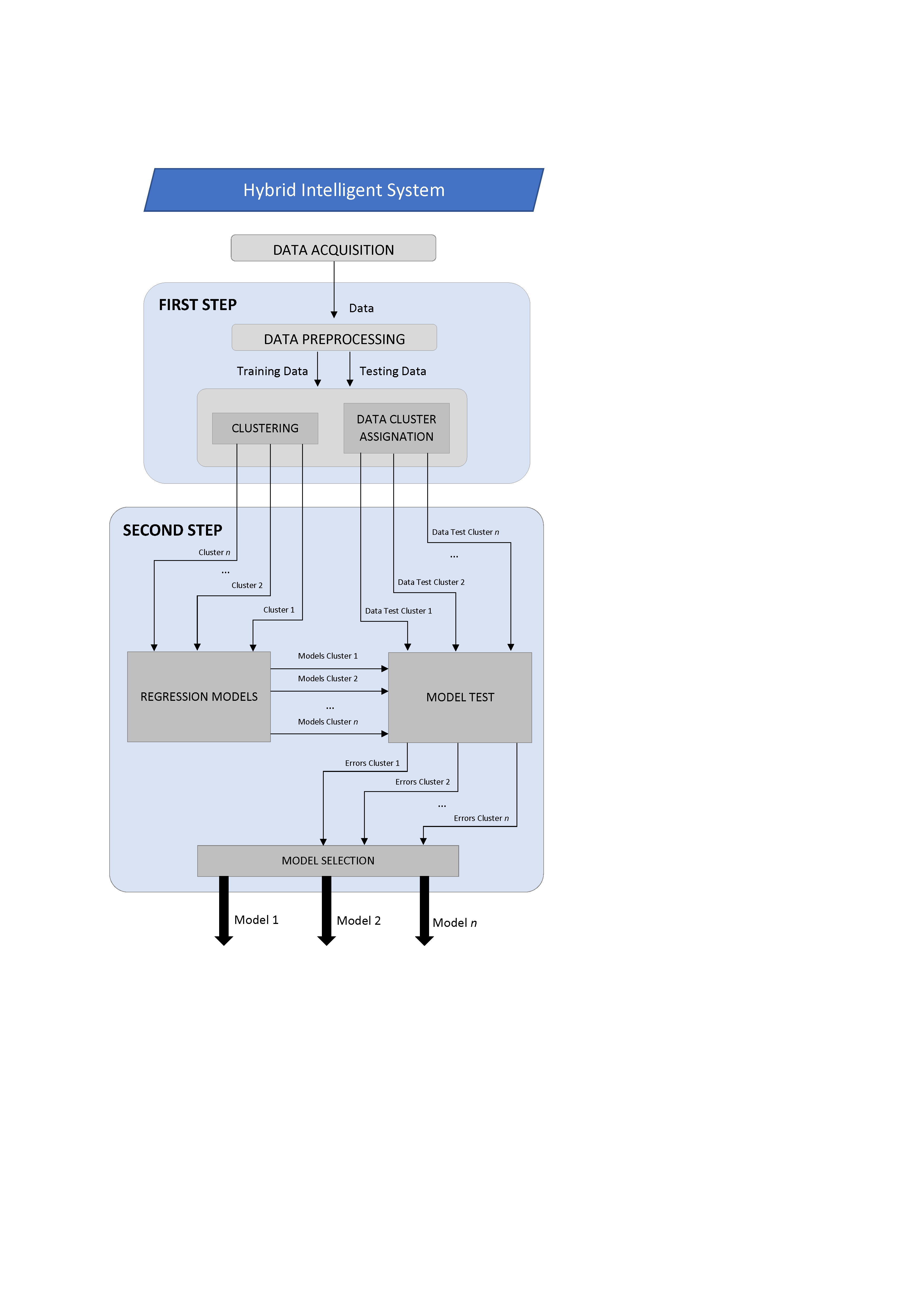
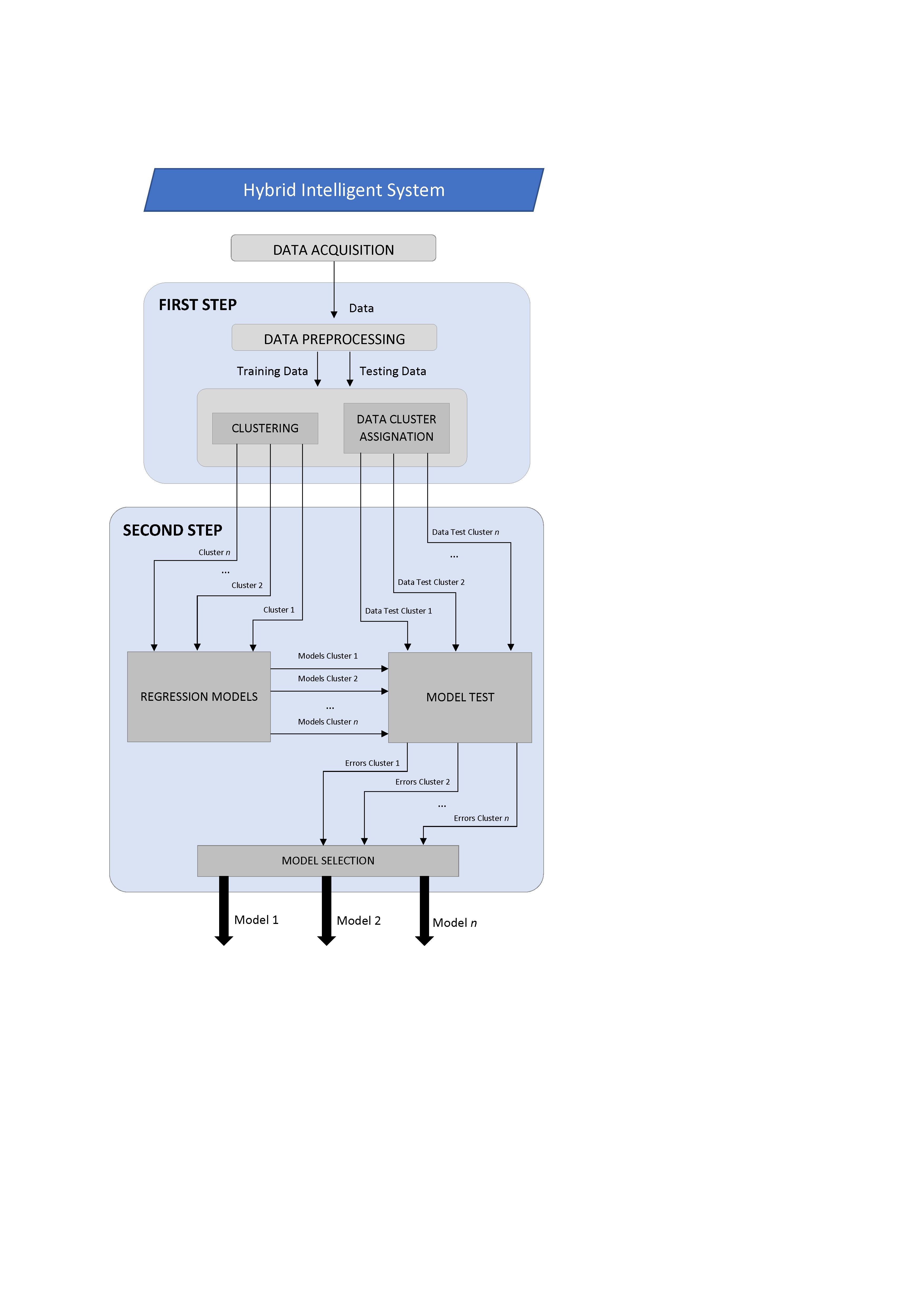
In supervised learning tasks, a data set is available, made up of several examples for which the values of certain variables are known and the aim is to obtain a model that relates the different variables with one of them, which is the one that is to be predicted . Depending on whether the variable to be predicted is nominal (or categorical) or numerical, we speak of classification or prediction. In the Rotation Forest method, predictions are obtained by voting on several decision trees or regression. It has been used successfully in very diverse applications.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
In various fields the method has demonstrated its robustness and good results, obtaining fewer errors in the prediction than the alternatives considered.
Main advantages of its use
Prediction, whether classification or regression, is useful in countless fields. Applications where the method has already been used include diagnosis industrial, medical diagnosis, bioinformatics, performance prediction (of industrial components, students ...)
Specifications
The proposed method is based on the techniques of combining models (ensembles). The models to be combined can be classification or regression models. In particular, in Rotation Forest the combined models are decision trees or regression. It is now accepted that better results are possible combining models than using a single model, both because of the theoretical properties of these combinations and because of the wide number of applications where they have been shown to be useful.
Applications
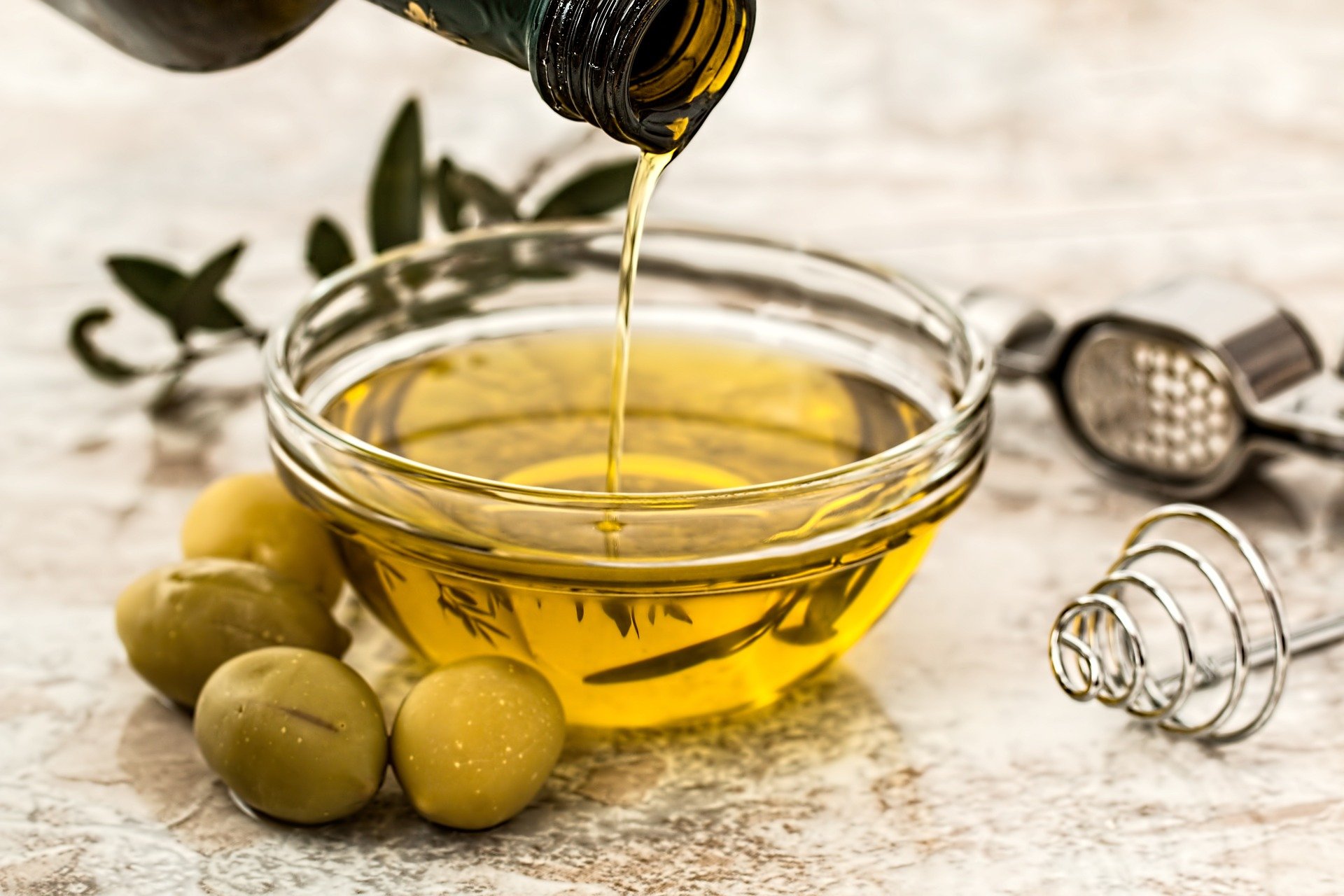
- Industrial diagnosis. The method has been used to monitor the quality of lubricating oils, since these degrade with use. To determine the relationships between soil properties and the deterioration of mechanical pipes. To establish the state of structures.
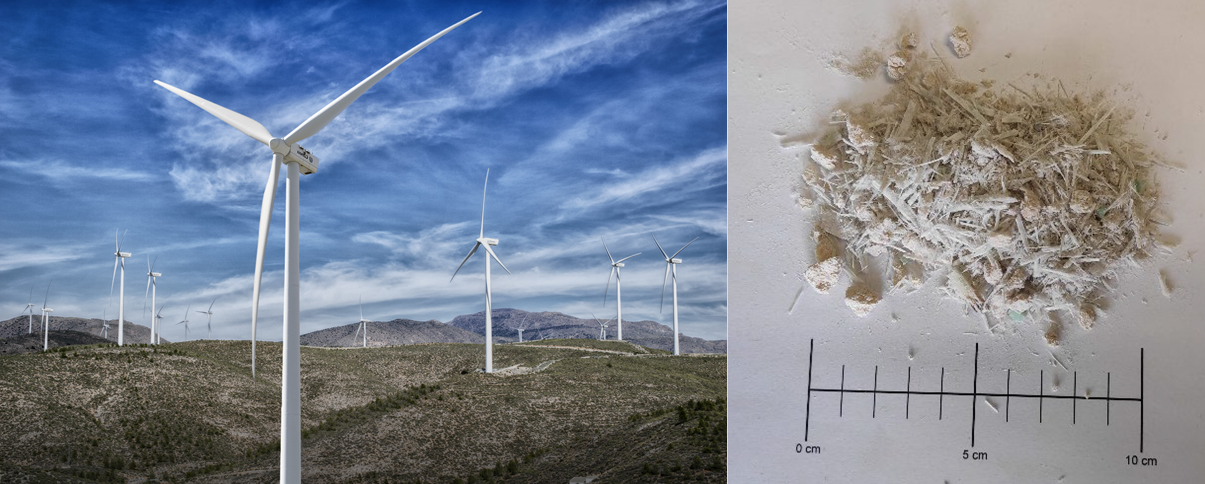
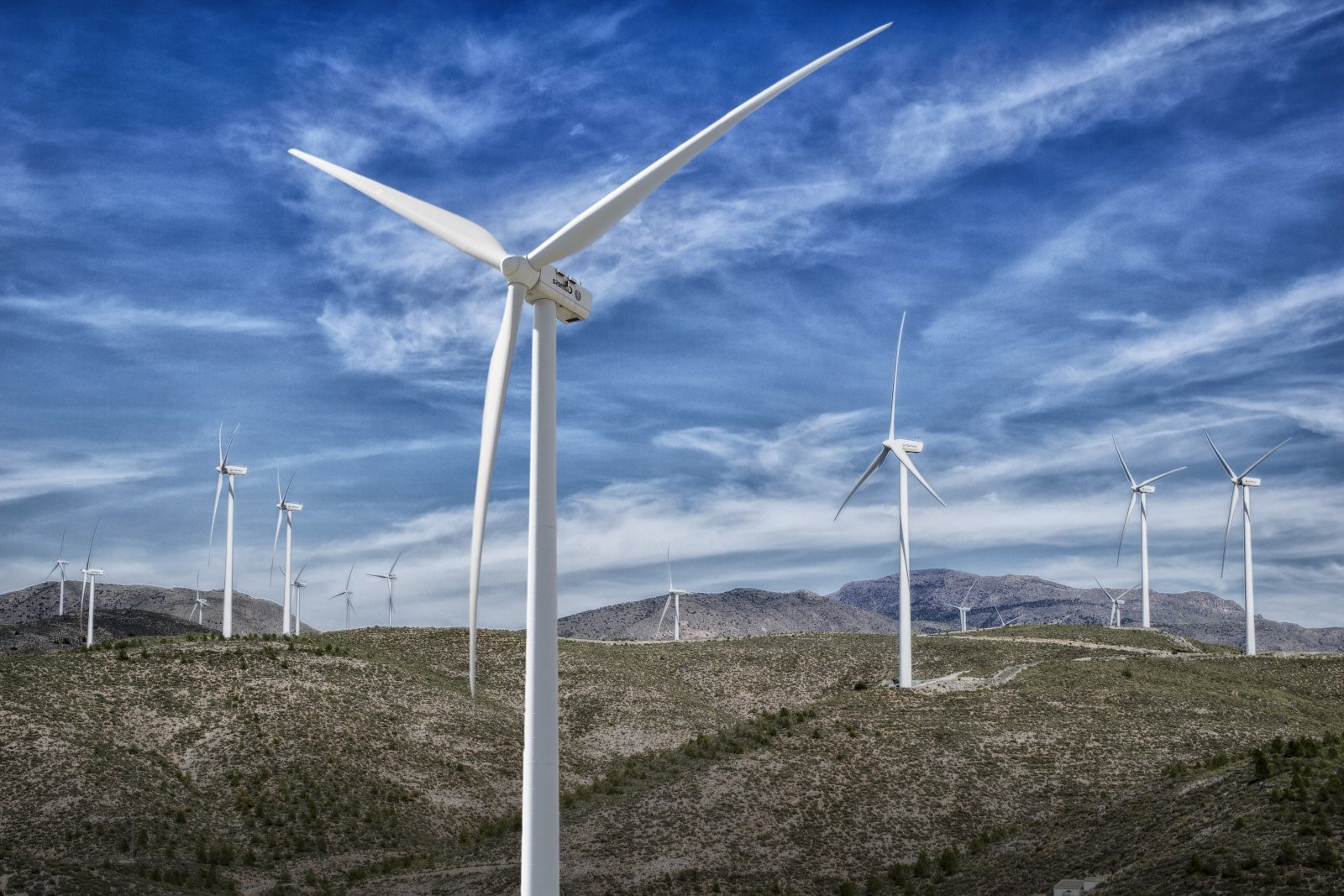
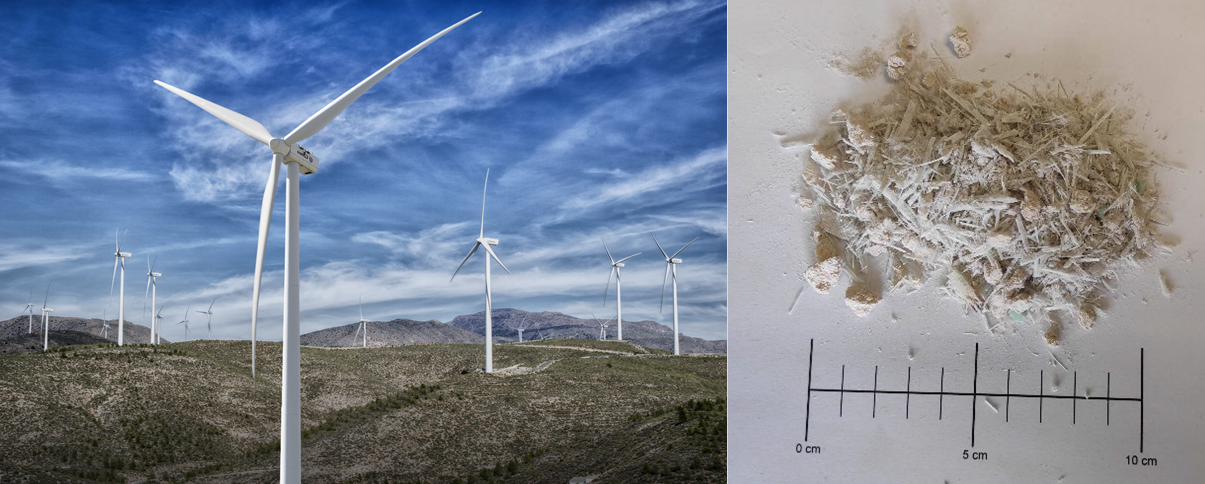
- Prediction of returns. The method has been used to predict the power generated by wind turbines.
- Medical diagnosis. The method has been used to analyze functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). These types of images are used to locate brain functions. Other applications are the diagnosis of erythematous squamous diseases or epilepsy. Also for the classification of cancer from microarrays.
- Bioinformatics. It has been used for the classification of genomic and proteomic data, for the annotation of promoter genes, for the prediction of the folding of proteins and interactions between them, prediction of molecular drug properties.
- Teaching. It has been used to identify students with learning difficulties.
- Financial. The method has been applied in predicting bankruptcies and customer risk; for municipal revenue predictio
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement for data processing and technical studies
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Training programs to develop technological innovations with a pedagogical structurefor its application in different social contexts to lifelong learningas a strategy for active aging and prevention of dependency.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
- Promotion of people's autonomy
- Prevention of dependency
- Taking advantage of time, lucidity and playful enjoyment of various learning
- Integration of motivational resources in individualized attention programs
- Monitoring systems on the use, adaptation and improvement of resources, with the direct participation of the user
- Connection with the current reality and the promotion of the use of ICT among the elderly
Main advantages of its use
Starting from the analysis of the specific needs of each group, planning objectives are set in the design of the training program and learning resources.It is taken as a motivating base from the knowledge, values and skills of the users, to have an adequate integration of the means used, to take advantage of the greatest possible simplicity and the playful values in its practical application by the users and to carry out a methodical monitoring of its effects and use to achieve continuous improvement in the quality of its processes and results.
Specifications
These are ICT applications and activities related to them based on knowledge of the realities and specific needs of their recipients.They are custom-built based on the precise situation to be addressed, counting, in any case, on a common pedagogical structure, so that they can be applied within specific training activities based on learning by doing active and participatory aging.
Applications
Companies, associations and public and private institutions, linked to the training, care, stimulation and / or residence of people belonging to the different groups of the elderly, under adaptation to their geographical and personal, mental and physical conditions, as well as activities own that said entities perform in the provision of their services. Including intervention programs "at a distance", for example, in the geographical area of the rural environment and its local development under the aspect of the participation of the elderly.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
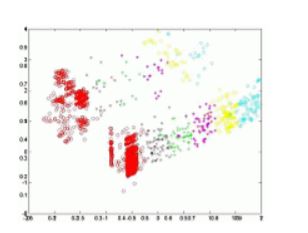
With the models developed by this group, the structure of high-dimensional data sets can be visualized first and subsequently analyzed. I mean, itallows a study of data for example with a large number of instances (examples) andalso a large number of variables for each of them.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
There are other data visualization methods, but most of them do not providea simple and intuitive way to identify the structure and analyze the behavior of thedata.
In this way, analysis times are reduced and preliminary results are obtained thatthey can guide later, more in-depth analyzes.
Main advantages of its use
By offering a projection that preserves most of the information in the data, maximizing the possibility of enhancing the structure of the data, a subsequent rapid analysis of the data is allowed. In the first place, the general structure of the data set can be identified, detecting their grouping (different types of customers, product groups, behavior of the analyzed machines, stages or regions of operation of the different processes ...). Once this general structure is known, it is possible to proceed to a detailed analysis of each of these groups, considering their internal structure. With all this, you can easily carry out an analysis of the data, drawing conclusions about them when interpreted by an expert in the field (factors that affect customer behavior, star products or with less success, optimal values adjustment of a certain machine, understanding of certain processes).
Specifications
Currently there is such a large amount of information that it cannot be easily processed to extract knowledge from it. An exhaustive analysis, on a case-by-case basis, would push the analysis of a large number of data that is captured today to unapproachable limits. These can refer to statistics of purchases of our clients, characteristics of different products, records of a certain machine or system, samples of a certain industrial process, etc. The projectionist models propose a data visualization with these characteristics; a large volume and also a high dimensionality (large amount of information for each of the customers, products, records, samples ...).
Applications
These models can be applied to any data set that needs to beanalyzed, regardless of the reality to which these data refer.Some application examples are those mentioned above: economic data, production data, operating or access statistics, etc.
Current development status
Device already developed and validated for industrialization.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Our technology meants to automate multi sensory rooms allowing the therapist to configure the sequence of activities beforehand. As a result the therapist is fully devoted to the patient. Our software allows the therapist to keep track of patient's evolution as well.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Flexible configuration of the activities in the room including the surrounding music, lighting control, etc. Patients database. Portable software to be used in any computer without installation.
Main advantages of its use
Cost, flexibility.
Specifications
It includes a hardware control card to be attached to a computer and a portable software application programme. Up to 8 stages can be included and easily configured.
Specifications
It includes a hardware control card to be attached to a computer and a portable software application programme. Up to 8 stages can be included and easily configured.
Current development status
In Use Testing Results Available
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Agriculture and Marine Resources (4)
Summary of the technology
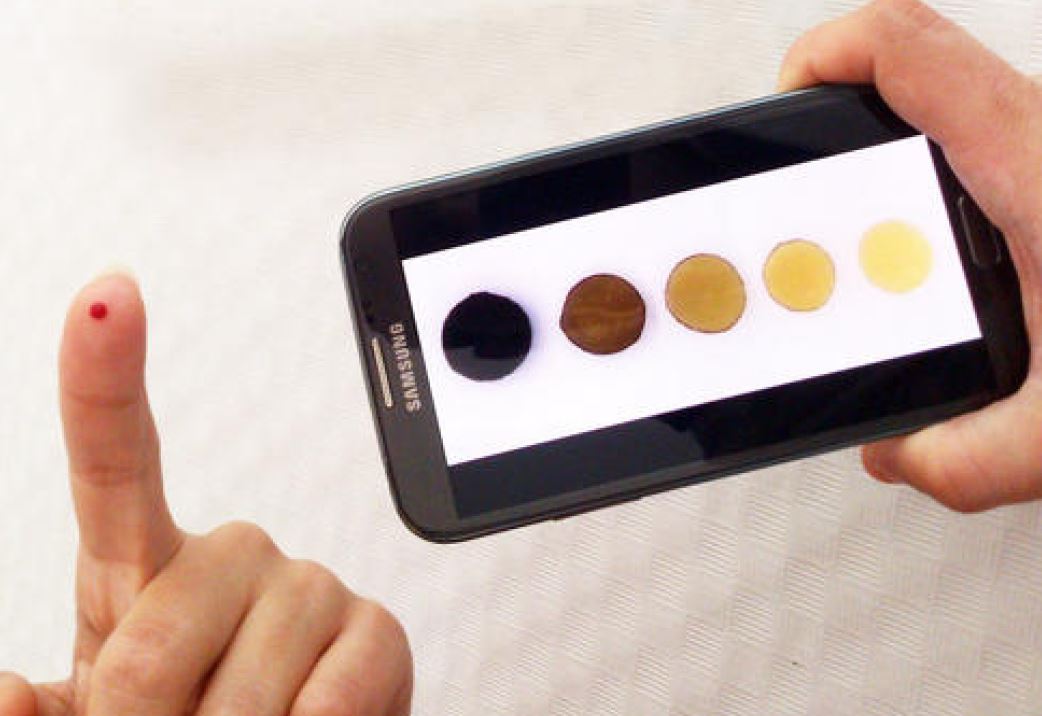
Researchers from the University of Burgos have developed a polymer that is capable of interacting with copper. In this context, it has been verified that, using this material, the concentration of copper in must samples can be determined quickly and easily.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Europe, led by Italy, France and Spain, is the world's largest producer and exporter of wine. This is due, in part, to the high quality of the final product and the high number of controls that are carried out. Among the latter, the measurements of pH, colour, biomolecules and metals stand out. Within this group is copper, and although it occurs in small quantities, this element is essential for proper fermentation of the must to take place. In this context, researchers from the University of Burgos have developed a polymeric material that is capable of interacting with copper and, through a simple photograph, provide both quickly easily the concentration of this metal.
It is important to control the levels of this element throughout the fermentation of the wine to avoid/detect the "cupric bankruptcy" that causes a decrease in the quality and safety of the wine for consumers.
Main advantages of its use
The reference method to determine the concentration of copper in wine and must samples is Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy or Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Compared to these methods, the developed material has a number of advantages:
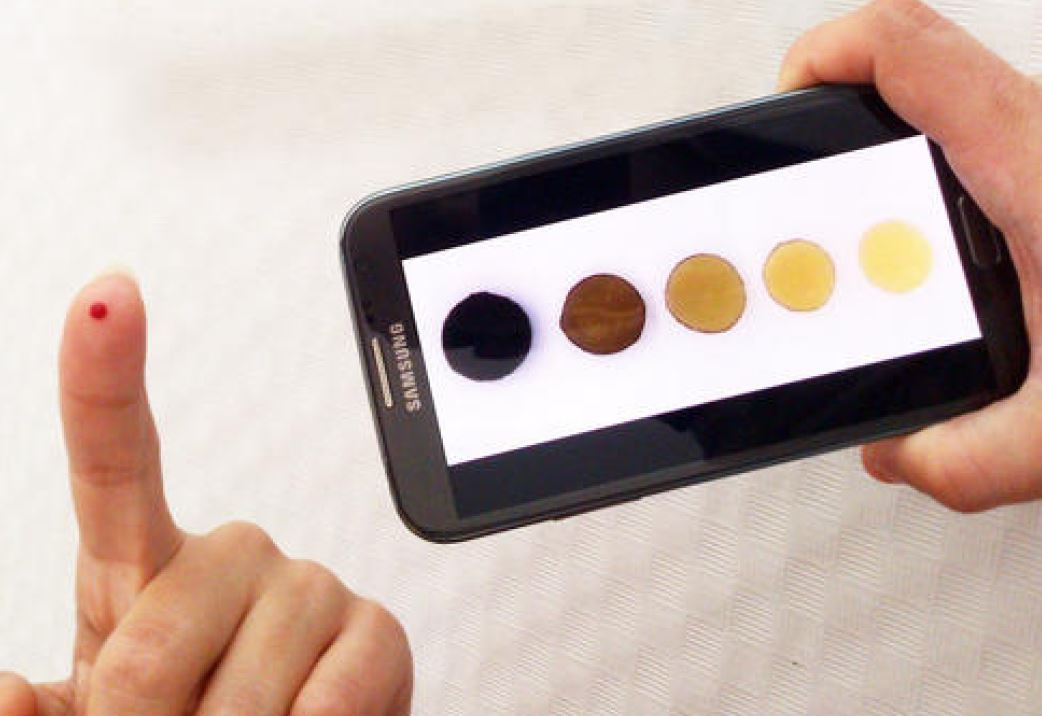
- The polymer, when interacting with copper, generates a colour change and the concentration value can be quantified by means of a photograph. This makes this method simple and does not require highly specialized personnel to carry out the measurement.
- The only necessary equipment is a smartphone to take the picture, while the equipment for reference techniques is extraordinarily expensive.
Specifications
The polymer was prepared by radical reaction starting from the previously functionalized monomer. The material was synthesized in the form of a film, and it was verified that it generates a colorimetric response in the presence of copper (I).
Tests carried out in the laboratory allowed us to determine that the detection limit is 0.08 ppm. The measurement procedure is as follows:
- The film is introduced into the sample together with pH 5 buffer.
- After 12 hours, the film is removed and washed with water.
- A photograph is taken together with a colour chart and, through the mobile application registered by this same Colorimetric Titration group, the corresponding concentration value is obtained.
Applications
The measurement material and method have proven to be suitable for determining copper levels in wine musts. The measurement is faster, cheaper and does not require specialized equipment.
Intellectual property status
Protected by a patent P202231015
Current development status
Research or Experimental
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Researchers at the University of Burgos are developing a technology of microencapsulation of proteolitic enzymes that reduces time cheese maturation process, maintaining their organoleptic characteristics.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Application of microencapsulation to control the function and action of the enzymes involved in cheese ripening and shorten processing times.
The addition of encapsulated enzymes eliminates the problems associated with the direct addition (loss of enzyme in serum, bad distribution, reduced performance and quality alteration cheese) allowing a gradual and control action, reducing time maturation and therefore giving a quicker exit of the product to market.
Main advantages of its use
Application of microencapsulation to control the function and action of the enzymes involved in cheese ripening and shorten processing times. The addition of encapsulated enzymes eliminates the problems associated with the direct addition (loss of enzyme in serum, bad distribution, reduced performance and quality alteration cheese) allowing a gradual and control action, reducing time maturation and therefore giving a quicker exit of the product to market.
Specifications
The cheese maturation process represents an important percentage of the total costs related to the cheese production. In order to reduce these costs, there have been numerous attempts to accelerate the process without taste or texture detriment (temperature rise of maturation, increasing population of starters and addition of exogenous enzymes ...). The initial success of the enzyme treatments is reduced both by the loss of the enzyme in the serum and early changes of aroma and flavor. In this respect, the technology of immobilized enzymes has been proposed as a tool which can overcome these difficulties. It aims to optimize the conditions of detention of proteases and lipases by microencapsulation in different supports and to investigate the effect of encapsulated enzymes on cheese maturation process.
Applications
This technique is aimed at the Food sector, especially for those cheese producing companies.
Relación comercial deseada
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Test kit for both qualitative and quantitative detection of different types of tertiary amines in situ.
Detection of tertiary amines is very important as they are classified in several occasions as toxic analytes and/or contaminants.
Among the tertiary amines capable of being detected by the developed method it is possible to include: pyrrolizidines, tropane alkaloids (scopolamine, atropine and cocaine), Opiates (Morphine, Codeine, Heroin).
New and innovative aspects
The main innovation is that the illumination of certain halogenated reagents in the presence of these amines causes intense fluorescence that is detectable by a spectrofluorometer, whose emission intensity correlates with the concentration of the tertiary amines.
Another important aspect is that the detection of tertiary amines are possible regardless of the origin of the samples (urine, blood, serum ..). On the other hand, this method allows drug discrimination working in a wide range of concentrations, without interfering with other drugs or with no tertiary amines, avoiding extraction techniques and complex separation.
Main advantages of its use
- Analytical Kit portable for measurements in situ
- Not specialized personnel required
- High sensitivity detection and quantification
- Determines a variety of pollutants or toxic substances (tertiary amines)
- More economic method in relation to the techniques used at present
Specifications
Method for determination through emitted fluorescence by tertiary amines in aqueous samples and using reactive halogenated xanthenes based pigments, when they are illuminated by a halogen lamp.
Applications
The kit or device can be used, among others, for the detection of substances of interest such as for instance drug quantitation as opiates and derivatives thereof, being possible to use, therefore, for the detection and quantification of heroin.
Other areas of interest are:
- Food Scope: Detection and identification and quantification of toxic or polluting substances.
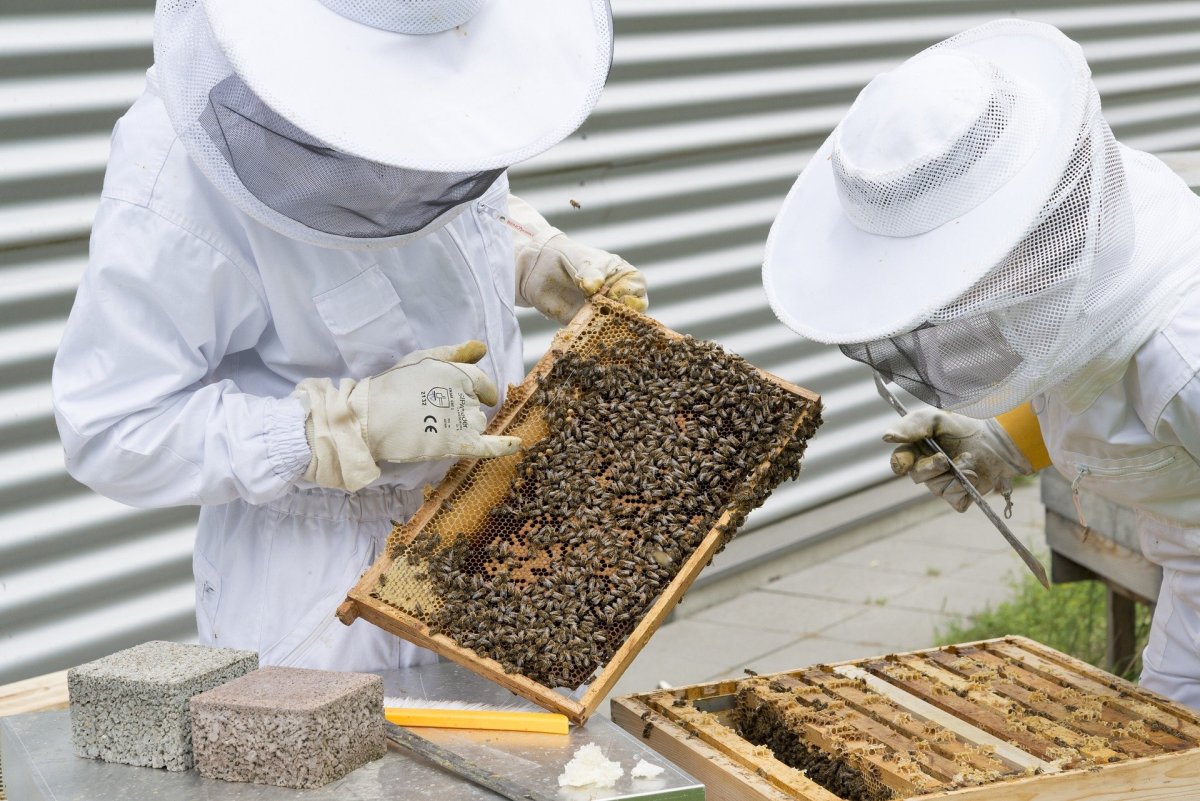
- Agricultural field (agricultural subsectors, farmer and beekeeper): food safety controls for animals and humans.
- Medical field: emergency diagnostics in hospitals, detox centers controls, etc.
- Cosmetic Scope: Detection of toxic substances in cosmetic industry.
- Traffic Safety Scope: prevention of drug use, security control of the road network
- Legal Scope: control drug trafficking or illegal drug abuse.
Intellectual property status
Protected by PCT/ES2017/070034
Current development status
Kit avalaible for testing.
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement, License agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Kit de análisis para la detección tanto cualitativa como cuantitativa de diferentes tipos de aminas terciarias in situ.
La importancia en la detección de aminas terciarias radica en que son clasificadas en muchas ocasiones como analitos tóxicos y/o contaminantes.
Entre las aminas terciarias capaces de ser detectadas por el método desarrollado se encuentran: Pirrolizidinas, Alcaloides Tropánicos (Escopolamina, Atropina y Cocaína), Opiáceos (Morfina, Codeína, Heroína).
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La principal innovación es el hecho de que la iluminación de ciertos reactivos halogenados en presencia de estas aminas provoca una fluorescencia intensa que es detectable mediante un espectrofluorímetro, cuya intensidad de emisión se correlaciona con la concentración de las aminas terciarias.
Otro aspecto importante es que se posibilita la detección de aminas terciarias independientemente de la procedencia de las muestras (orina, saliva, sangre, suero..). Por otro lado permite la discriminación de drogas operando en un amplio rango de concentraciones, sin interferir con otras drogas o con aminas no terciarias, evitando técnicas de extracción y separación complejas.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Kit analítico portátil para realizar medidas in situ.
- No requiere personal especializado.
- Alta sensibilidad a la detección y cuantificación.
- Permite determinar una gran variedad de contaminantes o sustancias tóxicas (aminas terciarias).
- Método más económico en relación a las técnicas utilizadas en la actualidad.
Características técnicas
Método para la determinación por fluorescencia emitida de aminas terciarias en muestras acuosas a través de reactivos que utilizan pigmentos basados en xantenos halogenados, cuando estos son iluminados por una lámpara halógena.
Aplicaciones
El kit o dispositivo se puede emplear, entre otras, para la detección de sustancias de interés como por ejemplo en la cuantificación de drogas como opiáceos y sus derivados, pudiéndose emplear, por tanto, para la detección y cuantificación de heroína.
Otros ámbitos de interés serían:
- Ámbito Alimentario: detección e identificación y cuantificación de sustancias tóxicas o contaminantes.
- Ámbito Agropecuario (subsectores agrícola, ganadero y apicultor): controles de seguridad alimentaria para animales y humanos.
- Ámbito Médico: diagnósticos de urgencia en centros hospitalarios, controles en centros de desintoxicación, etc.
- Ámbito Cosmético: detección de sustancias tóxicas en industria cosmética.
- Ámbito Seguridad Vial: prevención de consumo de estupefacientes, control de la seguridad de la red viaria.
- Ámbito Legal: control de tráfico de estupefacientes o drogas de abuso ilegales.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegido mediante PCT/ES2017/070034
Estado actual de desarrollo
Kit disponible para testar.
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Agrofood Industry (5)
Summary of the technology
Researchers at the University of Burgos are developing a technology of immobilization of enzymes that reduces bitterness in citrus juices.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Conventional methods, to reduce the bitterness in citrus juices, involve not only the removal of the bitter compounds (naringin and limonin), but also bioactive components (organic acids, flavonoids, limonoids…) from the juice. In this regard, biotechnological methods, either isolated enzymes or whole cells, are an interesting alternative way to remove bitterness, without affecting the nutritional and healthy properties
(antioxidants…) of the processed juice. Furthermore, the technology of enzyme immobilization onto or into solid supports improves catalytic activity and resistance to denaturation, and the possibility of enzyme separation from reaction mixtures and/or the reuse and the ability to operate continuously.
Main advantages of its use
The use of soluble enzymes in citrus juice processing presents several advantages as such reaction specificity, mild operating conditions and without contaminant effects (green technology). Nevertheless, in spite of the unquestionable advantages, there exist a number of practical problems in the use of soluble enzymes in such as their inactivation at the acidic pH conditions or their high cost. Immobilizing the enzyme on solid supports allows the modification of its catalytic properties, higher stability, prevention of contamination of the processed product, the reuse of catalytic activity, and the possibility of processing in continuous.
Specifications
Enzymes can be immobilized on various supports (ionic exchangers, polymers…) either by physical adsorption, covalent binding or entrapment.
Immobilization of enzymes is known to offer several advantages such as ease of separation from a reaction mixture and repeated use in continuous processes, enabling greater control over catalytic processes and process economics. Moreover, the use of an immobilized enzyme permits to greatly simplify the design of the reactor and the control of the reaction.
Applications
This technique is aimed at the Food sector, especially for those juice manufacturers.
Current development status
Device already developed and validated for industrialization.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Researchers at the University of Burgos have developed a technology of immobilization of glucose-oxidase that reduces the amount of glucose available in the must for reducing the alcohol content in wine.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Technological processes that are used to eliminate or reduce alcohol in wine require intensive practices and equipment that are not available to all wineries. As a generalisation, these processes tend to involve expensive equipment and the sensory quality of the wine is not always satisfactory. An alternative biotechnological approach is to use glucose oxidase (GOX) immobilized in solid support. The enzyme immobilization technique allows manipulation of the characteristics of enzyme catalysis and becoming active at the acidic pH of must. Furthermore, the operational stability of the enzymes is improved, as well as reuse and the ability to operate continuously.
Main advantages of its use
The use of soluble enzymes in wine processing presents several advantages as such reaction specificity, mild operating conditions and without contaminant effects (green technology). Nevertheless, in spite of the unquestionable advantages, there exist a number of practical problems in the use of soluble glucose-oxidase in the must such as their inactivation at the acidic pH conditions or their high cost. Immobilizing the enzyme on solid supports allows the modification of its catalytic properties (optimum pH), higher stability, prevention of contamination of the processed product, the reuse of catalytic activity, and the possibility of processing in continuous.
Specifications
The wine industry has developed and evaluated different strategies to reduce the ethanol content in wine mantaining a good quality of the final product. An biotechnological alternative is the treatment of must with glucose oxidase to reduce its fermentable sugar content, thereby reducing the ethanol content in the final product of fermentation without altering its quality parameters. However, the activity of the glucose-oxidase is reduced to the wort pH values. In this sense, it is developping the preparation of immobilized glucose oxidase active and stable to acidic pH values, with good operational stability, as well as with favorable mechanical and chemical properties that allow their reuse, and its application in winemaking low alcohol content.
Applications
This technique is aimed at the Food sector, especially for those wine producing companies.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
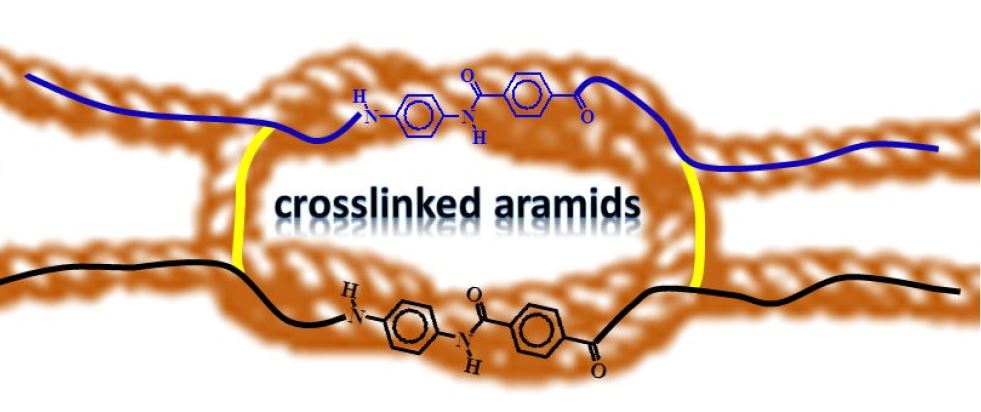
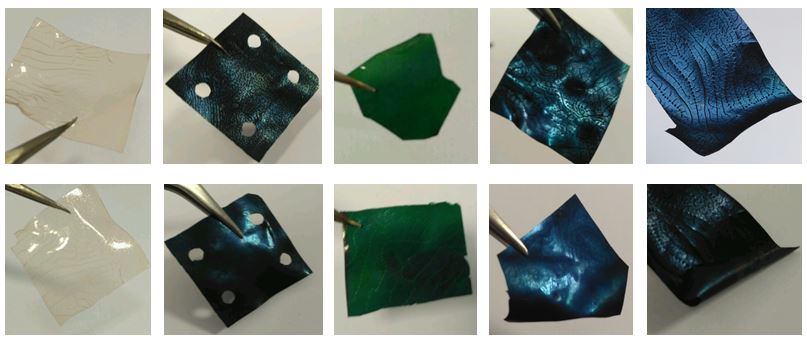
Polimeric film that acts as a colorimetric film for iron in acqueus media. Presence or lack of iron currently appears in several problems / issues such as legionella´s growth at air conditioning cooling towers. Furthermore, it causes iron chlorosis on fruit and wine trees and it can be transferred to the drinking water if is not controlled at the purifying plants.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Smart material is designed to save costs and time on reagents, lab material and personnel. The material allows not only qualitative but quantitative detection as well. This quantification can be obtained by means of conventional spectrophotometry equipment or by RGB parametres calibration on a digital picture of the membrane.
Main advantages of its use
- Qualitative and quantitative analysis "IN SITU "
- Change easily distinguishable color- Can be used by non-qualified personnel and under all weather conditions (as long as the water is going to analyze liquid )
- No cables or batteries required
- Allows a quick glance analysis- Avoid the use of equipment spectrometry expensive
- No reagents required for analysis
- As an organic polymer expiry date of the product is superior to 100 years
- Easily transported in an envelope, briefcase or without test kit
- Direct measurement without additional equipment
- Acts as detector of iron, aluminum and mercury separately. In the presence of iron changes to dark green in the presence of mercury switch to deep orange, and in the presence of aluminum becomes fluorescent-Behavior gel. Swelling in water, thus allowing the detection of the elements present in the medium in which it is immersed .
- High selectivity towards iron. The attraction with iron is very strong (K = 1040 , which can detect free iron and iron complexed in the case of wine and blood serum .
- Can be stored anywhere that does not involve some extreme environmental conditions- Does not require the use of protective measures ( gloves, goggles, etc. )
Specifications
Polymer membrane film based on two commercial biocompatible monomers polymerization, one sensor monomer and one crosslinking.The film presents an almost incolore feature. When submerged on acqueus iron media, the film abruptly changes to a dark green. If the media is contaminated with mercury of aluminum the film changes to an orange colour or fluorescent respectively. Additionally to this, it maintains excellent mechanical properties both dry and wet.
Applications
1. Cooling towers / evaporative condensers . Legionella . Legionella is a bacterium that produces significant health problems, even death, to those individuals who have their infection. The main point of growth of these bacteria in cooling systems and in particular industrial and humidification. This requires monitoring the presence of iron in these systems since an excess helps the grow1th / o2f the bacteria.
2. Sowing Fruit and Vine. Iron chlorosis . Iron chlorosis is a disease that affects the leaves due to iron deficiency in the soil for
planting. With a simple measurement can control their soils are rich in iron can even know what soil is suitable for planting.
3. EDAR and ETAP . Anticoagulants Iron and Aluminum . In sewage treatment plants and sewage treatment plants for drinking water are used daily and in large quantities based coagulants salts of iron and aluminum. Therefore, there is a real risk of contamination of water by these metals. This risk can be eliminated by our detector film, and when we would know if they are contaminated.
4. Industrial / process piping construction . Corrosion . In all systems containing iron pipes there is a danger that corrosion occurs and pollutes the water flowing through these circuits. The formation of these rusts causes problems in industrial processes that depend directly on the water supplied by these pathways. Similarly boiler systems or flow in this type of water eventually wear is stored so that the pipes have to be replaced.
Intellectual property status
Patented for the University of Burgos. P201300575.
Current development status
Working Prototype or Samples Ready for Testing
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Totally natural product derived from masses of vinification, seasoning with a high power allowing to reduce levels of salt from processed foods and making healthier (suitable for hypertensive population). It also has a preservative effect, reducing / eliminating the use of preservatives (egsulfites). The product is applicable throughout the food industry as well as the restaurant industry.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
New and Innovative aspects: the product is obtained for minimal processing of the masses of vinification, it is not an extract, therefore, is a natural product that in addition to seasoning and preservative, it is multiple source of bioactive compounds in grapes as are polyphenols, fiber, potassium and other minerals.
Main advantages of its use
The product has a value "per se" because it is 100% "natural", obtained by minimal processing with low power consumption and virtually no water, helps reduce carbon footprint of wine production, reduce waste and thus increase the profitability of the process. Adds value to products through additional bioactive components and rich in potassium.
Specifications
Natural preservative and common salt substitute with "functional" properties.
Applications
Food industry in general, especially those that need to reduce salt levels in their products without losing stability or endanger conservation. In addition, the product is suitable for being applied in restaurants, in the preparation of dishes, tapas, etc. Possible limitation: products that allow the incorporation of "colored" solid products.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P201300555
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Food-use collagen obtaining through pigskin degreasing using compressed carbon dioxide (yields above 90%). The method does not alter the nature of the protein contained in the skin and uses a safe solvent (CO2) in order to obtain a suitable feedstock.
New and innovative aspects
The nature of the protein in skin is not altered by using extraction solvent (CO2).
Met yields above 90% (in other inventions the yield can not reach values higher than 60%).
Diversification of the raw material from which the collagen is obtained for food use (usually cowhide).
Main advantages of its use
Revaluation of a product (pig skin) of little value in the meat industry.
Increased yields in the production of collagen free of acid wastes, making it usable for food use.
Getting purer product without residual fat difficult to treat.
Generating new byproducts of easy commercialization.
Specifications
In this treatment, mechanical procedures are used in order to remove the fat from the pig skin (hypodermis and dermis). Both the dermis and the hypodermis, that is not mechanically removed, are subjected to an extraction with carbon dioxide under supercritical conditions, in which rapid decompression extractor are made. This rapid decompression is followed by and compression and circulation of solvent to extract the fat which has become accessible. With successive compressions and decompressions the amount of fat and water from the pigskin is minimized, up to 1% of fat on a dry basis, therefore admissible for the processing of the skin and its transformation into collagen for food use.
Applications
It is aimed at companies in the meat sector, which currently are managing pig skins as waste, as low-value food product, or shed fat by conventional solvents for subsequent use of the collagen. In such conventional systems the fat content generated in the collagen is very high which makes difficult to manage / removal and thus has a significant cost. The use of alternative fat removal techniques allows companies to increase yields in the subsequent generation collagen without further fat wastes in a very significant way.
Cosmetic is other application sector. These products (collagen) application in cosmetics would involve a higher value of the product due the green properties, favouring its introduction in the market. The market would benefit from higher yields, with a purer product, fat-free hard waste management or treatment, at competitive costs.
Intellectual property status
Patent P200400390.
Current development status
Samples ready for testing.
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Biological Sciences (20)
Summary of the technology
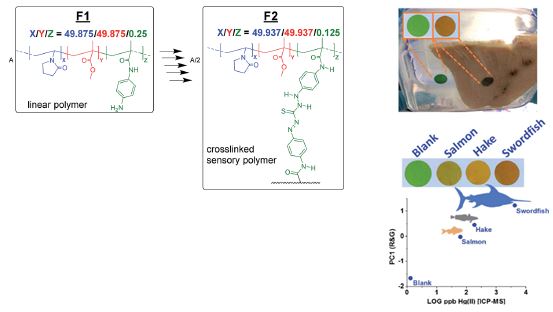
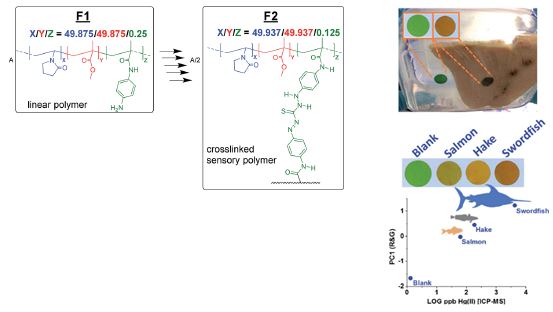
The invention describes a method for synthesizing a bifunctional copolymer designed for the detection and removal of specific anions, such as nitrates, in drinking water. This material can be easily regenerated, allowing for repeated use over time and resulting in cost savings. Additionally, the copolymer synthesis does not require polymers or organic solvents, making the process more eco-friendly and efficient. Its effectiveness in purification process is visible to the user through a visual signal, such as a color change, which facilitates monitoring of the filtering material, ensuring timely maintenance or replacement.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The copolymer combines visual detection and anion removal, particularly nitrates, in water.
Unlike existing technologies, this copolymer is reusable and more environmentally friendly, as it does not require high water consumption or produce highly concentrated waste streams.
It enables users to be aware of the purifier's status through a visual signal, making the purification process more accessible.
The invention offers versatile formats, such as tablets or sheets, in various sizes to facilitate use in different applications.
Main advantages of its use
The copolymer offers multiple advantages over currently available water purification technologies. Firstly, it is a reusable material that can be easily regenerated, allowing for multiple usage cycles without losing its effectiveness. Its design enables users to detect the presence of nitrate anions through a visual signal, such as a color change or fluorescence, simplifying the monitoring and control of the purification process without the need for additional instruments.Additionally, since it does not produce concentrated waste streams or consume large volumes of water during operation, it is a sustainable and low-maintenance alternative to technologies like reverse osmosis. By being implemented in everyday devices, it fosters greater user awareness of the importance of water quality.Another notable advantage is its portability and ease of use. Its practical design allows it to be installed in both standard households and rural residences or areas facing challenges with access to potable water. Furthermore, thanks to its flexible applications and various formats, this copolymer can be employed in diverse contexts. It is suitable for domestic filtration systems, such as individual pitchers, water reservoirs in rural settings, or even aquariums.
Specifications
The smart material is a copolymer designed to act as an ion-exchange resin with specific properties for nitrate absorption, making it particularly effective in water purification. The action time of this material largely depends on the initial concentration of nitrate ions in the water, but the integrated visual alert system eliminates the need for constant monitoring.This smart system notifies the user when the material has reached its saturation point, ensuring efficient and convenient use of the device without requiring specialized technical knowledge.
Applications
This copolymer offers a wide range of applications in water treatment and quality monitoring. In domestic settings, it can be integrated into water purification devices, such as pitchers or filters, to remove common contaminants in drinking water, including nitrates and other anions. Additionally, its portable format makes it convenient for use anywhere, making it ideal for treating water during travel or outdoor activities, ensuring continuous access to purified water.On a larger scale, the copolymer can be implemented in community systems, such as neighborhood water facilities, due to its versatility in adapting to different formats and treatment volumes.In the aquaculture sector, the copolymer is valuable for maintaining safe environments in commercial facilities as well as domestic aquariums. Many fish species are highly sensitive to nitrate levels, and this technology provides an effective solution for keeping water in optimal conditions.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202430881
Current development status
The development phase has been completed, and the technology has been validated for use in real-world applications. This technology is ready for implementation and commercialization.
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement, licensing agreement, or technical cooperation (Further development, new applications, or adaptation to specific needs).
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Electrochemical sensor capable of performing in-situ sampling to determine simultaneous concentrations of sulfur compounds and 4-ethylphenol.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Simultaneous Detection: One of the most innovative aspects is the ability to simultaneously detect mercaptans and 4-ethylphenol in wines. This functionality is essential for a comprehensive evaluation of wine quality, as both compounds can impact its organoleptic characteristics.
Non-Contact Method: The technology enables detection in the gas phase, avoiding direct contact of the sensor with the liquid sample. This feature is crucial for maintaining product integrity, particularly important in the wine industry.
Preventive Diagnostics: The capability for routine and on-site analysis facilitates early detection of issues, allowing for corrective measures to be taken preventively and at minimal cost.
Main advantages of its use6
Increased Analysis Efficiency and Sensitivity: The ability to simultaneously detect mercaptans and 4-ethylphenol in wines in the gas phase significantly improves analysis efficiency. Evaluating both critical compounds at the same time saves time and resources compared to traditional methods.
Preserved Product Quality: Non-contact detection with the liquid sample is a key advantage, ensuring that the wine is not affected or contaminated during the analysis process. This is essential for preserving the quality and integrity of the final product.
Early Diagnosis of Defects: The capability for routine and on-site analysis allows for early detection of defects in wines. This is crucial for taking corrective measures preventively and avoiding issues that may impact product quality.
Cost-Efficient: The ability to conduct preventive diagnostics with minimal cost is a significant advantage. It enables wineries and food companies to control the quality of their products without incurring excessive expenses.
Ease of Use: The capability for on-site analysis and the user-friendly nature of the technology make it accessible for a wide range of users, from small wineries to large food companies.
Specifications
This technology is based on an electrochemical sensor designed for the simultaneous detection of mercaptans and 4-ethylphenol in wines. The sensor utilizes dual-screen-printed carbon devices where the working electrodes are modified with cobalt phthalocyanine (CoPh) and fullerene (C60). The electrode modification enhances the conductivity, sensitivity, and selectivity of the sensor.
The detection method is conducted in the gas phase, avoiding direct contact of the sensor with the wine sample. This is crucial for maintaining product quality. The four electrodes (two working, the auxiliary, and the reference) are coated with a gelified polymer film composed of a mixture of polyvinylidene fluoride, 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidone, and 1-methyl-3-octylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate, which acts as a supporting electrolyte.
An additional advantage of this technology is its ability to efficiently and cost-effectively conduct preventive diagnostics of critical compounds without direct contact with the sample. This enables early detection of defects in wine and the implementation of corrective measures before they significantly impact product quality, providing an innovative and effective solution for the wine and food industry.
Applications
- In the wine industry, it ensures the quality and consistency of the final product through the detection of unwanted compounds.
- It enables compliance with specific standards and regulations by allowing for comprehensive quality control.
Intellectual property status
Protected by Patent P202330838
Current development status
Device already developed and validated for industrialization.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
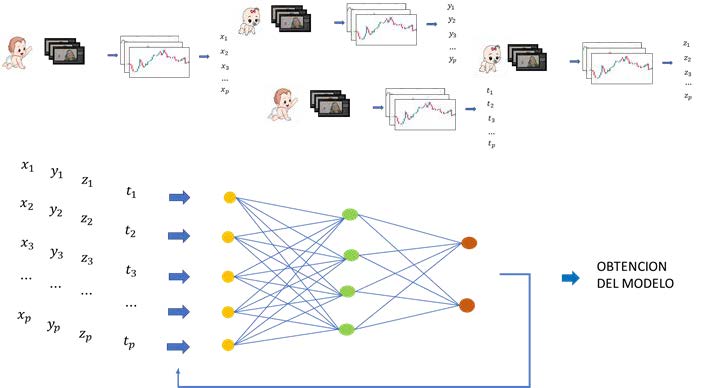
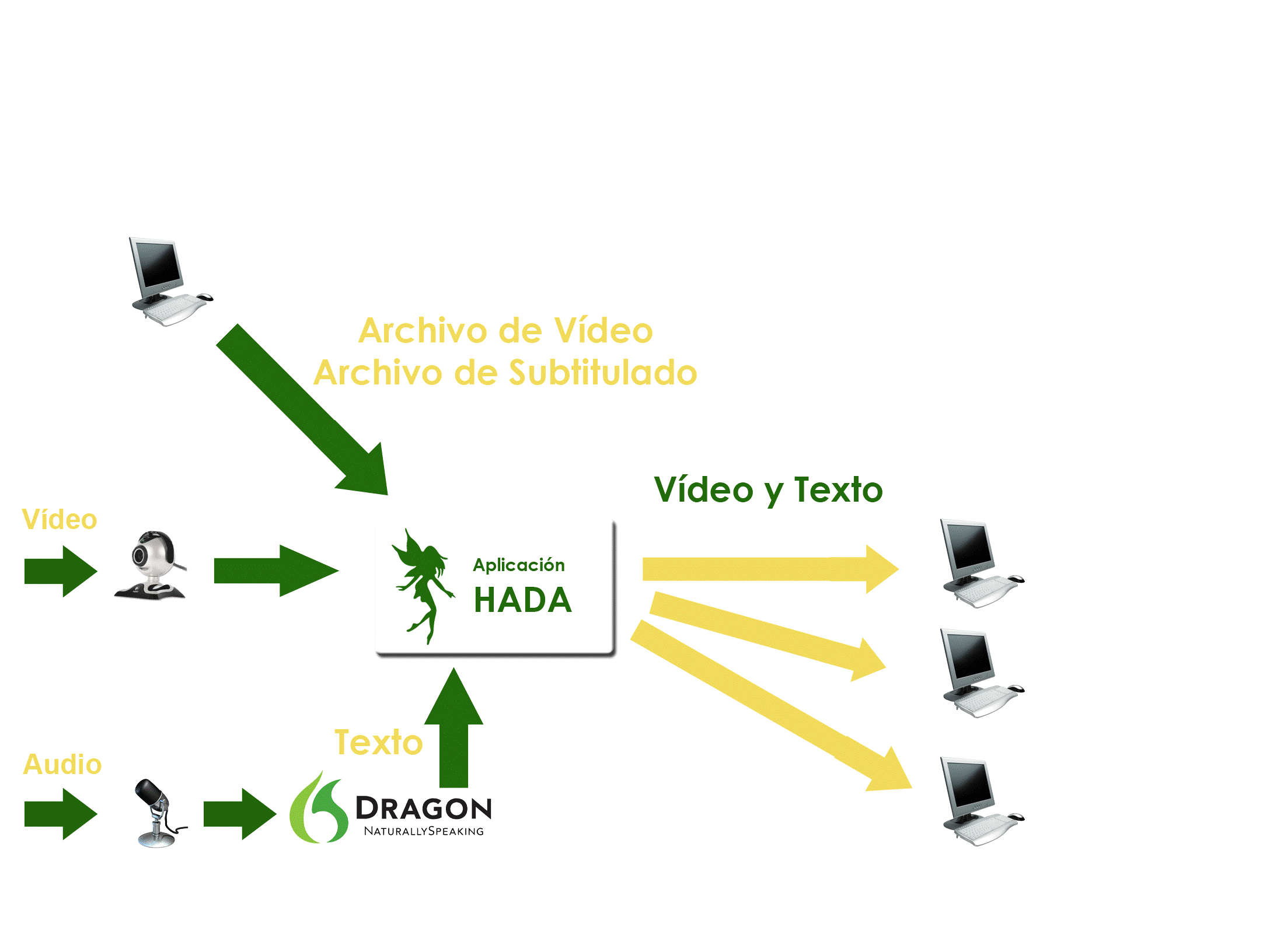
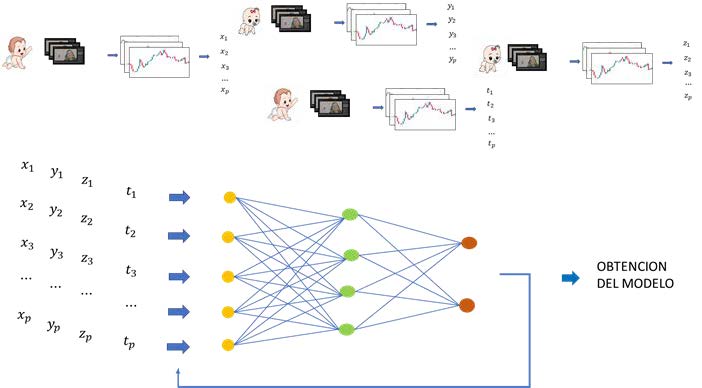
Software tool designed to assist in the early detection of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in children through the visual analysis of videos.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
- Eye Tracking Technology: Utilizes eye tracking to gather objective data on how children visually interact with videos.
- Artificial Intelligence: Employs neural network models to analyze visual patterns, enabling accurate and objective assessment.
- Continuous Adaptability: Can improve with new data, maintaining its effectiveness over time.
- Early and Objective Detection: Allows for the early and precise identification of ASD, which is crucial for early intervention and a better prognosis.
- Bias Reduction: Minimizes the influence of subjectivity in assessments, providing results based on objective visual data.
Main advantages of its use
- Time and Resource Savings: Compared to traditional methods, it can save time and resources in the diagnostic process.
- Remote Medicine Potential: Facilitates the remote evaluation of children, which is especially relevant in situations where in-person visits can be difficult or costly.
- Support for Research and Continuous Improvement: Contributes to scientific research by providing objective data for studies on ASD and its visual manifestations, allowing the tool to adapt and improve with new data.
- Facilitates Clinical Decision-Making: Assists healthcare professionals and psychologists in making more informed decisions in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Specifications
This innovative tool focuses on collecting data related to Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in children through the visual analysis of videos. The process begins by presenting a series of specially designed videos to the children. While watching these videos, eye-tracking technology is used to record and analyze in real-time where the children are directing their gaze.
The data collected from this eye-tracking is translated into a set of variables, which are used as input for artificial neural network models. These models have the ability to learn and detect complex patterns in the eye-tracking data. Furthermore, variable selection techniques are incorporated to ensure the robustness of the models and enhance their accuracy.
Moreover, this tool has the capability to adapt and improve over time as more data accumulates. This ensures that the system can continuously fine-tune itself and maintain consistent accuracy in detecting ASD.
The primary application of this tool is to provide accurate diagnoses of ASD in children, even at early ages. Early identification of ASD is crucial as it allows for timely intervention and the early commencement of therapies and support, which can significantly improve the long-term prognosis for children with ASD.
In addition to its clinical diagnostic use, this tool also has implications for ASD research, as it can help better understand the visual patterns associated with the disorder.
Applications
The software enables improved detection and diagnosis of ASD, with the potential to benefit children, families, healthcare professionals, as well as research and the development of more effective treatments.
Intellectual property status
Protected by software
Current development status
Device already developed and validated for industrialization.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Granted Patent
Software
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Researchers from the University of Burgos have developed a method capable of detecting sulphur compounds, specifically mercaptans, in wines. This new methodology allows analysis to be carried out quickly and with high sensitivity. Furthermore, the proposed electrochemical method is characterized by its low cost and portability.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Spain is the world's leading exporter in volume, with just over 2,300 million litres exported in 2021 and is responsible for 25% of wine production in Europe. The presence of sulphur compounds in wine causes the appearance of unpleasant odors, such as the smell of rotten eggs. The formation of these compounds represents one of the main reasons for complaints. Although methods for the determination of these compounds have been developed in recent years, the method developed at the University of Burgos is presented as a reference since it allows mercaptans to be quantified selectively without being in direct contact with the sample.
Main advantages of its use
The main advantages offered by this method are the following:
- Allows analysis to be carried out in the gas phase, reducing the number of interfering species and increasing selectivity.
- The sensor is not in direct contact with the wine, so it does not alter the product.
- No pre-treatment of the sample is required.
- The method is also characterized by its high sensitivity, its low cost and, due to its compact size, its portability.
For all these reasons, this methodology is positioned as one of the most suitable for the determination of mercaptans.
Specifications
Electrochemical measurements are performed using a potentiostat to which the CoPh-modified screen-printed device is connected, which has previously been immersed in a supporting electrolyte solution in such a way that it is pre-charged by adsorption. Amperometric measurements are subsequently made in the headspace of a sealed cell. Once a constant current is registered, a determined volume of the EtSH or wine solution is added to the cell, as appropriate, registering the corresponding increase in the registered current due to the oxidation process that takes place on the surface of the electrode. The current measured at the surface of the working electrode depends on the EtSH concentration in the cell.
The applicability of the developed method has been validated through truthfulness experiments, in which wines were analysed both in their original state and after the addition of a known amount of the analyte.
Applications
The main application of the developed sensors is in the wine industry as a technique for the determination of mercaptans. The analysis would make it possible to quantify these compounds throughout the winemaking process.
Additionally, this methodology could be widely implemented in the agro-food industry.
Intellectual property status
Protected by a patent P202231013
Current development status
Research or Experimental
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Researchers at the university of Burgos have developed a procedure to concentrate viruses from food samples (especially meat) and clinical samples. The new procedure is not only cheaper and easier to implement, but it is also a sustainable method as it does not use organic solvents.
New and innovative aspects
Current methods for virus detection in food have several limitations, such as low representativeness of the sample, difficulty in isolating viruses from inside cells and the use of organic solvents that are harmful to the environment and health.
In view of this situation, the need to develop an efficient method for virus detection has become evident. The procedure described by researchers at the university of Burgos has made it possible to overcome these limitations. This method makes it possible to achieve greater efficiency in the concentration of viruses; it makes it possible to extract viruses from inside the cells of the sample; and it is a more environmentally friendly and safer method.
Main advantages of its use
• The method is able to extract viruses found both on the surface of the sample and inside the cells. In this way, both the viruses on the surface and inside the cells of the food can be quantified.
• This method does not use organic solvents, making it a more sustainable method than the current ones.
• Lower economic cost.
• Lower risk in the workplace.
Specifications
• Viruses capable of being detected by this method are viruses causing food-borne diseases such as, for example, hepatitis E virus.
• The sample is subjected a double lysis, which increases the amount of virus that can be isolated from a sample, resulting in an increase in the sensitivity of the subsequent extraction and detection steps.
• The method is easy to implement in a routine laboratory setting as only routine equipment present in any laboratory is required.
Applications
- Companies in the food sector.
- Public and private health sector.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202230844
Current development status
Research or Experimental
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
A research group at the University of Burgos is carrying out studies on bioactive compounds with healthy properties, present in foods or in plant extracts. The aim of this study is to evaluate their antioxidant effects as well as their effects on biomarkers of diseases associated with oxidative stress (cardiovascular, cancer) through assays "in vitro", "ex vivo" with cell cultures and "in vivo" with animals of experimentation.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The role of both oxidative stress and natural antioxidants against the damaging effect of foods and against the pathogenesis of various diseases has led to the development of methods for assessing total antioxidant capacity and biomarkers of oxidative stress "in vitro" and "in vivo".
Many epidemiological evidences associate the consumption of vegetables and fruits with a lower incidence of chronic diseases related to oxidative stress, such as cardiovascular disease, hypertension, cancer, etc. This fact, together with an increasing consumers’ concern for keeping healthy has lead us to search for bioactive compounds obtained from foods. However, it is known that the health benefits of these compounds depend on the intake and bioavailability, which can vary greatly depending on factors such as the matrix, processing, interaction with other compounds, chemical structure, etc. Thus, is important studies conducing to the evaluation of bioactive compounds and of their health preventive effects.
Main advantages of its use
- Evaluate the potential healtly effect of food and of extracts with antioxidant capacity.
- Revaluation of agro-industrial wastes for the production of natural antioxidants with applications in food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical products.
Specifications
- Determination of antioxidant and antiradical capacity of foods, beverages or vegetal extracts.
- Evaluation "in vitro" of biomarkes of oxidative stress as indicators of the protective effect for bioactive compounds.
- Determination of cell viability, cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and ROS production.
- Evaluation of molecular biomarkers related to oxidative stress in cellular and animal models: malondialdehyde, carbonyl groups, 8-OHdG, NO, NOs, enzymatic (superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase) and no enzymatic antioxidant (GSH/GSSG, thioredoxin).
Applications
This technology can be applied to design functional foods or for the revaluation a product with health claims. Applications for food and pharmaceutical industry.
Current development status
Research or Experimental
Desired business relationship
Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
It is intended to apply biotechnological procedures (lipases), alternative to chemical treatments of transesterification and hydrolysis, for the modification of fats and oils. Lipases allow carrying out enzymatic processes for the formulation of "structured" lipid nutritional products, formulated to measure for a specific nutritional or technological function. Additionally, the oxidative stability of the synthesized lipids will be evaluated.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Lipases (EC 3.1.1.3) constitute a very versatile group of enzymes due to the large number of reactions they catalyze, with the advantage of their ability to act selectively on different substrates. Additionally, the action of enzymes, in terms of efficiency and stability, can be improved by immobilization techniques. Through this technology, the enzyme is fixed to a support or microencapsulated, which generally allows its stability and catalytic efficiency to be increased by reducing the possibilities of denaturing modification of its three-dimensional conformation. In addition, there are other additional advantages, such as its reuse, the possibility of using continuous reactors, rapid completion of reactions, controlled product formation, the greater variety of engineering designs and the greater efficiency in reactions with successive stages.
Main advantages of its use
With this enzymatic technology, it is therefore possible to develop edible fats or oils with nutritional, organoleptic and thermal stability properties, for each culinary use. In this way, it is possible not only to obtain nutritional benefits in patients with specific requirements, but also to prevent the risk of morbidity and mortality due to some highly prevalent pathologies, such as cardiovascular diseases, through the consumption of oils designed with a specific stereochemistry.
Specifications
The food industry uses chemical and enzymatic modification procedures for fats and oils in order to improve their organoleptic and nutritional characteristics and/or stability against processing. Due to the fact that chemical processes have many limitations and drawbacks, the application of technologies that use enzymes appears very promising for the development of new types of fats and oils. The use of lipases has allowed, through biotechnological techniques, the obtaining of structured lipids with an established and constant stereochemistry.
Applications
This technique is aimed at the Food sector, especially aimed at the design of functional foods.
Current development status
Research or experimental
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
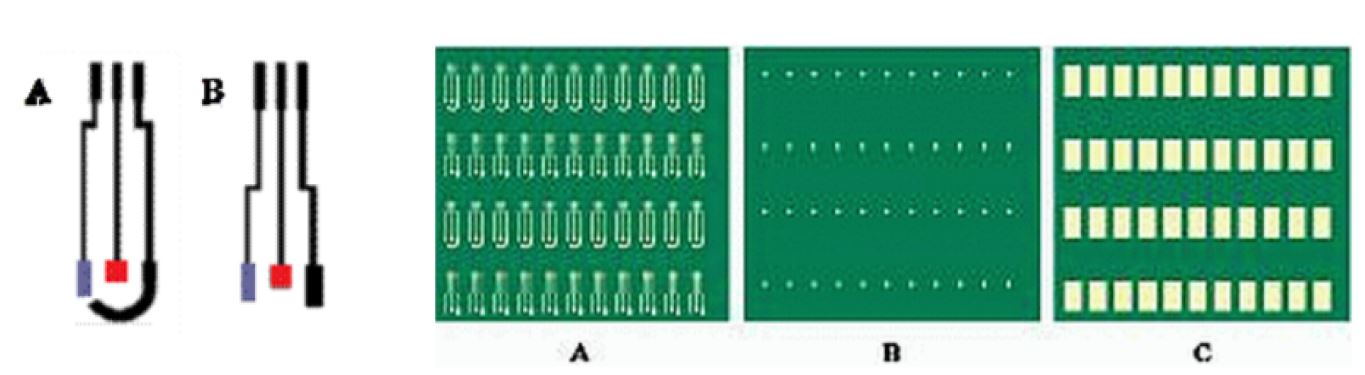
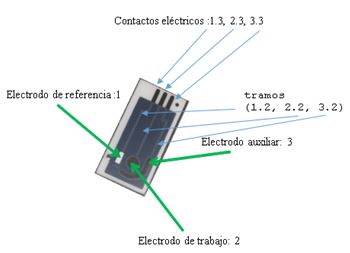
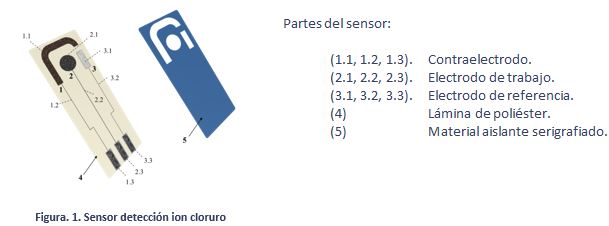
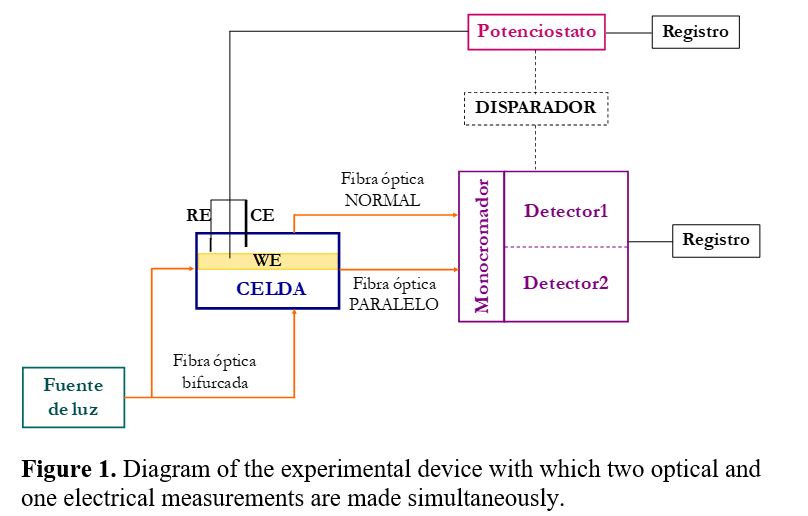
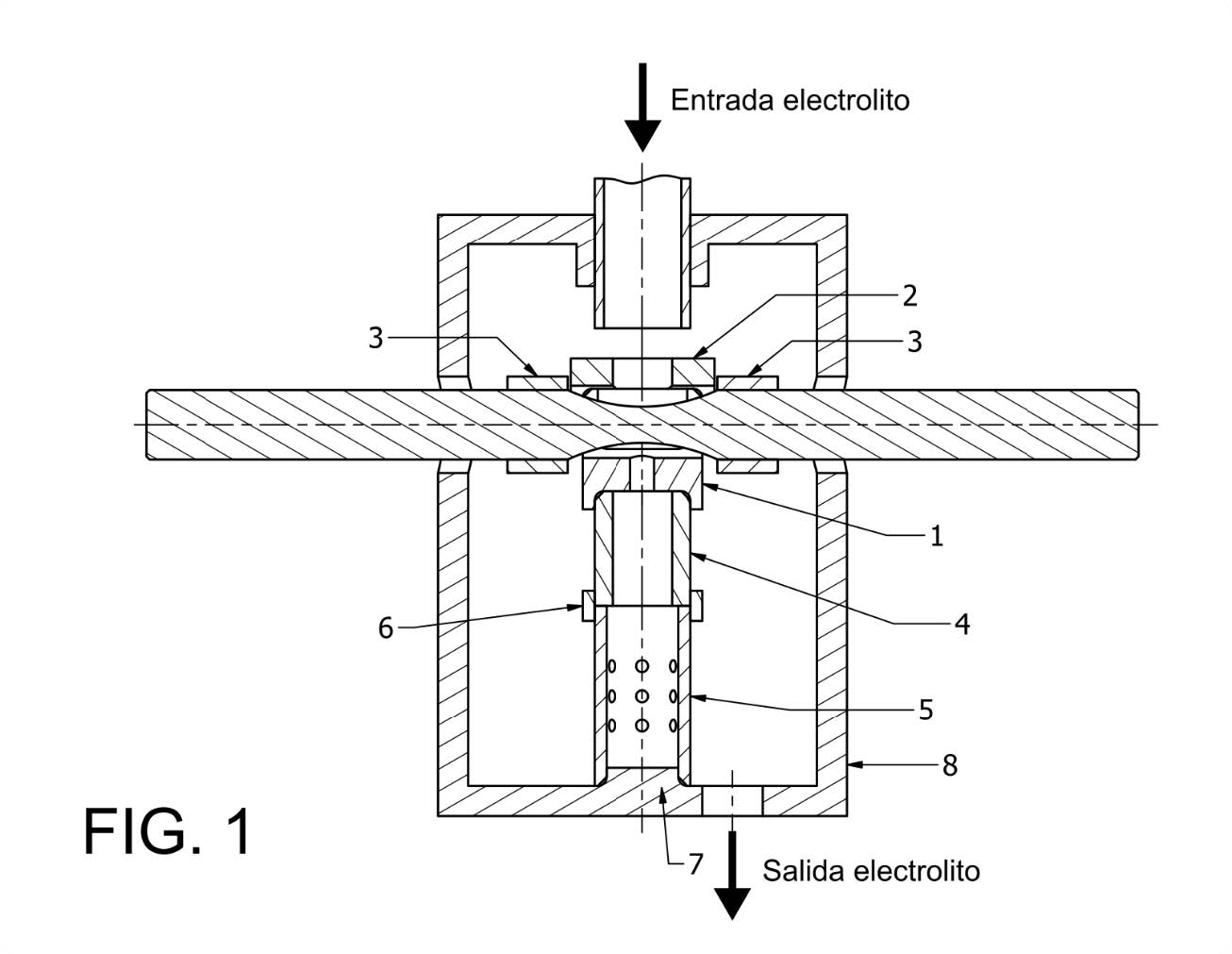
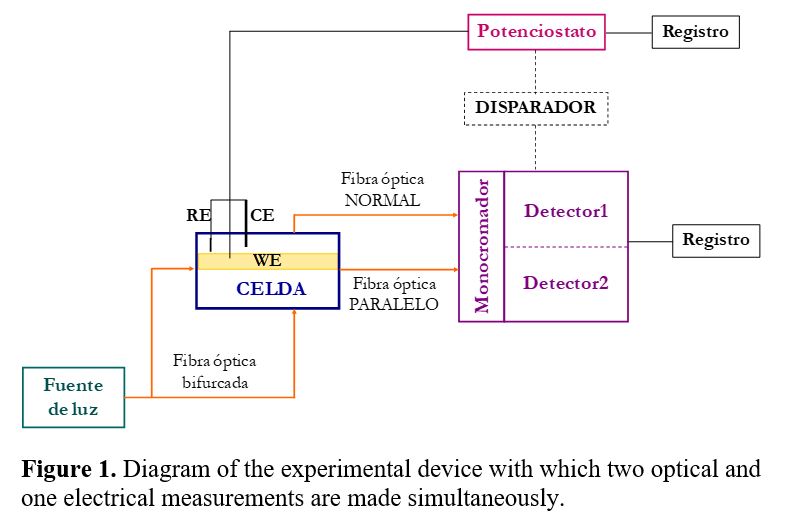
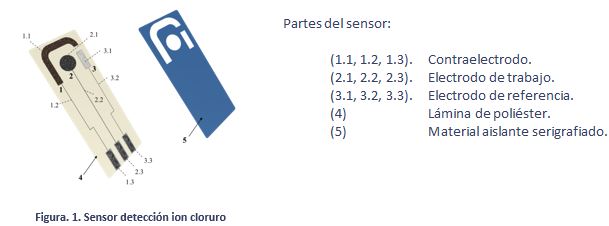
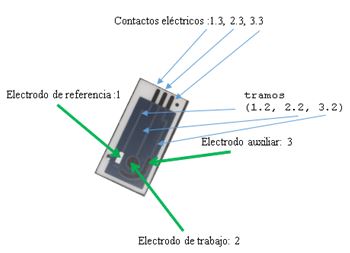
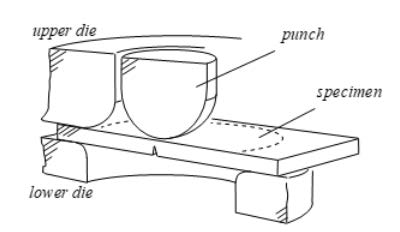
The design, construction and use procedure of a system of three electrodes (a work electrode subsequently modified with the immobilization of an enzyme, one for reference and another auxiliary), disposable screen-printed on a polyester (PET) support, has been carried out. space allows rapid “in situ” analysis of small sample volumes by electrochemical techniques.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The determination of cocaine has been carried out habitually using techniques very expensive chromatography. It is also a direct, fast, simple and inexpensive technique.
Main advantages of its use
The construction process by screen printing basically involves three stages consisting of the sequential deposition of the different inks and their subsequent curing. The first stage consists of the deposition of the graphite ink (Electrodag 407A) on the polyester substrate and its subsequent curing at 120 ºC for 30 min. The substrate, which already contains the motifs printed on it, is then properly aligned graphite ink, and the screen that defines the reference electrode. Ag / AgCl ink (Electrodag 6037 SS) is deposited, and cured under the same conditions.
Finally, and in order to define the electrochemically active area according to the design of figure 1, a last layer of an insulating ink is printed with the help of a third pattern, leaving free the upper part of the conductive bases of Ag to make the corresponding electrical connections.
Specifications
A device has been constructed containing three screen-printed electrodes. Two of the electrodes, silk-screened with carbon paste, will act as working electrodes, another silk-screened with an Ag / AgCl ink, it will act as a reference electrode and the third, also carbon, as a counter or auxiliary electrode.
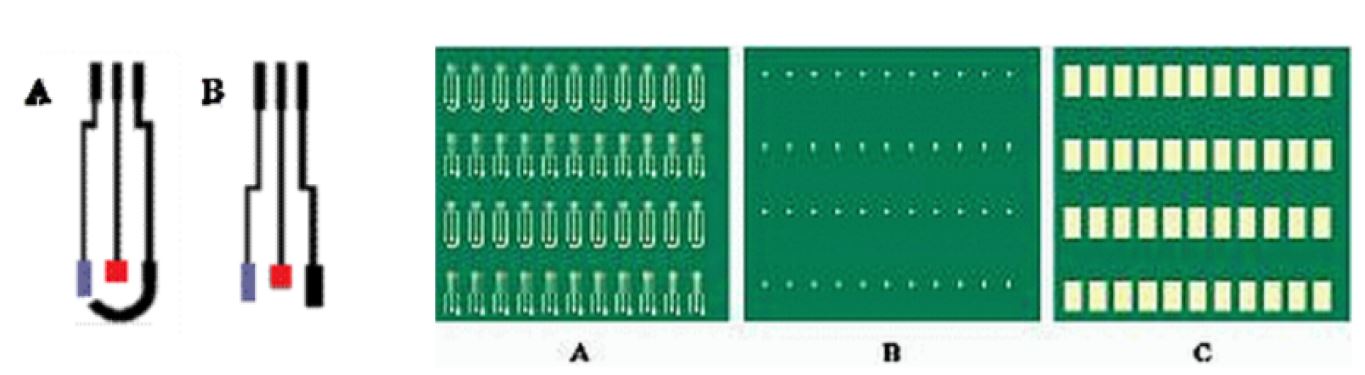
Figure 1.- Designs made for the manufacture of the serigraphic sensors: auxiliary electrode (black), reference electrode (gray), working electrode (red).
Figure 2.- Images of the screens used in the construction of the serigraphic electrodes:
definition of the conductive paths and the working and auxiliary electrodes in carbon (A), definition of the reference electrode in Ag / AgCl (B) and definition of the insulating material (C).
Applications
Of great interest for the determination of this substance in routine controls of biological samples. Equally useful for determining the purity of drug samples.
Companies related to doping control.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P201000738
Current development status
Developed but not commercialized.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
This technology is intended to eliminate the bitter compound oleuropein in producing green table olives, by employing new biotechnological processes alternative to the use of alkali.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Using biocatalysts as an alternative to chemical treatment with alkaline lye. The debittering of olives using enzymes is a very interesting alternative compared to traditional chemical process since apart from the advantages in terms of reduced conditioning times and the overall costs of the process, also would decrease the environmental impact created by the use of NaOH.
Main advantages of its use
Researchers at the University of Burgos are developing a technology, based on the used of enzymes, directed to the removal of bitter compound oleuropein, as alternative to the use of alkali in the production of green table olives.
Specifications
Processing of green table olives consists of a treatment with an alkaline lye (NaOH) which causes loss of soluble constituents and nutrients responsible for the sensory properties of typical high quality olives. The aim of this biotechnological process is apply the enzyme technology for removing the bitterness due to oleuropein, avoiding the physical and chemical changes that the addition of NaOH produces, and, moreover, reduce fermentation times during the conditioning step.
Applications
This technique is aimed at the food industry, especially for companies producing of green table olives.
Current development status
Device already developed and validated for industrialization.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
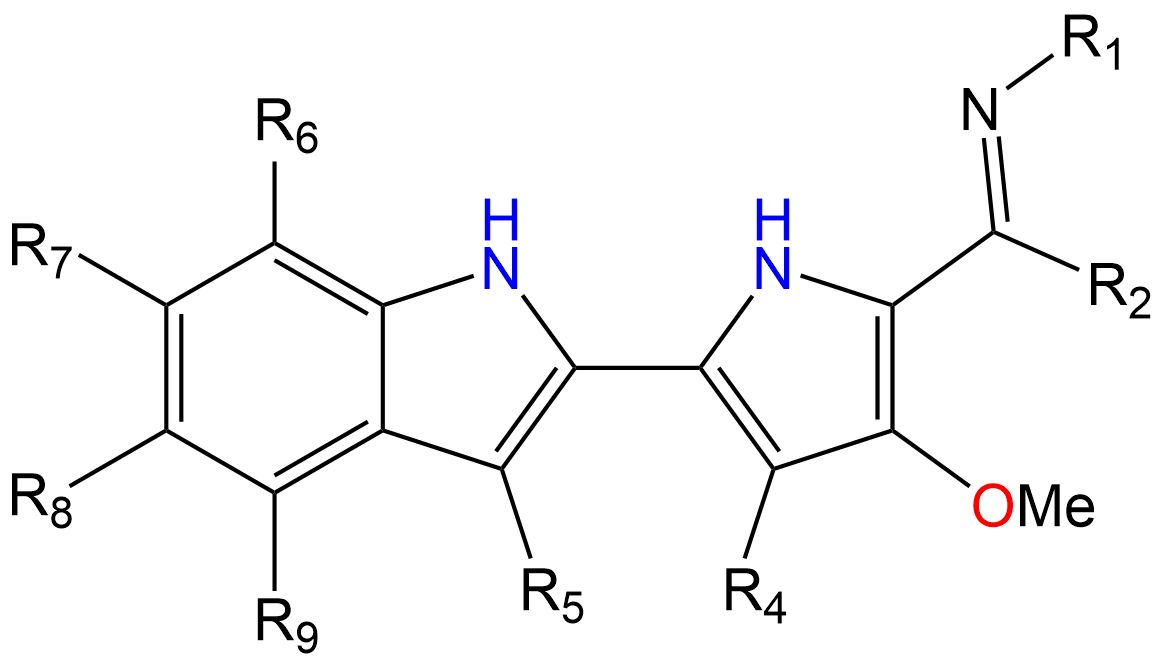
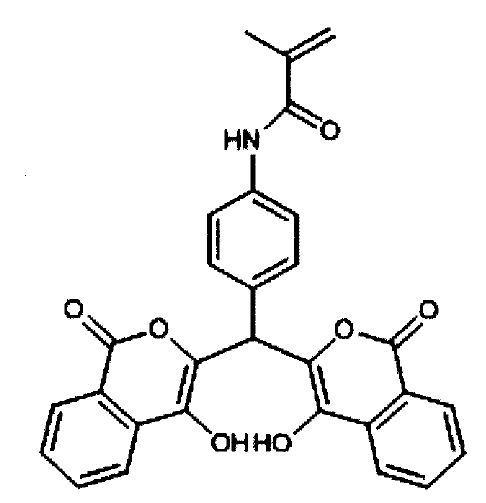
Summary of the technology
Researchers from the University of Burgos have described a procedure for the synthesis of hydroxyalkylamide derivatives from the corresponding O-aryl N,N-diethylcarbamates and an epoxide, which has allowed them to prepare several series of new chiral compounds with potential applications in the pharmaceutical industry.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Chiral organic compounds with hydroxyl groups are important synthetic precursors of amino acids, alkaloids, carbohydrates, and other chiral compounds with possible biological and / or pharmacological activity. That is why one of the main challenges of current organic chemistry is the search for new efficient and clean synthesis procedures that allow access to chiral compounds. The novel procedure described by the UBU researchers makes it possible to obtain a new family of derivatives of (6-hydroxyphenyl)-N,N-diethyl-3-hydroxyalkylamides, which are not described in the literature and which are obtained as a single diastereoisomer. The pharmacological relevance of both chiral organic compounds and epoxides is demonstrated by the fact that they are found or precursors of numerous biologically active compounds or natural products.
Main advantages of its use
- The process that makes it possible to obtain a new family of derivatives of (6-hydroxyphenyl)-N,N-diethyl-3-hydroxyalkylamides is novel.
- The compounds are not described in the literature and are obtained as a single diastereoisomer.
- The process can also be carried out using chiral epoxides, thus making it possible to obtain the final products in an enantiospecific way.
Specifications
The described procedure allows the synthesis of new compounds derived from (6-hydroxyphenyl)-N,N-diethyl-3-hydroxyalkylamides from O-aryl N,N-diethylcarbamates as starting substrates, being able to present groups of different chemical nature on the aromatic ring, such as halogens, methoxy groups, or unsubstituted. Likewise, the use of sec-butyllithium or lithium diisopropylamide is required, in tetrahydrofuran, at –78 ºC, atmospheric pressure and in an inert nitrogen gas atmosphere, for the ortho-lithiation reaction of the starting carbamates. The subsequent addition of lithium 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidide and the addition of a terminal epoxide, which can be alkyl or with a functional group, both racemic and enantiomerically pure, gives rise to the homologous regrouping of Snieckus-Fries 1,4 -O → C of the carbamoyl group by the evolution of the reaction at room temperature for 3 hours.
Applications
The potential application of the described procedure is the synthesis of chiral aromatic organic compounds that contain alcohol groups in their structure, as well as halogens and other functional groups, for which they are postulated as highly versatile synthetic intermediates with great applicability in the pharmaceutical, agrochemical, industry. chemistry, etc.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202130635
Current development status
Laboratory tested procedure.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Researchers from the University of Burgos, the University of Barcelona and the Spin-off Nostrum Biodiscovery, have described the use in medicine of asenapine or the possible combinations of it with other anticancer agents, as well as pharmaceutical compositions and kits that contain them, in particular as anticancer agents.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Survivin is a therapeutic target for treating cancer. Asenapine is an atypical antipsychotic sold in the form of its maleate salt under the name SAPHRIS. The role of asenapine in the treatment of cancer could be related to its ability to inhibit survivin. The main established functions of survivin are the regulation of cellular mitosis and the inhibition of apoptosis. No experimental data have been found to support the use of asenapine against cancer.
Researchers from the UBU, UB and Nostrum have found that asenapine can be used effectively in the treatment of cancer as it is not only capable of showing moderate carcinogenic activity against various cancer cell lines in vitro, but it has also shown antitumor effects in vivo.
Main advantages of its use
The inhibitory action of survivin exerted by asenapine would allow:
- induce apoptosis in tumor cells
- inhibit the cell cycle
- sensitize tumor cells to standard chemotherapeutic agents or other anticancer agents, without being toxic to healthy cells.
Specifications
In the tests, asenapine reduced cell viability in adenocarcinoma of the lung (A549) and colon (SW620), and it was not cytotoxic for healthy cells. Asenapine also showed in vitro anticancer effects against pediatric neuroblastoma (LAN-1), pediatric sarcoma (RD), and glioblastoma (U87) in the same efficacy range as other chemotherapeutic agents such as cisplatin.
Applications
Due to its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB), asenapine may be of particular interest in the treatment of brain tumors, including primary brain tumors or cancers with brain metastases. Its potential has also been observed in lung adenocarcinoma, colon adenocarcinoma, pediatric neuroblastoma, pediatric sarcoma, and glioblastoma.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent EP21382721
Current development status
Laboratory tested procedure.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The University of Burgos, in co-ownership with the Complutense University of Madrid, has registered a new accessory that allows controlling the visual and body posture of whoever wears it, including a vibration sensor as a warning system.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The postural control system consists of a simple accessory, without connections to other devices, that allows control of visual and body posture. This system includes accelerometers for calculating the position of the body and vibration sensors as a warning system.
Main advantages of its use
- Allows you to measure your real position on three different axes
- It has vibration sensors as a warning system
- It is located in a sealed box together with the computer chip
Specifications
The case of the device is placed close to the user's skin to perceive the movements that he performs. This box is made of elastic plastic material and can be customizable. The accelerometers measure in the three axes and this data is compared with the data of the correct position previously measured. If the results go outside these limits, the warning system is activated so that the user can correct their visual and/or body posture.
Applications
- Body posture control
- Visual posture control
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202130256
Current development status
Device under development.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Researchers from the University of Burgos have patented a synthetic process of cationic Iridium(III) complexes with formula (I). Moreover, they have developed a one-pot protocol for the regioselective synthesis of 3-thiocyanato indoles (II) from their corresponding indolines. On the other hand, the use of these Ir(III) complexes as potential therapeutic photosensitizers for antitumor photodynamic therapy is also protected.
New and innovative aspects
The Iridium(III) complexes described in this patent exhibit singular characteristics that differentiate them from known complexes. They show significant activity as photocatalysts or photosensitizers, absorbing energy from light and transferring it to oxygen to form reactive oxygen species (ROS) that act as efficient and environmentally friendly oxidants. Furthermore, the synthesis of the Iridium(III) complexes is carried out under mild conditions and shows good yields.
Main advantages of its use
- High stability of Iridium(III) complexes in solution.
- They present excellent photostability under different light sources, then the range of possible applications increases considerably.
- As photocatalysts, the use of the low energy visible-light prevents secondary reactions from taking place and therefore the reactions are more selective.
- The one-pot regioselective synthesis of 3-thiocyanato indoles from indolines, is more economical, since it is not necessary to isolate and purify the intermediate products.
- In therapeutic applications, the new complexes show high photocytotoxicity index (PI = IC50,dark/IC50,light).
Specifications
The cationic Iridium(III) complexes of formula (Mn+)(X-)n show two 2-phenylpyridinate ligands coordinated to the Ir(III) ion through the nitrogen atom of the pyridine ring and one of the carbon atoms of the phenyl group; and a ligand derived from β -carboline, which is bonded to the Ir(III) via two nitrogen atoms. These complexes can be used as photocatalysts in organic synthesis or as photosensitizers.
In organic synthesis, these complexes allow the regioselective synthesis of 3-thiocyanato indoles from indolines through a one-pot process. First, the process involves two steps: dehydrogenation of indolines and, subsequently, thiocyanation of the intermediate indoles. Both reaction steps imply the use of oxygen in the presence of light and the use of Iridium(III) complexes as photocatalysts.
Applications
Potential applications of the new Ir(III) complexes are as follow:
- Photooxidation reactions in organic synthesis
- Use as photocatalysts in thiocyanation reactions of indoles.
- Photosensitizers in photodynamic therapy in the treatment of cáncer.
- Preparation of a drug for the treatment of cancer, in combination with radiotherapy, that is, the drug is administered together with, or before, the administration of radiotherapy.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202031190
Current development status
The technology related to the synthesis method is developed.
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement; License agreement; Technical cooperation: further development; Technical cooperation: testing new applications; Technical cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Patent already applied for
P202031190
https://www.ubu.es/otri-transferencia/propiedad-industrial-e-intelectual/patentes-y-modelos-de-utilidad-de-la-ubu/134-p202031190-complejos-de-iriii
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Composición farmacéutica para la preparación de un medicamento destinado al tratamiento y/o profilaxis de enfermedades derivadas del transporte anómalo de aniones a nivel celular que comprende un compuesto de fórmula (I).
Description of the technology
Figura 1. Viscosidad del moco en cultivos epiteliales. Las barras representan la viscosidad promedio después de 24 horas de incubación con los compuestos señalados. Los epitelios no tratados con CF (n = 8) y sin CF (n = 6) se incubaron con DMSO al 0,1% como control. Los epitelios CF se incubaron con 0.25 µM de MM3 (n = 7) o 0.25 µM de MM34 (n = 8). Los cultivos se obtuvieron de dos donantes no CF y dos pacientes homocigotos diferentes F508del-CFTR. * indica p <0,05.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Existen numerosas enfermedades relacionadas con disfunciones de las proteínas encargadas de facilitar el transporte de iones a través de membranas biológicas o canales iónicos. Estas enfermedades son muy diversas y entre ellas se encuentra la fibrosis quística (FQ).
Actualmente, son conocidos fármacos como el Kalydeco u Orkambi que regulan farmacológicamente la actividad de la proteína CFTR. Sin embargo, la eficacia de estos tratamientos depende en gran medida de las mutaciones específicas que presentan los pacientes y no son eficaces para todos los enfermos diagnosticados de FQ. Hay que tener en cuenta que se han identificado más de 1.700 mutaciones con cuadros clínicos muy diversos.
Los compuestos de la invención sustituyen la acción de la proteína CFTR, facilitando el transporte de iones a través de las membranas lipídicas. Esta actividad constituye una estrategia terapéutica independiente de la mutación causante de la enfermedad de CF y, por tanto, con posibilidad de beneficiar a todos los pacientes de FQ.
Características técnicas
El compuesto de la invención ha demostrado corregir parámetros funcionales indicadores de fisiopatología de FQ en modelos de cultivo de epitelio pulmonar de pacientes. Así, el pH, la reabsorción de fluidos y la reología del moco producido en estos cultivos alcanza valores similares a los del epitelio no afectado por FQ tras el tratamiento con dosis de estos compuestos que no inducen citotoxicidad significativa.
Aplicaciones
- Ingrediente farmaceútico activo (API), con capacidad anionóforas para el tratamiento de pacientes con fibrosis quística, independientemente de la mutación detectada.
- Síntesis de moléculas con capadidad anionóforas como antimicrobiano para el tratamiento de infecciones causadas por bacterias resistentes (pacientes con FQ / sin FQ).
- Aplicación en estudios de correlación de citotoxicidad con actividades de transporte de anionóforos.
- Aplicación en estudios de actividades aniónofóricas que influyen en los gradientes de pH transmembrana (membrana celular, compartimentos intracelulares).
- Líneas celulares biosensoras y ensayos basados en células para la investigación de biomembranas.
- Nanoformulaciones de compuestos y ensayos de sensores de iones para investigación en biología molecular.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegido por patente PCT/EP2019/057696
Estado actual de desarrollo
La tecnología relativa al método de sintesis esta desarrollada.
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Pharmaceutical composition for the preparation of a medicament for the treatment and /or prophylaxis of diseases derived from the abnormal transport of anions at the cellular level, comprising a compound of formula (I).
Description of the technology
Figure 1. ASL mucus viscosity. Bars represent the average viscosity after 24 hours of incubation. Untreated CF (n=8) and non-CF (n=6) epithelia were incubated with 0.1% DMSO as control. CF epithelia were incubated with 0.25 µM of MM3 (n=7) or 0.25 µM of MM34 (n=8). Data were obtained from two non-CF donors and two different homozygous F508del-CFTR patients. * indicates p<0.05.
New and innovative aspects
There are a group of diseases related to abnormal function of channel proteins facilitating the transport of ions through biological membranes. These conditions, known as “channelopathies”, are very diverse and include cystic fibrosis (CF).
Currently, approved drugs such as Kalydeco or Orkambi target pharmacological correction of CFTR protein. However, the therapeutic outcome of these depends dramatically on the specific mutations of the patients. More than 1,700 mutations have been identified and there is a cohort of patients lacking CFTR production for whom the current strategies are not effective.
The compounds of the invention replace the faulty transport activity of the CFTR protein, providing an alternative path for anion transport through lipid membranes. This therapeutic strategy is independent of CFTR production and activity, being potentially useful for all CF patients regardless of the mutation causing CF disease.
Specifications
The compound of the invention has demonstrated to correct key functional parameters in model epithelial cultures derived from CF patients. Thus, Air surface liquid pH and volume as well as mucus rheology in CF epithelium are corrected to values comparable to those of normal tissue upon application of the compounds. Importantly the dose required to observe these effects did not induce significant cytotoxicity due to unspecific anion transport activity.
Applications
- Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), with anionophore capacity for the treatment of patients with cystic fibrosis, regardless of the detected mutation.
- Synthesis of molecules with anionophore capacity as antimicrobial agents for the treatment of infections caused by resistant bacteria (patients with CF / without CF).
- Application in studies of correlation of cytotoxicity with anion transport activities of anionophores.
- Application in studies of anionophoreic activities that influence transmembrane pH gradients (cell membrane, intracellular compartments).
- Biosensor cell lines and cell based assays for biomembrane research.
- Nanoformulations of compounds and ion sensors assays for molecular biologyresearch.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent PCT/EP2019/057696
Current development status
The technology related to the synthesis method is developed.
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement; License agreement; Technical cooperation: further development; Technical cooperation: testing new applications; Technical cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The invention provides new crosslinked copolymers derived from ninhydirin, and their use, in film, membrane or gel form, as chromogenic sensors in the presence of amino acids, small proteins or peptides present in aqueous samples, wounds, wound exudates, biological samples and medical samples.
The capable of colour change of the new sensors in the presence of healing parameters allows monitoring the evolution of chronic wounds using RGB parameters of a digital photograph, anticipating the diagnosis and treatment of patients.
New and innovative aspects
The difficulties of healing of skin wounds is a problem of the first magnitude that affects approximately 1-2% of the population and the great harm to patients, while it represents an enormous economic cost.
The healing process is complex, and the diagnosis and treatment of chronic wounds is challenging. Medical staff perform these evaluations through visual inspections to establish treatments that can last for long periods of time.
This monitoring technology based on the quantitative detection of healing parameters is a great advance in the realization of preventive diagnoses, control of infections in real time, reduction of the additional response time of the sanitary economic cost.
Main advantages of its use
The main advantage is the ability to detect healing markers such as protease, amino acids, small proteins or peptides present in aqueous and/or biological media, by means of a simple color change quickly, without prior manipulation, and without interference.
Specifications
The synthesis of the structure (I) derived from ninhydrin within the polymeric material itself, by means of direct modification in the polymer chains, allows obtaining a stable material for years without any type of storage or special treatment.
Applications
This development allows the detection, quantification and monitoring of chronic wounds by using the RGB parameters of a digital photograph. The chronic wound monitoring device can reduce the number of infections of patients, decrease prolonged hospitalizations, to follow the evolution of the patients after being discharged from hospital and reduce laboratory tests associated with the diagnosis of chronic wounds.
Intellectual property status
Protected by Patent P202030077
Current development status
The technology related to the synthesis method is developed.
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement; License agreement; Technical cooperation: further development; Technical cooperation: testing new applications; Technical cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The method developed in this patent is based on the preparation of new polymeric materials, which act as fluorometric sensors, for anions and, especially, for chlorides, in aqueous solution, for example in industrial water, potable water and/or sweat.
The detection of chlorides is very important both for the pre-diagnosis of diseases, such as cystic fibrosis, and for the water quality control.
New and innovative aspects
The copolymers of the present invention are completely reusable, being only necessary a water wash to be used again.
They can be used as continuous chloride detectors (in the case of industrial waters or for human consumption), as well as in dressings (in the case of sweat).
Main advantages of its use
This method can be applied in different media without any previous treatment of the sample. In addition, the presence of chlorides can be detected qualitatively at first sight, thanks to the change in fluorescence that takes place.
As advantages respect to other methods, it does not require electricity, previous calibration before the measurement or manipulation of chemical reagents, some of them being costly, which also supposes a limitation when carrying out routine tests.
Specifications
This invention is based on the preparation of a copolymer (linear or cross-linked), comprising preferably a bromide salt, by the polymerization of at least two monomers. This polymerization is carried out by direct reaction of polymerizable groups present in each of the monomers and the result is presented in the form of films, solid membranes (dense or porous), like as coatings and in the form of a dressing.
The resulting copolymers can be used as sensors for the qualitative or quantitative detection of anions, and especially of chlorides, in water and / or in aqueous solution such as sweat. The measurement of chloride concentration in sweat is applicable in the detection and diagnosis of diseases, particularly cystic fibrosis.
The method is based on that, in the presence of anions, large changes take place in the fluorescence of the copolymer. As the concentration of chlorides increases, the fluorescence disappears and the result can be measured using, at least, a method independently chosen between:
- visual detection by the naked eye; or
- the use of spectroscopic techniques based on fluorescence.
Applications
It presents a high responsiveness in:
- Drinking water.
- Industrial water.
- Bio relevant fluids: Healthcare system: monitoring and or diagnisis of various conditions through the measurement of chlorides in sweat and other biofluids.
Intellectual property status
Protected by PCT/EP/2018/067048
Current development status
Several prototypes have been manufactured in laboratory tests.
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement, License agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
El método desarrollado en esta patente se basa en la preparación de nuevos materiales poliméricos que se comportan como sensores fluorimétricos para aniones y, en particular, para cloruros, en medios acuosos, como por ejemplo en aguas industriales, en aguas de consumo humano y/o en sudor.
La detección de cloruros es muy importante tanto para el pre-diagnóstico de enfermedades, como por ejemplo la fibrosis quística, como para el control de la calidad de aguas.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Los copolímeros de la presente invención son totalmente reutilizables, siendo solo necesario un lavado con agua para volver a ser usados.
Se pueden utilizar como detectores de cloruro en continuo (en el caso de aguas industriales o de consumo humano), así como en apósitos (en el caso del sudor).
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Este método se puede aplicar en diferentes medios sin ningún tipo de tratamiento previo de la muestra. Además, se puede detectar cualitativamente la presencia de cloruros a simple vista, gracias al cambio de fluorescencia que tiene lugar.
Como ventajas respecto a otros métodos, no requiere de tomas de corriente eléctrica, ni calibrado previo a la medición y tampoco manipular diversos reactivos químicos, algunos de los cuales alcanzan precios bastante altos, lo cual también supone una limitación a la hora de realizar ensayos rutinarios.
Características técnicas
Esta invención se fundamenta en la obtención de un copolímero (lineal o reticulado), que comprende una sal de bromuro preferentemente, mediante la polimerización de al menos dos monómeros. Esta polimerización se lleva a cabo por reacción directa de grupos polimerizables presentes en cada uno de los monómeros y el resultado final se presenta en forma de filmes, de membranas sólidas (densas o porosas), de recubrimientos y en forma de aposito.
Los copolímeros resultantes se pueden utilizar como sensores para la detección cualitativa o cuantitativa de aniones, y en particular de cloruros, en agua y/o en medios acuosos como el sudor. La medida de la concentración de cloruros en el sudor es de aplicación en la detección y el diagnóstico de enfermedades, en particular la fibrosis quística.
El metodo se basa en que, ante la presencia de aniones, se producen grandes cambios en la fluorescencia del copolimero. A medida que aumenta la concentración de cloruros, la fluorescencia va desapareciendo y el resultado se puede medir empleando, al menos, un método seleccionado independientemente entre:
- detección a simple vista; o
- la utilización de técnicas espectroscópicas basadas en fluorescencia.
Aplicaciones
Presenta una alta capacidad de respuesta en:
- Aguas de consumo.
- Aguas industriales.
- Sector sanitario: detección de diversas enfermedades a través de medición de cloruros en sudor.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegido mediante PCT/EP/2018/067048
Estado actual de desarrollo
Se han fabricado varios prototipos a nivel de laboratorio.
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The field of the invention is related to compounds containing a triazole-dipyrromethene core which facilitate the anion transport through lipid membranes. These molecules are capable of mimicking the function of transmembrane proteins and thus replacing their function at cellular level. These compounds are particular useful for the treatment of diseases related to malfunction of natural anion transport mechanisms such as Cystic Fibrosis.
New and innovative aspects
There are very limited studies in the literature concerning the possibility of using synthetic transport systems to replace the missing transmembrane anion transport activity characteristic of Cystic Fibrosis. Most of them referred to the use of peptides which degradability limited the potential scope of this approach.
The current invention provides a significant contribution related to the characterization, design and synthesis of small molecules with anion transport capacity, and their biological activity.
Main advantages of its use
The current standard therapies for Cystic Fibrosis are based mainly in palliative treatments of the illness symptoms. Recently it has been approved for use a drug that acts on the root of this problem, enhancing the transport of ions through natural channels, but only applicable to patients suffering from certain genetic mutations of the CFTR transmembrane protein.
These small molecules facilitate the transmembrane transport of anions independently of the genetic mutation, therefore they are therapy applicable to all Cystic Fibrosis patients, regardless of the type of mutation they harbor.
Specifications
Compounds bearing triazole-dipyrromethane moieties are capable of facilitating transport of anions such as chloride and of bicarbonate in phospholipid vesicles models and cells.
Applications
Use of the compound for preparing a medicament for the treatment and / or prophylaxis of conditions arising from abnormalities in the anion transport at the cellular level such as Cystic Fibrosis.
Intellectual property status
Protected by PCT/ES2016/070859
Current development status
Samples ready for testing
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
El campo de la invención está relacionado con compuestos de tipo triazol-dipirrometeno capaces de facilitar el transporte de aniones a través de membranas lipídicas. Estas moléculas son capaces de suplir la función perdida en enfermedades relacionadas con deficiencias en el transporte de aniones a nivel celular. Los compuestos de la invención son particularmente útiles en el tratamiento de enfermedades como la fibrosis quística.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Existen muy pocos estudios publicados relativos a la posibilidad de utilizar sistemas de transporte sintéticos que sustituyan deficiencias en los mecanismos naturales de transporte de aniones a nivel celular, característicos de enfermedades como la fibrosis quística. La mayoría de ellos se refieren al uso de péptidos cuya inestabilidad ha limitado el potencial de este enfoque.
La presente invención presenta como novedad la caracterización, diseño y síntesis de moléculas pequeñas con capacidad transportadora de aniones y su actividad biológica.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Las terapias seguidas hasta la actualidad se basan fundamentalmente en tratamientos paliativos de los síntomas de la enfermedad. Más recientemente ha sido aprobado para su uso un medicamento que actúa sobre la raíz de este problema, potenciando el transporte de iones a través de los canales naturales, pero aplicable sólo a pacientes afectados de determinadas mutaciones genéticas de la proteína transmembrana CFTR.
Los compuestos objeto de esta invención son capaces de facilitar el transporte de aniones independientemente de la mutación genética que origina la enfermedad. Por tanto son potencialmente de aplicación terapéutica para todos los pacientes de fibrosis quística.
Características técnicas
Los compuestos de tipo triazol-dipirrometeno son capaces de de facilitar el transporte de aniones como cloruro y bicarbonato en modelos de vesículas de fosfolípidos y células.
Aplicaciones
Uso del compuesto para preparar un medicamento destinado al tratamiento y/o profilaxis de enfermedades derivadas de anomalías en el transporte de aniones a nivel celular como la fibrosis quística.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante PCT/ES2016/070859
Estado actual de desarrollo
Muestras listas para pruebas
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Electronics, IT and Telecomms (29)
Summary of the technology
- We use the new technologies and its combination to make proffesional media projects.
- The media projects are very useful in the dissemination of culture, heritage, learning and events. New technologies are essential to communication in these areas and we know how to use them.
- Our work in new tecnlologies increases de effectiveness of the communication because the users and the audience is most attentive to the meaning of the message.
Description of the tech for sale
We have a specialized teamwork that works on new technologies as media production, graphic design and computer graphics. We can develope projects for differents kinds of aims, but we have experience working on the dissemination of culture and heritage, media development for events (video, 3D design, marketing 2.0, augmented reality...) and the development of new technologies and media for education and learning.
Specifications
- We have facilities and a specialized teamwork. We have a virtual reality room, a media lab and media equipment for develope any kind of project (in theese areas) - We can develope projects of 3D design, video, videogames, augmented reality, graphic design, web apps, social media and virtual reality.
Main advantages of its use
- - We have a multidisciplinary teamwort and we are able to manage the whole project.
Applications
- Events
- Dissemination of culture and heritage
- Education and learning
- Entertaiment
About Universidad de Burgos
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The use of new technologies (Internet/mobile phones) can involve a competitive advantage for small and medium sized firms. The advice can be focused on the development of a new business or on the complementarion of a new business at a low cost with an existing one. Introducción en el campo de las nuevas tecnologias como ventaja competitiva para empresas de cualquier tamaño. el asesoramiento puede ser tanto para empresas nuevas que desean entrar en un mercado con bajo coste como de complemento para empresas ya posicionadas en el mercado offline.
Description of the tech for sale
Strategy planning and design to analyse a market, define the target, market segmentation and develop a new electronic or mobile business as exclusive or complementary to an offline business. Planificación y diseño de estrategias y asesoramiento para lanzar un negocio online o móvil. Estudios de mercado e identificación del público objetivo y segmentación del mercado.
Specifications
Market research design; questtionaire; collection of primary information from firms or consumers; statistical analyses (uni, bi and multivariant) and managerial implications and recommendations. Diseño de estudio de mercado, cuestionario, recogida de información primaria de consumidores o empresas, análisis estadísticos uni, bi y multivariantes y recomendaciones empresariales
Main advantages of its use
- Businesses support who wish to combine their offline commerce with other online or mobile. Ayuda a las empresas que deseen compatibilizar su negocio offline con uno online o móvil
Applications
- Development of online and mobile commerce.Desarrollo de un negocio online o móvil.
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Mobile application that allows to anticipate the risk situation in order to increase the driver's attention during the stretch of coincidence with a fragile vehicle. This application collects geolocation data of the subjects and stores them so that the main companies offering GPS services can use them to include a reference in their maps.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
This invention addresses an existing gap in geolocation and accident prevention applications for fragile vehicles, such as cyclists, on urban and interurban roads. DEVECA introduces the ability to communicate the presence of cyclists, improving awareness and road safety.
Main advantages of its use
- Accident Prevention: Anticipates risky situations, allowing drivers to increase their attention when approaching cyclists, reducing the possibility of accidents.
- Inclusivity: It does not require additional infrastructure, as it works on standard mobile devices.-
- Simplicity: It is intuitive for cyclists and drivers, allowing a fast learning curve.
Specifications
The software presents the approach of a "publisher-subscriber" communication model. In this scheme, the mobile application acts as the "publisher", notifying the location of fragile vehicles, such as cyclists, to other GPS devices on the road. This communication relies on the efficient use of the memory, battery and standard geolocation system present in the smartphones of the issuing users.
The application is distinguished by its ability to integrate with geolocation platforms, which have an extensive global user base. This type of collaboration significantly expands the scope of information on the presence of cyclists on the roads, as the DEVECA mobile application can collect geolocation data from the subjects and store it in a way that it can be used as a reference in its maps. This technical approach not only simplifies implementation by not requiring additional infrastructure, inputs or machinery, but also allows both the publishing and information consuming applications to run effectively on standard mobile devices, facilitating their adoption by users.
In addition, the invention suggests future applications, such as the detection of other vehicles in risky situations and its potential use in the development of autonomous vehicles.
Applications
The software improves road safety by enabling cyclists to share their position on national and local roads. Its application extends to both urban and interurban roads, focusing on preventing accidents caused by inattention or unawareness of the presence of fragile vehicles.
Intellectual property status
Protected by software
Current development status
Device already developed and validated for industrialization.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Granted Patent
software
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Decision Support Tool for Production Flexibility (Volume and Mix) (specifically, the Extended Goldratt PQ Problem) based on Hybrid Simulation (discrete simulation and agent-based intelligent simulation).
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
In contrast to traditional approaches that employ deterministic or heuristic methods for optimizing manufacturing and production systems, the innovative approach adopted by the Extended PQ Problem is to address the intrinsic complexity of the PQ Problem and extend it with uncertainty in both volume and mix through modeling and simulation techniques. These methods enable the capture of both internal interactions within the production system and external uncertainties, potentially leading to more realistic and effective solutions. By considering stochastic situations and applying simulation-based approaches using both discrete simulation and intelligent agent techniques, the limitation of oversimplification in traditional approaches is overcome, resulting in more informed and efficient decision-making in complex production systems.
Main advantages of its use
-Allows for the identification of current issues and potential improvements in the sequencing of manufacturing and production systems.
-Takes into account sources of uncertainty, both in production volume and mix, thereby enhancing the practical utility of the proposed solutions.
-Facilitates experimentation before implementing decision-making in real manufacturing and production systems.
Specifications
In general terms, the PQ Problem Extended simulator is a tool that allows experimentation with the well-known Goldratt PQ Problem production system. To provide greater realism and similarity to a real production system, the PQ Problem Extended has been extended with uncertainty in both production volume and mix. In this way, the PQ Problem Extended offers an appropriate framework for analyzing the behavior of managers and the impact of their decisions on manufacturing system flexibility.
To implement this PQ Problem Extended, hybrid modeling and simulation techniques have been used. Modeling has been done through Petri Nets, a common choice for capturing the dynamics of agent-based systems, representing the operation of the production system over time. Regarding simulation, discrete simulation has been used to implement a future event list, which is necessary for advancing the simulation clock and managing the sequence of discrete events that trigger actions. Additionally, intelligent agent-based simulation has been utilized, as this decentralized approach is considered highly suitable for analyzing the complex behavior of flexible manufacturing systems that rely heavily on interdependencies in variable environments. Systems are created from the interaction of their basic units, agents, so the global system is modeled as a multi-agent system, where individual agents interact in a changing environment and cooperate to achieve collective objectives.
Please do not hesitate to contact the University of Burgos for further information regarding the technical features of this software.
Applications
This simulation tool enables the analysis of a manufacturing system's behavior while considering various levels of uncertainty in production volume and product mix. Through experimentation, it becomes possible to anticipate outcomes before making changes to real production systems. The tool assists in decision-making by identifying how these sources of uncertainty can impact the economic performance of the system. Furthermore, it offers managers insights into the system's behavior over time.
Intellectual property status
Protected by software
Current development status
Device already developed and validated for industrialization.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Granted Patent
Software
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Software tool designed to assist decision-making and thereby enhance the supply chain based on hybrid simulation, simulating detailed behavior collaboratively and non-collaboratively, at different levels of noise.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The tool extends the Beer Game in a way that allows the configuration of different levels of uncertainty and the working philosophy of the supply chain (collaborative and non-collaborative). Through simulation, different alternatives can be experienced beyond those offered, facilitating decision-making.
Main advantages of its use
- It allows the identification of current issues and potential improvements within a specific supply chain.
- Fosters a paradigm shift from a non-collaborative approach to a collaborative approach.
- Facilitates experimentation before implementing decision-making in real supply chains.
Specifications
In broad terms, the Beer Game Extended simulator is a tool that enables experimentation with the well-known Beer Game production and distribution system. In addition to the two classic sources of uncertainty considered in the Beer Game—consumer demand and distortion caused by fixed waiting times (production and shipments)—to offer greater realism and similarity to a real supply chain, the Beer Game Extended has been expanded with different sources of noise: defective product rate, production capacity constraints, transportation capacity constraints, production costs, shipping costs, and storage costs. In this way, the Beer Game Extended provides an appropriate framework for analyzing managers' behavior and the impact of their decisions on the supply chain's dynamics. To implement this Beer Game Extended, hybrid modeling and simulation techniques have been employed. On one hand, discrete-event simulation has been used to implement a list of future events, which is necessary to advance the simulation clock and manage the sequence of discrete events that unfold actions. On the other hand, agent-based simulation has been used, as this decentralized approach is considered very suitable for analyzing the complex behavior of supply chains. Thus, the supply chain has been modeled as a multi-agent system, where individual agents interact within an environment and cooperate to achieve collective objectives. Feel free to get in touch with the University of Burgos to learn more about the technical features of this software.
Applications
The software assists managers in understanding the underlying effects when making decisions in all sectors that involve a supply chain.
Intellectual property status
Protected by software
Current development status
Device already developed and validated for industrialization.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Granted Patent
Software
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
It is an educational virtual reality tool that aims to increase success in learning basic computer science.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
In basic computer classes, practical exercises on the components of a computer are not usually carried out (assembly-disassembly), due to the cost involved. This could result in a lack of basic knowledge (function and main characteristics of the components of a computer). To meet this need, the PC Virtual LAB tool has been created. The aim of this tool is to give students of technical degrees a better understanding of the function and main characteristics of the components of a computer and thus increase the success in learning basic computer skills in a very large number of students.
Opening a computer, removing components or replacing them with others involves a high cost, which is why this video game is a valuable tool. This video game allows the student to deepen this knowledge outside the classroom in an autonomous way.
The results of the validation of this educational tool show statistically the improvement in learning performance, comparing its use with other more traditional learning methodologies (visualisation on flat screens of the same software or a traditional classroom in which only the teacher has access to the inside of a computer).
Main advantages of its use
• It allows for increased success in learning basic computer concepts.
• It allows to deepen basic computer skills outside the classroom in an autonomous way.
• Provides basic computer skills.
• It provides a better understanding of the function and main characteristics of the components of a computer.
• It generates greater student interest and engagement compared to conventional learning environments.
Specifications
The main novelty of this tool is that it can be viewed both on computer screens and in Virtual Reality environments. This virtual reality educational game allows "doing" rather than just observing. Students can learn experientially and progress at their own pace. In addition, the use of virtual reality provokes greater interest and engagement compared to conventional learning environments.
Applications
The tool is specifically developed for students of basic informatics, mainly a young people. Although the main target audience would be computer science teachers who want to use this educational game in classes or to recommend their students to use it as a complement to what they have seen in class. Secondly, there would be students who wish to learn more about informatics concepts and finally, computer enthusiasts who are interested in the latest advances in computer science. Regarding entities, the tool is also aimed at educational institutions so that they decide to incorporate this game into their teaching methodology within the basic computer science programmes. Finally, there is another, more secondary target, which is the technological hardware and software development companies that want to cooperate in the development and improvement of this simulator in exchange for their brands appearing in this technology.
Current development status
The videogame is temporarily available for free download on the Steam
under the name "PC Virtual LAB"
(https://store.steampowered.com/app/1825460/PC_Virtual_LAB/).
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ceQjUx9PMyc
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Patent already applied for
Software
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Cancer is one of the leading causes of death in the world. Therefore new improved chemotherapeutic agents are needed. The tambjamines are a class of marine alkaloids with intriguing pharmacological properties, including antitumor activity. Inspired in the structure of these compounds we have synthesized a family of synthetic analogs displaing interesting antitumor activity "in vitro", promoting apoptosis in several cancer cell lines.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The compounds described in this invention display interesting antitumor activity "in vitro" showing low toxicity against normal cells. Their action mechanism is proposed to be their ionophoric activity. These compounds can function as anion carriers upsetting the ionic balance of cells. They are cytotoxic and through thios activity they induce apoptosis indifferent cellular cancell lines.
Main advantages of its use
The mechanism of action of these compounds allow them to be used in resistant cell lines against conventional chemotherapies.
Specifications
The compounds described in this invention are inspired by the structure of marine alkaloid bearing a 4-methoxybipyrrol unit. Substitution of this moiety by different enamine group yields the active derivatives. These compounds can promote the transmembrane transport of anions such as chloride an bicarbonate.The ionophoric activity of these compounds change the intracelular pH of the treated cells. Vital tinction assays using acrinidine orange revealed the deacidification of acidic organelles such as lysosomes. It is known that this process triggers apoptosis and IC50 values in the low micromolar range were calculated for these compounds in different cancer cell lines.
Applications
These compounds should be of interest for pharmaceutilcal companies willing to conduct preclinical studies to assess their potential in the clinic. They can be used for the treatment of different cancer conditions.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P201201039
Current development status
Research or Experimental
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Electrical and topological modeling of electrical distribution networks for visualization in Google Earth and subsequent optimization studies and calculations of load flows and connection capacities of electrical generators according to RDC / DE / 001/21 of the National Commission of the Markets and the Competence. Export of the model to software in PTI RAW and Powerworld format.
Software developed to process the files of the electrical distributors and obtain files format for Power Flow calculation software.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The modeling of distribution networks is automated from files that all electricity distributors in Spain are obliged to report to the CNMC. As it is plain text from the GIS of each distributor, the output format is unified to view it in a universal and free software (Google Earth).
Main advantages of its use
- It allows to visualize in a geolocated way the correction and consistency of the numerical data of the distribution networks.
- A network model is obtained for study in power flow software that is otherwise very laborious to obtain.
Specifications
The software, developed in Visual Basic NET, processes the tables of plain text files to generate the models of the networks and export them in KML format or from another software provider.
Applications
Processing of the files of the Spanish Electric Power Distributors for visualization and subsequent exploitation calculations.
Current development status
Software developed and validated for your use.
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement for data processing and technical studies
Intellectual property status
Granted Patent
software
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
This application provides the user with a personalized tourist route over a defined town or city, devised according to certain preferences expressed by himself. The user will define the time of beginning and ending of the route along with which types of activities/sites he would enjoy the most (monuments, museums, restaurants, parks…). These are selected in an intuitive way, defining an overall degree of preferences. The application will present the user a personalized route that will comply with the user's time restrictions and visiting interests. To do this, it will use public information about the town to visit obtained from a constantly updated database, which will be completed with information obtained from the device from where the request is sent (with Andriod O.S.).
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Available in the market for mobile devices are many applications that provide the user with two main different services (a) to calculate the fastest route to reach a certain determined destination (as GPS devices do) (b) to display a list of places of interest (sometimes located in the vicinty of the requesting device) that can be found in a certain town (similar to a tourist guide). However we are not aware of any application that can recommend a tourist route, that usually includes several intermediate destination points, which facilitates the way to reach each of them and that includes only interesting locations for the user. The proposed application offers several advantages to the final user: he can delegate into the application the decision of which could be the most interesting points to visit given a certain amount of time (leaving out of the route points that do not match his/her iterests), in which order should be visited or how which is the best route to reach each of them.
The application is completed with characteristics that make it useful in the moment of completing the route: indicatin in which point of the map is the user located at each moment, storing the user preferences for their use when the user requests new routes, or showing comments or advice from previous visitors to the same spot the user is headed to. All this information can be accessed by a great variety of mobile devices, depending on the preferences of the user.
Main advantages of its use
The application is proposed as a valuable addition to the advice or information that could be given by a tourist office employee on a given town, recommendeing certain points of interest and advising a route between them and giving a general overview of the town to visit. All this having the advantages of knowing in advnace which are the user's interests and beaing able to consult or modify the request at any moment (before, during or after the visit).The system inteds to facilitate a pleasing
visit to any town:
- By means of a selection of the user's preferences, the system can offer routes including only points of interest that can appeal each user individually. This system is flexible enough to support a "degree of preference" form 0 to 100 for each of the main location categories (culture, leisure, gastronomy, nature) or to filter certain types of points belonging to each of the main categories (i.e. including "restaurants", but no "terraces" in the "gastronomy" grouping).
- By using the location classification obtained from the OpenStreetMap data and the valuation that can be introduced by users that have visited each location previously (stored in the D.B.), the system can propose the current user a route that includes the most interesting locations for him/her and that can be visited in the alotted time. That is, the system is able to maximize the interest of the visit for the user without exceeding the alloted time for the route.
-The automated calculation of a route lets the user stop worrying about many of the details related to the planning of a tourist visit: look for maps or travel guides of the city, read them, plan a determined route, carry the map or guide along when completing the visit… In this case the route is offered to the user at the precise moment he/she needs it, using as a base the information of the time and location at the time of the request.
- The sytem would work at any town or city of the world, as long as there is data available about it included in the OpenStreetMap project (which is quite complete for most touristic cities).
Applications
As the main objective of the system is to increase the satisfaction of a tourist visiting a determined town or city, one of the main stakeholder of the sytem would be the town or city council of a locality interested in promoting its tourist appeal.As explained before, the system is prepared to function with as much locations are needed, as long as they have their data maped in the OpenStreetMaps project. It is also adpatable to calculate longer routes, that can span along several locations.As two of the main categories of locations of the system are "gastronomy" and "leisure" and information about each location is stored in the D.B.; it is an interesting possibility that the owners of each of the establishments publicise them to their potential clients by means of the application. That way, conditioned to the client requesting for some locations included in the same category, the application can include a certain business/restaurant/bar in the routes of the users with a higher probability depending on the quote the owner of the business is subscribed to. This type of advertising has the advantage of being quite
effective and at the same time very unobtrusive, as the promotions are showed to the client only when he/she demands precisely that service/activity.
Intellectual property status
The software is registered at the Burgos Local Office of the Spanish Central Intelectual Property Registry (application BU-143-13).
Intellectual property status
Granted Patent
BU-143-13
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Application designed to solve problems of urban movement and parking, aimed at people with disabilities or reduced mobility.
The operation is based on an exchange of information on the availability of places reserved for people with reduced mobility or disability in a specific environment, such as a city, a municipality, etc.
The user leaves his position marking the space as in use so that other users know that it is occupied and which are the closest alternative spaces.
Currently, the occupancy information is entered by the users themselves, but it is possible to expand it with sensors or other ways of incorporating information on the use and occupancy of a car park.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
This application takes advantage of the possibilities of mobile phones to fix, fundamentally by satellite, the user's position and benefit from information about the environment.
Main advantages of its use
Previous knowledge on the part of the user, people with disabilities or reduced mobility, of the availability of parking spaces, avoiding the transfer or displacement in case of total occupation.
Specifications
Client server application for Android mobile devices whose objective is to know the availability of places reserved for people with reduced mobility or disability in a specific environment, thus facilitating their day to day life.
Applications
It can be used in any town or municipality that has parking spaces for people with disabilities.
Current development status
Functional prototype or samples ready for testing
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Granted Patent
APP
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The detection of explosives in gas phase crucial both in the field of civil security and forensic chemistry, i.e., in determining the explosive used in terrorist attacks.
This technology describes the development and use of an array of three solid fluorescent sensory films for the selective detection of gas phase nitrated explosives. The statistical analysis of the data obtained from fluorescence spectroscopy of the three films in contact with the atmosphere containing explosive traces allows for the differentiation of not only the explosives from non-explosive similar compounds (explosive mimics), such as 1-chloro-4-nitrobenzene (ClNB) , 2-nitro-m-xylene (NX), 1,3-dinitrobenzene (1,3-DNB), 2-nitrotoluene (2- NT), 4-nitrotoluene (4-NT ) and 2,4- dinitrotoluene (2,4-DNT), but also the unambiguous distinction between a set of nito-explosives, such as TNT (2,4,6-trinitrotoluene), cyclotrimethylenetrinitramine (RDX), and pentaerythritol tetranitrate (PETN).
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Novel solid polymeric materials which allow for the detection and differentiation of non-explosive nitro-compounds from nitro-explosives (TNT, RDX and PETN) by the mathematical processing of spectral changes in fluorescence associated to the presence of vapor of these compounds.
With respect to other known solutions represents a step forward in terms of economy of use and ease of application because nowadays technologies are sensitive and selective, e.g., ion mobility spectrometry (IMS) and gas chromatography (GC), require expensive equipment and costly maintenance.
Main advantages of its use
Inexpensive technology for detecting explosive vapors. It is based on a system of sensory films whose fluorescence changes in the presence of explosive vapors. Allows not only for the detection of explosives but also their differentiation and discrimination of similar non-explosive compounds.
Specifications
Solid polymeric materials for the fluorogenic detection of nitro-explosives based on new vinyl monomers.
The polymerization of these monomers with others, including polyfunctional monomers, renders dense films or membranes, materials with good mechanical properties in both dry and swollen state, which behave as fluorogenic sensors for nitroderivatives solid vapor explosive compounds TNT, RDX and PETN. Furthermore, the combined use of these sensors in a sensor array and the statistical treatment of the data obtained from its use allow for the selective detection of these compounds and their differentiation from interference or explosive-mimics.
Applications
- It may be of interest to companies that use this kind of explosives.
- Detection of explosives in terrorist attacks (forensic chemistry).
- Civilian security: detection of explosives in cargo, luggage, mail, vehicles, aircrafts and on personnel (airports, stadiums, stations, etc.).
- Mining and quarrying.
- Companies whose area is the manufacture of explosives and weapons.
- Companies using explosives for demolition.
Intellectual property status
Protected by P201400073
Current development status
Functional prototype or samples ready for testing
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Strategy planning and design to analyse a market, define the target, market segmentation and develop a new electronic or mobile business as exclusive or complementary to an offline business.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The use of new technologies (Internet/mobile phones) can involve a competitive advantage for small and medium sized firms. The advice can be focused on the development of a new business or on the complementarion of a new business at a low cost with an existing one.
Main advantages of its use
Businesses support who wish to combine their offline commerce with other online or mobile.
Specifications
Market research design; questtionaire; collection of primary information from firms or consumers; statistical analyses (uni, bi and multivariant) and managerial implications and recommendations.
Applications
Development of online and mobile commerce.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The virtual or interactive visit consists of recreating, by means of a computer, a real element such as a landscape, an urban environment, the interior of an establishment..., allowing the observer to move through said environment and obtain information on the different elements included. in it, such as historical data, characteristics of a product, name of a store and price of products.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Access to these visits is generally through the web, which allows universal access to the places visited and also makes it possible to make complementary information available to the visitor but integrated into the visit, such as audio, video and other resources.
Main advantages of its use
The main advantage we offer is the grouping of all phases of the activity, compared to the multiplicity of companies that are necessary in other cases: photography, design, IT... This represents a clear saving, both in time and money.
The fact of being able to count, in the same research group, with people from different fields of activity, provides added value to our offer since it enables the solution of problems that, otherwise, would make it necessary to resort to third parties or companies with the consequent increase in price and time invested.
Another advantage is the rapid incorporation into our work mechanisms of the results obtained in their investigations by the members of our group, which results in higher quality and better customer service.
Specifications
Through photographic shots, through the software, virtual visits are generated. A series of initial corrections are applied to the images, after which they are processed by the corresponding software, which allows corrections in the projection and linking of the photos. After verifying the correct quality of the fusion of the final image, it is rendered and a new control phase is carried out to eliminate details that would have gone unnoticed in previous stages.
The final image, thus prepared, is adapted to the viewer used by the client, generally of the Flash type due to its universality and its independence of platforms and versions.
This adaptation includes references added to the photo as well as hyperlinks that allow jumping from one point to another in the panorama or providing additional documentary or multimedia information.
Currently, and in the process of development, we are adding the possibility of making the connection between images and databases to provide added value to virtual visits.
Applications
The main utility of virtual and/or interactive guides lies in making available to a practically universal public those visual elements specific to each business that want to be disseminated and are interested in making their territory or facilities known interactively so as to the user. Being able to control the quantity and quality of the information that complements the visual information is very important.
The companies and organizations to whom these guides are addressed are very varied, ranging from small companies, which through their implementation on the Internet want to make themselves known physically, to large companies or organizations that want to inform the public those parts of its facilities and work techniques that it deems appropriate.
Companies, particularly those dedicated to hospitality, home sales, recreational activities, residences, etc. are the recipients of virtual visits, especially if they are accompanied by the possibility of obtaining valuable data, be it multimedia, or
come from a database.
So are those public administrations such as town halls, county councils, museums, etc. who wish to publicize their heritage or their facilities in a virtual and attractive way to potential future visitors.
To do this, they have these technologies as a first-rate tool to make the object of their work known to the general public in detail.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The Intrusion Detection System developed combines different paradigms of the fieldof Artificial Intelligence to offer an intuitive visualization of the traffic that circulates through acomputer network that enables the identification of intrusions and attacks in early stages.To do this, it processes and analyzes the packets that travel through the network to be monitored,selecting from the headers of these, non-sensitive information.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
So far there are very few technologies applied to the visualization of network trafficfor its monitoring and / or identification of anomalies.
Main advantages of its use
Regarding the few solutionsexisting, MOVICAB-IDS provides the following advantages:
- It offers a much more intuitive visualization than other tools, whichrequires little training for security personnel, as well as minimal setup.
- Network monitoring tasks can be relegated to personnel with little experience,thus freeing up the most experienced staff to carry out critical tasks.
- It can be used in the training of security personnel. Other security tools may be working at the same time, being able tocombine the output / display of both.
- Reduction in the time required to process the output compared to other IDSs, whichthey generate a large number of false positives and negatives.
Specifications
MOVICAB-IDS combines different paradigms from the field of Artificial Intelligenceconstituting a hybrid artificial intelligence system (HAIS). It is based on a systemmultiagent that includes deliberative agents capable of learning and evolving with theirenvironment. These agents combine a projectionist neural model based on non-learningSupervised and Case-Based Reasoning Paradigm.By applying the aforementioned neural model, MOVICAB-IDS extracts projectionsinteresting data from a set of network traffic data and presents them through adisplay, which can be mobile (telephone, PDA, etc.). As a result of viewing eachpacket and preserve the temporal context, MOVICAB-IDS offers the network administrator asynthetic and intuitive view of network traffic and interactions between differentprotocols. This visualization allows the detection of anomalous situations and intrusions of asimple glance and subsequent identification. In addition, it helps to know the internal structure and thebehavior of network traffic, allowing monitoring of the activity in it. Additionally, work is continuing on this technology to ensure that thereal-time display.
Applications
This technology can be applied for the supervision of any computer network,regardless of its size. For large networks or with a large volume of traffic, filtering and segmentation processes have been developed, which allow the correct visualization to be carried out.
Current development status
Device already developed and validated for industrialization.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
El Sistema de Detección de Intrusiones desarrollado combina diferentes paradigmas del campo de la Inteligencia Artificial para ofrecer una visualización intuitiva del tráfico que circula por una red de ordenadores que posibilita la identificación intrusiones y ataques en etapas tempranas. Para ello procesa y analiza los paquetes que viajan por la red que se pretende monitorizar, seleccionando de las cabeceras de estos, información no sensible.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Hasta el momento existen muy pocas tecnologías aplicadas a la visualización de tráfico de red para su monitorización y/o identificación de anomalías.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Respecto a las pocas soluciones existentes, MOVICAB-IDS proporciona las siguientes ventajas:
- Se ofrece una visualización mucho más intuitiva que las de otras herramientas, lo que requiere escasa formación para el personal de seguridad, así como una configuración mínima.
- Las tareas de supervisión de la red pueden relegarse en personal con escasa experiencia, liberando de esta forma al personal más experimentado para llevar a cabo tareas críticas.
- Puede emplearse en la formación de personal de seguridad.
- Otras herramientas de seguridad pueden estar trabajando al mismo tiempo, pudiendo combinarse la salida/visualización de ambas.
- Reducción del tiempo necesario para procesar la salida en comparación con otros IDSs, que generan una gran cantidad de falsos positivos y negativos.
Características técnicas
MOVICAB-IDS combina diferentes paradigmas del campo de la Inteligencia Artificial constituyendo un sistema híbrido de inteligencia artificial (HAIS). Se basa en un sistema multiagente que incluye agentes deliberativos capaces de aprender y evolucionar con su entorno. Estos agentes combinan un modelo neuronal proyeccionista basado en aprendizaje no supervisado y el paradigma de razonamiento basado en casos.
Mediante la aplicación del mencionado modelo neuronal, MOVICAB-IDS extrae proyecciones interesantes de un conjunto de datos de tráfico de red y las presenta mediante un interfaz de visualización, que puede ser móvil (teléfono, PDA, etc.). Como resultado de visualizar cada paquete y preservar el contexto temporal, MOVICAB-IDS ofrece al administrador de red una visión sintética e intuitiva del tráfico de red y de las interacciones entre los diferentes protocolos. Esta visualización permite la detección de situaciones anómalas e intrusiones de un simple vistazo y su posterior identificación. Además, ayuda a conocer la estructura interna y el comportamiento del tráfico de red, permitiendo la supervisión de la actividad en ésta. Además, se continúa trabajando en esta tecnología para garantizar que se muestra la visualización en tiempo real.
Aplicaciones
Esta tecnología puede aplicarse para la supervisión de cualquier red de ordenadores, independientemente de su tamaño. Para redes de gran tamaño o con un gran volumen de tráfico, se han desarrollado procesos de filtrado y segmentación, que permiten llevar a cabo la correcta visualización.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Additional information (attached documents)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
ARQuiz is a customizable educational game for mobile devices. ARQuiz is an application designed with the purpose of learning and whose possibilities are limitless.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
- New platforms such as Android
- New technologies such as Augmented Reality
- Education sector: children, seniors, disabled population
- Figures interaction when selecting them
Main advantages of its use
- Ease of use of the tool
- Can be used by children, the elderly and people with disabilities
Specifications
The game shows various objects (represented by the use of augmented reality anywhere on the screen of the mobile device) and the user's goal is to find the objects through clues.
initially, by default, there are several categories (geometric figures, animals, objects, kitchen, bathroom ...) and levels of difficulty, which can be varied, for example from searching a cube to find the 3-dimensional shape that has 30 edges.
You can create your own categories, questions, levels, and add your 3D designs from internal storage with simple menus, allowing you to create a custom game.
The software applies augmented reality in smartphones and tablets that have the Android operating system and the corresponding camera.
Applications
Educational sector. Children education, disabled population and aging support. It emphasizes the training on forms, colors, words, concepts, languages, etc.
Intellectual property status
Protected by intellectual property registration BU-146-13
Current development status
Commercially Available
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Granted Patent
BU-146-13
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Due to the hybrid nature of most real-life problems, both data and knowledge must be applied to find a proper solution. In keeping with this idea, hybrid intelligent systems combines different artificial intelligence techniques and paradigms (symbolic and sub-symbolic) to construct more robust and reliable problem solving models.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Hybrid Artificial Intelligent Systems (HAISs) proved to overcome previous proposals when dealing with real-life and complex problems. This new paradigm from the AI (artificial intelligence) field enables the successful application of combined techniques and models to deal with complex problems.
HAISs have been applied to many different problems, getting nice performance results.
Main advantages of its use
By the combination of different AI technologies, the limitations of individual models and paradigms are overcame.
Specifications
The research group has wide experience on the design, development and deployment of such intelligent systems, to solve practical problems from a range of different applications: parameter tuning of machine-tools, network security, knowledge management, etc.
It requires choosing the appropriate techniques (Artificial Neural Networks, machine learning models, evolutionary learning techniques, optimization mechanisms, etc.) and combining them for each one of the problems, adjusting to the specific nature of the problem.
Applications
Problems with a hybrid nature, whose solution requires the combination of different techniques.
Current development status
In Use Testing Results Available
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
This is a set of socio-communicative software that has been designed for use by people with Autism Spectrum Disorders or for people who have difficulty in social situations with different levels of difficulty, such as can be people with brain damage, social phobia, nonverbal learning disorder, specific language disordes, among others. Its purpose is to facilitate the understanding of complex circumstances these people.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Most of related works only are dedicated to iOS platforms (iPhone and iPad). These devices are expensive. On the other hand Socio-Ruta, being developed for Android platform, has the advantage of can operate in Android tablets low cost (up to 10 times lower than an iPad). Thus Socio-Ruta can reach more people and with price more reduced.
• It can be create customized scripts, thus providing the option to create a script for each different case.
• The resulting application can be reusable for other uses that were not the original.
• By editing graphs can be constructed e.g. test of any kind and for any purpose.
• It could be consider the option to make a desktop application for the end user, in order to reach a wider audience.
• Today there is no such tool in Spanish.
Main advantages of its use
Specific product. Spanish language. Customizing scripts. Possibility of expansion by translation
Specifications
Software based desktop for social scripting and Android for viewing by people with ASDs.
To help people with ASDs, tutors have a desktop Java application with which can generate complex scripts while end users have an Android app for tablets, in which can access a set of social scripts that respond to different environments (school, work , street, meetings in the home, day center ... ) and various social situations or relationships which frequently develop in these environments or suppose a problem for the person with the social deficit . These scripts represent structured fragmentation step-by-step of the development of social situations that may represent different levels of complexity.
It is totally modelled on individual needs, it can be add new scripts simply by educators, family or by the person , keeping in mind their particular social situations, age , preferences, and the complexity that can handle the child or adult who use it. Thus, it can be choose the content that appears (images, video or audio ) and also the level of complexity based on whether or not the child can manage categories and writing sentences. Also this software could be readjusted for educational environments at all levels to complement the traditional method of teaching with new technologies.
Applications
In adition to autism centers, this software can be useful for training in domestic environment and this way complement the education of these centers. Also it may be applicable to other types of institutes as schools, colleges or universities.
Intellectual property status
Copyright - BU-144-13
Current development status
Working Prototype or Samples Ready for Testing
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Granted Patent
BU-144-13
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
This software makes the use of the computer possible to a number of disabled individuals. It shows on the computer’s screen a configurable interface where the user has access to all keyboard and mouse functionalities.
It is presented as a scanner keyboard where the active key is moving through rows and columns at a configurable speed. In its journey the active key encounters the mouse functions and other useful keys as well.
When the user wants to select the active key the click function has to be performed. The way it is performed is also configurable: mouse click, a specific key on the keyboard, the space bar, any key… Once the key has been selected it works as it had been press on the real keyboard or mouse and the active key keeps going to give the user access the rest of the functions on the screen on a round basis.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
There many scanning keyboards on the market. What makes our product different from the rest is its highly configurable character.
This was a major objective when we decided to tackle this challenge as it was mainly intended to help people suffering from cerebral palsy. These patients are affected by the disease in many different forms either physically, intellectually or both. For this reason, the program had to be very flexible.
Main advantages of its use
Due to its flexibility, this product can be used by many users affected by different diseases. It was designed for cerebral palsy but its use can be extended to many other disabilities. As stated before, it has two major utilities:
- As a training tool used by therapists to train patients on the use of the computer, to teach them how to write, etc.
- For the disabled population to make the computer more accessible to them
Specifications
The application program can be installed in any computer running under Windows XP or latter. As stated before, the software is highly configurable for two reasons:
- To provide adaptability for any user whatever his or her mobility impairments may be.
- To adapt it to any application the user may want to control or to any kind of training on the use of the computer. What the users sees on the screen can vary in size, color, speed of the active key’s displacement, etc. It is also possible to decide which keys are to be displayed: all letters, vowels only, consonants only, numbers, mouse, etc. The way the keyboard is scanned can also be configured: rows after columns or vice versa.
Sound can also be added so the computer “tells” where the active key is located at any moment. This is especially useful to people with low or null eyesight.
Applications
According to statistics, the number of disabled people in Spain is up to 3,8 millions, what means nearly 9% of the population. Among them, 120.000 are affected by cerebral palsy. The intensity of the disease varies. There are individuals who are able to conduct a normal lifestyle whereas some others are totally dependent on other persons on a daily basis. The application itself can be used by this percentage of the total population. There are different user profiles though:
- Individuals, men or women, who have a computer at home.
- Associations, foundations and social services.
- State or private schools where disabled students may be present
Intellectual property status
Protected by intellectual property registration BU-157-12
Current development status
In Use Testing Results Available
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Granted Patent
BU-157-12
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Game chips based on virtual reality for the disabled. A tool where children with cerebral palsy interact with the computer by using properly designed chips that can be recognized by a webcam, and thereafter show by screen where would be the chip, a phrase, or 2D image 3D, as appropriate to the combination of these chips.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The technique of viewing by the camera chips and subsequent screen representation that represent the same concept is called augmented reality. This process is carried out with the collaboration of the Cerebral Palsy Association of Burgos (APACE).
Main advantages of its use
We found with the difficulty that have a person with cerebral palsy and much more if it is a child to operate a computer. Also concerned about people who have big problems to engines, using learning tools such as puzzles, although very simple, causes them a lot of frustration because the disease are often unable to properly interact with them. Relying on the use of the webcam and augmented reality got a very visual and attractive to them because they see the place where they are on screen, combined with graphics or text which change position while they move sheets provided to them. We intend to approach the management of these computer users, you find it useful and stimulating though not handle typical applications and programs of a computer.
Specifications
The application is written in object-oriented language Action Script (similar to Java) developed by ADOBE and is freeware. The libraries needed to work the project are:
- Papervision 3D which is used to make graphical support for the application and it is free software. Programmed in Action Script.
- FLARToolKit which is used for the treatment of the augmented reality cards, webcam and 3D images. This case has a GNU license which is not to pay a license if the application you do not used for commercial purposes, otherwise, would have to pay in order to develop and profitable idea. Programmed in Action Script.
The 3D models are designed in the free program Blender.
The greatest strength of the project is that with a minimal amount of resources can create a viable application, since we only need a PC with Flash Player (free download Internet is to see such videos on youtube ) installed a web Cam and application. In the event that the availability of more financial resources could be improved as a better camera tools, use more programmers to improve the application or designers to detail and expand the catalog of objects and 3D animations, etc.
Applications
Although this tool is intended for learning and stimulation for people with cerebral palsy, is for use and support of psychologists and therapists and in no event shall use the patient / student solo. In other words, is an educational tool for use by special education teachers. It can be said that the development of applications in the field of augmented reality is quite advanced and covers many fields such as video games, marketing companies, mobile phone. However, in the sector in which we're moving we do not we are aware that there is no similar tool and addressed to such people with such problems.
Current development status
Working Prototype or Samples Ready for Testing
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Patent already applied for
In process
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The University of Burgos has developed a web application, accessible from a browser, that implements a tool for traffic analysis. It uses GPS data of vehicles that are moving and this data is used to obtain a sample of the traffic during their movements. The use of Big Data technology in the monitoring and analysis of transport activities in the physical world (goods or passengers) will allow contracting companies to draw conclusions about the transport or logistics processes that are currently implemented, and the prediction of the conditions of the trips in the near future, being able to plan or anticipate different situations and allowing, therefore, an optimization of their activities. This type of service can be very beneficial to courier companies, transport logistics, passenger transport (taxis or buses), public administrations or municipalities, etc.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
There are various commercial software solutions dedicated to traffic analysis. These companies perform the analysis using geospatial data and traffic cameras mainly. The TraVisAna software is based on the analysis of GPS trajectories, which lowers the cost of infrastructures since only a device with GPS is necessary and, now almost all public and private vehicles have one. Like these solutions, an application that runs on a server and on these devices is needed to be able to collect the routes and analyze them.
Main advantages of its use
- The treatment of the data generated allows identifying the traffic segments into which the transport activity can be divided and analyzing and even predicting the direction and speed of the traffic.
- Only a device with GPS is necessary.
- It is configurable and easy to use.
- It does not rely heavily on geospatial data, making the application adaptable to any city, which saves costs on software of this type. The app can also collect information from pedestrians, bicycles or scooters.
- By dividing the data, more detailed analyzes can be made by neighborhoods, sectors, hours or specific days.
- The cost is much lower than other existing solutions, since only the costs of renting or purchasing the server and the maintenance of the application are incurred; which makes the service affordable for SMEs or smaller companies, which can obtain relevant information in their business area.
Specifications
The prototype is based on Big Data technology and on the “Application of traffic analysis through geopositioning routes (AATRG)”. By combining both technologies, it is possible to build, from the raw data collected through the GPS devices of the users, a model of the traffic state. Using this technology, large amounts of raw data can be processed and that data can be enriched with information from other sources. By processing the enriched data, a model is generated that allows the information contained in these data to be described and analyzed.
The model generated in the prototype is a directed graph that describes the traffic between different locations in the city. This graph is associated with additional information in its relationships such as average speed and traffic density. Representing this graph graphically on a map, it allows a visual understanding of the traffic state. In addition, it is possible to make predictions of specific days and hours, so that companies can adapt their logistics to daily conditions. This would allow transport and logistics companies to adapt to daily changes in traffic in order to optimize their resources which would improve their competitiveness.
Applications
- Provide both consulting and personalized analysis services as well as custom applications that allow analysis to the company itself.
- Transport companies and parcel or merchandise delivery, which would allow them to go one step further in optimizing planned routes.
- Public administrations, city councils and those companies subcontracted by them, since it allows an analysis of the traffic that is key for the development of strategies known as Smart Cities or Smart Tourist Destinations.
- Public administrations since it allows making informed decisions for the regulation of traffic lights, planning of the public urban transport system, planning of emergency systems (ambulances, evacuation for emergencies), urban plans and in general all kinds of decisions that may affect traffic.
- Individual users who are either self-employed whose commercial activity depends on urban transport, or are developers of other applications that can use the processed traffic data for their own operation or simply want to know the state of traffic in their city to plan their own trips.
Intellectual property status
Protected by software BU-121-20
Current development status
Software already developed and constantly improving.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Granted Patent
BU-121-20
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The tool allows the automation, registration and evaluation of the “Functional Skills Detection Scale in children 0-6 years old” (e-EarlyCare) and the development of personalized programs through a web application. This application is aimed at professionals from Early Care centers, specific to Special Education and other centers that carry out interventions at an early age. In addition, it can be applied in other centers such as Nursing Homes, Modular Injury Rehabilitation Centers, etc.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The objective of the application is the automation, registration and evaluation of the Functional Skills Detection Scale in users with ages of evolutionary development of 0-6 years and, as a result of the evaluation, the specification of the priority functional areas for intervention therapy, through a web application (eEarlyCare Therapeutic Program).
This application allows the correction and interpretation of the user's development in the 11 dimensions of functional analysis that the Scale measures: Autonomy in feeding, Personal care and hygiene, Autonomy in dressing and undressing, Toilet control, Functional mobility, Communication and Language, Social interaction skills, Interactive and symbolic game, Routines of daily life, Adaptive behavior and Attention.
In addition, it provides a personalized intervention program for each user that covers the different functional areas in which affectation has been detected.
Main advantages of its use
- It allows the automation of registration and interpretation, which facilitates its use by professionals from Early Care centers, Specific Special Education Centers and other centers that carry out interventions at these ages, depending on Town Halls, Provincial Councils or Autonomous Communities.
- The interpretation of the results occurs practically in real time to know the functional development of the user.
- It allows the individualized monitoring of a user and the comparison of the development in the functional abilities of different users of the same center.
- The technologies used for the development of the web application facilitate high-quality visualizations and interactivity and allow the storage of data in file bases or in the cloud.
- The technology makes it possible to carry out more complex statistical analyzes with the application of supervised Machine Learning techniques (classification and / or regression) and unsupervised (Clustering) through the export of files to more powerful statistical packages. In particular, classification techniques are very useful for the personalized learning proposal.
- Its use makes it possible to enhance the efficiency and profitability of the resources of the center where it is implemented.
- The application is oriented to a desktop environment due to its ease of installation and necessary resources.
- The expansion allows the development of personalized therapeutic intervention programs in the areas in which affectation has been detected.
Specifications
The application created consists of a functional skills development scale (EHFI), an algorithm for correction and interpretation through visualization graphs and a software (eEarlyCare Therapeutic Program) for recording, interpretation and visualization of the results of the user's evaluation to ages 0-6 years in functional skills. This software allows the intervention professional to carry out quarterly evaluations on the development of users, both individually and in groups. All this information is represented in graphics that can be exported to png and / or pdf format. Also, it supports the export of evaluation records to Excel sheets. Likewise, the application is offered in a bilingual Spanish-English format.
Applications
Potential applications of the software created are as follow:
- The automation of the measurement of functional abilities in users with developmental ages 0-6 years.
- Specification of the priority functional areas for therapeutic intervention in the user.
- Individualized monitoring of evaluation in the acquisition of said functional abilities in a user and/or a group of users in education or therapy centers in development ages 0-6 years.
- Chronological age may be higher, which is why the radius of intervention is also extended to people with involutive pathologies such as senile, presenile dementias or affectations in the areas of autonomy.
- Its use would also be applicable in nursing homes or rehabilitation centers for spinal cord injuries, with the aim of studying the evolution of these functional abilities in pathologies such as presenile and senile dementias (Alzheimer's ...), stroke, stroke, spinal cord injuries, etc.
Intellectual property status
Protected by intelectual property BU-120-20
Current development status
Software already developed and constantly improving.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Patent already applied for
BU-120-20
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Ruthenium (II) photocatalysts of formula (M +) nXn- are described, in which Xn- is an anion and M + is a cationic complex of formula (Ia) comprising an 8-arylsulfonamidoquinoline ligand, as well as its method of obtaining it. The use of said ruthenium (II) photocatalysts in the synthesis of imines by photooxidation of amines in the presence of oxygen and by the use of visible light is also described.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The procedure for the synthesis of mono-cationic complexes of Ru (II) of the polypyridine type described, presents activity as photocatalysts despite not being considered as good candidates for photocatalysis according to the state of the art. Specifically, the Ru (II) complexes of the invention have a superior stability to the equivalent photocatalysts known in the state of the art, such as ruthenium (II) complexes of the type, [Ru (bipi) 3] 2+ .
Furthermore, the ruthenium (II) complexes of the invention provide a high yield for the conversion of amines to imines (greater than 90%), with very good selectivity and without producing undesired by-products. This imine synthesis procedure is performed in the presence of O2 by irradiating with visible light at room temperature, between 20-30 oC.
Main advantages of its use
• Conversions of benzylamine to imine with yields greater than 90% and without additives, at room temperature and with the use of oxygen or air as an oxidizing agent.
• The use of visible light allows synthesis to be carried out with substrates more sensitive to over-oxidation or the degradation of their products by photoactivation of bonds, avoiding the formation of unwanted secondary products.
• Present a photostability equal to or greater than that of the analogous complexes of the state of the art of ruthenium (II) of the formula [Ru (bipi) 3] 2+.
• More selective procedure and with optimal yields.
Specifications
Design of new Ru(II) photosensitizers bearing 8-arylsulfonamidoquinolines and the successful evaluation of their photocatalytic properties in a new method the smooth and selective oxidation of primary and secondary benzylamines using O2 as the oxidant.
In this proposed method three key features must be highlighted: the photosensitizing ability of the Ru(II) complexes that promotes the production of O2; the electrophilic nature of O2 that facilitates its reaction with nucleophilic amines and the weak acidic character of the in situ generated H2O2 that assists in the catalytic activation of the primary aldimine.
Applications
- Synthesis of new drugs and diagnosis due to their interaction with DNA.
- Acting as luminophores in Bioimaging techniques (cell visualization).
- Photodynamic Therapy (PDT). Some of these Ru (II) complexes are known for their cytotoxic activity after irradiation with light, generating highly reactive singlet oxygen that causes cell death.
- Photocatalysis acting as photosensitizers (PS) in synthetic organic reactions or in hydrogen production.
- Electroluminescent devices such as LED emission diodes, including OLED (Organic Light Emiting Diodes) type.
- Obtaining Sulfóxidos from the oxidation of sulfides of application in the obtaining of different drugs.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202030245.
Current development status
The technology related to the synthesis method is developed.
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement; License agreement; Technical cooperation: further development; Technical cooperation: testing new applications; Technical cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Smart device focused on real-time water management. Applicable both drinking water and industrial and waste waters, monitored parameters include cations (Fe (III), Hg (II), Al (III), etc.), oxidants (Cl, nitrites, peroxide, etc.), biogenic amines, trinitrotoluene, pH, turbidity, conductivity, etc.
This developed technology, composed by a series of sensors, small biochips, which experiment a change of colour when contacting the analyte of interest. This change is captured by a digital camera and is sent via Wifi to a database, where it is analysed and registered. It is also possible to issue a report and/or inform clients in real-time.
New and innovative aspects
Biochips used in this device, compared with other related patents, do not require the use of chemical reagents and are less complex, which allows designing and developing a-la-carte sensors for specific demands.
In addition, by providing real-time results, it allows a quickly answer in case of the detection of pollutants harmful to health and/or the environment.
Main advantages of its use
- Ease of installation and maintenance of both the device and the biochips.
- Smart connectivity
- Multi-analytical approach for analytes of interest.
- Qualitative and quantitative analysis "on-site".
- Usable by non-specialized personnel under any weather conditions and does not require IPE (Individual Protection Equipment).
- Calibration is not needed and chemical reagents are not required.
- Online database
Specifications
COLORS device is a solution developed within the framework of the Internet of Things (IoT), integrating some technologies with the aim of obtaining a product capable of giving an integral response to quality control in water and other aqueous media.
Biochips, which can be developed in 8 mm diameter discs or 5 mm side squares, have a thickness of between 100 and 200 microns. These sensors are placed on a stand, a disc or a cartridge, that are low cost consumables. Cartridge, unlike the disc, has no limitations in terms of the number of biochips to be incorporated. It is also possible to combine different biochips to monitor several species.
Applications
- Water quality management laboratories.
- Wastewater and drinking water treatment plants.
- Agri-food industries.
- Extractive industries.
- Environmental management of wastes and pollutants.
Current development status
Protected by patent P201830631
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement, License agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical cooperation: adaptation to specific neds.
Related keywords
Device, monitoring, water, detection, pollutant, iron, mercury, aluminium, management, residual, wastes, metals, pH, biogenic amines, turbidity, chlorine, nitrites, conductivity.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Design of virtual environments and visits for industry, tourism and culture. It is possible to recreate real elements as sceneries or interiors, adding historical information, product characteristics, room names or product prices.
The access to these virtual visits through a worldwide available website. The visit also includes audio-visual media.
This way, companies and other organisms can expose through the internet, allowing potential visitors to access virtually and attractively their facilities.
Accessibility
For more information and examples, please visit: http://3dubu.es/
Contact:
- Andrés Bustillo Iglesias, Advanced Data Mining Research and Bioinformatics Learning (ADMIRABLE).
- E-mail: abustillo@ubu.es
- http://www.ubu.es/otri-transferencia/oferta-cientifico-tecnologica/centro-de-creacion-digital-de-la-universidad-de-burgos-digiubu
Short description of how tool can be used
All contents necessaries are created for each product, from audiovisuals to the web environment, according to the preferences and needs of the organization or Company. The use of virtual visits is a tool to be known and show the facilities, attracting this way potential customers or visitors.
Fees
The created guides and visits are highly personalized. They can include a high variety of audiovisual services. Generally, the web app costs between 2.000 and 30.000€, but the technical or creative potential of the group allows services that can imply and increase of time and cost.
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Artificial vision system and data capture for counting people in adverse environmental conditions. The real time data is used to analyse the occupation or people flows in a reliable way, becoming a tool to improve the decision making more efficiently.
New and innovative aspects
People counting systems with real time information, are used to make decisions in multiple sectors as commerce, public transport, museums or other public spaces.
The obtained data is useful to make a detailed analysis of people flows, spots of concentration, buying habits, marketing influence and furthermore, to optimize material and human resources.
To ensure the system is working properly in adverse brightness situations ensuring the operability and the data collection. Thus, the system becomes a reliable choice to control people in an enclosure.
Main advantages of its use
- Contributes with real time information of people flow and attendance in commerce, public transport, museums, etc.
- Allows analysing automatically de people flow with video cameras.
- Makes it easier to control de concurrence and making decisions in halls or vehicles.
- Functionality granted in adverse brightness conditions.
Specifications
Artificial vision system to detect and counting people transiting through a limited area. Images are captured using cameras and they are automatically analysed by computer vision.
Those solutions requires high calculus power, while the system is able to select those images in a video sequence stable enough to extract information. Over these images, an approximation with rectangles is made in those zones where movement is detected, and a filter discerns if it is a person.
The system also can perform a tracking of the flow of people in an establishment or an enclosure, using the image analysis explained above. Moreover, automatic decision making can be implemented, for example: warning if the maximum capacity or traffic is exceeded.
Applications
- Access and concurrency control in establishments: Commerce, museums, public transport and other sites.
- Analysis of effectiveness of marketing campaigns and other buyer influence factors.
- Optimization of resources by clients or assistants presence.
Intellectual property status
Property register BU-43-17.
Current development status
Proof of concept. Evaluation of results.
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement; License agreement; Technical cooperation: further development; Technical cooperation: testing new applications; Technical cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
New device for direct “in situ” detection of ascorbic acid in different types of liquid samples, for example biological samples or food products.
The equipment consists of an electrode system formed by three disposable electrodes, obtained by silkscreen printing.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Commonly employed methods present some disadvantages such as a poor selectivity and a progressive deterioration of the sensitivity of the electrode when used in complex matrices.
This new device solves these disadvantages by employing disposable electrodes that allow the determination of ascorbic acid with greater sensitivity in different types of samples, for example in biological and food samples.
Main advantages of its use
This low cost electrochemical method, applied to chemical analysis, simplifies the commonly applied techniques, can be performed by non-qualified personnel, with a short analysis time, allowing “in situ” detection of the analyte.
Specifications
The analysis is based on the oxidation of ascorbic acid into dehydroascorbic acid.
The device developed is of an electrode nature, characterized by comprising three disposable electrodes: one working electrode, one auxiliary or counter electrode, and one reference electrode. Each one includes a contact or terminal, a section and an active area. All electrodes have been manufactured by silkscreen printing with conductive material ink on a plastic polyester (PET) sheet. Each electrode has a specific shape, to be adapted easily to their respective functions.
The terminals and sections have been printed with an Ag-based ink. The active surfaces of the counter electrode and working electrode have been printed with a conductive ink of C, and the active surface of the reference electrode has been printed with an Ag/AgCl ink. At the same time, the active area of the working electrode is modified with gold nanoparticles.
Applications
It presents a high responsiveness in sectors such as health, food and beverages.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P201631238.
Current development status
Currently, the device is in prototype phase, validated in laboratory
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement; License agreement; Technical cooperation: further development; Technical cooperation: testing new applications; Technical cooperation: adaptation to specific needs
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The University of Burgos has developed a new solid electrical conductive polymer material, preferably as film or coating, using non-conductive polymers. This material can be used in the production of resistive or conductive sensors for substances of interest, both in gas phase and in solution, or for use in electrical and electronic systems.
New and innovative aspects
The process of obtaining the conductive polymer material allows getting a series of tailored properties depending of the use that is desired to give at the material. This is possible based on the selected monomers that form the initial non-conducting structure which can present characteristics such as flexibility, stiffness, chemical resistance, thermal resistance, hydrophilicity, hydrophobia, to name some relevant property in the area of materials applications, where the conductivity can play a special role in innovative applications.
Main advantages of its use
The main advantage is that this polymeric material can be produced easily and the fact that there are chemical bonds between the starting acrylic material and the conductive polymer chains. In this way homogeneous materials are obtained in the form of solid membranes, easy to handle and with good mechanical properties. At the same time this polymeric material owns conductivity values of a semiconductor material or even a metal.
Specifications
The invention relates to conductive polymers based on polyaniline sequences and, therefore, it is included in the area of conductive and semiconductor materials.
To be precise, the invention provides conductive polymeric and semiconductor electrical materials prepared by growing polyaniline side chains from non-conducting polymers with aminophenyl side groups in their structure, in the form of films or coatings.
Applications
- They can be used as semiconductors in electronics, as substitutes for metallic conductors, in the preparation of photovoltaic cells. It can be used as a conductor in electronic circuits and also in the lightening of parts that have to conduct electricity (metal substitute), sensors of chemical species, etc.
- In fields such as automotive and aeronautics, for example, it can mainly be used as antistatic material in paints, inks, fabrics and adhesives.
- As a material that can change color depending on the state of oxidation, it can be used in the manufacture of electrochromic devices, smart windows and electronic paper.
- Application in the field of Bioengineering.
- Application in the field of Nanotechnology.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P201631147.
Current development status
In use, test results available.
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement; License agreement; Technical cooperation: further development; Technical cooperation: testing new applications; Technical cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Electronic device capable of detecting lactic acid in sweat, in real time, through screen-printed electrodes. The device includes an enzymatic biosensor capable of measuring the specific activity of the enzyme lactate oxidase on lactic acid, substance generated during physical exercise and partly excreted through sweat.
New and innovative aspects
- At present, no measuring device capable of lactic acid in sweat is recognized.
- Currently it has not been detected any device capable of measuring lactic acid in sweat
- Lactate is a good indicator of the level of physical effort of a person, and plays an important role in sports medicine, where its determination is useful for monitoring respiratory failure, shock, heart failure and metabolic disorders.
- The device is autonomous and portable and includes all electrical and electronic elements necessary to perform the measurement without connecting to an external device.
- The device includes a miniaturized potentiostat and the biosensor, disposable, single-use, and replaceable for each measurement.
Main advantages of its use
- Simple measures, just with the contact between the electrode and the sweat
- Non-invasive measures, unlike those that can be made through blood, which require long and complex procedures
- Real-Time measurements
- A small amount of sweat is required, one drop, for the measurement, consuming a low voltage
- The measurement obtained is transformed into digital signal and transmitted to the user
Specifications
The biosensor is a disposable system comprising three screen-printed electrodes on a flexible textile support. It has the ability to extract information from the biological system and quantify the signal into electrical current. In contact with sweat, the electrical signal will be modified in proportion to the concentration of lactic acid, allowing its quantitative measurements. The biosensor requires a potentiostat to work.
Applications
Sports Equipment and Health.
Intellectual property status
Patent P201630518.
Current development status
Prototype.
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Energy Technology (11)
Summary of the technology
The patent is based on the production of sustainable concrete using wind turbine blade waste, recycled concrete aggregates and conventional components. The production process guarantees good workability of the concrete and its efficient transportation. The wind turbine blade waste, composed of fibers, wood and polyurethane, is integrated into the concrete, offering advantages such as improved resistance to bending and contributing to the circular economy by reducing waste disposal and reducing the consumption of natural resources. The technology seeks a balance between sustainability, structural efficiency and minimization of environmental impact.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
- Use of wind turbine blade waste compatible with recycled concrete aggregate: This approach contributes to the reuse of industrial waste and the reduction of its environmental impact, in addition to solving the problem of the complex recycling of wind turbine blades.
- Use of recycled concrete aggregate: Integrating these components, optimizes the reuse of recycled materials and helps mitigate the demand for natural resources.
- Contribution to the circular economy: By minimizing the discharge of wind turbine waste and reducing the need for the production of new materials, it is aligned with the principles of the circular economy.
Main advantages of its use
- Adequate workability: Despite the presence of recycled concrete aggregate and wind turbine blade waste, a concrete is obtained that has adequate pumping capacity.
- Improved structural properties: The presence of the components used in this patent provides greater resistance to bending, post-cracking and post-breakage, improving the mechanical properties and increasing the safety of the structures.
- Reduction of C02 emissions: Reduces cement clinker production, reducing associated carbon dioxide emissions.
Specifications
This innovative concrete is characterized by effectively integrating wind turbine blade waste and recycled aggregates, highlighting its contribution to sustainability and the circular economy. It presents fresh properties with a fluid consistency and low density. At 28 days, it exhibits compressive strength of 26.8-42.6 MPa, flexural strength of 4.9-6.4 MPa and improved mechanical properties thanks to the inclusion of glass fibers and polyurethane in the waste. This versatile concrete adapts to several construction applications, establishing itself as a technically and environmentally advanced option.
Applications
This sustainable concrete, composed of recycled concrete aggregate and wind turbine blade waste, finds applications in a variety of construction fields. From structural elements such as beams and columns to pavements, tubes and prefabricated elements, this versatile material adapts to several construction needs. Its improved strength, thanks to the inclusion of GFRP and polyurethane fibers in the waste, makes it a suitable choice for projects seeking both structural efficiency and environmental sustainability.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202430081
Current development status
The patent has been tested in the laboratory, obtaining satisfactory results, and is ready for its production phase.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
In the search for organic compounds for redox flow batteries, researchers from the University of Burgos have developed a synthetic procedure that allows obtaining a viologen, 3,3'-([4,4'-bipyridin]-1,1'-diio-1,1'-diyl)bis(butane-1-sulfonate), in a simple, selective and multigram scale. The use of this molecule can replace metals such as vanadium, giving as a result more economical and ecological batteries, among other advantages. Moreover, compared to other viologens, batteries built with the compound developed at UBU have a superior stability.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Viologens are a type of cationic organic compound characterized by rigid structures deficient in π electrons and excellent reversible redox properties. Researchers at the University of Burgos have been able to develop a new methodology for the synthesis of a novel organic structure in a simple way (a single reaction step), efficiently (yields greater than 90%) and in multigram quantities. This new 3-butylsulfonate viologen has been used as an electroactive molecule for the anolyte of organic redox flow batteries.
Main advantages of its use
- By using the methodology described by the authors, the desired organic compound is prepared from accessible starting materials and in a single reaction step.
- The novel viologen is isolated with a yield greater than 90% and in amounts higher than one gram.
- Flow batteries built using this molecule as an anolyte have a superior stability.
- It allows to replace vanadium, positioning itself as a more economical and ecological alternative.
Specifications
The patented method describes the preparation of 3-butylsulfonate viologen from 4,4'-bipyridine and 1,3-butanesultone. Through a double alkylation of the nitrogen atoms of the bipyridine, the final compound is obtained (1.61 grams, 93% yield) using dimethylformamide as solvent and thermal heating. The flow battery constructed using this organic compound resulted in a lower capacity loss obtained (0.15% h-1) than the corresponding battery containing the viologen of propylsulfonate (0.49% h-1).
Applications
Among the various applications of 3-butylsulfonate viologen, finds its use as an electroactive molecule for the anolyte of flow batteries (energy storage).
The developed methodology could be applied to the synthesis of other viologens of interest.
On the other hand, the viologen described by the researchers at the University of Burgos could have other applications typical of viologens (herbicides, electrochromic elements, etc.).
Intellectual property status
Protected by a patent P202230676
Current development status
Prototype available for demonstration.
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Researchers at the University of Burgos have developed a process for the anaerobic treatment and biogas production from wastewater with high oil and grease content.
It is known that even low levels of oil and grease produce important upsets of the conventional anaerobic treatment process in long term operation. In the same way, in the MBR technology it is recommended pre-degreasing oily wastewater to avoid fouling problems. However, the anaerobic treatment with membrane biomass retention and the application of advanced fouling control methods let recover the methanogenic potential of lipids making it a robust and competitive treatment method for wastewater with high oil and grease content.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Direct treatment of wastewater with high oil and grease content without pre-degreasing. Chemicals costs and sludge production are reduced by doing without the coagulation-flocculation-flotation processes. Oils and grease, according to their chemical composition, have a high methane potential that this process allows to recover.
Main advantages of its use
Adsorption of long chain fatty acids reduces degassing capacity of microbial flocs hindering the ability to settle required in the conventional suspended cultures processes. The proposed technology is based on suspended cultures but the retention takes place by micro or ultrafiltration membrane processes that can fully retain the biomass, even dispersed, regardless of its density.
Specifications
The membrane anaerobic reactor AnMBR is equipped with submerged hollow fiber modules. The reactor consists of two stages: upflow anaerobic suspended sludge and filtration tank which are in series with recirculation. The separation of the two stages prevents direct contact of the oils and greases with the membranes and facilitates cleaning operations since it allows performing maintenance tasks in the membrane tank without any upset in the anaerobic reactor.
The biomass retention by filtration avoids sludge losses, typical problem of the anaerobic process based on the separation by gravity when are employed in the treatment of wastewater with high oil and grease content.
Applications
Treatment of oily wastewater from the food processing industry.
Intellectual property status
Protected by P200201891, U200501010, P200703231
Current development status
Device already developed and validated for industrialization.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Granted Patent
P200703231
https://www.ubu.es/otri/propiedad-industrial-e-intelectual/patentes-y-modelos-de-utilidad-de-la-ubu/13-procedimiento-fisico-quimico-y-biologico-para-la-depuracion-de-liquidos-residuales-que-contengan
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
In compliance with the UNE standards, the results of this kind of tests have to be corrected by means of energy efficiency. In order to calculate these corrections, a device was design by means of monitoring a steel bar and by a signal acquisition and conditioner equipment. In Spain, up to now, this is the only equipment available.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
If the results from the dynamic probing are not corrected by means of an energy efficiency factor, these results are greater than the real ones, so we will be unnecessarily deep in the safety side. This way, the engineering elements will be over designed with greater dimensions than necessary, so the cost will be unnecessarily greater than if we apply this energy efficiency factors.
Sometimes, due to this greater energy efficiency of the modern dynamic probing equipments, the safety factors are reduced. Most of the times this reduction is made without any real measure of energy efficiency, but making a guess. This implies that if the reduction of the safety factor is not enough, we will have an increasing cost. Otherwise, we could use safety factors more little than necessary that could lead the structure to failure. This way, it is demonstrated the need of measuring the energy efficiency.
Main advantages of its use
The main advantage is the economical save. Some engineering elements are design by the results from these dynamic probing tests. If we do not apply the energy efficiency corrections, the safety factors will be greater than necessary, so there will be an overrun.
Specifications
Bar instrumented to measure real energy in dynamic penetration tests of continuous recording, used in in-situ geotechnical characterization, identification, determination of strength and / or soil deformability. This bar enables sensors measuring equipment attached to it, making access static and dynamic data, which then can calculate the actual energy that traverses the bar stem of a continuous recording dynamic penetration equipment during a penetration test on ground.
Applications
This device could be used by any company who has dynamic probing equipments.
Intellectual property status
Protected by Utility Model U200900809
Current development status
Device Commercially Available.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The University of Burgos (UBU) has developed a new technology aimed at obtaining rockrose extracts with high antioxidant capacity due to their levels of polyphenols and flavonoids, through the use of fluids in conditions below their critical point (subcritical conditions).
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Rockrose (Cistus ladanifer, the most common species), like other plant species, contains essential oils and bioactive compounds (polyphenols, flavonoids) with high antioxidant capacity that can be used in the production of cosmetics, pharmaceutical preparations and as ingredients in products in human food.
To obtain bioactive compounds from plants, conventional extraction techniques usually require high reaction / extraction times (on the order of hours) and the use of organic solvents (such as ethanol, acetone, etc.). The final product obtained by techniques that use organic solvents requires a purification process to be carried out.
The technology developed by the UBU refers to a green technology known as extraction with pressurized liquids in which the liquid used for the extraction is water. The advantage that water offers as a solvent is the zero environmental and human toxicity compared to organic solvents, so it does not pose a risk of contamination during its use, as well as it does not make the purification of the final product necessary, in addition to being a solvent abundant and readily available.
Main advantages of its use
- The patented process allows working in a semi-continuous and discontinuous regime.
- The process incorporates a line called "bypass" that allows the solvent to acquire the optimal extraction conditions prior to its passage to the extractor without being in contact with the raw material, preventing the composition of the raw material from being modified.
- Control system based on "friendly" and open programming hardware, reducing the cost of automation.
- Water can be used as a solvent or a mixture of water with organic solvents (ethanol).
- The biocomposites dissolved in the solvent are separated from it by drying techniques in which recoverable fluids are used and that do not leave residues in the final product.
- The heating system can be a clamp-type electric heater, which requires less space than an oven.
- Organic solvents are not used to extract compounds from the raw material, reducing total toxicity and causing economic savings in the process.
- The use of a "green" solvent such as water does not leave toxic residues in the final product, so it is not necessary to purify it.
- Reaction times for extraction to occur are shorter when superheated liquids are used as solvents (hours to minutes). At an industrial level it is an important factor.
- By modifying one of the two operating parameters, temperature or pressure, or both, the compound of interest can be extracted.
Specifications
The technique proposed in the present invention is based on the use of a harmless solvent present in large quantities and easily available, such as water, which, by modifying its physical and chemical properties through changes in temperature and/or pressure, acquires similar properties to organic solvents, and can be used for the same purpose, eliminating toxic risks and subsequent treatment of the extracted product.
The installation for obtaining rockrose extracts, consisting of the input of a solvent, mainly water, which is pumped up to a work flow by the pumping system while it reaches the working pressure. This solvent or fluid will pass through a heating device. A bypass divides the line system into two ways: one way allows the fluid to reach the extractor that will house the raw material that contains the compound to be extracted, and the second way diverts the flow of the fluid towards the outlet of the system. The change from one way to another of the bypass is carried out by means of a flow cut-off device such as a valve. The solvent that passes through the extractor and the raw material and contains the compounds of interest, or the solvent that comes from the other bypass line. This procedure allows operation in a semi-continuous or discontinuous regime.
Applications
- Obtaining bioactive compounds from rockrose that can be used in pharmacy magisterial formulas, cosmetics and ingredients in food products.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202130306
Current development status
Device already developed and validated for industrialization.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Researchers from the University of Burgos have developed an installation for the purification of wastewater in small towns, offering an economic and environmental solution, with multiple advantages. In Spain, 47% of the municipalities have less than 500 inhabitants, the possible beneficiaries of this technology.
New and innovative aspects
The installation of the wastewater treatment plant can be adapted to the problems of small towns in the national territory. It is of simple construction and ease to operate, it does not need electricity consumption for its operation; and it has very low maintenance costs. In addition, it offers the possibility of using the biogas generated. In particular, the multi-stage installation, four successive stages connected in series, allows a considerable improvement in the physical-chemical quality of the water treated in the installation.
Main advantages of its use
- This wastewater treatment plant develops the biological activity of microorganisms, achieving higher percentages of organic matter reduction, in addition to retaining non-sedimentable solids.
- Compared to aerobic systems, the growth rate of anaerobic microorganisms is lower than the growth rate of aerobic microorganisms, which translates into less sludge production, prolonging the operating period of the installation without the need for purge sludge to prevent its collapse.
- The use of anaerobic digestion avoids the need to aerate the water with blowers or air pumps.
- Anaerobic digestion allows organic matter to be converted into biogas, a renewable energy source that can be used to generate energy in the form of heat or electricity.
- Ease of construction.
- A pumping system is not necessary to circulate the water from one stage to another, but the natural unevenness of the terrain is used.
Specifications
The wastewater treatment installation is based on the use of multi-stage hybrid anaerobic reactors, made up of four successive stages connected in series, where the first three of these successive stages are configured as a hybrid anaerobic reactor, the last stage operating as a decanter. The latter favors the retention of particles that can escape from the first three stages, improving the quality of the treated water. In addition to the advantages, it allows to obtain an efficient wastewater treatment system, with high performance of the physical-chemical quality of the treated water and very little sludge production.
Applications
Potential applications of the installation are as follow:
- Wastewater treatment in small population centers.
- Economically efficient wastewater treatment.
- High physical-chemical quality of the treated water.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202031093
Current development status
Device already developed and validated for industrialization.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Biorreactor compuesto por dos depósitos cerrados comunicados (tanque de digestión anaerobia y tanque de filtración) para el tratamiento anaerobio de aguas residuales complejas con producción de biogás. Se emplea material de relleno, de forma desordenada, aumentando la capacidad de acumulación de biomasa activa y permitiendo trabajar con flujo descendente en el tanque de digestión.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La tecnología de biorreactores anaerobios de membranas se emplea desde hace tiempo con buenas eficacias de depuración, pero presenta altos costes de instalación y operación.
Esta patente utiliza material de relleno plástico para la retención de la biomasa en el tanque de digestión anaerobia y recirculación gas-lift en el tanque de filtración, minimizando el daño que el bombeo provoca a la biomasa.
La fijación de la biomasa activa en el material de relleno permite trabajar con flujo descendente en el tanque de digestión, sin el arrastre de biomasa que tendría lugar en los reactores de cultivo suspendido.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Debido al empleo de este material de relleno se aumenta la capacidad de acumulación de biomasa activa y su capacidad de tratamiento.
- Como consecuencia de la disminución de la deposición de sólidos sobre la superficie de las membranas, se reduce la frecuencia de las operaciones de limpieza y se aumenta su vida útil.
- La recirculación asociada al burbujeo, por el efecto conocido como gas-lift, reduce los costes de bombeo y, especialmente, el estrés mecánico provocado por el uso de bombas electromecánicas que producen daños en la biomasa y empeoran la calidad del efluente.
Características técnicas
El problema técnico que resuelve esta tecnología es que permite mantener elevadas concentraciones de biomasa activa y baja concentración de sólidos suspendidos en las corrientes internas, lo que reduce el ensuciamiento de las membranas de filtrado de la instalación, con vistas a aumentar el rendimiento y efectividad de dicha instalación.
Los rendimientos de eliminación de materia orgánica pueden alcanzar valores del 91-98%, con una producción de biogás de 460-690 l/kg DQO, con un contenido en metano de 60-70% en base seca, dependiente de la composición de la materia orgánica contaminante.
Aplicaciones
El mercado potencial es relativamente amplio y presenta necesidades en el ámbito de la mejora de procesos de depuración.
Las principales industrias en las que se emplean estas tecnologías son:
- Biocombustibles
- Cervecerías
- Lácteas
- Destilerías y bodegas
- Mataderos y subproductos cárnicos
- Procesado de productos de pesca
- Conservas
- Platos precocinados
- Papelería
- Farmacéutica y cosmética
- Química
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante PCT/ES2018/070461.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Planta piloto operativa instalada en matadero industrial.
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Bioreactor formed by two connected closed tanks (anaerobic digestion tank and filtration tank) for the anaerobic treatment of complex wastewater with biogas production.
A support material is used, in a non-arranged way, increasing the active biomass accumulation capacity and allowing downwards flow in the digestion tank.
New and innovative aspects
Anaerobic membrane bioreactor technology is currently used with good removal efficiencies, but it presents high installation and operation costs.
This new technology uses plastic carriers for the biomass retention in the anaerobic digestion tank and gas-lift recirculation in the filtration tank, reducing the damage caused to the biomass by pumping.
Biomass adhesion on the support material allows water flow direction downwards in the digestion tank, without the biomass sweeping that would take place in suspended-culture reactors.
Main advantages of its use
- The active biomass accumulation capacity and its treatment capacity are increasing due to the use of the support material.
- The frequency of the membrane cleaning operations is reduced, and its lifetime is increased as a consequence of the decrease in the solids deposition over the membranes surface.
- The recirculation associated to gas bubbling, by the effect known as gas-lift, reduces the pumping costs and, specially, the mechanical stress caused by the use of electromechanical pumps that damages the biomass and deteriorates the effluent quality.
Specifications
The technical issue solved by this technology is that allows keeping high active biomass concentrations in the digestion tank and low suspended solids concentration in the internal streams. This reduces the membrane fouling, with the aim of increasing the efficiency and efficacy of the system.
Organic matter removal efficiency can reach values of 91-98%, with a biogas production of 460-490 l/kg COD, with a methane content of 60-70% on a dry basis, depending on the composition of organic matter of the wastewater.
Applications
The potential market is wide in the field of improving waste water treatment processes.
The main industries in which these technologies are used are:
- Biofuels
- Breweries
- Dairy industry
- Distilleries and wine cellars
- Slaughterhouses and meat by-products
- Fishing industry
- Canned food
- Convenience food
- Pulp and paper industry
- Pharmaceutical and cosmetics industry
- Chemical industry
Intellectual property status
Protected by PCT/ES2018/070461.
Current development status
An operational pilot plant is installed in an industrial slaughterhouse.
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement, License agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
At present, and since the introduction of wind turbine parks high altitude, it is difficult to clean the outside of the towers and wind turbine blades with traditional systems.
For reasons of typical maintenance tasks, often occur spills of fluids and lubricants transmissions machinery transforming the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy which is sent to the network. These fluids to spill soiled the wind turbine tower.
On the other hand, it must undertake periodical cleaning of wind turbine blades on them because remains of insects that collide with the blades are. These remains make the blade is losing its effectiveness.
Furthermore periodic revision is necessary due to fatigue that are subjected to wind turbine blades forcing periodic visual inspections to prevent breakage thereof and therefore stopping the wind turbine.
Researchers at the University of Burgos have developed a solution that perform such tasks without being necessary that operators should climb the tower of the wind turbine.
New and innovative aspects
In general, the systems currently used for exterior cleaning of wind turbine towers and blades often use similar systems to cleaning windows on the facades of buildings. It means operators have to hang from the gondola and turbine hub and manually clean both the blade and the tower.
The system has been patented, is a climbing system with the tools necessary for cleaning and rinsing of the towers and blades, and the collection of soapy water as waste fluid after cleaning. The location of the mechanism minicameras allows visual inspection in detail all of the blades as welds towers.
It is not necessary that any operator would have to rise to the climbing system for cleaning functions.
Main advantages of its use
- The main advantage of the system is that it don’t requires personnel to do the tasks of cleaning, so the need for people exposed to work at heights and possible risks of fall is eliminated.
- Personnel performing maintenance and inspection of the wind turbine is limited to the assembly of the mechanism on land as well as government and subsequent control automation mechanisms governing cleaning and inspection.
Specifications
The mechanism is designed for wind turbine towers and blades powerful that require large blades and high-rise towers.
The movement of opening and closing of both belts climbing mechanism supports its use for different ranges of maximum / minimum diameters tower, being able to increase the size of the mechanism by increasing the size of the sides that make up both upper and lower or belts increasing number of sides of the polygon that make up both belts.
Applications
Maintenance companies large wind turbines (cleaning, painting and inspection of towers and blades)
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P201100665.
Current development status
It has not developed a full-scale prototype of the mechanism.
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement, License agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical cooperation: adaptation to specific neds.
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The technology involves a machine that supports solar modules (photovoltaic, thermal or hybrid) increasing significantly its energy efficiency.
The main feature of both solar trackers is its simplicity of the machine and its parallel kinematics working principle. Its structure provides a robust support and wider distribution of efforts and a great modularity. Thus, these systems adapt better to the geometric constraints for tilting and facing and restrictions of size and weight of the supporting structure.
New and innovative aspects
Technology comes to solve one of the main problems in the design of the solar tracker structure for buildings, which is related to the size required for the installation of the same weight. Usually these structures are characterized by complex mechanical frames that are generally designed for flat planes and large areas, but not for small and uneven spaces as a roof or covered with houses and buildings.
In order to solve this problem, we have developed two technologies that are characterized by a robust support structure and a reduced volume that has greater modularity and distribution of efforts. Along with this, it is able to integrate geometric constraints (tilt and face of the covers), mechanical (size and weight of the structure) and economic (costless materials and simple drivers). Furthermore, the kinematics for the solar tracker of the invention is applicable to any system requiring track with two degrees of freedom.
Main advantages of its use
This type of system increases the energy efficiency of modules to fixed systems, as the proposed technology can be adapted to surfaces tilted or with small area. Moreover, they can be oriented according to the geographical position of the building and overcome physical restrictions. Its manufacture does not require a high cost.
Specifications
Solar trackers are designed in a modular philosophy and are based on parallel kinematics. One model is driving in line and the other supports single drive (see drawings). They have a fixed support and a movable platform which supports the solar modules. The movable platform is supported by four rods of defined length that also allows to track the sun. Other features in both technologies are:
- Degreees of freedom: 2-axis, horizontal and vertical.
- Energy power: It is estimated that the two axis sun tracking could increase the energy generation by between 24% and 26% compared to a fixed system.
- Adaptability: Adaptable to any form of panels.
- Design: sun trackers can be optimized for particular projects, taking into account the physical characteristics of the installation site, either in homes or in solar parks.
Applications
Solar tracking technologies are applied to the field of solar thermal and photovoltaic. These applications focus on two sectors with different dynamics: construction (power generation for domestic use) and large solar power plants that generate energy on a large scale basis frame.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patents P200901628 and P200901629.
Current development status
Concept.
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Device that allows simultaneous diffuse radiation in four spatial directions and in both horizontal and vertical planes. Model the diffuse radiation over any facade or cover surface is possible using this mechanism.
New and innovative aspects
Current devices measure the diffuse radiation by a sensor called pyrometer that determines the value of the diffuse radiation due to an element that blocks the direct radiation. These known solutions allow the shadow projection only over a unique sensor, which must be placed in a particular orientation.
The designed device, patented by the Universidad de Burgos, enables to overcome these limitations measuring the diffuse radiation with several sensors at the same time, with four orientations (north, south, east west), in planes perpendicular to the surface, and with different inclinations.
Main advantages of its use
The major benefit of its use is the save of time. This new mechanism allows having four structures, one for each sensor, in only one system (up to now the structures are independent). Moreover, the device is provided with a calculation system that corrects the data obtained, depending on the ring features.
Specifications
The device comprises a structure and four radiation sensors, and attached thereto, a ring lobular fixed to the frame, with one lobe for each sensor so that each lobe projects a shadow to a corresponding sensor. In this way the lobular ring provides simultaneously shadow to all sensors. Thus, measurement of diffuse radiation can be performed with several sensors simultaneously and with the possibility that such sensors are in different orientations to one another and with different inclinations.
Applications
Manufacturers and marketers of devices that measure climate variables and particularly solar radiation and illuminance, especially for the advantages of its use:
- Implementation of the data to the energy efficiency in buildings
- Energy installations on facades and roofs
-Design and light energy availability on building facades. Knowledge of the solar resource through diffuse radiation data allows the design of lighting in buildings
- Optimization comfort cooling by estimating thermal stress by radiation through the walls
The Research Group can offer a specialised service based on the preparation of technical reports and data interpretation to companies / energy auditing, energy engineering and consulting.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P201400714
Current development status
Prototype ready for testing
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Industrial Technologies (15)
Summary of the technology
A chimney flue closure device comprising a bracket configured to be attached to the chimney wall.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Automation and Remote Control: Thanks to the integrated sensors, implementing automation functionality and remote control of the device could be a significant innovation in industrial environments. This would allow efficient adjustments and monitoring of the flue closure, optimizing the process without requiring physical intervention.
Advanced Materials and Special Coatings: The use of advanced materials and special coatings for the blades can improve corrosion resistance, durability and the ability to withstand high temperatures.
Main advantages of its use
Energy Management: This system would allow a more effective coordination of resources and an overall optimization of energy consumption as opposed to current natural draft systems.
Scalability and Adaptability: The device is scalable and adaptable to different sizes of industrial chimneys. This allows its implementation in a variety of industrial contexts, from production plants to processing facilities.
Large Scale Efficiency: An effective shut-off of the passage of a fluid, in this case combustion smoke, is achieved with a very low pressure drop.
Specifications
The chimney closure device has innovative technical features designed to optimize its operation. With deployable blade assemblies controlled by drive shafts, it achieves a synchronized and efficient closure of the chimney draft. The choice of advanced materials, such as Teflon or polyester, in some blades ensures corrosion resistance and dimensional stability, even in high temperature environments. In addition, the implementation of a planetary gear system in the motion transmission allows smooth and controlled deployment, minimizing load losses. Optionally, the inclusion of automation and remote control functions provides flexibility and ease of adjustment in industrial environments. These combined features position the device as a robust and versatile technical solution for efficient chimney closure in various contexts.
Applications
This patent allows the closure of the chimney flue in all types of environments, including large industrial facilities, its implementation allows to efficiently control the flow of smoke and combustion gases, improving energy efficiency, extending the life of the facilities and equipment (both firetube and watertube boilers) and reducing unwanted emissions to the environment.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202331051
Current development status
Device developed
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
New structural concepts that are cheaper than those currently used, being able to make estimates of the residual mechanical capacity and of the useful life with elements on a 1:1 scale. This is possible both to the facilities and to the equipment that is available.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The fundamental advantage is economic, using less quantity of material from the new conceptual designs that the research group is capable of analyzing for different structural types. This is especially important in the industrial sector, which by its nature has a tendency to run a multitude of identical units.
Main advantages of its use
In the case of structural concrete, due to its nature, small-scale tests are insignificant, making it necessary to carry out full-scale tests.
The Large Structures Laboratory of the University of Burgos has suitable facilities to carry out 1:1 scale tests on concrete elements up to 30 meters long and weighing up to 40 tons.
Optimizing structural solutions is essential (especially in the industrial sector, in which the number of units to be executed can be very high), as this can provide the customer with a competitive advantage for their product compared to that of the competition.
Specifications
There are more and more structural situations in which concrete elements are subjected to load states of a dynamic nature. Noteworthy, for example, are the structures located on the High-Speed Rail lines, as well as towers and foundations for wind turbines, foundation slabs for heavy machinery.
The optimization of the structural solutions to be used in these cases necessarily involves knowing, precisely, their structural response, both under static stresses and dynamic stresses.
For this last situation, it is important to know how the mechanical capacity (and, consequently, the structural safety factor) evolves with the number of cycles; and, from this, determine, in a more exact way, the useful life of our element.
Based on numerical models alone, it is currently not possible to know this data and it is necessary to support the necessary numerical calculations with experimental test campaigns.
In the case of structural concrete, due to its nature, small-scale tests are insignificant, making it necessary to carry out full-scale tests.
The Large Structures Laboratory of the University of Burgos has suitable facilities to carry out 1:1 scale tests on concrete elements up to 30 meters long and weighing up to 40 tons.
Applications
Companies in the Civil Engineering sector that work with large structures.
Companies in the energy sector, especially linked to wind generation, since especially the new prototypes include concrete elements (foundation and towers).
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Large scale structural testing can be developed in our laboratory. The main field is civil engineering, but others industrial sectors can be held, as energy industry, aerospace, automotive industry, etc.
Static and or dynamic testing can be carried out, including large cyclic testings, seismic testing, etc.
Our services include testing design (both conceptual and detailed design), FEM models development, results analysis, improve proposal of the initial design provided by customer, etc.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The integration of numerical simulation technologies and testing capacities, improved designs can be obtained, making them optimal for their intended use.
Using a own protocol, it is possible to test 1:1 scale parts of a structure. Through the development of finite element models of the testings, it is possible to compare the failure modes of the testing specimens with the ones of the complete structure. Using the safety factors obtained in the test, it is possible to accurately determine the real safety factor of the
whole structure.
Main advantages of its use
Large-scale testings help to optimize the design, minimizing cost. This is especially useful in the industrial sector, because many equal pieces are casted. In this case, the optimization of the design allows significant cost reduction. Usually, international standards are over-conservative, and this is not always usefull to the industry. Testings can allow to use "out of standards" solutions, more effective in terms of cost.
Specifications
The new Laboratory of Large Civil Engineering Structures is in the west of the new civil engineering building of the University of Burgos (Burgos – Spain).
The lab consists of a 66 ft x 98 ft building. It includes a 39 ft x 78 ft strong floor with 13 ft thickness, and 225-kip capacity tie-downs on a 2.6 ft x 2.6 ft pattern. It is provided of two 10 ft x 10 ft and 10 ft x 13 ft strong walls with 3.2 ft thickens, and 225-kip capacity tie-downs on a 2.6 ft x 2.6 ft pattern.
To move specimens and equipment around the lab, two 16-ton 52-ft span simple girder overhead cranes will be furnished with two 80 ft long runways. A forklift provides additional mobility for lab activities.
One two-legged 23-ft high steel test frame with 1800-kip capacity and one two-legged 13-ft high steel test frame with 225-kip capacity will allow simultaneous loading of various structural components.
The lab will be served with a central 53-gpm hydraulic punt; one 1125-kip and four 450-kip compression servo controlled hydraulic actuators (ENERPAC models), one 225-kip, one 112-kip and one 11-kip tension/compression servo controlled fatigue-rated hydraulic actuators with 10-in stroke (MTS models); computerized controller for simultaneous use of four actuators; one 96-channel and three 36-channel high-speed data acquisition systems (HBM models); and comprehensive array of sensors to allow static and dynamic loading of large to full-scale structural components and systems.
Applications
The target companies of this technology are, mainly, civil engineering companies, and industrial companies, i.e, energy, aeronautics, aerospace, automotive, etc.. The main applications are the development of a new product, the optimization of an existing product, the analysis of the properties of a product beyond its service life, etc…
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P200801660
Current development status
Commercially Available
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Researchers from the University of Burgos have developed a procedure to produce powdered honey by lyophilization or by vacuum drying using maltodextrin as a dehydration aid, so that a fine and pleasant powdery solid is obtained. This maintains the sensory and physicochemical properties of honey as much as possible.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Honey contains a high concentration of sugars with low glass transition temperatures (Tg), which makes drying difficult since during dehydration an extremely sticky, hard and very difficult to handle product is formed. The invention that is described manages to avoid these drawbacks by drying the honey by lyophilization exclusively using honey and potato maltodextrin as a dehydration aid. The most innovative aspect that is presented with respect to other procedures described for the dehydration of honey, is that related to the temperatures of grinding the product and its conservation. The honey powder obtained contains 75% (freeze-drying) or 60% (vacuum drying) of honey solids and 25% (freeze-drying) or 40% (vacuum drying) of maltodextrin solids, being of fine texture and silky, with excellent sensory and physicochemical characteristics.
Main advantages of its use
- Obtaining powdered honey with a concentration of total honey solids of 75% (lyophilization) or 60% (vacuum drying).
- Use of maltodextrin as the sole drying aid additive at a total solids concentration of 25% (lyophilization) or 40% (vacuum drying).
- Higher process yield: 73.6% -96.4% (lyophilization); 80.6%-97.9% (vacuum drying).
- Greater solubility and less hygroscopicity in the powdered honey obtained.
- Better physical-chemical and sensory characteristics of powdered honey.
- Possibility of marketing powdered honey within the demand for "clean labels" and the name "real food", as it contains only honey and maltodextrin.
Specifications
The lyophilization and vacuum drying procedures described in this invention achieve the production of powdered honey with a floury texture, using only one additive (potato maltodextrin), with a greater amount of honey in the final solid product, a greater solubility, higher performance and lower hygroscopicity. It was found that the best honey dehydration procedures were vacuum drying and lyophilization, using maltodextrin as aid, because they presented the lowest percentages of water and were the best valued in sensory analyzes.
The honey powder obtained presented the highest values of antioxidant capacity against the peroxyl radical and the highest results for in vitro anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial activities. The grinding and preservation of the product must be carried out at temperatures below the Tg of the honey powder obtained, which maintains optimal texture characteristics of this food without the need to incorporate anti-caking additives.
Applications
The possible applications of powdered honey is its use in haute cuisine desserts as an ornament, or in the preparation of candies and confectionery products, pastries, chocolate with honey or cosmetics with honey. The sectors with potential application are:
- High kitchen
- Biscuit industry
- Bakery and pastry industry
- Confectionery industry
- Cosmetic industry
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202130603 and P202130604
Current development status
Device already developed and validated for industrialization.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The present invention provides a methodology for the synthesis of derivatives of perylene-diimide (PDI, for which there was no obtention process, and its use in different applications such as bioimaging or biomarkers.
New and innovative aspects
The large versatility of the developed methodology permits to obtain compounds with two positions of functionalization, in the imide positions allowing to interact with different targets and, in this way, to control the biological specificity (what will be detected and to what parts of the cell it will go), and in the bay positions choosing the emission colour for the modulation of the fluorescent emission.
The bioconjugation, chemical strategy to form stable links between different biomolecules, presents some disadvantages, solved using this new proposed methodology. In addition, it avoids having to develop specific systems for each application, which suppose a great cost saving and increases its field of action in multiple sectors.
Main advantages of its use
The available market alternatives show low photostabilities, are very sensitive to pH or to ionic strength and their fluorescent emission intensities are low. In addition, they usually have low emission wavelengths, so no desirable phenomena such as energy self-absorption or scattering may take place.
The perylene-diimide (PDI) obtained by this invention have many desirable characteristics that solve the market deficiencies, such as: high fluorescence, high chemical and optical stability, stability against radiation, different wavelengths of fluorescent emission depending on the substituents in that positions and the possibility of an easy functionalization in N and N' positions. In addition, they exhibit high quantum yields, which can even reach one unit.
Specifications
The modifications made in the substituents of organic molecules known as perylene-diimide (PDI) or perylene bisimides (PBI) modify their solubility, making them versatile in different media, both organic and aqueous. Variations in the substituents of the imide positions do not significantly affect to their fluorescent properties, allowing the inclusion of bioconjugate biomolecules, while in the substituents of the bay positions, they modify their luminescent properties, allowing to modulate the emission wavelengths of the resultant fluorophore.
Thanks to the bioconjugation, novel systems with unique characteristics are obtained, such as fluorescent emission. In this case, the possibility of its use as a specific biomarker in fields such as bioimage, therapy and diagnosis is considered
Applications
The potential market is relatively wide due to the versatility of this technology. Its possible applications are in multiple sectors, such as: medicine, material science and agrofood industry. More specific applications can be mentioned, such as:
- Development of individual kits for bioconjugation, specifically fluorescent markers in medicine field that allow the realization of diagnoses and monitoring of specific treatments.
- Detection of biological contaminating species of high interest in agrofood industry such as enterotoxins or avidin (PDI-Biotin systems).
- Study of epithelial cells (PDI-Mupirocin systems).
- Marking, monitoring or determination of protein biodistribution.
- Monitoring of cell events such as drug administration to target cells and the study of enzymatic functions among others.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P201830029
Current development status
The technology related to the synthesis method is developed.
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement; License agreement; Technical cooperation: further development; Technical cooperation: testing new applications; Technical cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
This patented technology is focused on the development of a sensor for the detection and determination of the chloride ion content in fluid samples. This determination is of interest in the diagnosis of diseases, like for example cystic fibrosis, and in the analysis of samples, both food, pharmaceutical and environmental.
New and innovative aspects
his new technology allows carrying out the chloride ion measurement without the need to add any reagent, without producing interference and increasing the range of its possible applications, such as: cystic fibrosis diagnosis, analysis of food and pharmaceutical samples, etc.
Main advantages of its use
The developed sensor, which solves the disadvantages of already known sensors, (complex preparation and limit of application), is characterized by being very simple, easy to use, economical and with more sensitivity and versatility. As it presents a low cost, it is possible using it only once as well as being reused more than 100 times without affecting its operation.
Regarding to the sensors based on potentiometric methods, the sensor developed in this patent needs less reaction time, only 20 seconds. It can be used in a greater number of matrixes and of more complexity. The addition of electrolytes is not needed, process that requires more preparation in the analysis.
Specifications
he sensor is made up for three electrodes, produced by silkscreen printing, on a plastic sheet, of a conductive ink of platinum (for the conductive sections, the auxiliary electrode and the working electrode), facing those based on carbon usually used, and with a Ag/AgCl ink (for the reference electrode). The method includes an activation step, a calibration step and a measurement step. The electrochemical reaction, that takes place on the platinum surface, produces signals that are registered in a voltammogram.
Applications
It presents a high responsiveness in:
- Diagnosis of diseases related to low or high concentration of chloride ion in different biofluids, such as cystic fribosis, etc.
- Food and beverages industry, like for example, the determination of sodium chloride (salt).
- Pharmaceutical industry.
- Environment, such as studies of water pollution.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P201830271.
Current development status
The sensor is developed and ready for being used when connected to a potentiostat.
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement; License agreement; Technical cooperation: further development; Technical cooperation: testing new applications; Technical cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The method developed in this patent is based on the use of cross-linked copolymers, which act as colorimetric sensors, for the detection and / or quantification of divalent metals: mercury [Hg (II)] and copper [Cu (II)]; and anions: nitrite (NO2-). It is applicable in different matrices, both aqueous mediums and food products.
New and innovative aspects
The possibility of detecting and/or quantifying, with the same method, both divalent metals (mercury and copper) and oxidizing anions (nitrites), makes it very versatile and turn it into unique in the market. In addition, this versatility is transferred to the measurement, which can be carried out with different equipment. In addition, it does not produce colour migrations.
The developed device can be applied to any type of sample without prior treatment, in a simpler way than the other available methods.
Main advantages of its use
This method does not require the utilization of chemical reagents or the use of extremely expensive laboratory equipment. The results are shown quantitatively with great precision.
Specifications
This invention is based on the preparation and development of new cross-linked copolymers, obtained by structures of formula I, derived from dithizone.
The polymers are obtained by copolymerization of three or more monomers, among which polyfunctional monomers are included, to give rise to materials with good mechanical properties, both in dry and in swelling, which behave as solid colorimetric sensors. They can be presented as films, dense or porous membrane and/or gel.
These cross-linked copolymers are membranes that act as chromogenic sensors, i.e., they are materials that change their color in the presence of certain substances. That color change takes place when divalent metal cations and/or oxidazing anions are present in the medium.
For the detection of analytes, it is required, at least, the use of a method, independently chosen between: the use of the RGB parameters of a digital photograph or the use of spectroscopic techniques.
Applications
It presents a high responsiveness in:
- Drinking water.
- Industrial water: for example, in the gold mining industry.
- Food products: mercury can be present in different fish and, due to its toxicity in the body, it is very important to detect it before its consumption.
- Biomedical healthcare industry: urine, saliva, blood serum, etc.
Intellectual property status
Protected by PCT/EP2018/055317
Current development status
Several prototypes have been manufactured in collaboration with a research centre.
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement; License agreement; Technical cooperation: further development; Technical cooperation: testing new applications; Technical cooperation: adaptation to specific needs
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
El método desarrollado en esta patente se basa en el uso de copolímeros reticulados, que actuan como sensores colorimétricos, para la detección y/o cuantificación de metales divalentes: mercurio [Hg(II)] y cobre [Cu(II)]; y de aniones: nitrito (NO2-). Es aplicable en diferentes matrices, tanto medios acuosos como productos alimentarios.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La posibibilidad de poder detectar y/o cuantificar con el mismo método tanto metales divalentes (mercurio y cobre) como aniones oxidantes (nitritos) hace que sea muy versatil y lo convierte en único en el mercado. También esta versatilidad se traslada a la medición, que puede ser llevada a cabo con diferentes equipos. Además, no produce migraciones de color.
El sensor desarrollado se puede aplicar a cualquier tipo de muestra sin necesidad de tratamiento previo, de una forma más sencilla que el resto de métodos disponibles.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Este método no requiere del uso de reactivos químicos ni del empleo de equipos de laboratorio extremadamente costosos. Los resultados se muestran de manera cuantitativa con una gran precisión.
Características técnicas
Esta invención se fundamenta en la preparación y desarrollo de nuevos copolímeros reticulados, obtenidos mediante estructuras de fórmula I, derivadas de ditizona.
Los polímeros son obtenidos por copolimerización de tres o más monómeros, entre los que se incluyen monómeros polifuncionales, para dar lugar a materiales con buenas propiedades mecánicas, tanto en seco como en hinchado, que se comportan como sensores sólidos colorimétricos. Se pueden presentar tanto en forma de filmes, de membrana densa o porosa y/o de gel.
Estos copolímeros reticulados son membranas que actúan como sensores cromogénicos, es decir, son materiales que cambian de color en presencia de determinadas sustancias. Dicho cambio de color ocurre cuando hay cationes metálicos divalentes, y/o aniones oxidantes presentes en el medio.
Para la detección de los analitos se requiere, al menos, del uso de un método, seleccionado independientemente entre: la utilización de los parámetros RGB de una fotografía digital o la utilización de técnicas espectroscópicas.
Aplicaciones
Presenta una alta capacidad de respuesta en:
- Aguas de consumo.
- Aguas industriales: por ejemplo en la industria de extracción de oro.
- Productos alimentarios: el mercurio puede estar presente en diferentes pescados y, debido a su toxicidad en el organismo, es muy importante detectarlo antes de que se produzca el consumo.
- Industria biomédica: orina, saliva, suero sanguineo, etc.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegido mediante PCT/EP2018/055317
Estado actual de desarrollo
Se han fabricado varios prototipos en colaboración con un centro de investigación.
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
A research group at the University of Burgos have patented different materials whose base are cement and have improved for the construction and civil engineering properties, especially for the use thereof as indoor / outdoor carpet, as landfill soil and grouting factories. The feature common to all is that different wastes are used for which the criteria for their use and basic dosages to ensure strength and durability are set as well as a high degree of performance and application.
New and innovative aspects
New lightweight mortars with interesting properties were fabricated, offering an innovative way to recycle polymer wastes. In addition to the advantage of the recycling of waste, the use of residue in masonry mortar allows obtaining enough mechanical properties to be applied even with 100% of replacement of fines, but also with a lower density than traditional mortars, with a suitable raw materials distribution.
Main advantages of its use
The main advantages are the environmental and economic as well as improvements in product performance. To obtain these materials are recycled and reused materials of various kinds, usually very difficult to degrade by non-mechanical methods, due to their chemical stability.
Specifications
The materials are patented by the University of Burgos are:
Lightweight cement-polymer composite construction obtained from recycled rigid polyurethane foam wastes.
Lightweight concrete-polymer composite construction obtained from recycled rigid Polyurethane foams, useful as a new building material that replaces the traditional lightweight mortars, removing the expansive aggregates used in the fabrication of these products, replacing sand by different percentages of rigid polyurethane foams from industrial byproducts..
Process for obtaining lightweight mortars with the addition of polyamide powder wastes.
The patent is based on obtaining lightweight material obtained from recycled polyamide powder as aggregate in masonry mortar, in which varying quantities of sand were substituted by polymer to fabricate these products.
Process for obtaining mortars with crosslinking melamine.
Masonry mortar made from binder, aggregate and water with different replacement of arid for powder melamine (urea-formaldehyde or melamine formaldehyde). The invention is based on obtaining a construction material with improved properties as bigger adhesion and less open porosity.
Masonry mortar with lime and cement using slates as recycled arid
The patent produce recycled masonry lime mortars and concrete with slates wastes, which are tritured and trated to evitate arid-alkali reactions.
Applications
Civil Companies and Construction sector. Cement-based materials and use thereof as interior / exterior coating and as a filler soil and grouting factories.
Intellectual property status
Protected by Patents P200902028, P201100664 , P201300297 y P201531132.
Current development status
In use, test results available.
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
A research group at the University of Burgos have patented different materials whose base is the lime and they have improved properties for construction, particularly for the use thereof as coatings used in Artistic Heritage. The feature common to all is that different wastes are used for which the criteria for their use and basic dosages to ensure strength and durability are set as well as a high degree of performance and application.
New and innovative aspects
Lightweight materials with improved properties in relation to conventional mixtures (eg optimizing some of the basic properties such as trajabilidad, permeability and rheological behaviour to force loads) and a good performance of provision
Main advantages of its use
The main advantages are the environmental and economic as well as improvements in product performance. To obtain these materials are recycled and reused materials of various kinds, usually very difficult to degrade by non-mechanical methods, due to their chemical stability.
The results obtained for these patents lead us to affirm that the mortar lime designs present physical and mechanical properties equivalent to those of traditional materials, with enough adherence, suitable water vapor permeability and complying with the regulatory requirements and with durability test.
Specifications
- Lime mortars fabricated with polyamide powder residues.
The invention protects the product and the preparation method according the use, improving some of the basic properties such as workability, absorption and adhesion resistance.
- Lime mortar for construction and rehabilitation manufactured with steel slag waste.
The production of air and hydraulic lime mortars as binder as well as industrial by-products obtained in the manufacture of steel as black and white slag. New material can be used in construction or rehabilitation as an alternative to the standard products.
Applications
Companies in the construction sector. Use of materials for rehabilitation of historical heritage.
Intellectual property status
Protected by Patents P201300847, P201400382.
Current development status
In use, test results available
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
A research group at the University of Burgos have patented different materials whose base is gypsum and construction have improved properties, especially for the use of the same mass as coatings or to prefabricated interior. The feature common to all is that different wastes are used for which the criteria for their use and basic dosages to ensure strength and durability are set as well as a high degree of performance and application.
New and innovative aspects
Getting lightweight materials with improved properties compared to conventional mixtures (eg optimizing some of the basic properties such as workability, permeability and rheological behavior to force loads) and a good performance of provision.
The values obtained are similar to other construction materials used for thermal insulation, which suggests that he plaster with same polymer wastes could be an alternative to these products as a material with improved thermal properties.
Main advantages of its use
The main advantages are the environmental and economic as well as improvements in product performance. To obtain these materials are recycled and reused materials of various kinds, usually very difficult to degrade by non-mechanical methods, due to their chemical stability.
Specifications
- Process for obtaining lightweight plaster to fabricated polyurethane foam wastes.
This invention involves the obtaining of new lightweight plaster material for use in construction, in which matrix are incorporated industrial rigid polyurethane foam wastes. Polymers are mixed after ground with gypsum to different granulometric sizes depending on the final use..
- Process for obtaining lightweight gypsum with polyamide powder residue.
This patent is focused on the use of polyamide powder waste to produce a new lightweight plaster material with improved thermal properties for industrial applications according to building regulations. Plaster blends were prepared using different volumetric proportions of polyamide.
- Design and properties of plaster mortars manufactured with ladle furnace slag
This material is made with a series of plasters containing different proportions of ladle furnace slag used as mineral aggregate. The tests characterise the influences of two admixtures: a superfluidifier to reduce the water absorption of mortar plaster and an adhesive emulsion to improve the surface adherence. The physical and mechanical results confirm the feasibility of employing ladle furnace slag as a mineral aggregate, which induces an increase in density, in vapour permeability and in porosity.
- Process for obtaining building plaster mortars with artificial crushed quartz stone.
This invention obtain clusters of gypsum and plaster with rejected industrial quartz aggregates for its use in construction, with different colors and design with improved fire properties compared with reference products.
- Prefabricated plasterboard with lightweight polyurethane wastes
The invention proposes the development of a process for producing lightweight plasterboards for use in interior walls in a simple way. The material allows plates with different dimensions and thicknesses depending on the application. The non-combustibility test confirms that the polyurethane waste may be used in the manufacture of gypsum plasterboard in compliance with the specifications that are found in the standard.
- Prefabricated plasterboard with polyamide powder waste
This patent shows that the increase in the quantity of polymer waste implies important reductions in its mechanical resistance and surface hardness, while improving its thermal resistivity.
Applications
Companies in the civil construction sector. Use in coatings for interior mass or precast
Intellectual property status
Protected by patents P201001011, P201100886, P201200092, P201300296, P201300464 and P201300846.
Current development status
In use, test results available.
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Telescopic intramedullary device for the elongation of long bones, mainly for patients with achondroplasia (1 in 25,000 live births), which has a motorized tight mechanism, that increases its length by request of the patient, without any physical connection to the device. For its self-supporting character the patient can walk while the effect of elongation and hardening bone happens.
New and innovative aspects
Surgical procedures currently employed to correct the effects from the disease or other facts, are generally traumatic and long lasting, meanwhile the patient has to be resting during long periods of time, with a low quality of life.
The proposed device allows progressive, self-supporting and autonomous prosthesis (incorporates a reducing micromotor inside the fixed cylinder, driven by the energy stored in the battery attached to the motor), it limits the risk of infections and allows a high control capacity of the elongated distance.
Main advantages of its use
- The patient only has a surgical operation for each bone.
- The patient does not need to be seated or in bed for long months, but has ability to move on their own legs that are in process of elongation.
- Ease of management mechanism regrowth by the patient.
Specifications
The device comprises two coaxial cylindrical tubular elements with a longitudinal notch; so that the outer cylinder is fixedly attached by screws to one of the two parts of the bone to lengthen, and the sliding inner tube is attached at the other end by screws the other part of the bone. The outer tube has inside at their end, an accumulator of electric power or battery that recharges through electrical induction.
The chosen material is titanium alloy Ti6Al4V -ELI, bio-inert material, high corrosion resistance and high mechanical strength. Allows attachment of bone on the oxide layer overlying and a coating of "hydroxyapatite" to improve and accelerate bone anchorage.
Applications
The application of this progressive prosthesis focuses exclusively to medical or hospital sector and within this, to the section of traumatology.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent protection: P201530996
Current development status
Functional prototypes
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
It is known the high toxicity of nitro-explosives, namely TNT, which are easily absorbed by the skin and the intestinal tract. It is also known the presence of this compound in contaminated civil areas arisen from older military installations, or even from terrorist attacks. This causes both health and environmental problems.
In order to meet this need we have developed new colorimetric, simple, rapid and cheap colorimetric sensor for the in situ detection of trace amounts of TNT by non-specialized personnel and by conventional techniques sensors (replacing the commonly known IMS, GC, HPLC).
New and innovative aspects
They are solid substrates as sensors that could be easily handle both in the dry and wet state. Moreover, the possibility of conventional fibers coated with polymeric materials such sensors have the advantage of preparing smart fabrics capable of indicating the presence of molecules of interest by colour changes, in the case of chromogenic materials. It would further be advantageous to use sensory aqueous solutions of polymer materials in forensic or detecting contamination in situ, as spray, to use over the area to assess.
Main advantages of its use
Allows for the colorimetric visual detection of traces of TNT by non-specialists, in situ, in real time, and at minimal cost. TNT can be detected directly on surfaces, or measure the concentration in water and wastewater, soils, etc. The quantification of TNT can be carried out by a photograph taken with a digital camera or with a mobile phone.
Specifications
Visual detectors of TNT are new polymeric materials based on sensory monomers.
The polymerization of these monomers allows for the obtention of water soluble linear polymers, films or dense membranes, and smart fibers, by copolymerization of these monomers with others, including polyfunctional monomers, in order to provide polymeric materials with good mechanical properties, both in dry and swollen, which behave as TNT colorimetric sensors in water and / or aqueous media.
Polymeric materials change color when traces of TNT are present. This specific behavior allows for the detection of TNT by changes in the visible color spectrum, so that in addition to using a spectrophotometer, its concentration can also be assessed by the naked eye. Moreover, its quantification can be carried out using the digital parameters (RGB ) of a photograph taken with a camera materials or by smartphone.
Applications
It may be of interest to companies that use this type of explosive. Detection of explosives in terrorist attacks (forensic chemistry). Governments that need to establish the degree of contamination by this compound due to activities such as old milatares facilities, terrorist attacks, former wars, etc.Mining and quarrying. Companies whose area is the manufacture of explosives and weapons.
Companies using TNT for demolition.Environmental management and treatment of contaminated areas.
Intellectual property status
Protected by Patent P201301187
Current development status
In use, test results available
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
A new procedure for the oxidation of a sulfoxide group to a sulfone group has been patented. This new process consists in the oxidation of the sulfoxide with air in the presence of a molibdenum compound as catalyst, preferentially dioxomolibdenum (VI) bis(acetilacetonate) or dinuclear derivatives coming from its partial hydrolisis.
New and innovative aspects
The main novelty of the present method is the use of air as oxidating agent, while clasical procedures make use of hydrogen peroxide, risky to store and handle due to its corrosive nature and explosive vapors.
Main advantages of its use
This new procedure is more efficient than other procedures described for the process. Moreover, air stands out for being the cheapest, most available, easiest to handle and safest oxidizing agent. Additionally, molibdenum catalysts are less toxic that commonly used ones, and are resistant to degradation under reaction conditions. Finally, byproduct formation is not observed and sulfones are easily isolable. Overall, the procedure is efficient, simple, cheap, and enviromentally friendlier than previous methods.
Specifications
The present invention relates to a procedure for the oxidation of sulfoxides to sulfones using the oxygen from the air as oxidizing agent, in the presence of a molibdenum complex as catalyst, preferably dioxomolibdenum (VI) bis(acetilacetonate) or dinuclear derivatives coming from its partial hydrolisis in the presence of dimethylsulfoxide, dimethylformamide or triphenylphosphine oxide. The amount of catalyst varies from 1 mol% to 10 mol%. The synthesis is performed at atmospheric pressure and the temperature varies from 15-50 ºC. The solvent used is a low molecular weight ether. The products are obtained in excellent yields and byproducts are not observed in the reaction.
Applications
Synthesis of sulfones, that can show diverse already demonstrated propierties (drugs, pesticides, materials,…). Therefore, applications in pharmaceutical and agrochemical industries.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P200703331
Current development status
In use, test results available
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The invention relates to a new general method for the reduction of nitroarenes to anilines using a Mo(VI) catalyst and pinacol as reducing agent. The products obtained show excellent yields. It should be noted that this new method uses an easily available and non-toxic reducing agent that generates non-toxic byproducts which are easily separated from the amine synthesized.
New and innovative aspects
The main novelty of the present invention is the use of pinacol as reducing agent that entails undeniable advantages over clasical methods for the reduction of nitro compounds, which are encompassed in the two following groups: (a) catalytic hydrogenation using molecular hydrogen, and (b) chemical reduction, usually with a metal in acidic media.
Main advantages of its use
The advantages of the new method over the clasical ones are:
-Over catalytic hydrogenation: the reaction is more selective, avoinding side-reduction of other groups such as olefins, carbonyls, nitriles or halogens. The new method does not implie the use and storage of hydrogen gas, all the reactives are solids or liquids easy to handle.
- Over the reduction with metals in acidic media: The new method is more selective, allows the reduction of compounds with acid-sensitive fuctional groups and uses catalytic amounts of the metal complex (not always posible in the reductions in acidic media).
-Over both clasical methods: the new process generally involves shorter reaction times and milder conditions. The reaction is set up in open air, there is no need of inert atmosphere. Main byproducts are water and acetone, environmentally friendly and easy to remove from the reaction media. The amines are isolated in pure analytical form whithout column chromathography (economic and environmental advantages).
Specifications
The present invention relates to a procedure for the catalytic reduction of organic compounds that contain a nitro functional group to compounds that contain an amino functional group by using pinacol (2,3-dimethyl-2,3-butanediol) as reducing agent in the presence of a Mo (VI) catalyst at atmospheric or higher pressure and a temperature between 110-150 ºC, generating as main byproducts water and acetone.
Applications
Synthesis of aromatic amines, that can show diverse already demonstrated properties (drugs, pesticides, materials,…). Therefore, applications in pharmaceutical and agrochemical industries.
Intellectual property status
Protected by Patent P201100596. Patent granting date: 05/07/2013
Current development status
Research or Experimental
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Industrial manufacturing, Material and Transport Technologies (33)
Summary of the technology
Researchers at the University of Burgos have developed polymers that are capable of detecting the compounds released by certain decomposing foods.
Using this technology is possible to know quickly and safely if packaged food, specifically fish, is still suitable for consumption. These materials can be presented in the form of films, porous membranes and integrated into other fabrics, such as cotton fibres.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Until now, the expiration date (or best before date) is the only information available to the consumer to know the useful life of a food. The polymers developed by the University of Burgos make it possible to determine the presence of biogenic amines that a food releases during its putrefaction. By applying this technology, the presence of, for example, putrescine and cadaverine (two of the most common amines) can be determined quickly and efficiently. This technique is positioned as a viable alternative to the determination of these compounds by techniques that are more complex.
Main advantages of its use
The main advantages of this material and its use in the determination of the chemical compounds of interest are:
- Simple and cheap. It does not require handling of reagents or pre-treatment.
- Specific. The detection of amines in the gas phase has no interferents.
- Response time. The analysis is practically immediate (colour change and fluorescence).
- Versatile. The polymer can be presented as a film, a membrane or covered by fibres, such as cotton.
Specifications
The synthesized aromatic polyamides (figure 1), which contain structures derived from 1,8-naphthalimide anchored to the main chain, are obtained by polycondensation reaction of the initial monomers. These structures, when interacting with amines and biogenic amines, undergo a change in colour and/or fluorescence. Specific:
Colour change: B-ethylenediamine, cadaverine, trimethylamine, morpholine and putrescine.
Fluorescence change: β-ethylenediamine, cadaverine, morpholine and putrescine.
The final material can be obtained as a film or, by foaming, as a porous membrane. Additionally, these polymers can be integrated into other fabrics, such as cotton fibres.
Applications
The material developed can be applied in the food industry as an intelligent label to account for the freshness of food packaged with a controlled atmosphere, such as packaged fish.
A more general use would consist of using this material as a sensor against the presence of a wide variety of amines in the gas phase.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P201730765
Current development status
Research or Experimental
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
A research group from the University of Burgos has developed a procedure for the manufacture of a lightweight cement eco-cobble with industrial polymer waste. This technology allows waste from car roofs to be disposed of, building a material with very good properties and with application in the construction and civil engineering sector.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
This invention was born with the aim of reusing the polymer present on the roofs of vehicles, thus contributing to the circular economy. This material is mainly composed of polyurethane, mixed with additives, metal oxides, paint remains, among others. The procedure described by the researchers from the University of Burgos produces waste whose recycling process was practically non-existent.
Main advantages of its use
The main advantage offered by this procedure is the use of all the waste to produce the final material, thus avoiding the separation of the different components (polyurethane, metal oxides, additives, etc.).
The addition of this industrial residue improves the physical and mechanical properties of the paving stone, reducing its weight by up to 13% compared to traditional paving stones.
It is possible to maintain and even improve various mechanical properties, of the eco-cobble, such as resistance to breakage.
On the other hand, the building material described, complies with current regulations, which facilitates its application in the construction and civil engineering sector.
Specifications
The final material has dimensions of 200x100x60mm, although these can be modified according to demand. Regarding the appearance of the eco-cobble, it does not present significant cracks or imperfections.
The tests carried out result in an improvement in the mechanical properties, of which the resistance to wear due to abrasion, resistance to slipping and breakage stands out.
Applications
The final material can be used for the construction of flooring, paving, slabs and similar structures depending on the type of traffic and the type of soil, both in the building sector and in civil works.
Intellectual property status
Protected by PCT/ES2023/070553
Current development status
Research or Experimental
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Un grupo de investigación de la Universidad de Burgos ha desarrollado un procedimiento para la fabricación de un ecoadoquín de cemento aligerado con residuos poliméricos industriales. Esta tecnología permite dar salida a los residuos de los techos de los automóviles construyendo un material con muy buenas propiedades y con aplicación en el sector de la construcción y de la ingeniería civil.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Esta invención nace con el objetivo de reutilizar el polímero presente en los tejados de los vehículos, contribuyendo de esta forma a la economía circular. Este material está compuesto principalmente por poliuretano, mezclado con aditivos, óxidos de metales, restos de pintura, entre otros. El procedimiento descrito por los investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos da salida a un residuo cuyo proceso de reciclaje era prácticamente inexistente.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
La principal ventaja que ofrece este procedimiento es la utilización del conjunto del residuo para elaborar el material final, evitando de esta forma la separación de los distintos componentes (poliuretano, óxidos metálicos, aditivos, etc.).
La adición de este residuo de la industria mejora las propiedades físicas y mecánicas del adoquín reduciendo hasta en un 13% de su peso con respecto a los adoquines tradicionales.
En el ecoadoquín se consiguen mantener e incluso mejorar varias propiedades mecánicas, como por ejemplo la resistencia a la rotura.
Por otro lado, el ecoadoquín descrito cumple con la normativa vigente, lo que facilita su aplicación en el sector de la construcción e ingeniería civil.
Características técnicas
El material final cuenta con unas dimensiones de 200x100x60mm, aunque estas pueden ser modificadas en función de la demanda. En cuanto al aspecto del ecoadoquín, este no presenta grietas ni imperfecciones significativas.
Las pruebas realizadas dan como resultado una mejoría de las propiedades mecánicas, de las cuales destaca la resistencia al desgaste por abrasión, resistencia al deslizamiento y a la rotura.
Aplicaciones
El material descrito puede ser utilizado para la construcción de solados, pavimentos, losas y estructuras similares en función del tipo de tránsito y del tipo de suelo, tanto en el sector de la edificación como en obra civil.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante PCT/ES2023/070553
Estado actual de desarrollo
Investigación o experimental
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
A research group at the University of Burgos has developed a procedure for the manufacture of a prefabricated gypsum using polyurethane foam waste (of industrial origin). The cost of the sustainable prefabricated product is lower than the traditional one and it also presents improvements in terms of weight reduction, increased insulating capacity and represents a viable solution for the recycling of polyurethane foam. In this way, it contributes to the circular economy, positioning itself as an alternative to traditional prefabricated gypsum.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
One of the greatest environmental challenges of the 21st century is the reduction, reuse and recycling of plastics. In view of this situation,, the need to seek alternatives for the recovery and recycling of the plastic waste generated is evident. The procedure described by researchers at the University of Burgos has enabled the development of a sustainable prefabricated gypsum using polyurethane foam waste, which means economic and energy savings, with the consequent benefit in terms of reducing the carbon footprint.
Main advantages of its use
- Cost reduction. The final cost of the material obtained is 12% lower than that of a traditional gypsum prefabricated product.
- Improvement in the physical characteristics of the prefabricated material.
- Weight reduction of up to 25% compared to standard boards.
- Increase in the insulating capacity of the material produced.
- Increased recycling rates of this waste.
Specifications
- The origin of polyurethane foam waste is varied: refrigeration industry, construction industry and automotive industry. The characterisation (physical, chemical and microscopic) of this waste has been carried out in order to establish a standard manufacturing process.
- It contains reinforcement fibres, which improve the mechanical properties of the prefabricated product.
- It contains additives of various kinds, which improve the performance of the product.
Applications
- Companies in the building, construction and refurbishment sector.
- Companies related to the refrigeration and automotive industry interested in recycling polyurethane foam waste.
Intellectual property status
Protected by utility model U201931952
Current development status
Device already developed and validated for industrialization.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
A research group at the University of Burgos has developed a procedure for the production of concrete from wind turbine blade waste. The concrete object of the invention not only has good performance both in fresh and hardened state, but also represents a viable solution for recycling wind turbine blades, thus contributing to the circular economy and positioning itself as an alternative to traditional concrete.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
In Spain, it is estimated that by 2030 around 40% of wind turbines will have to be renovated. In view of this situation, the need to seek methods for recycling them has become evident. In the literature, there are few options for the use of this residue, and the vast majority go through the separation of part of its components (glass and carbon fibres, polymeric resins, polyurethane foam, balsa wood and polyester resins) by pyrolysis, solvolysis or gasification processes. The procedure described by researchers from the University of Burgos has allowed the production of sustainable concrete using the crushed waste of wind turbine blades without having previously separated the different components, which allows saving both time and money, and in turn reducing the carbon footprint.
Main advantages of its use
- Obtain a concrete with good technical properties, showing the viability of these residues for use in structural elements.
- Reduction of costs by using raw waste (separation of its components is not necessary) reducing production times and not requiring the hiring of specialized workers.
- Dispose of the raw waste from the grinding of wind turbine blades as recycled fibre for use in concrete. Contributing to the minimization of climate change, while favouring a more circular economy.
Specifications
- The method developed allows the use of up to 6% by volume of waste from the blades of wind turbines.
- The produced concrete retains the flexural strength of traditional concrete despite containing a lower percentage of cement by volume. Moreover, the final material has rload-bearing capacity, providing more security. Its good workability makes it a valid alternative for use in any type of structural element according to current applicable regulations.
- The optimization carried out by the researchers has allowed the creation of a procedure with low technical difficulty and low economic cost.
Applications
- Construction and civil construction companies.
- Companies related to the construction, maintenance and/or removal of wind turbines interested in recycling them.
Intellectual property status
Protected by a patent P202230623
Current development status
Research or Experimental
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Researchers from the University of Burgos have developed a procedure to produce powdered products by freeze drying or vacuum drying from syrupy products (SP) using optionally maltodextrin as a dehydration carrier, so that fine and pleasant powdery solids are obtained. The dehydrated products preserve as close as possible the sensory and physicochemical properties of the starting products.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
SP (syrups and food products with a thick consistency) contain a high concentration of sugars with low glass transition temperatures (Tg), which makes drying difficult, since during dehydration, an extremely sticky, hard and pretty unmanageable product is obtained. The described invention manages to avoid these drawbacks by drying the syrupy products by freeze drying and it has also been possible to carry out the process without the need to add any carrier for dehydration.
The most innovative aspect of the invention in comparison with other procedures is related to the temperatures of product grinding and preservation. High yields of up to 96% are obtained by freeze drying and up to 94% by vacuum drying.
The obtained PS powder contains up to 100% PS solids, being occasionally necessary the inclusion of potato maltodextrin (25% for freeze drying or 40% for vacuum drying). The texture of PS powder is fine, exhibiting excellent sensory and physico-chemical characteristics.
Main advantages of its use
• Obtaining a powdered SP with up to 100% SP solids
• Obtaining a powdered SP without additives
• High process yield: 80%-96% (freeze drying); 80%-94% (vacuum drying).
• Good solubility and low hygroscopicity of the SP powder.
• Good physical-chemical and sensory characteristics of the PS powder.
• Possibility of labelling, marketing and commercializing the SP powder within the consumer-driven initiative "clean labeling" and "real food" movement, as only one natural ingredient is listed: SP, and optionally, potato maltodextrin.
Specifications
The freeze drying and vacuum drying procedures described in this invention achieve the preparation of a SP powder with a fine and pleasant texture, using optionally, a natural carrier (potato maltodextrin), with a high amount of SP in the final solid product, a good solubility, high performance and low hygroscopicity. The grinding and preservation of the product must be carried out at temperatures below the Tg of the SP powder obtained, which help keep optimal texture characteristics of this food, not being needed further anti-caking additives.
Applications
The possible applications of SP powder are related to its use for human and animal feeding products. The sectors with potential application are:
• Fine Cuisine
• Biscuit industry
• Bakery and pastry industry
• Confectionery industry
• Cosmetic industry
• Pharmaceutical industry: drug manufacturing
• Production of food enriched with prebiotics
• Production of food enriched with prebiotics
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202230308 and P202230309
Current development status
Device already developed and validated for industrialization
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Multiple response techniques are all those in which more than one response is obtained simultaneously on the same chemical system or process. Electrochemistry is usually used as a means of controlling the oxidation state of the analyzed material, obtaining in the same experience one or more spectroscopic information or another type of signal, such as that from a high-precision balance.
Color modifications, electronic structure changes, vibrational structure changes, mass variations due to oxidation or deposit on an electrode can be studied with multiple response techniques. Our group has successfully used them in the study of different materials (carbon nanotubes, conductive polymers, metallic nanoparticles, semiconductor nanoparticles and hybrid materials), although they can provide high-quality qualitative and quantitative information on any other type of material.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The techniques developed in our group have still been commercialized in compact instruments in collaboration with the company Metrohm Dropsens, however, the most advanced combinations are not yet commercially available. The modularity of the components allows them to be combined in the appropriate way to obtain the best results depending on each problem posed. Although the components used are well known, their assembly represents state-of-the-art technology in the international context.
Main advantages of its use
These techniques are relatively inexpensive compared to other types of instruments and are capable of providing a great deal of information.
Specifications
One of the techniques developed in our group, Bidimensional Spectroscopy, is outlined in the section "3. pictures". It shows a device for the simultaneous measurement of two optical signals and one electrical signal. In this particular case, the equipment consists of a light source whose radiation reaches the cuvette containing the studied material through optical fibers. Three electrodes connected to the potentiostat are inserted into the cell. The cuvette holder has anchor points for optical fibers, with lenses that collimate the incident light beam. This, after passing through the electrode and/or the solution in which the reaction is taking place, decreases or increases its intensity in proportion to the amount of absorbent material or reagents present in the cell. The emerging light is collected by optical fibers that lead it to the corresponding monochromator, where it is scattered at different wavelengths on a diode array detector. The temporal synchronization of the electrochemical and spectroscopic equipment is key, since small errors in the time record can lead to large errors in the calculated potentials. The control of the experiment and the registration of the data is carried out with two independent computers.
This scheme (see figure 1) of the experimental device is modified depending on the analytical techniques used, being able to work with different spectral ranges and even with laser sources that cause optical phenomena such as Raman scattering or molecular fluorescence. Our devices also allow the acquisition of Raman spectra simultaneously with measurements in the UV/Vis spectrum in both normal and parallel configuration. In addition, photoluminescence techniques combined with electrochemical and other spectroscopic techniques can be used.
Currently, suitable SERS substrates are also being developed for the detection/determination of molecules of interest in a particular way, obtaining high sensitivity and selectivity with good reproducibility.
Applications
Our technologies have been successfully applied to the study and characterization of new materials:
1. Conductive polymers
2. Metallic nanoparticles
3. Semiconductive nanoparticles
4. Carbon nanotubes
5. Graphene
6. Biomolecules
Undoubtedly, they can be used with more “classic” materials, as long as they are susceptible to being oxidized or reduced or undergo some type of transformation over time.
Current development status
Prototype phase
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The new cross-linked aramid polymers have shown improved properties, in particular, electrical insulation, thermal, stability, and/or mechanical properties while maintaining ease of processing. Further, the properties shown by the new cross-linked aramids of the invention render the product especially suitable for advanced technological applications. The crosslinking can be done without investment in nowadays aramid fiber industrial production facilities.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Crosslinking of aramid fibers by conventional production technologies (wet, dry, and dry-jet wet spinning). The crosslinking of armid fibers will render materials with even higher fire, mechanical and electrical-isolation performance.
Main advantages of its use
The crosslinking of armid fibers will render materials with even higher fire, mechanical and electrical-isolation performance.
Specifications
The technology relates to a process for the preparation of a cross-linked aramid polymer comprising the step of heating a non-crosslinked polymer comprising the repeating unit of formula (I), figure 1 (see attached document), at a temperature comprised of from 150 to 400ºC for a period of time comprised of from 1 second to 20 minutes, wherein A and B are independently selected from meta-phenylene and para phenylene (see Figure 2 in the attached document), and R1 and R2 are independently selected from H and N3, with the proviso that at least one of R1 and R2 is N3, and R1 and R2 are attached to any of the positions 1, 2, 3, or 4 in para phenylene and 1, 2, 3 in meta-phenylene.
The heating step of the non-crosslinked polymers comprising the repeating unit of formula (I) at a temperature from 150 to 400ºC yields thecross-linking of the polymeric materials and gives rise to improved mechanical and thermal properties, while maintaining ease of processing. In particular, the cross-linked polymers of the invention have shown advantageous Young´s Modulus and Tensile Strength, and lower dielectric constant, when compared with non crosslinked aramids.
Applications
Aramid fiber proudction companies, such us DuPont, Teijin, Kolon industries, Hyosung, SRO Group, Yantai Sapndex co., Woongjin, Huvis, and Kermel.
Intellectual property status
Protected by PCT/EP2013/062824
Current development status
Device already developed and validated for industrialization.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Granted Patent
PCT/EP2013/062824
https://www.ubu.es/otri/propiedad-industrial-e-intelectual/patentes-y-modelos-de-utilidad-de-la-ubu/61-cross-linked-aramid
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
It is a device to be attached to wheelchairs to provide protection for their users from adverse weather conditions such as rainfall, snow or hail or against wind and protection from direct sunlight.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
- Is a rigid hood that gives stability to the assembly of the chair and increases the degree of protection against rain and wind.
- It has a mechanism which is operated automatically so that the user thereof has no impediment to operate it without help from another person.
- It has sunscreen and sidewalls that protect against the elements when gusts are lateral wind or rain.
Main advantages of its use
Today devices to cover users of wheelchairs are scarce and limited benefits. Our hood has the following advantages:
- Being a rigid hood protects the wearer from the rain and the wind and gives stability to the assembly of the chair.
- The folding and unfolding is automatic.
- It has a distinction between upper translucent zone (for sun exposure protection) and front transparent zone (for perfect visibility of the user).
- It covers the sides protecting the user from rain side bursts.
- It allows isolated from wind and cold as it covers the user through the top and front of his body.
Specifications
The retractable hood for motorized wheelchairs has a rigid upper deck formed by three toroidal hoods slide one inside the next, a drive shaft which is connected to an electric motor secured to the hood body, two articulated quadrilaterals of rods both sides of the hood (responsible for transmitting the folding and unfolding motion to the cover) of toroidal hoods and side plates of a circular sector which are opened and closed sequentially on both sides of the chair wheel and offering the user lateral protection.
Applications
This application is of interest to companies wheelchair manufacturers that want to implement a solution which would solve the problem that day still has not been resolved satisfactorily.
Intellectual property status
Protected by P201201037
Current development status
It is developed at design level and protected by patent.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The oxidative cleavage of vicinal diols to the corresponding aldehydes or ketones is a highly useful transformation in organic synthesis. Traditional methods for carrying out this transformation encompass the use of lead tetraacetate or periodates, that show obvious disadvantages such as the high toxicity of lead tetraacetate and its use in stoichiometric amounts, that implies the generation as byproduct of big amounts of lead diacetate, also toxic. On the other hand, the use of periodates shows limitations in the scope, as ditertiary diols cannot be used.
Therefore, a new method has been developed that uses as oxidant dimethyl sulfoxide, easily accessible and environmentally friendly, for the efficient synthesis of aldehydes and ketones by oxidative cleavage of 1,2-diols.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Dimethyl sulfoxide, used as oxidizing agent in this procedure, is an easily accessible and low cost reagent, that generates as only byproduct dimethyl sulfide, that is a volatile compound that can therefore be easily removed from the reaction media allowing a straightforward isolation of the synthesized aldehyde or ketone without the use of column chromatography.
Main advantages of its use
This is an efficient method for the synthesis of aldehydes and ketones from diols, that uses an easily accessible and environmentally friendly oxidant. Moreover, the reaction is carried out in an open vessel (there is no need of using inert atmosphere) and without the use of organic solvents (economic and environmental advantages) and the aldehydes and ketones are isolated with analytical purity without the need of column chromatography.
Specifications
The present invention relates to the use of dimethyl sulfoxide as oxidizing agent for the oxidative cleavage of 1,2-diols to carbonyl-type compounds including an aldehyde or ketone functional group, in the presence of a molibdenum (VI) catalyst, in an organic solvent or in a solvent free media, under atmospheric pressure and a temperature of 100-180 ºC or, alternatively, by irradiation in a monomode microwave oven at a maximun power of 300 W and a temperature of 120-180 ºC.
Applications
Synthesis of compounds containing an aldehyde or ketone in its structure, which are highly versatile synthetic intermediates. Therefore, applications in pharmaceutical and agrochemical industries. Manufacture of enamels in the Cosmetic Industry. In the Food Industry, as an intermediate product to give smell and flavor to food. Plastic industry, resins, paints, solvents. Explosives manufacturers.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P201301117
Current development status
Laboratory tested procedure.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The research group develops new selective fluorogenic probes for organic molecules of low molecular weight and high social and environmental impact. The newly developed fluorogenic probes are able of show large differences of fluorescence in the presence of certain analytes and they are oriented to the resolution of detection problems for contaminants of high environmental impact for which a satisfactory solution does not exist, such as phosphorylating reagents from chemical weapons, methylmercury, cyanide ion, doping substances and recreational abuse drugs. By incorporation of the fluorogenic probes to silica nanomaterials, the research group generates new luminescent sensory materials of toxicological and environmental utility.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The fluorogenic sensors have acquired an enormous social and economic impact, this is due to the importance that may have in the everyday life. The chemical sensors imply the design of isolated molecules or ensembles of molecules that specifically recognize a particular species in a reversible manner, in an appropriate range of concentration, ideally in trace amounts. The necessity of reversibility is an essential requisite for the continuous or “in vivo” monitorization, but for isolated individual measurements it is not necessary. On the other hand, in the most recet period the detection of an isolated analyte has been surpassed by new systems that are able of detecting diverse classes or mixtures of chemical compounds in a similar way that nature has been using in the development of human smell and taste senses. In this case, the requirements to get these objectives are very complex, therefore the preparation of luminescent signaling systems as well as luminescent devices is greatly advantageous because the fluorescent measurements are usually very sensitive, of low cost, easily performed and extremely versatile, attaining sub-micromolar detection limits. Consequently, luminescent chemical sensors play an important role in key fields such as industrial detection, medical and therapeutic diagnose in health sciences and in diverse environmental monitorization. Nanotechnology is the natural frame of evolution and progression of chemical sensors, therefore combining nanotechnology and luminescent signaling may give rise to the preparation of unique materials on the way to important developments in diverse technical areas such as optical and luminescent chemical sensors for organic analytes of high environmental impact and their implementation in more complex structures to get materials capable of signal amplification to be included in detection devices. From the programmed systems of supramolecular base we are interested in the development of fluorogenic probes for their use in chemical sensors where the recognition process is bonded to a signaling process. The chemical sensors for biomolecules such as neurotransmitters, glutamate and acetylcholine, glycine, aspartate and dopamine, NO and ATP, are very useful. In the environmental sciences, it is known that mercury derivatives, in particular methylmercury, lead and cadmium are very toxic for living organisms and their detection in the environment is very convenient. On the other hand, the chemical sensors of explosives and nerve agents are currently developed for the detection of mines and chemical weapons. With the war to the terrorism, the necessity of reliable and precise chemical and biological sensors that work in real time has notably increased. There are many types of organic molecules of critical importance for which there are not chemical sensors able to detect them, therefore it is important to expand the field of analytes that can be detected and quantified, therefore it is necessary to design and develop new specific fluorogenic probes. Fluorescence is one of the most potent mechanisms of transduction to report a chemical recognition process. The integration of fluorescent molecular probes into suitable devices gives rise to chemical sensors. Reseach has focused in the preparation of new receptors but there are very few commercial fluorogenic probes, therefore the molecular probes developed by the research group fills an empty technological space that nowadays exists.
Main advantages of its use
Many problems of biodetection or biosafety have not yet been resolved. Because of this fact, the research group designs and develops new fluorogenic sensors of environmental organic contaminants for which there are not reliable detection methods in the present days, such as phosphorylating reagents in trace amounts that can come from toxic leakages or chemical weapons reagents, methylmercury, and cyanide ion, and selective fluorogenic sensors for biomolecules of low molecular weight, especially organic metabolites of toxicological or environmental interest. To get these goals, the research group has developed a new family of fluorogenic probes capable of display large differences in the fluorescent signal in the presence of specific analytes, from which the group has developed some fluorescent probes able to discriminate between biomolecules of the same series. The advantage that the new fluorogenic probes offer is that their way of action differs from the known probes, permitting the selective detection of species for which there in no current accessible protocol, for instance discrimination between sport doping substances or abuse recreational drugs. Therefore the research group develops new fluorogenic probes suitable for analytes of high social and environmental impact and with by means of supporting the fluorogenic probes to silica nanomaterials the research group develops new sensor devices of clinical or environmental utility...
Specifications
1.- Development of new OFF-ON fluorogenic probes for the fluorogenic detection of phsphorilating reagents, nerve agents or chemical weapons reagents.
Development of new sensor materials targeted to the detection of environmental organic contaminants of high interest and their application to phosphorylating reagents, nerve agents or chemical weapons reagents.
2.- Development of new fluorogenic probes for methylmercury cation and its selective detection with respect to mercury cation.
Development of new sensor materials targeted to the detection and speciation of methylmercury and mercury cations.
3.- preparation of new OFF-ON fluorogenic probes for fluorogenic recognition processes of organic contaminants and metabolites, cyanide anion and aminoacids.
Development of new sensor materials targeted to the detection of organic contaminants of environmental interest and organic metabolites derived from aminoacids.
4.- Development of new luminescent material sensors based on silica nanomaterials for the detection of organic contaminants and metabolites of high environmental impact.
Development of new sensor materials supported on silica nanomaterials, targeted to the detection of organic contaminants and metabolites of high environmental interest.
5.- Development of new luminescent sensor materials of multiple response, chromogenic, fluorogenic and paramagnetic spin resonance, for the detection of biogenic amines and their analogs of high toxicological and environmental impact.
Development of new sensor materials of multiple response, targeted to the detection of biogenic amines and their analogs used as pharmacological or recreational abuse drugs.
Applications
Enterprises of pharmacological interest, food safety and food defense industry, companies involved in production of chemical compounds with environmental concerns, industry involved in toxicological and environmental detection of chemical compounds.
Current development status
Research or Experimental.
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Researchers from the University of Burgos have developed an APP which measures substances of interest (biocompounds, polluting substances, etc.) with a simple photograph.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Nowadays the reference technique to evaluate the concentration of species of interest using colorimetric sensors is ultraviolet visible (UV-vis) spectroscopy. Nowadays the reference technique to evaluate the colour changes of colorimetric sensors is ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy. This type of technique requires specialized personnel to handle this type of equipment, in addition to a long and tedious experimental procedure that requires a prior calibration that allows calculating the concentration of the species of interest in a test sample.
This app would let measure the analyte concentration quickly, easily and efficiently with a simple digital photograph. To carry out the measurements, it is necessary to photograph the sample calibration and the samples problem.
Main advantages of its use
- Fast, simple and efficient
- Only a smartphone is required
- Not require personnel or equipment specialised
- Wide range of application such as analytical chemistry, quality laboratories, industrial waters, quality control, etc.
Specifications
This application allows the determination of the analytes concentration or chemical species of interest, performing a colour analysis of both the calibration curve and analyte problem. To do this, a photograph is taken of both the calibration curve and the analyte problem. Next, the circular selector is placed on each sample for the colour analysis, and finally the application will show the graphical representation of the concentration against different colour parameters (R, G, B, H, S, V, RGB, ΔRGB). The best fit curve (linear or quadratic), that is, the fit curve with the highest R2 parameter, will appear in the first position, and the application displays the calculated concentrations of the analyte problem. The most innovative aspect is the speed, simplicity, and efficiency when performing a concentration analysis.
Applications
The possible applications are the analysis of substances of interest in analytical chemistry, quality laboratories, industrial waters, quality control, etc.
Intellectual property status
Protected by intellectual property registration BU-122-20
Current development status
The application is temporarily available for free download on the Google Play Store and Apple Store under the name Colorimetric Titration.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Granted Patent
BU-122-20
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Researchers from the University of Burgos have described a new polymeric material that has biocidal capacity (both bactericidal and virucidal capacity) against bacteria of food or environmental origin, as well as for viruses present in food or of respiratory transmission.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The polymeric material described in the invention interacts with bacteria and viruses, and in particular altering and pathogenic bacteria of food or environmental origin and enteric or other food-borne viruses, as well as viruses of respiratory transmission. Due to this, there is an inhibition of the spread of these microorganisms, which allows the use of these materials in the preparation or manufacture of biocidal materials intended for use as bactericidal absorbents in food packaging, and in textile fiber coatings for manufacturing of masks.
Additionally, bactericidal absorbents can also be dissolved in an organic solvent so that they do not constitute plastic waste, and can be managed as liquid waste.
Furthermore, the copolymers of the present invention are totally reusable, so that, if said copolymer is washed with water and ethanol, once used as bactericidal absorbents in food packaging, or in textile fiber coatings or biosanitary material, it becomes totally operational.
Main advantages of its use
- Inhibition of the spread of microorganisms.
- Copolymers are fully reusable.
- Copolymers can be dissolved in an organic solvent so that they do not constitute a plastic waste, and can be managed as liquid waste.
- There is no migration or release of substances from the material
Specifications
The method of inhibiting the growth and propagation of bacteria and viruses, as well as the inhibition of the formation of bacterial biofilms, described in the patent is therefore based on the ability of said copolymers to interact with bacteria and viruses. The monomer (I), present in the developed copolymers, is a group derived from vanillin linked to the polymer chain by a diazo bond.
Applications
The potential applications are:
- Bactericidal absorbents in food packaging.
- Coatings of textile fibers or biosanitary material for the manufacture of masks with biocidal capacity or drainage tubes or probes
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202130734
Current development status
Laboratory tested procedure.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Researchers from the University of Burgos, in collaboration with other research centers, have described a new invention that consists of the geometric definition of a specimen to carry out characterization tests of the tensile strength of concrete and other secondary binding materials, specific for the direct tensile test.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Tensile characterization tests of concrete and other secondary binder materials are mainly carried out by means of indirect tensile tests, which are simpler from the point of view of their execution, but less reliable. Direct tensile tests, being more complex, are less common. There is no standard specimen geometry for these tests, and specimens with a wide variety of geometries have been used. The geometric design of the test specimen is essential for successful direct tensile testing.
The solution proposed by the researchers makes it possible to determine geometrically a test specimen that guarantees that the break will occur, in the highest possible proportion, in the central area and that it is not affected by the local effects derived from the anchoring system. from the specimen to the load application system.
Main advantages of its use
This specimen is intended to serve as a basis for conducting, in a more reliable way, direct traction tests on concrete and other secondary binding materials, in such a way that all the specimen show a break in the central zone and, therefore, all direct traction tests can reach the "valid" condition.
Specifications
The geometry of the test specimen described by the researchers by the present invention comprises a body of revolution made up of a central straight section, first and second straight end sections, and two first and second transition curved sections, which are arranged between the straight section. central and the first and second extreme straight sections respectively. This proposed specimen manages to substantially reduce the quotient between the maximum stress in the specimen and the maximum stress in its central straight section, approaching unity. To do this, the maximum principal tensile stress fields that appear in different examples of specimens have been calculated, all of them, with a geometry of revolution, subjected to a uniform tensile load, in such a way that the maximum principal stress in the area of the central straight section is the unit.
Applications
This specimen is of great interest for laboratories for the characterization of hydraulic binding materials (such as concrete, cement mortars, lime mortars or plaster mortars, among others). It is also of interest to research centers that are investigating the mechanical properties of concretes and secondary binding materials.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202130588
Current development status
Developed exclusively in the laboratory and validated for industrialization
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Researchers from the University of Burgos (UBU) have developed a high-performance concrete (HPC) and improved shrinkage, made with recycled concrete aggregate (RCA) and reactive magnesium oxide (MgO). The developed concrete has a high workability, which allows a simple and economical installation, and a high strength, which allows using it in any type of structural element according to the current applicable regulations. The use of magnesium oxide allows reducing shrinkage, which is very high in HPC due to its high cement content. This, in turn, reduces the cracking caused by this phenomenon and improves the durability of the structural elements.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
High-performance concrete is a type of concrete with high strength and durability thanks to its high cement content. Nevertheless, this high content of cement also implies that it has a high heat of hydration during setting and high shrinkage, in addition to low workability. Recycled concrete aggregate is a waste from the precast concrete industry that is characterized by its very high water absorption. Magnesium oxide (MgO) is a chemical compound that exhibits expansive properties when mixed with water. In addition, this expansion occurs during the concrete setting process and its production generates 70% less CO2 emissions than the manufacture of ordinary Portland cement.
The solution proposed by the researchers focuses on solving the existing problems in the traditional manufacture of concrete. The invention seeks to take advantage of recycled concrete aggregate and magnesium oxide to produce a sustainable, high-performance concrete optimal for structural use from the point of view of placement (high workability), from the point of view of strength (high strength) and regarding shrinkage (decreased shrinkage).
Main advantages of its use
- The sustainability of high-performance concrete is maximized by adding recycled concrete aggregate and reactive magnesium oxide as a secondary binder.
- The dumping of waste, clinker consumption and CO2 emissions are reduced and, with leads to the consequent reduction of climate change.
- The workability and strength of high-performance concrete made with recycled concrete aggregate and reactive magnesium oxide are simultaneously maximized.
- Minimizing shrinkage (shortening) of high-performance concrete and the cracking associated with this phenomenon is achieved by adding reactive magnesium oxide with expansive characteristics.
Specifications
The designed high-strength concretes are composed of type I cement (ordinary Portland cement) as the first binder and reactive magnesium oxide as the second binder in a content between 10% and 15% of the total binder mass of the high-strength concrete. The coarse aggregate fraction and the fine aggregate fraction are exclusively manufactured with recycled concrete aggregate. In addition to these components, the designed concretes also incorporate water and a superplasticizer admixture to increase the workability of concrete.
Applications
Potential applications are as follow:
- Construction and civil engineering sector
- Sector of new materials valid for structural applications
- Technical sector for the recycling and use of waste from the prefabrication industry
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202130466
Current development status
Developed exclusively in the laboratory and validated for industrialization
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Researchers from the University of Burgos (UBU) have developed a fire-resistant cement precast lightened with industrial waste of polymeric origin, from recycled vehicle roofs, made in the form of a block for the construction of walls or a similar structure.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The novelty of the invention is based on the use of the waste from the roofs generated in the automobile industry, which is valued as raw material with added value for its incorporation into the precast industry of the Construction Sector. The percentage of residue present in the final material depends on the required properties of the final product, obtaining properties in the hardened state sufficient to be able to apply the current legislation.
Main advantages of its use
- Replacement of part of the fine and coarse aggregate of the precast mortar by residues of complete roofs from the automotive industry.
- Additives “à la carte”, polymeric in nature, which are added, maintained and even improved mechanical resistance within the necessary reference values required by European regulations. It supposes a saving of base structure and a greater workability.
- Greater thermal insulation of the final envelope, as well as a good behavior against temperature and against fire (non-combustibility).
- Recycling of waste for the construction of materials, moving from waste to new raw materials, with the reduction of the environmental impact that it entails.
- Reduction of the weight of the material without affecting its properties.
Specifications
The characteristics and nature of construction materials, based on cement, make it possible to enhance foams that come from polyurethane insulating panels with remains of other materials (adhesives, metal oxides, remains of paint and / or plasters, etc.). The cement is of the Portland Cement type with a mass composition of 95-100% clinker and 0-5% minor components. This alteration in the components of the precast cement object of the invention helps to maintain its mechanical strength, obtaining recycled materials with certainly structural capabilities, but at the same time, with a low density compared to conventional light mortars. This precast cement lightened with polymer matrix residues provides improvements in the physical characteristics of the precast, with weight reductions of up to 70%.
Applications
Potential applications of the tank are as follow:
- Blocks of compact cement that are installed by joining courses with mortar and are worked in a similar way to brick.
- Lintels to be installed on top of joinery frames where bricks are left unattached.
- Panels, plates and foundations for buildings, industrial buildings, etc.
- Manholes for sanitation networks or electrical networks used in urbanizations.
- Concrete pavements and paving stones for pedestrian walkways, landscaped areas and low-traffic roads.
Intellectual property status
Protected by Utility Model U202131039
Current development status
Developed exclusively in the laboratory and validated for industrialization.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Researchers from the University of Burgos have patented a new gypsum-based material that has improved properties for construction, especially for use as coatings where high fire resistance is required. This material is made up of waste from the iron and steel industry for which the criteria for its use and basic dosages are set to guarantee its resistance and durability, as well as a high degree of performance and implementation, as well as resistance to fire.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The proposed solution allows the obtaining of a densified material with improved properties compared to conventional mixtures (for example, optimizing some of the basic properties) and with a good performance in the performance regime in relation resistance and reaction to fire.
Main advantages of its use
• Improvement of the non-combustibility properties of conventional plasters.
• Increase in applications of gypsum-based materials in special atmospheres.
Specifications
It is an ecoprefabricated gypsum board with high fire resistance, the board being made up of a gypsum core incluiding iron and steel residues from the steel industry, said residues essentially composed of CaO, SiO2, Al2O3 and MgO.
Applications
The potential applications are:
- Companies in the construction sector.
- Use in mass coatings as materials with high resistance and reaction to fire.
- Prefabricated for use in buildings partitions and industrial with protection against fire requirements.
Intellectual property status
Protected by Model Utility U201930281
Current development status
In use and validated.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
A research group at the University of Burgos (UBU) has developed new aromatic polyamides (aramids) models and polymeric materials reinforced with carbon nano-fillers, chemically functionalized previously with these polyamide models, constituting materials with exceptional mechanical and thermal properties.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
These new aramids and / or polymers reinforced with carbon nanofillers can be prepared in the form of a porous membrane, dense membrane, coating, fiber, etc., constituting materials with exceptional mechanical and thermal properties. Nano and microporous materials are made by adding an ionic liquid in the preparation process and its subsequent removal in a solvent, producing high-performance materials with a reduced density.
Main advantages of its use
- Simplicity of the manufacturing process. The porosity generation process is simpler, faster and more homogeneous than other techniques such as phase inversion or the use of supercritical CO2.
- Versatility, since it can be applied to both membranes and thicker materials (up to several mm).
- It is possible to control the porosity parameters based on the process conditions (quantity and type of ionic liquid used, mainly).
- The functionalization of the nano-fillers allows an optimal dispersion in the polymer.
- The porous structure notably improves the mechanical properties compared to dense polymers (without porosity). These specific properties (values relative to density) are superior in porous materials compared to dense materials.
Specifications
Aramids reinforced with nano-fillers are prepared by dispersing the functionalized nano-filler in a solution of the aramid, and subsequent removal of the solvent. These polymers can be prepared in the form of a porous membrane, dense membrane, coating, fiber etc. obtaining materials with exceptional mechanical and thermal properties. Nano and microporous materials are made by adding an ionic liquid in the preparation process and its subsequent elimination in a solvent, producing high-performance materials with reduced density.
Applications
These materials can be used as high-performance polymers in different applications, such as:
- Reinforcement in different structures
- High resistance textile fibers
- Flexible conductive materials
- Energy storage elements in electrochemical applications
- Filtration membranes and water purification.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202030044
Current development status
Device already developed and validated for industrialization.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Sustainable roller-compacted concrete comprises Portland cement as primary binder, aggregates, water and admixtures. Concrete is characterized as comprising metallic and/or plastic fibers, ground granulated blast furnace slag as secondary binder and ladle furnace slag as ternary binder, the aggregates comprise recycled concrete aggregate.
Sustainable roller-compacted dry steel concrete comprises Portland cement as primary binder, aggregates, water and admixtures. Concrete is characterized by comprising metallic and/or plastic fibers, ground granulated blast furnace slag as secondary binder and ladle furnace slag as ternary binder, the aggregates comprise electric arc furnace slag.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Roller compacted concrete manufactured with recovered components obtained from other processes or substances, such as by-products from the steel industry (iron and steel concrete) or waste from the precast concrete industry (sustainable concrete) that increase its sustainability.
The use of construction waste and by-products from the steel industry gives these concretes an innovative installation process, achieving the same technical characteristics as self-compacting concretes whose composition is based on the use of fractions with natural aggregate with additional technical and economic advantages.
The dosage of iron and steel concrete with a dry consistency is shown in Table 1:
|
Components (kg/m3) |
RCC-E-M |
RCC-E-P |
|
Ordinary Portland Cement (CEM I 52.5 R) |
140 |
140 |
|
Ground granulated blast furnace slag |
115 |
115 |
|
Ladle furnace slag |
40 |
40 |
|
Water |
115 |
115 |
|
Electric arc furnace slag: coarse fraction |
390 |
390 |
|
Electric arc furnace slag: middle fraction |
700 |
700 |
|
Electric arc furnace slag: fine fraction |
535 |
535 |
|
Limestone sand (< 0.50 mm) |
485 |
485 |
|
Siliceous sand (< 0.50 mm) |
245 |
245 |
|
Plastizier |
5,0 |
5,0 |
|
Fibers (M, metallic; P, plastic) |
55 (M) |
6,5 (P) |
Table 1. Dosage of dry steel concrete mixes (kg/m3)
(M: metallic fibers; P: plastic fibers)
The dosage of sustainable dry consistency concrete is shown in Table 2:
|
Components (kg/m3) |
RCC-AH-M |
RCC-AH-P |
|
Ordinary Portland Cement (CEM I 52.5 R) |
140 |
140 |
|
Ground granulated blast furnace slag |
115 |
115 |
|
Ladle furnace slag |
40 |
40 |
|
Water |
130 |
130 |
|
Electric arc furnace slag: coarse fraction |
275 |
275 |
|
Electric arc furnace slag: middle fraction |
495 |
495 |
|
Electric arc furnace slag: fine fraction |
375 |
375 |
|
Limestone sand (< 0.50 mm) |
485 |
485 |
|
Siliceous sand (< 0.50 mm) |
245 |
245 |
|
Plastizier |
5,0 |
5,0 |
|
Fibers (M, metallic; P, plastic) |
55 (M) |
6,5 (P) |
Table 2. Dosage of dry sustainable concrete mixes (kg/m3)
(M: metallic fibers; P: plastic fibers)
Main advantages of its use
- Roller-compacted concrete of high workability, easily pumpable and great self-compactability.
- Reduction of energy consumption in the production stages minimizing and increase of yields in its implementation.
- Elimination of vibratiuon reducing fuel consumption and CO2 emissions.
- Recycling of slag from electric arc furnaces in the case of roller-compacted siderurgic concrete.
- Recycling of concrete aggregate in the case of roller compacted recycled-aggregate concrete.
- High resistance to cracking due to the inclusion of metallic and / or plastic fibers together with slag from an electric arc furnace.
- Sustainable concrete.
Specifications
The novel roller-compacted dry concretes comply with international EN 206 specifications and EFNARC recommendations.
The properties in the fresh state of the different mixtures of the iron and steel concrete of dry consistency are shown in table 3:
|
Property |
RCC-E-M |
RCC-E-P |
|
Time of vibrating consistometer Vebe (s) |
7,5 |
6,5 |
|
Vebe consistometer seat (cm) |
4,0 |
4,5 |
|
Vebe consistometer density (Mg/m3) |
2,68 |
2,63 |
Table 3. Fresh properties of dry steel concrete
The properties in the fresh state of the different mixes of sustainable concrete of dry consistency are shown in table 4:
|
Property |
RCC-AH-M |
RCC-AH-P |
|
Time of vibrating consistometer Vebe (s) |
6,0 |
5,5 |
|
Vebe consistometer seat (cm) |
4,5 |
5,0 |
|
Vebe consistometer density (Mg/m3) |
2,27 |
2,22 |
Table 4. Properties in fresh state of dry sustainable concrete
The properties in the hardened state of the different mixtures of the iron and steel concrete of dry consistency are shown in table 5:
|
Property |
Age (days) |
RCC-E-M |
RCC-E-P |
|
Hardened density (Mg/m3) |
28 |
2,59 |
2,54 |
|
Compressive strength (MPa) |
1 |
46,9 |
41,4 |
|
28 |
59,6 |
56,9 |
Table 5. Properties in the hardened state of dry iron and steel concrete
The properties in the hardened state of the different mixtures of the sustainable concrete of dry consistency are shown in table 6:
|
Property |
Age (days) |
RCC-AH-M |
RCC-AH-P |
|
Hardened density (Mg/m3) |
28 |
2,19 |
2,16 |
|
Compressive strength (MPa) |
1 |
12,5 |
43,1 |
|
28 |
53,4 |
51,8 |
Table 6. Properties in hardened state of dry sustainable concrete
Applications
- Structural elements subjected to very high loads; beams, columns, floors or walls.
- Pavements.
- Large walls and dams of any type, such as gravity dams, arch or vault.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202030878 and P202030881
Current development status
Developed exclusively in the laboratory and validated for industrialization.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Self-compacting concrete with electric arc furnace slag in all fractions that is composed of Portland cement as primary binder, ground granualted blast furnace slag as secondary binder and ladle furnace slag as ternary binder, in addition to aggregate, water and admixtures, metallic and/or synthetic fibers. Due to its innovative composition and installation procedure, it achieves excellent results of durability, sustainability and aesthetics.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The use of construction wastes and by-products from the steel industry gives these concretes an innovative installation process, achieving the same technical characteristics as self-compacting concretes whose composition is based on the use of fractions with natural aggregates with additional technical and economic advantages.
Its dosage is shown in Table 1:
|
Components (kg/m3) |
T |
M |
P |
|
Ordinary Portland cement (CEM I 52.5 R) |
215 |
215 |
215 |
|
Ground granulated blast furnace slag |
115 |
115 |
115 |
|
Water |
170 |
180 |
185 |
|
Electric arc furnace slag - coarse fraction |
750 |
750 |
750 |
|
Electric arc furnace slag - fine fraction |
550 |
550 |
550 |
|
Limestone sand (< 0.50 m) |
950 |
950 |
950 |
|
Plasticizer additive |
5,5 |
5,5 |
5,5 |
|
Fibers (M, metallic; P, plastic) |
20 (M) |
40 (M) |
4,5 (P) |
Table 1. Dosage of mixtures (kg/m3)
Main advantages of its use
- Self-compacting concrete of high workability, easily pumpable and great self-compactability.
- Minimization of energy consumption in the production stages and increase of yields in its implementation.
- Elimination of the vibration, thus reducing fuel consumption and CO2 emissions.
- Recycling of slag from electric arc furnaces.
- High resistance to cracking due to the inclusion of metallic and/or plastic fibers together with slag from an electric arc furnace.
- Sustainable concrete.
Specifications
The new self-compacting concretes meet the international specifications EN 206 and the recommendations of the EFNARC.
The properties in fresh state of the different mixtures are shown in table 2:
|
Property |
T: metallic fibers 0,25% concrete volumne |
M: metallic fibers 0, 5% concrete volumne |
P: plastic fibers 0,5% concrete volume |
|
Slump flow (mm) |
720 (SF2) |
650 (SF1) |
620 (SF1) |
|
Fresh density (Mg/m3) |
2,71 |
2,67 |
2,60 |
|
Occluded air (%) |
2,2 |
2,0 |
1,9 |
|
Setting shrinkage (mm/m) |
1,1 |
0,9 |
1,0 |
Tabla 2. Propiedades en estado fresco
SF: clase de escurrimiento
The properties in the hardened state of the different pre-cracking mixtures are shown in Table 3. In parentheses, the standard deviation.
|
Age (days) |
T |
M |
P |
|
|
Densidad endurecida (Mg/m3) |
90 |
2,63 (0,3) |
2,57 (0,3) |
2,54 (0,2) |
|
Compressive strength (MPa) |
7 |
47,1 (1,5) |
38,2 (0,4) |
33,3 (0,1) |
|
28 |
59,7 (5,7) |
53,1 (1,5) |
46,1 (1,0) |
|
|
90 |
75,3 (4,1) |
63,6 (3,6) |
56,8 (5,3) |
|
|
180 |
76,1 (3,5) |
65,2 (3,5) |
59,1 (3,2) |
|
|
360 |
77,9 (0,2) |
68,8 (5,3) |
60,5 (2,7) |
|
|
Modulus of elasticity (GPa) |
90 |
40,1 (0,7) |
34,7 (1,5) |
31,6 (0,9) |
|
Poisson's coefficient (ν) |
90 |
0,23 (0,1) |
0,22 (0,1) |
0,22 (0,1) |
|
Flexural strength (MPa) |
90 |
7,93 (2,3) |
5,97 (1,1) |
5,04 (0,3) |
|
Splitting tensile strength (MPa) |
90 |
5,11 (0,4) |
4,84 (0,6) |
4,35 (0,4) |
|
Direct tensile strength (MPa) |
160 |
4,25 (0,2) |
3,77 (0,4) |
3,66 (0,4) |
|
Tensile modulus of elasticity (GPa) |
160 |
38,5 (1,0) |
37,9 (2,8) |
35,5 (0,3) |
|
Maximum water penetration height (mm) |
90 |
16 (6,1) |
19 (5,4) |
20 (4,7) |
|
Average water penetration height (mm) |
90 |
10 (4,5) |
12 (4,8) |
12 (5,1) |
Table 3. properties in pre-cracking hardened state
The properties in the hardened state of the different post-cracking mixtures are shown in Table 4. In parentheses, the standard deviation.
|
Test |
Property |
T |
M |
P |
|
Bending test on four points |
Flexural fracture toughness (Nm) |
8,61 |
21,38 |
11,72 |
|
Resistance to first crack (MPa) |
7,59 (2,1) |
4,89 (1,4) |
4,13 (0,5) |
|
|
Fracture energy (N/mm) |
0,749 |
2,153 |
1,190 |
|
|
Bending test on three points in notched specimens |
Limit of proportionality (MPa) |
5,20 |
5,98 |
3,66 |
|
Residual strength (MPa) |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
Crack open mouth: 0.5mm |
5,50 |
6,52 |
1,21 |
|
|
Crack open mouth: 1.5mm |
4,80 |
5,70 |
1,17 |
|
|
Crack open mouth: 2.5mm |
3,65 |
3,96 |
1,29 |
|
|
Crack open mouth: 3.5mm |
3,93 |
3,01 |
1,31 |
|
|
Fracture energy (N/mm) |
1,124 |
2,235 |
0,598 |
|
|
Fracture energy according to notch opening (N/mm) |
1,133 |
2,637 |
0,707 |
Tabla 4. Properties in the hardened state after cracking
Applications
- Structural elements subjected to very high loads; beams, columns, slabs or walls.
- Applications of prestressed concrete both in situ and precast.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202030750
Current development status
Developed, validated and ready to use.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Self-compacting concrete with recycled concrete aggregate in all fractions, using Portland cement as primary binder, and ground granulated blast furnace slag as secondary binder. Its innovative composition and installation procedure allow achieving excellent results of durability, sustainability and aesthetic finishing.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The use of construction waste and by-products from the steelmaking gives these concretes an innovative installation process, achieving the same technical characteristics as self-compacting concretes whose composition is based on the use of natural aggregate with additional technical and economic advantages.
All three mixtures are suitable for use, although the MIX50 mix provides an adequate balance between material performance and product sustainability.
Its dosage is shown in Table 1:
|
Material/Mix |
MIX0 |
MIX50 |
MIX100 |
|
CEM I 52.5 R |
208 |
||
|
Ground granulated blast furnace slag |
208 |
||
|
Recycled concrete aggregate (< 0.50 mm) |
305 |
||
|
Water |
225 |
280 |
335 |
|
Coarse recycled concrete aggregate |
405 |
||
|
Fine recycled concrete aggregate |
0 |
430 |
865 |
|
Siliceous sand |
935 |
470 |
0 |
|
Viscosity regulator |
2,30 |
||
|
Plasticizer |
4,50 |
Table 1. Dosage of mixtures (kg/m3)
Use of waste for the production of sustainable self-compacting concrete optimal for structural use.
Main advantages of its use
- Great flowability and ease of filling molds for structures with complicated shapes.
- Elimination of the pre-soaking stage in the recycled concrete aggregate
- High self-compactability of concrete. Compaction without vibration.
- Homogeneous finishes without imperfections.
- Economical and sustainable implementation by using waste from the precast-concrete industry and by-products from the steel industry known as slag.
- Reduction of energy consumption in its implementation.
- Excellent physical and mechanical properties.
Specifications
The technical characteristics for the MIX50 mix are as shown here:
|
Slump flow |
820 mm |
|
Compressive strength at 28 days |
39,6 MPa |
|
Splitting tensile strength at 28 days |
2,4 MPa |
|
Flexural strength at 28 days |
4,5 MPa |
|
Density |
2,08 Mg/m3 |
|
Maximum agrgegate size |
12,5 mm |
The new self-compacting concretes meet the international specifications EN 206 and the recommendations of the EFNARC.
|
Property |
Time since kneading (min) |
MIX0 |
MIX50 |
MIX100 |
|
Slump flow (mm) |
0 |
800 (SF3) |
820 (SF3) |
830 (SF3) |
|
15 |
770 (SF3) |
780 (SF3) |
780 (SF3) |
|
|
30 |
715 (SF2) |
700 (SF2) |
705 (SF2) |
|
|
60 |
570 (SF1) |
560 (SF1) |
555 (SF1) |
|
|
T500 (s) |
0 |
2,4 (VS2) |
3 (VS2) |
3,6 (VS2) |
|
15 |
3,4 (VS2) |
4,6 (VS2) |
5,8 (VS2) |
|
|
30 |
5,6 (VS2) |
6,8 (VS2) |
8,4 (VS2) |
|
|
60 |
8,6 (VS2) |
11,2 (VS2) |
12,8 (VS2) |
|
|
Empting time V-funnel test (s) |
15 |
10,6 (VF2) |
19,2 (VF2) |
24,8 (VF2) |
|
Blocking ratio L-box test |
15 |
0,80 (PA1) |
0,82 (PA1) |
0,86 (PA1) |
|
Resistance to segregation (%) |
30 |
1,86 (SR2) |
1,67 (SR2) |
1,31 (SR2) |
|
Fresh density (Mg/m3) |
- |
2,22 |
2,16 |
1,96 |
|
Occluded air (%) |
- |
4,5 |
5,3 |
5,9 |
Table 2. Properties in fresh state
SF: slump-flow class, VS: slump-flow-viscosity class, VF; V-funnel-viscosity class, PA; passing-ability class & SR; segregation-resistance class
|
Age (days) |
MIX0 |
MIX50 |
MIX100 |
|
|
Compressive strength on cubic specimen (MPa) |
1 |
12,5 |
9,9 |
5,2 |
|
7 |
36,4 |
32,1 |
22,3 |
|
|
28 |
45,9 |
39,6 |
31,8 |
|
|
90 |
47,8 |
43,3 |
35,5 |
|
|
Compressive strength on cylindrical specimen (MPa) |
7 |
29,5 |
25,1 |
16,7 |
|
28 |
41,8 |
34,5 |
27,3 |
|
|
Hardened Density (Mg/m3) |
28 |
2,15 |
2,08 |
1,81* |
|
Modulus of elasticity (GPa) |
7 |
26,6 |
24,5 |
13,9 |
|
28 |
29,3 |
27,1 |
16,1 |
|
|
Splitting tensile strength (MPa) |
7 |
2,7 |
2,1 |
1,4 |
|
28 |
3,2 |
2,4 |
1,8 |
|
|
Flexural strength (MPa) |
7 |
4,1 |
3,8 |
2,9 |
|
28 |
4,9 |
4,5 |
3,3 |
|
|
Hammer rebound index (dimensionless) |
1 |
11 |
10 |
10 |
|
7 |
28 |
26 |
20 |
|
|
28 |
31 |
28 |
26 |
|
|
90 |
32 |
30 |
27 |
|
|
Ultrasonic pulse velocity (km/s) |
1 |
2,82 |
2,77 |
2,43 |
|
7 |
3,83 |
3,75 |
3,21 |
|
|
28 |
4,03 |
3,93 |
3,68 |
|
|
90 |
4,07 |
4,01 |
3,89 |
Table 3. Properties in hardened state
Applications
- On site placement by pouring, pumping or injection.
- Manufacture of concrete pieces with complicated shapes with high aesthetic requirements.
- Foundations and structures.
- Heavily armed structures.
- Construction of large infrastructures such as bridges or tunnels where compaction is complicated.
- Concreting in situations of difficult access and high-rise buildings.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202030746
Current development status
Developed, validated and ready to use.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Self-compacting concrete with recycled concrete aggregate and low shrinkage is characterized by its composition based on Portland cement as first binder, ground granulated blast furnace slag as second binder, and ladle furnace slag as third binder. Its innovative composition and installation procedure allow achieving excellent durability, sustainability and aesthetic results.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The use of construction wastes and by-products from the steel industry gives these concretes an innovative installation process, achieving the same technical characteristics as self-compacting concretes whose composition is based on the use of natural aggregate with additional technical and economic advantages.
Its dosage is shown in Table 1:
|
Material/L |
L0 |
L5 |
L10 |
|
CEM I 52.5 R |
210 |
190 |
170 |
|
Ladle furnace slag |
0 |
20 |
40 |
|
Ground granuatled blast furnace slag |
210 |
||
|
Recycled concrete aggregate (< 0.50 mm) |
305 |
||
|
Water |
335 |
||
|
Coarse recycled concrete aggregate |
405 |
||
|
Fine recycled concrete aggregate |
865 |
||
|
Viscosity regulator |
2,3 |
||
|
Plasticizer |
4,5 |
Table 1. Composition of mixtures (kg/m3)
Use of waste for the production of sustainable self-compacting concrete optimal for structural use.
Main advantages of its use
- Great flowability and ease of filling formworks of structures with complicated shapes.
- Elimination of the pre-soaking stage in the recycled aggregate.
- Highly self-compactability of concrete. Compaction without vibration.
- Homogeneous finishes without imperfections.
- Economic and sustainable placement by using waste from the precast-concrete industry and by-products from the steel industry known as slag.
- Reduction of energy consumption in its implementation.
- Excellent physical and mechanical properties.
Specifications
The new self-compacting concretes fulfill the international specifications EN 206 and the recommendations of the EFNARC.
|
Property |
Time since kneading (min) |
L0 |
L5 |
L10 |
|
Slump flow (mm) |
0 |
830 (SF3) |
825 (SF3) |
810 (SF3) |
|
15 |
780 (SF3) |
770 (SF3) |
755 (SF3) |
|
|
30 |
705 (SF2) |
700 (SF2) |
675 (SF2) |
|
|
60 |
555 (SF1) |
550 (SF1) |
550 (SF1) |
|
|
T500 (s) |
0 |
3,6 (VS2) |
4,0 (VS2) |
4,4 (VS2) |
|
15 |
5,8 (VS2) |
6,0 (VS2) |
6,6 (VS2) |
|
|
30 |
8,4 (VS2) |
9,0 (VS2) |
9,8 (VS2) |
|
|
60 |
12,8 (VS2) |
13,8 (VS2) |
15,2 (VS2) |
|
|
Empting time V-funnel test (s) |
15 |
24,8 (VF2) |
25,6 (VF2) |
26,2 (VF2) |
|
Blocking ratio, L-box test |
15 |
0,86 (PA1) |
0,85 (PA1) |
0,82 (PA1) |
|
Resistance to segregation (%) |
30 |
1,31 (SR2) |
1,26 (SR2) |
1,19 (SR2) |
|
Fresh density (Mg/m3) |
- |
1,96 |
1,97 |
2,01 |
|
Occluded air (%) |
- |
5,9 |
5,7 |
5,4 |
Table 2. Properties in fresh state
SF: class of runoff, VS: viscosity in flow, VF; viscosity in the V-funnel test, PA; passsing ability & SR; segregation
|
Age (days) |
L0 |
L5 |
L10 |
|
|
Compressive strength on cubic specimen (MPa) |
7 |
22,3 |
21,8 |
20,5 |
|
28 |
31,8 |
32,6 |
34,5 |
|
|
Hardened Density (Mg/m3) |
28 |
1,81 |
1,86 |
1,89 |
|
Modulus of elasticity (GPa) |
7 |
13,9 |
13,4 |
13,3 |
|
28 |
16,1 |
16,3 |
16,8 |
|
|
Setting shrinkage (mm/m) |
2 |
0,65 |
0,51 |
0,63 |
|
Long-term shrinkage (mm/m) |
180 |
1,30 |
1,08 |
0,83 |
Table 3. Properties in hardened state
Applications
- On site application by pouring, pumping or injection.
- Manufacture of concrete pieces with complicated shapes with high aesthetic requirements.
- Foundations and structures.
- Heavily armed structures.
- Construction of large infrastructures such as bridges or tunnels where compaction is complicated.
- Construction with difficult access and high-rise buildings.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202030748
Current development status
Developed, validated and ready to use.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Researchers from the University of Burgos have developed a new tank for compression pressure measurement cells, for geotechnical application, which represents a significant improvement over existing devices on the market by facilitating their manufacturing process, reducing the cost per piece.
New and innovative aspects
The proposed solution focuses on solving the technical problem of configuring a device so that it is simpler and less expensive than known metal tanks. The technology developed is characterized by the use of a thermoplastic material for the manufacture of small tanks. This material allows the use of common techniques for the manufacture of parts with thermoplastic material, such as manufacturing by adding material or 3D printing or rotational molding, so the cost per piece is lower. In addition, it is possible to develop special total pressure cells, specific for specific solutions.
Main advantages of its use
- Thermoplastic polyurethane presents mechanical resistance combined with some flexibility and chemical resistance to oils.
- It is possible to improve the impermeability with a sheet of waterproof latex material or similar.
- Diameter between 30 mm and 150 mm, less than that of known tanks that usually start at a minimum diameter of 200 mm.
- Maximum height between 5 mm and 30 mm.
- Cheaper manufacturing process by using a thermoplastic material.
- It is easier and cheaper to develop special total pressure cells, specific for specific solutions, without a significant cost increase.
Specifications
A total pressure cell (or simply pressure cell) is device with a sensor that allows to measure compression pressures inside a material in a specific direction. It is commonly used to know the compression pressures that are exerted at a point inside the ground or the final linings in tunnels. The device includes a tank. There is a direct relationship between reservoir size and pressure measurement accuracy, the smaller a total pressure cell the more accurate it will be. The traditional manufacturing process of the metal tank is laborious, which makes the final product more expensive. In addition, the demand for this type of sensors is low and consequently, its manufacturing process is poorly mechanized.
The technical problem to be solved is to configure the deposit to be simpler and less expensive than known metal deposits. The material used is a thermoplastic polyurethane, suitable for this type of application, due to its mechanical resistance combined with certain flexibility and chemical resistance to oils. The diameter and height of the tank, and the thickness of the walls, are considerably lower than those of known metal tanks. There is the option of increasing the impermeability placing inside a sheet of waterproof latex or similar material.
Applications
Potential applications of the tank are as follow:
- In geotechnical instrumentation to know the compression pressures that are exerted at a point inside the ground in a certain direction or inside the final linings in tunnels, or between them and the ground.
Intellectual property status
Protected by utility model U202031698
Current development status
Device already developed and validated for industrialization.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Test for components subjected to high pressure (pipes and driving elements) (up to 6000 bar) which allows:
1. To assess structural integrity and failure analysis.
2. To reproduce the work cycle (0-6000bar-0).
3. To know the performance of new components subjected to high pressure.
4. To determine the fatigue of the real component under the working pressure.
5. To perform hydraulic fracture and fatigue tests up to 6 000 bars.
Accessibility
- Isidoro Iván Cuesta Segura and Jesús Manuel Alegre Calderón, Structural Integrity (GIE) E-mail: iicuesta@ubu.es; jalegre@ubu.es https://www.ubu.es/structural-integrity-gie
Short description of how tool can be used
New components subjected to high internal pressure can be verified with a quickly and easy method knowing their perfomance to fracture and fatigue (fatigue life), allowing preventive maintenance of the equipment.
Fees
Request an offer, the cost is variable depending on the type of test to be performed (fracture, fatigue of low number of cycles, fatigue of high number of cycles, ...).
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
A device for testing components subjected to high pressure (pipes and conduction elements), being able to hitch in any universal machine of dynamic tests to reproduce the work cycles (0-6000bar-0) of the different components to analyse. Thanks to this new equipment, it will be possible to verify quickly and easily new components subjected to high pressure knowing their corresponding fatigue lives, allowing preventive maintenance of the equipment.
New and innovative aspects
The majority of industrial components subjected to high pressure only pass static pressure tests for validation, in which the pressure rises up to 1.5 times the working pressure.
Currently, there aren´t any commercial devices for fatigue testing of the real component under work pressure, which means that some of the component broken due to fatigue even after passing the pressure test.
Main advantages of its use
The device integrates the technology (HPP, High Pressure Processing) that can be coupled to any universal dynamic testing machine to reproduce the high-pressure work cycles of any industrial component. In this way it will be possible to carry out tests of components subjected to high pressure (pipes and conduction elements), which allow:
1. To assess structural integrity and failure analysis.
2. To reproduce the work cycle (0-6000bar-0).
3. To know the performance of new components subjected to high pressure.
4. To determine the fatigue of the real component under the working pressure.
5. To perform hydraulic fracture and fatigue tests up to 6 000 bars.
Specifications
A device for testing components under high pressure in a traction-compression machine that allows to evaluate them under static and fatigue efforts, It comprises:
- A pressure intensifier with a cylinder and a rod,
- Two clamps comprises in the traction-compression machine,
- A supporting tube that houses the pressure intensifier
- A test tube,
In this way, the movement of the rod inside the test tube can compress a liquid arranged in the chamber.
Applications
A device for testing components under high pressure in a traction-compression machine that allows to evaluate them under static and fatigue efforts, It comprises: 1. A pressure intensifier with a cylinder and a rod, 2. Two clamps comprises in the traction-compression machine, 3. A supporting tube that houses the pressure intensifier 4. A test tube, In this way, the movement of the rod inside the test tube can compress a liquid arranged in the chamber.
Current development status
Available for demonstration-field tested.
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement; License agreement; Technical cooperation: further development; Technical cooperation: testing new applications; Technical cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Heat exchange system with internal energy storage with sensors that detect performance alterations and take decisions about energy efficiency of the system, saving energy and economical loses.
New and innovative aspects
Heat exchangers include mechanisms to store energy from renewal sources when those sources but demand needs to be cover (for example, solar energy during the night). There is a material (PCM) responsible of energy storage by absorbing or giving thermal energy. The PCM goes through behaviour changes not detectable currently, increasing unnecessarily the energetic consumption.
The new system detects this changes and consequently, it permits taking decisions and/or and automatized energetic system to save energy.
Main advantages of its use
- Energy storage with energy sensors to know the status and proper working of the heat exchanger.
- Allows taking decisions about energy efficiency of storage systems.
Specifications
Heat exchanger system automatized with energy storage systems, combinable with intermittent renewables or conventional low cost energies.
The exchanger consists of an internal cavity filled with a phase changing material (PCM) as the storage energy system. It is also has cold and hot ducts to absorb and give thermal energy.
In addition, it includes energy sensors for that PCM, and both hot and cold ducts, in the internal cavity, the inlet and the outlet.
Temperature measure permits and automatized energy management, for example, in an air conditioning installation that includes the heat exchanger, evaluating in real time the energy efficiency and the status of the exchanger.
Applications
Air conditioning installations including heat exchangers with energy storage systems (renewables and conventional).
Applicable in building construction.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P201730420.
Current development status
In use, test results available.
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement; License agreement; Technical cooperation: further development; Technical cooperation: testing new applications; Technical cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The vast majority of metal products in the industrial level are obtained from sheet metal forming, which are used in a diversity of applications, from car bodies, appliances and planes, together with beverage packaging.
In order to define the final design and structure of a stamped component there are two fundamental steps: the manufacturing process to perform the part and the structural simulation to overcome the requirements for performance specifications.
The University of Burgos has patented procedure for the design and manufacturing of cold stamped metal part components that establishes an interconnection between the process simulation and the structural simulation during the development of the stamped components, so the mechanical properties of the material are modified in function of the predefined level got in each zone of the component.
New and innovative aspects
The methodology developed improve the correlations numerical-experimental obtained by structural simulation programs currently used:
- Reducing the difference between the simulation data and manufactured elements.
- Optimizing - at start-up time - the process manufacturing for a new components and in materials used for the manufacture of parts.
Main advantages of its use
All the programs currently used in the market do not take into account the mechanical properties in function of the level of predeformation attained during the component stamping.
The main advantage is that this procedure controls and defines the optimal method of transferring the deformation results (produced during the simulation of the stamping process) to the structural simulation programs.
It is also defined a working methodology, applicable at the industry, to estimate by simulation the structural rigidity of the stamped components.
Specifications
The product is a methodology that incorporates data processing software mainly applied to the development of metallic products obtained by cold stamping.
Applications
The users for: car bodies, household appliances; aircraft, beverage containers
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P201630414
Current development status
In use, test results are available.
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement; License agreement; Technical cooperation: further development; Technical cooperation: testing new applications; Technical cooperation: adaptation to specific needs
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Curved poles rotor with agglomerated permanent magnets for synchronic three-phase motors, increasing torque and performance more than a 20% against known electric motors with rectangular poles.
New and innovative aspects
The circular arch shape of the permanent magnets layout of the new rotor, improves the reluctant component of the torque, forming a double layer magnetic field.
Moreover, the use of rare earth elements powder agglomerated magnets (elements like cerium, yttrium or neodymium) results energy values similar to those obtained with known sintered magnets.
Main advantages of its use
- The use of rare earth elements powder agglomerated magnets shows a better behaviour than sintered ones in the face of temperature increases.
- 20% more torque versus the current rectangular magnets rotors.
- Cost reduction due to less use of rare earth materials, reduced weight and better energy efficiency.
Specifications
Permanent magnets rotor for use in synchronic three-phase motors for hybrid vehicles. There are two magnetic layers in the rotors that generates the motor action, disposed as an arch of a circular segment geometrically optimized, improving the reluctant and magnetic components of the torque.
To set both magnetic layers, rare earth elements powder agglomerated magnets are used, instead of sintered ones, allowing different geometry that improves the reluctant torque. The magnets used are made with agglomerate materials, conforming magnets with less materials and similar energy values than does used currently.
The combination of the double magnetic layer and the characteristics of the new magnets, the new rotor obtains a 20% more torque than known rotors. The weight of the motor, its cost, and the economical loses are also reduced.
Applications
Electric motors for hybrid and plug-in vehicles.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P20173042.
Current development status
In use, test results available.
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement; License agreement; Technical cooperation: further development; Technical cooperation: testing new applications; Technical cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Lifting platform as a tool attachable to three-point hitch for agricultural tractors constituted by an articulated mechanism that has a lifting platform with a cage to elevate people and to make agricultural work in height with safety.
New and innovative aspects
There isn´t any tool designed for the different task at height in the rural and
agricultural-livestock sector.
Main advantages of its use
- Enabling vertical telescopic movement, longitudinal and transversal to make agricultural work in height with safety.
- It can feed from the battery electric of the tractor, allowing the elimination of noise and saving of fuel.
Specifications
Lifting platform as a tool, attachable to front or rear Three-point hitch for agricultural tractor, it´s not self-propelled, is feeds by tractor battery,
It has several systems and devices that provide security services like:
- Emergency switch that disconnects the entire electrical system from the battery of the tractor.
- Electrical inclinometer, located on the work platform oriented vertically.
- Electric level sensor, located at the base of the working platform with longitudinal orientation.
Applications
Users of the agricultural machinery industry for height tasks in the rural and Agricultural-livestock world such, like:
- Grafting and budding fruit trees.
- Fruit picking of fruit trees.
- And any height work with safely.
Intellectual property status
Protected by invention patent P201630499
Current development status
The device is in the market validation phase.
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement; License agreement; Technical cooperation: further development; Technical cooperation: testing new applications; Technical cooperation: adaptation to specific needs
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Software developed for route optimization as intended for companies or entities interested in solving their problems of transportation planning (delivery to customers or delegations, collection suppliers, etc.).
The aim of using this system is to help obtain cheaper solutions, more convenient, secure and balanced routes (according to the goals considered) and conform to the restrictions of each situation.
New and innovative aspects
The novel aspect and that gives added value to the product compared to other commercial solutions is the optimization algorithm used which is where it resides the innovation of the software developed. This algorithm is the result of an extensive and profound work, since not all methods are equally good and therefore the development of a suitable algorithm is critical in obtaining good solutions.
Main advantages of its use
Among others the use of this system has the following advantages:
- Easy to use
- Fast calculation
- Cost reduction
- Reduced CO2 emissions and Sustainability
- Improved customer service level (with the consequent improvement of image)
- Adapting to different objectives, conditions and / or restrictions
- Helps decision making
Specifications
The developed system offers a user friendly visual environment, easily manageable. Basically manage the following elements:
- Data entry, which can be done by file or interactively
- Optimization algorithms to suggest the most appropriate solutions
- Data output: Full Road map with all the information.
- A GIS (Geographic Information System) to display more convenient locations (warehouses, customers, suppliers, etc.), roads, and routes learned.
Applications
This software has application in the field of route optimization in companies or entities interested in solving their problems of Logistic and Transportation planning (delivery to customers or delegations, collection suppliers, etc.). One area of particular interest is in the Logistics Industry, and specifically in the field of logistics operators that are a very important actors in this industry.
Intellectual property status
Protected by Intelectual Property BU-117-15.
Current development status
Kit avalaible for testing. Demo Test is avalaible as well.
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement, License agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Regenerative braking device capable of storing the kinetic energy absorbed during the braking process of the bicycle, by compressing ambient air and storing that energy as compressed air. This compressed air is used as an energy source in case of need extra help in cyclist’s pedalling.
New and innovative aspects
The main novelty is the accumulation of kinetic power through a pneumatic regenerative braking system instead of an electrical one, as usually occurs in mainly all the similar technologies nowadays.
It uses simpler and cheaper elements, fact that decreases manufacturing and maintenance costs.
Main advantages of its use
- Possibility to be joined, as a "kit" to any bike model, from mountain bikes to city ones (the set of mechanisms associated with this process are inside the rear wheel).
- Facilitates displacement going uphill sections or high effort through the consumption of the stored energy.
Specifications
Bicycle with the purpose of use the energy lost in braking process to dispose of it when necessary, similar to KERS cars racing applied to cycling. This converts the kinetic energy of the user and his bike in pressure by compressing atmospheric air to an engine / rotary vane pump and stores it in a tank of carbon fibre.
When user needs extra power, turns the accelerator and the system delivers the energy stored in the reservoir to the compressor, so it does motor functions.
This device includes an electro-hydro- pneumatic control system that implements the regenerative brake, non-regenerative brake and accelerator functions.
Applications
Users who want simultaneous access to a conventional or impulse bicycle according to the effort requested in each section of the journey.
Users with special needs for moving.
Intellectual property status
Protected by PCT/ES2016/070534.
Current development status
Proof of concept.
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Dispositivo de frenado regenerativo neumático capaz de almacenar la energía cinética absorbida durante el proceso de frenado de la bicicleta, mediante compresión de aire ambiente y su almacenado como aire comprimido. Éste es utilizado como fuente de energía en el caso de necesitar ayuda adicional en el pedaleo del ciclista.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La principal novedad consiste en que la acumulación de energía cinética se produce a través de un freno regenerativo neumático en lugar de eléctrico, como se produce en las tecnologías existentes más parecidas.
Utiliza elementos más sencillos y económicos y por lo tanto los costes de fabricación y mantenimiento son por tanto menores.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Posibilidad de poder acoplarlo, a modo de “kit”, a cualquier modelo de bicicleta, desde BTT a bicicleta de paseo (el conjunto de mecanismos asociados a este proceso se encuentra dentro de los radios de la rueda).
- Facilita el desplazamiento en tramos de pendiente ascendente o de alto esfuerzo a través del consumo de la energía almacenada.
Características técnicas
Dispositivo para bicicletas destinado al aprovechamiento de la energía que se pierde en el proceso de frenado para disponer de la misma cuando sea necesaria, a modo de KERS de los automóviles de competición aplicado al ciclismo.
Éste convierte la energía cinética del usuario y su bicicleta en presión mediante la compresión de aire atmosférico en un motor/compresor rotativo de paletas y lo almacena en un depósito de fibra de carbono.
Cuando el usuario lo considera necesario, acciona el acelerador y el sistema entrega la energía almacenada en el depósito al compresor, que ahora hace las funciones de motor.
Incluye un sistema de control electro-hidro-neumático que implementa las funciones de freno regenerativo, freno no regenerativo y de acelerador.
Aplicaciones
Usuarios que quieran a acceder de forma simultanea a una bicicleta convencional o impulsada según el esfuerzo requirido en cada tramo del trayecto.
Usuarios con cierta limitación de movilidad.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida PCT/ES2016/070534.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Prueba de Concepto. Fase de optimización de resultados
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
It is well known that there are correlations between fiber orientation and mechanical and/or physical properties of the composite. Knowing the real orientation of the fibers within a composite material can help to optimize the design and manufacturing process.
A composite material contains materials of different densities (fibrous material and matrix), and these have different X-rays absorption capacity, generating different grey levels in scanned images. This allows later identification and separation by the computed tomography scan (CT-scan), a non-destructive technique that provides scanned images with the orientations of fibrous or filamentary components contained inside a composite material, and therefore its mechanical and/or physical properties. However the interpretation of these images depends on the criterium of the technicians, being a subjective opinion.
This subjective interpretation can be solved by our computer implemented method that allows a numeric objective valoration of the orientations of fibres or filaments inside the composite. The final result is a more efficient use of the fiber, and therefore an optimal design, from both structural and economical points of views.
New and innovative aspects
The technology provides:
- a real and exact orientation of fibers inside matrix
- a numeric objective valoration of the data
- a global and local interpretation. It is possible to obtain parameters from different parts of the composite (edges, center, etc..)
- a non-destructive and economic measurement, CT-scan testings are cheaper than mechanical testings
Main advantages of its use
Our procedure is almost totally automatized. The routine is easy to use, extremely accurate and the results can be obtained in a short period of time. The error level on fiber orientations is extremely low. This can help companies to know the quality of their manufacturing process.
This technology can ensure small and medium enterprises a quantum leap in productivity and competitiveness. Improvements in product quality, to have more objective information manufacturing processes in real time for analysis and decision making, improved inspection cycles, improved product design, etc.
Specifications
Using a single algorithm implemented into a mathematical analysis software (MATLAB, OCTAVE, SCILAB or similar) all post-processing processes of the tomographic scans are automated.The segmentation of the fibres is more accurate because this method uses a predictive detection technique that clusters the spatial points into different fibres to subsequently obtain the fibre orientations into space.
The fact of using a predictive technique, i.e. predict the position of the group of points which are in the same fibre, makes it possible to separate points belonging to different fibres, even there is small distance between them. Clustering the points belonging to a single fibre, the dominant orientation of each of these fibres can be determined automatically using the interpolation line of the points.The entire process is grouped into a single algorithm. Tolerance criteria are introduced as an input value. So, the accuracy of the analysis protocol.
Applications
This technology is useful to all industrial companies related to fiber reinforced composite, when fibers show a different value of density compared to matrix. So, it is possible to identify separetely the fibers from the matrix, for instance in automotive and aeronautical companies, construction companies that use fiber reinforced concretes, etc..
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent PCT/EP2013/067219
Current development status
In use, test results available.
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Lightweight (2)
Summary of the technology
Rotating bending fatigue machine are essential for testing material properties. It is usual to face samples of the different materials to conditions that differ from the usual ones, such as corrosive environments, to evaluate their behavior.
Researchers from the University of Burgos have developed a device that allows this type of analysis to be carried out, allowing, unlike many of the current methods, that the material to be analyzed is in direct contact with the electrolyte responsible for generating conditions other than the usual ones. Additionally, thank to the design of the device, it can be used in more than one experiment.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Currently, there are devices that allow electrochemical cells to be coupled to fatigue machines and, in this way, carry out these measurements, but not all of them allow the volume of electrolyte that is in contact with the test tube (material) to be controlled. The invention of the UBU researchers not only allows the test tube to be in continuous contact with the electrolyte, but also allows the device to be attached to and uncoupled from the fatigue machine without making any modifications to it.
Main advantages of its use
The main advantages of this technology are the following:
- The device allows the test piece to be in contact with the electrolyte throughout the entire test, maintaining a constant volume of the same and controlling the surface of the material that is in contact with the electrolyte.
- The technology allows the renewal of the electrolyte during the analysis.
- The electrochemical cell object of the invention can be used without the need to make modifications to the fatigue machine.
- The material can be subjected to different environments likely to alter the fatigue behavior in a simple and efficient way.
- The ease of implementation makes the cost per test very competitive.
Specifications
The device is a removable minicell or box that would be arranged surrounding the test tube without coming into contact with it. The device has an input and an output for the electrolyte with measures that allow controlling the volume contained by it. By means of a series of elements, the cell is arranged, without mooring, on the fatigue machine. At the end of the experiment, when the test tube breaks, the cell design allows its recovery, and it can be used again to carry out more tests.
Applications
This technology is of great interest to determine the physical properties of different materials. Being useful in the construction, energy, petrochemical and metal industry sectors, among others.
Intellectual property status
Protected by a patent P202330236
Current development status
Prototype available for demonstration.
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
In recent decades, many researchers have used the miniature punching test in order to obtain the mechanical and fracture properties of a material, in cases where there is not enough material to carry out standardized tests. such as in the case of welds or irradiated material. In this sense, a procedure has been developed to evaluate the fracture toughness using pre-cracked miniature punching specimens.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
A new test procedure is proposed, which allows the fracture properties of the material to be obtained, in cases where a sufficient quantity of material is not available to be able to carry out standardized tests.
Main advantages of its use
The methodology developed aims to become a new test procedure, which allows obtaining the fracture properties of the material, in cases where a sufficient quantity of material is not available to carry out standardized tests.
The generation of the initial crack in the SPT specimens, prior to the test, has been carried out through laser microcracking. After an initial calibration, the laser is applied longitudinally from the bottom face, from the center of one side of the specimen to the center of the opposite side.
Specifications
The miniature punching test or “Small Punch Test” (SPT) basically consists of punching a small square or circular specimen, by means of a highly rigid punch, with the periphery of the specimen embedded by two dies (see image section ).
On the other hand, the FAD diagram (failure assessment diagrams) is a procedure for evaluating the structural integrity of any cracked component. Said diagram considers the effect of the crack, geometry and material properties such as fracture toughness, taking into account its plastic behavior. It is assumed that the failure of the component or specimen occurs at the moment in which the failure line defined by the FAD diagram is reached, which can be defined through different levels of analysis, depending on the properties of the available material.
An integrated procedure has been established between the test of pre-cracked SPT specimens and the FAD diagram, supporting the study in numerical simulation, with the aim of estimating and quantitatively determining the fracture toughness of steels. From a portion of material the size of a cent coin, the work carried out allows estimating the most important properties from the point of view of strength and fracture.
Applications
The miniature punching test could be applied in the characterization of welds. It would also be valid for studying degraded material from thermal and nuclear power plants within their inspection programs.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Measurements and Standards (2)
Summary of the technology
The University of Burgos, through the AUSINCO research group (Auscultation, Instrumentation and Control of Structures), makes available to the civil works sector (construction companies, quality control companies, research centers, Public Administrations, etc.) and industry, a technology based on laser sensor technology for the monitoring of movements in structures.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Being able to monitor movements in large structures, such as bridges for road and / or rail traffic, among others, is essential to know their status and define in a more efficient and economical way the maintenance actions to be carried out to maintain the maximum levels of safety by structural aging processes with optimal resource consumption. The technical problem to be solved is how to measure, accurately and economically, the movements experienced by a construction structure.
The proposed solution, which is more efficient and less costly than it is currently available, allows obtaining very useful information on the state of structures, in order to be able to design structural maintenance tasks more efficiently and thus avoid catastrophic damage to them.
Main advantages of its use
- Continuous monitoring of movements over time.
- High precision of displacement measurement.
- Low cost of production and installation.
- Sensors located so that the environmental and lighting conditions are favorable.
- Real-time data analysis.
Specifications
The displacement meter has a measurement set with a fixed reference and another with a moving reference. Each of said measurement assemblies includes at least one target element and a laser displacement transducer pointed towards said target element. The laser displacement transducer is adapted to measure distance variations with respect to the corresponding target element, where said distance variations are generated by vertical movements in the constructive structure to be monitored. The device is characterized in that the target element and the laser displacement transducer are arranged on the constructive structure, where the target element is the fixed reference and the laser displacement transducer is the mobile reference.
The installation of the sensors is carried out by specialized personnel, in collaboration with the personnel involved in these functions of the contracting company. The tests and monitoring take place on site, with specialized personnel from the University of Burgos in charge of carrying out the entire process traveling to the site.
Applications
- Large-scale civil works structures, such as bridges for road and / or rail traffic.
- Industrial structures.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P201830539
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The development of simple, fast and inexpensive colorimetric sensors for timeless and in-situ detection of trace amounts of iron, aluminium and mercury in aqueous media by non-specialized personnel has become a major challenge, mainly because the presence or absence of these compounds can lead to a number of problems, e.g., contamination issues.
As a result of the above described requirements, a new low cost polymer material has been developed and patented for the rapid visual colorimetric detection and quantification of iron, aluminium and mercury. A precise quantification of the species can be done in minutes using a picture taken with the camera of a mobile phone, and a broad quantification can be visually achieved.
New and innovative aspects
These new materials have the advantage of providing good physical properties and to facilitate naked eye detection of the chemical species in water solution, or to quantify these species by processing the colour parameters of digital photographs. Moreover, mobile phone can take the picture and automatically process it for giving the accurate concentration of these species.
Main advantages of its use
- The polymeric film changes its color upon entering into contact with water containing the chemical species (target) allowing for rapid and in-situ qualitative and quantitative analysis.
- The sensory system can be used by non-specialized personnel and under any ambient conditions). Quick analyses can be carried out without any equipment or energy source.
- The use of expensive equipment reagents is avoided.
- The sensory material is extremely stable (over 100 years).
- It is light and dimensionless and, accordingly, can be easily transported and no additional kit is needed.
- The material can detect iron in free form or in complex form, e.g., in wine and in blood serum.
- It can be stored anywhere where there is no extreme environmental conditions.
- Does not require the use of personal protective equipment (gloves, glasses, etc.)
Specifications
Polymer membrane based on two commercial biocompatible monomers, a sensory monomer, and a crosslinker. The film is colorless and transparent.
The sensory material detects selectively iron, aluminum and mercury. It turns dark green upon entering into contact with iron, deep orange with mercury, and in the presence of aluminum becomes fluorescent.
Moreover, quantification can be carried out using digital parameters (RGB) of a photograph taken with a digital camera or using a smart phone.
In addition to this, the material is highly handable both in dry and water-swelled state.
Applications
- Detection of Legionella in cooling towers and evaporative condensers.
- Iron chlorosis in orchards and vineyards. An in-situ, costless and rapid measurement shows if soils have the correct iron content, showing whether the soil is suitable or need to be treated.
- Wastewater and drinking water treatment plants use daily large amounts of coagulants (salts of iron and aluminum). Therefore, there is a real risk of water contamination by these components. This risk can be deeply diminished by using this detector.
- Piping in industry. All systems containing iron pipes exhibit a corrosion risk and in paralled a contamination hazard. The formation of iron oxides causes problems in industrial processes that depend directly on quality of the water flowing through these pipes. Similarly, boiler systems have also this problem.
Intellectual property status
Protected by Patent P201300575
Current development status
In use, test results available
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Physical Sciences and Exact Sciences (10)
Summary of the technology
Researchers from the University of Burgos have developed a device that attaches to the rod of dynamic penetration tests (DP) to measure the in-situ electrical resistivity of the soil. It allows obtaining resistivity values at different depths and can be adjusted to the standard rod. This invention offers a practical and efficient solution for measuring the electrical resistivity of the soil during penetration tests.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The device presents several new and innovative aspects in the field of measuring electrical resistivity of the soil during dynamic penetration tests. These aspects include the integration of the device with the standard rod used in penetration tests, the use of an insulated plastic cylinder with metallic ring electrodes, the connection to the resistivity meter through a multi-wire cable, and the utilization of the resistivity meter's own battery as a power source. These features enable precise and efficient measurement of electrical resistivity at different depths, thus improving the characterization of the soil in this type of test.
Main advantages of its use
The main advantages of this device are as follows:
- Seamless integration: The device easily attaches to the standard rod used in dynamic penetration tests, allowing for easy implementation into existing equipment without requiring additional modifications.
- In-situ measurement: It enables the measurement of electrical resistivity directly at the location where the dynamic penetration test is being conducted. This provides a real-time and direct assessment of the soil's electrical properties.
- Adjustable precision and depth: The device allows for measurements at different depths by adjusting the rod. This provides a more detailed characterization of the soil along the penetration profile.
- Time and cost savings: By conducting the measurements during the dynamic penetration test, there is a reduced need for additional testing, optimizing equipment usage and resulting in significant time and cost savings.
- Compatibility with different electrode configurations: The device can be adapted to different electrode configurations, such as the Wenner or Dipole-dipole configuration, providing flexibility for the operator to choose the most suitable configuration based on the study's requirements.
Specifications
The device for measuring electrical conductivity is characterized by its robust construction, featuring an insulated plastic sleeve, embedded metallic electrodes, connection to the resistivity meter via a multi-wire cable, adaptability to the standard rod, and secure attachment with adhesive tape. These features ensure reliable operation and seamless integration with dynamic penetration equipment, enabling accurate measurements of soil electrical conductivity.
Applications
The main applications of this device are:
- Identification of soil physical properties and moisture indices.
- Detection of clay layers in granular soils.
- Determination of the groundwater level in the soil.
- Measurement of resistivity for the design, verification, and maintenance of grounding systems in electrical installations.
- Therefore, it is of particular interest in sectors such as geotechnical and subsurface exploration, civil engineering and construction, hydrogeology, and geophysics.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202330366
Current development status
Prototype available for demonstration.
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
A group of researchers from the University of Burgos, in collaboration with the University of Barcelona and IDIBELL, has patented a family of molecules that have the ability to transport lactate in living cells. The ability of these molecules to alter the lactate concentration in cells can have a significant impact on cancer therapy, as it has been observed that high levels of lactate in the tumor microenvironment are associated with progression and treatment resistance in some cancer cases. This technology represents a new advancement in the search for therapeutic strategies against cancer.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
This pioneering research carried out by a group of scientists from the University of Burgos in collaboration with the Universitat de Barcelona has achieved an innovative discovery by identifying and developing the first molecules capable of effectively transporting lactate across biological membranes. As an example, one of the synthesized molecules (AS37) is capable of interacting with lactate, forming a complex that, unlike lactate, can traverse the cell membrane. This allows for the alteration of lactate concentrations in cells, with lactate playing a relevant role in the characteristic metabolism of cancer cells. In vitro studies have shown that these compounds can make cancer cells more sensitive to other drugs used in chemotherapy, presenting potential applications in this field.
Main advantages of its use
The main advantages of this technology are as follows
It is the first family of molecules capable of facilitating the transport of lactate across biological membranes.
These molecules transport lactate independently of the cell's own transport mechanisms, such as monocarboxylate transporters (MCTs).
The molecule AS37 is capable of altering intracellular and extracellular lactate concentrations in the presence of an MCT inhibitor.
The ability of this compound to act synergistically with widely used chemotherapy agents such as cisplatin has been demonstrated in in vitro experiments with tumor cells.
Specifications
The described molecules are capable of interacting through hydrogen bonding with lactate anions, forming a supramolecular complex that can diffuse through lipid membranes. In this way, it is possible to facilitate the passage of lactate across cell membranes independently of the cellular mechanisms responsible for this process, known as monocarboxylate transporters (MCTs), which are transmembrane proteins. This mechanism can be demonstrated by using an inhibitor of this type of MCT protein, such as syrosingopine. In the presence of syrosingopine, the molecules are capable of altering the intracellular and extracellular lactate concentration in cancer cells according to the obtained in vitro results. It has been demonstrated in this in vitro model that this strategy sensitizes tumor cells to chemotherapy agents such as cisplatin. This synergistic activity opens the door to exploring the utility of these molecules in the development of new therapies for cancer treatment.
Applications
The described compound allows for the alteration of lactate permeability and homeostasis in vitro. As lactate is a therapeutic target in cancer treatment, the possibility of developing compounds with therapeutic application for the treatment of this disease arises. The mentioned compounds can serve as tools for biochemical and cellular biology research in this context, either alone or in combination with MCT inhibitors.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202330370
Current development status
In vitro tests
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The present invention describes a procedure for the synthesis of p-cymene from monoterpenes or mixtures thereof, using dimethyl sulfoxide as an oxidizing agent and solvent, in the presence of a molybdenum catalyst. This sustainable and economically competitive route for the synthesis of p-cymene from renewable sources derived from biomass represents a viable alternative to the currently employed procedures. This procedure offers advantages in terms of selectivity, low toxicity, availability of raw materials, and ease of purification.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The invention proposes a new method for the synthesis of p-cymene from monoterpenes or their mixtures derived from biomass, using dimethyl sulfoxide as an oxidizing agent and a dioxomolybdenum(VI) catalyst. This innovative approach overcomes the issues associated with previous techniques, such as the generation of isomeric mixtures, sensitivity to sulfur commonly present in some starting materials, and the use of toxic products. Additionally, the procedure is more efficient, safe, and sustainable, providing a promising alternative for the production of pure and high-quality p-cymene.
Main advantages of its use
- Obtaining pure p-cymene: The method allows for the synthesis of isomerically pure p-cymene through a simple distillation process.
- Use of biomass-derived monoterpenes: Renewable and low-cost starting materials are employed, such as crude gum turpentine and citrus oil generated as waste or byproducts in the paper and citrus juice industries.
- Low-toxicity oxidizing agent: Dimethyl sulfoxide is used as the oxidizing agent, which is biodegradable and easily removable from the reaction medium.
- Sulfur-resistant catalyst: The catalyst used is resistant to the presence of sulfur or its derivatives in the crude gum turpentine starting material.
- Mild reaction conditions: The synthesis is carried out at atmospheric pressure and a moderate temperature of 150 °C.
- Economic and safety considerations: The method is economical, easy to operate, and does not require toxic chemicals or an inert atmosphere in the reactions.
Specifications
- Starting material: Monoterpenes or mixtures thereof derived from biomass.
- Oxidizing agent: Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is used as a stoichiometric oxidizing agent and solvent in the reaction.
- Catalyst: A dioxomolybdenum(VI) catalyst is employed, specifically bis-(dimethylformamide)diclorodioxomolybdenum(VI), MoO2Cl2(dmf)2, in amounts of 3-5 mol%.
- Reaction conditions: The reaction is carried out at atmospheric pressure, at a temperature of 150 °C, and for a reaction time of 24 hours.
- Product purification: The obtained p-cymene is purified through extraction with different solvents and fractional distillation.
Applications
P-Cymene synthesis method described by scientists from the University of Burgos presents an economically sustainable alternative to the current method, which relies on toluene derived from non-renewable petrochemical resources.
The synthesized p-cymene has various applications in industries such as perfumery, pharmaceuticals, herbicides, dyes, polymers, and high-value chemicals. The new methodology provides a more efficient way, utilizing industrial waste and/or renewable resources derived from biomass, to obtain pure p-cymene. This benefits these industries in terms of product quality, cost reduction, and sustainability.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202330367
Current development status
Prototype available for demonstration.
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Researchers from the University of Burgos have developed a methodology for the deoxygenation of sulfur compounds (sulfoxides). To carry out this transformation, natural compounds from the biomass and a molybdenum catalyst are used. The products are obtained with high yields and high purity.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The reduction of sulfoxides (1) to the corresponding sulfides (2) is a very useful transformation both in the chemical industry and in the pharmaceutical industry.
There are several methods to carry out this transformation, however, the procedure patented by the University of Burgos allows obtaining these compounds quickly, efficiently and and sustainably, using a novel reducing agent and a molybdenum catalyst. The reaction conditions make the purification of the final compounds extremely easy.
Main advantages of its use
The main advantages of this method are the following:
- Use of natural compounds, monoterpenes from biomass, environmentally benign and sustainable.
- Monoterpenes act as a solvent, reducing costs and their by-products can be easily removed.
- The products are obtained with yields greater than 75% and high purity.
- The transformation does not require an inert atmosphere and is completed in two hours by heating to 160 ºC.
- High tolerance of functional groups.
Specifications
The monoterpenes obtained from the biomass are used in equimolar amounts, acting both as reducing agents and the solvent. The dioxomolybdenum (VI) compound, MoO2Cl2(dmf)2, is added in catalytic amounts (5 mol%) and is responsible for accelerating and facilitating the process.
The by-products obtained in the reaction are p-cymene and water, which allows the purification of the deoxygenated product quickly and easily, without the need to resort to complex separation techniques.
The low toxicity of the reagents used allows the reaction to be carried out with a higher degree of safety and from a more environmentally friendly point of view.
Applications
This technology has direct application in the chemical industry and the pharmaceutical industry.
Intellectual property status
- Protected by a patent P202330200
Current development status
- Prototype available for demonstration.
Desired business relationship
- Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
A research group from the University of Burgos has developed a new procedure that allows transforming nitro groups (1) to amines (2) in short times and with yields that reach 95%. The key to this transformation lies in the molybdenum catalyst used and the reducing agent.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
In the literature, there are a wide variety of methods that allow the transformation of the nitro group (1) to an amine (2). Given the importance of these last compounds in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries, the methodology described by the researchers from the University of Burgos represents a fast, simple and cheap way to obtain amines. On the other hand, the reaction conditions are compatible with a wide variety of functional groups, even those that can be reduced. Another of the innovative aspects of this synthetic strategy is the use of γ-terpinene as a reducing agent and a dioxomolybdenum (VI) catalyst.
Main advantages of its use
The main advantages derived from the use of this methodology are:
- Obtaining the final compounds with yields ranging from 50 to 95%.
- High tolerance to other functional groups such as carbonyl groups, nitriles, unsaturated chains, etc.
- γ-Terpinene is a natural product from biomass. When used as a reducing agent, in the presence of the dioxomolybdenum (VI) catalyst, the reduction of the nitro group to an amine is achieved, forming easily separable reaction by-products.
- The transformation does not require an inert atmosphere or high pressure, which is an advantage from an economic, environmental and safety point of view.
Specifications
γ-Terpinene acts as a reducing agent, in equimolar amounts, and dimethylacetamide is used as a solvent. The dioxomolybdenum (VI) compound, MoO2Cl2(dmf)2, is added in catalytic amounts (5 mol%) and can be easily prepared from commercial reagents.
Using microwave heating, the reaction is complete in 60 minutes. Furthermore, the transformation can be carried out in the absence of solvent.
The by-products obtained in the reaction are p-cymene and water, which allows the purification of the deoxygenated product in a simple and fast way, without the need to resort to complex separation techniques.
Applications
This technology has direct application in the chemical industry and the pharmaceutical industry.
Intellectual property status
Protected by a patent P202330202
Current development status
Prototype available for demonstration.
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Researchers from the University of Burgos have designed a method to synthesize a compound that is extremely useful in the detection of explosives, such as triacetone triperoxide. This explosive is very simple to prepare and extremely difficult to detect. The project has been subsidized by NATO and, given the potential of the molecule, a patent has been applied for to protect and commercialize it.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs) pose a great threat to society, which is why, in recent years, methods have been developed to detect them. However, explosives such as triacetone triperoxide (TATP) are extremely difficult to detect and, given the ease with which it can be obtained, it is imperative to have simple, robust methods with sufficient sensitivity to detect these compounds. The technology developed by the University of Burgos was born to respond to these demands and position itself as an effective, affordable and easy-to-use method.
Main advantages of its use
The proprietary molecule has proven to be perfect for use as an active element in the preparation of fluorogenic sensors.
The main advantage of this technology is that it allows detecting traces of TATP in the air without the use of large and expensive equipment in a selective and ultrasensitive manner.
The detection limit is significantly low, reaching concentrations lower than 60 pM.
To add value to this technology, this method is useful for detecting a wide variety of oxidant molecules.
Specifications
The naphthalimides described in the present invention, when interacting with an oxidizing molecule, undergo a modification of their fluorescence that is directly related to the concentration of oxidizing analyte.
The synthesized molecule is absorbed in different materials (anatase, silica, etc.) and, once absorbed, the interaction with the molecules of interest takes place on its surface. The detection limit of TATP has been shown to be as low as 13 ng.
Applications
Ultrasensitive detection of triacetone triperoxide, TATP, (very difficult to detect and frequently used in improvised explosive devices) in the air in real time.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202330107
Current development status
Prototype available for demonstration.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The present invention describes the obtaining of a copolymer capable of specifically extracting aromatic polyphenols, in food samples or aqueous solutions thereof, specifically, from honey samples. Removing these components from the sample greatly facilitates the determination of various food quality parametres, directly related with the quality and authenticity of honey
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The polymeric material object of the invention is capable of interacting with polyphenols (at least two -OH groups in contiguous positions) by reactions of condensation.
The extraction of these alcohols is of great relevance, since they are present in many foods and, although they are very beneficial for health, they pose a great problem when it comes to determining certain parameters of food quality, such as the activity of the enzymes catalase and glucose oxidase (related to antioxidant capacity).
One of the innovative aspects of this method, unlike several of the previously used procedures, is that the copolymer only interacts with the polyphenols and allows their extraction quickly and efficiently. By removing these compounds from the sample, enzyme activity determination can be performed without such interferents. This determination, at present, is not usually made due to its complexity.
Main advantages of its use
The main advantages offered by the method described by researchers from the University of Burgos allows the removal of polyphenols in 90 minutes, compared to 24 hours of the previous method. In addition, the volume of reagents to dilute the sample goes from 6 litters (current honey dialysis process) to 12.5 millilitres, representing a reduction of more than 99%.
The material described has a receptor capable of interacting with catechol derivatives (1,2-dihydroxybenzene) and a specific matrix designed to eliminate or reduce interactions with other honey components.
Specifications
The copolymer is made up of:
1) A receptor based on phenylboronic acid for interaction with structures derived from 1,2-dihydroxybenzene.
2) A matrix specifically designed to eliminate or minimize interaction with other structures with two -OH groups on adjacent carbons, such as fructose and glucose.
The procedure for the extraction of aromatic polyphenols is based on:
1) Dilution of the sample with phosphate buffer pH 7 (reducing more than 99% of its volume compared to the procedure currently used).
2) After 90 minutes, the material is removed and the enzyme activity can be measured, thus reducing the extraction time by more than 93% (compared to the current honey dialysis process).
Applications
Determination of the enzymatic activity of catalase and glucose oxidase in honey samples. The developed copolymer can be applied in a wide variety of industrial processes related to food
Intellectual property status
Protected by a patent P202230376
Current development status
Research or Experimental
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Vinasse treatment was performed using membrane separation technologies. The combined use of ultrafiltration and nanofiltration allowed to reach levels of above 99% discoloration. Waste streams from these processes with high content of colored compounds were subjected to an adsorption - ultrafiltration hybrid process reaching 90% of discoloration.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Use of membrane separation processes for decolorization of vinasse by clean technologies and treatment of the final residue by an adsorption-ultrafiltration hybrid process. Yields above 95%.
Main advantages of its use
Simplicity of installation and operation of the plant. Continuous process with low operating costs. Increased yields discoloration. Getting colorless effluent that allow the direct discharge.
Applications
It is aimed at companies in the sugar sector, distilleries and wastewater treatment plants for the treatment of
effluents with high content of melanoidins.
Current development status
In Use Testing Results Available
Desired business relationship
Technical cooperation - testing of new applications
Technical cooperation - adaptation to specific needs
Powered by
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The agronomic use of sewage sludge has as main constrain the presence of high content of heavy metals. The proposed process optimizes their dissolution by a suitable combination of acid and complexing agents as extractant and thereafter the recovery of metal-enriched fractions using membrane separation and cation exchange techniques.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Different processes have been effectively used for the demetallization of sewage sludge: chemical extraction, bioleaching, electrokinetic processes and supercritical fluid extraction. Of all these, is the chemical extraction which achieved the most promising results of implementation, although due to the high variability in the origin and state of sludges, the high treatment volume and the associated cost, is essential to achieve the maximum metal recovery with the minimum operating cost, which is achieved by optimizing the extractive agent and an appropriate combination of membrane separation processes and cation exchange resins.
Main advantages of its use
The experiments carried out by the research group UBUCOMP, show that it is possible to achieve a significant decrease in the metal content of sewage sludge, whether from primary, secondary or after anaerobic digestion processes. The scaled to pilot plant is feasible from an operational point of view and costly efficient, constituting one interesting option for obtaining a final demetallised sludge with a potential use as organic fertilizer.
Specifications
The reduction in the metal load of sewage sludges in an in situ process to be introduced in the treatment plant, is a feasible option in terms of technical and economic balances and can be added to the actual management scheme of sewage sludge. The improved process allows the recovery of metal fractions and a final product with a high organic matter and nutrient contents, that can constitute the basis for the formulation of an organic fertilizer.
Applications
This technique would be of interest to stakeholders involved in sewage sludge management, sewage treatment plants, landfills or industrial plants that generate effluents with high organic and metallic charge.
Current development status
Research or Experimental
Desired business relationship
Technical cooperation - further development
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Teeth analysis using software to obtain information from palaeontological remains by semi-automatic image processing. This way the human error due to the repetitive works are minimized. Moreover, it can be used in forensic odontology.
New and innovative aspects
It is possible to obtain relevant information about our predecessors’ way of life through the teeth image analysis. Mainly the age, nutrition problems during its growth and the diet can be estimated. Thus, it is possible to make guesses about its life, behaviour and environment.
The new analysis method uses semi-automatic image treatment modules. This avoids the human mistakes often committed during this analysis based in a repetitive process.
For each module, marks and indicators of feed or growth problems are identified in a semi-automatic way instead of current solutions. Now an image treatment is needed with a posterior identification and analysis.
Main advantages of its use
- Semi-automatic teeth surface images analysis
- Increase of dental analysis speed.
- Decrease of analysis mistakes.
- Decrease of analysis duration.
It is important to remark that this analysis do not substitute the professionals who are essential to get results, but erases the possibility of getting human mistakes in repetitive tasks.
Specifications
Semi-automatic software that has various modules to obtain information from a dental analysis:
- Age estimation. In first place, a reconstruction of the global image of the teeth is done from various microscopic frames.
In second place, an analysis of the marks in the teeth are made, obtaining what’s known as the perikymata rings. The thickness of those rings, is characteristic for each specie and informs about the age or problems during growth.
- Estimation of feeding problems. In this case, a selection of the upper and lower mandibles is made from a radiography, separating them by a spline. A posterior image processing, locates the teeth separation to distinguish it. Further analysis is made detecting scratches.
- Diet estimation. In this case, the image is treated and relevant lines are traced to detect marks and estimate hominids diet.
Applications
Palaeontological teeth analysis. It could also be usable in forensic odontology. More data could be required in this second case.
Intellectual property status
Intellectual property registered BU-75-17, BU-76-17 and BU-77-17.
Current development status
Continuously improving software.
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement; License agreement; Technical cooperation: further development; Technical cooperation: testing new applications; Technical cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Protecting Man and Environment (9)
Summary of the technology
Researchers from the University of Burgos have designed an innovative device for the vertical installation of hoses, specifically used by firefighting teams, with the aim of improving working conditions and reducing risks during operations. The device addresses the deficiencies and limitations of existing devices in the market. Among its advantages, it stands out for its ability to provide a secure anchoring point in various locations, its adjustable width to accommodate different hose sizes, its prevention of hose collapse, and its reduced weight for easier transportation and placement.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
- Secure and adaptable anchoring: The device provides a secure and adaptable anchoring point in different locations for versatile installation.
- Dual non-branching outlets: The device features two integrated outlets that allow connecting two hoses without the need for an additional branching device, reducing volume and weight.
- Independent ball valves: The device has independent ball valves to regulate the water flow in each hose, providing individualized control.
- Integration of fastening and braking elements: The device incorporates fastening elements and a brake to improve anchoring and stability during use.
- Additive manufacturing: The device is manufactured using additive manufacturing technology, allowing flexibility in design and production.
- Improvement of working conditions: The patent aims to improve working conditions by reducing risks such as hose breaks, falls, and flow limitations, providing greater safety and efficiency in firefighting interventions.
Main advantages of its use
The dual-opening securing device offers the following advantages:
- Secure anchoring in different locations.
- Adaptability in width for versatile installation.
- Direct connection of two hoses without the need for an additional branching device.
- Independent control of water flow using ball valves.
- Improved stability with integrated fastening and braking elements.
- Efficient and flexible manufacturing using additive technology.
- Reduction of occupational hazards, such as hose breaks and falls, improving firefighter safety.
Specifications
The device features secure anchoring, adaptability in width, independent control of water flow, integrated fastening and braking elements, additive manufacturing, and offers improvements in stability and reduction of occupational hazards.
Applications
This device, due to its technical features and the advantages it offers, could be employed in the following settings/by the following entities:
- Firefighting departments
- Emergency services
- High-rise buildings
- Naval industry
- Petrochemical industry
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202330365
Current development status
Prototype available for demonstration.
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
This is an angled connector element for fire hoses that improves the working conditions of fire brigades and enables them to improve their performance during an intervention.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
When fighting a fire, firefighters have a device for securing a vertical hose installation which has a series of shortcomings or deficiencies that can compromise its performance. In response to this need, a clamping device has been developed for the vertical installation of hoses by means of additive manufacturing. This device makes it possible to reduce the occupational risks of the personnel and improve their performance during an intervention.
Main advantages of its use
• The device is quick and easy to install.
• It improves the working conditions of firefighters.
• It can be securely anchored to the various locations that firefighters may encounter in buildings (railings, walls, window sills, etc.). This reduces the risk of any incident or accident caused by falling vertical lines and dragging firefighters who are working to extinguish the fire.
• It adapts or adjusts in width depending on the point where it has to be located.
• It prevents the hoses from collapsing or folding against the ground, thus avoiding limiting the flow to tackle the fire.
• The weight of the device has been optimised by additive manufacturing.
• It avoids working with high working pressures, which means a reduction in the risk of hose rupture and therefore reduces the risk to personnel.
Specifications
The device developed integrates an elbow with two connectors together with the connecting elements of a clamp.
Possible accidents (falls, sprains, etc.) that may occur on the stairways of damaged buildings are avoided, as the stairs would be free of obstacles. The use of the anchoring device would allow a vertical installation through the stairwell or facade, leaving the staircase as a free and safe resource in case of being used for evacuations, rescues and mobilisation of human and material resources during the intervention.
It is avoided that the necessary flow is not achieved to counteract the calorific power of the fire in high-rise buildings (EGAs) since with the developed device it is possible to reduce pressure losses by safely using a vertical laying of hoses and thus establishing a sufficient available flow.
Applications
The developed device can be used for the vertical installation of hoses during fire brigade operations in high-rise buildings.
Intellectual property status
Protected by utility model U202231148
Current development status
Laboratory tests have been carried out.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
This software allows an interaction between rehabilitators, patients, and their families in a way that makes the therapy carried out simple, motivating and effective.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
This software allows an interaction between patients, rehabilitators and their families in a way that makes the work done simple, motivating and effective. It consists of several modules: manager of evaluations and results, manager of cognitive exercises, manager of physical exercises (exercise cards with drawings and explanation of the correct way to perform them, videos and photographs), agenda manager (sessions, treatment, medication, coordination between different professionals and family members), manager, application of support products. This software allows individualized programs aimed at the prevention and maintenance of physical and psychosocial capacities of a person according to their level of dependency.
Main advantages of its use
- Allows the development of individualized programs
- Allows the prevention and maintenance of physical and psychosocial capacities in dependent people
- Allows interaction between patients, rehabilitators and their families
- Simple, motivating and effective
Specifications
The manager consists of several modules, all of them integrated and currently in application.
- Manager of Ratings and results.
- Manager of Cognitive Exercises.
- Physical Exercise Manager (exercise cards, videos and photographs).
- Manager Schedule treatment sessions, medication, coordination between different professionals and family members. The manager allows family members to continuously monitor the treatment of the patient with continuous communication with the therapist.
- Support product application manager. It allows monitoring of those patients who perform treatment at home
Applications
The possible places of application are socio-sanitary centers such as day centers, specialized clinics, associations and hospitals.
Intellectual property status
Protected by Intellectual property registration BU-49-17
Current development status
Device already developed
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Granted Patent
BU-49-17
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
HADA (Hearing Impaired Assistance Tool) is a tool ready for the hearing-impaired, which facilitates communication breaking down barriers in society with those deficiencies.
User interface, simple and intuitive, with the posibility of choice and configuration of different modes (receiving text, video, video subtitled).
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
By means of a speech transcription component, our application collects the text and outputs it to clients connected to our server in real time.
In addition to the collected text, we can broadcast the video captured from our WebCam, a text video file that we have on our own computer.
It has extensive functionality. In addition to data transmission, HADA allows you to process subtitling files, recording, playback, etc.
It has a simple and intuitive interface, a simple application screen, with descriptive access buttons, according to its functionalities. Different display modes, depending on the user's choice, different interfaces are offered (text reception, subtitled video, etc.)
The configuration options are multiple, the application is completely configurable, to the needs of the user.
It presents privacy of use, closed to the group of connected users.
Main advantages of its use
- This tool helps to understand the environmental information to the hearing-impaired and whose information can not capture in situations where communication is primarily oral.
- One way to eliminate communication barriers suffered by the hearing impaired community, is developed with our software HADA, that by streaming the captured text (as a result of transcription from the audio received from our microphone) ends these problems.
Specifications
Desktop computer-based software with voice recognition. Its configurable use as a client and as a server.
Applications
It is especially useful for people with hearing impairments in workplace situations, conferences, presentations and meetings, teaching community (schools, colleges, universities), leisure, home use.
Intellectual property status
Protected by intellectual property registration BU-39-11
Current development status
Device in concept stage
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Granted Patent
BU-39-11
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Researchers from the University of Burgos have developed a wastewater treatment facility based on membrane bioreactors. This installation makes it possible to maintain high concentrations of active biomass in the reaction stages and a low concentration of suspended solids in the filtration tank, reducing the fouling of the filter membranes of the installation and thereby improving the performance and effectiveness of said installation.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
This installation for the treatment of wastewater is based on membrane bioreactors and consists of four stages of which three are biological treatment (one suspended culture bioreactor and two attached culture bioreactors), and a filtration stage.
The "sludge blanket” bioreactor is a tank where the microorganisms that biodegrade the organic material present in the wastewater form a suspended culture of biomass composed of granules and flocs. The "attached culture” bioreactors are those where the water to be treated comes into contact with adhered films of microorganisms, in this case to the surfaces of the disordered materials present in the said tanks.
Main advantages of its use
- Maintains high concentrations of active biomass.
- The concentration of suspended solids is low in the filtration stage.
- The fouling of the filter membranes of the installation is reduced.
- The volume of carrier material is limited.
- The performance and effectiveness of the installation is improved.
Specifications
The installation for the treatment of wastewater characterized by being made up of four stages, three of biological treatment (1, 2, 3) and one of filtration. The first stage of biological treatment (1) houses in its interior an inert filling material where the microorganisms responsible for the biological treatment of wastewater form biofilms. The second stage of biological treatment (2) includes a suspended culture of the sludge blanket type where the microorganisms responsible for the biological treatment of the wastewater from stage (1) are housed, and allows maintaining a high concentration of active biomass with a minimum construction cost. The third stage of biological treatment (3) has in its interior filling material suitable for retaining biomass leaking from sludge blanket (2). This stage has a protective function of the membranes of the filtration tank and allows to agregated the flocs of microorganisms carried by the upward flow of water and degassing defects of the main bioreactor. The filtration stage (4) houses submerged ultrafiltration membrane modules. This filtration tank also has a gas sparging system.
Applications
Potential applications of the installation are as follow:
- Industrial wastewater treatment
- Urban wastewater treatment
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P202130509
Current development status
Device already developed and validated for industrialization.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Researchers from the University of Burgos have patented a new hybrid solar panel, which allows optimizing the process of joint generation of electrical and thermal energy, achieving higher performance and better heat storage in conditions of low light energy through optimal use of space.
New and innovative aspects
The innovative aspects it presents are:
• It has an integrated heat collection using phase change materials (PCM)
• The patented concept makes the design easily scalable and adaptable, unlike other panels.
• The phase change material is heated both by the radiation transmitted from the photovoltaic panel and by the heat pipe, this supposes an optimized heat transmission.
• Use of non-polluting materials
Main advantages of its use
The main advantages of its use
• Allows the simultaneous generation of heat and electricity. It also allows the storage of the thermal energy generated.
• It allows increasing the value of thermal energy generated, being able to vary the heat / electricity ratio adjusting it to the needs of each specific application.
• It allows to be able to use the heat when it is necessary, although the solar radiation is reduced.
• The solar panel allows an improved energy efficiency compared to other known panels, thanks to the extra cooling that is provided to the photovoltaic panel, with the phase change material.
• The design allows the residual energy in the form of heat to be used to heat the collector fluid and the phase change material, achieving a very high overall efficiency, up to 60-70%, or even higher.
• It allows the generation of two energy resources through the same device, not requiring the installation of two panels (photovoltaic and thermal) to generate energy. The need to use fewer supporting structures reduces the cost of installation.
For practical purposes, the use of this panel implies:
• An increase in electrical energy: + 15%
• Generation of hot water (or air)
• Space saving (2x1)
• Optimization and great overall performance of the panel
• Cost savings: structure, collector, fuel
• Maintenance is not required
Specifications
Hybrid solar panel designed to achieve better heat storage in low light energy conditions, comprising a photovoltaic panel, a thermal collector arranged on the face of the photovoltaic panel, opposite to solar radiation and a phase change material. The thermal collector is embedded in the phase change material, the mentioned thermal collector is arranged in correspondence with the face of the photovoltaic panel, opposite the one that receives solar radiation. A heat pipe, closed at both ends, in correspondence with the face of the thermal collector opposite the photovoltaic panel, allows the evaporation and condensation of the fluid that it houses inside. At least a portion of the heat pipe is in contact with the phase change material and another portion of the heat pipe receives solar radiation.
Applications
The Hybrid Solar Kit can be used in general in:
• Hotels
• Nursing homes
• Sports centers
• Farms
• Industry
• Hospitals
• Residential buildings
• Single-family homes.
In addition, the advantages and technology of this panel make it suitable to be installed in confined places such as:
• Mobile homes,
• Boats,
• Construction huts,
• Portable offices
Intellectual property status
Protected by Patent P201930047
Current development status
They have several prototypes as well as an installation that allows testing with different operating conditions.
Desired business relationship
Commercial agreement; License agreement; Technical cooperation: further development; Technical cooperation: testing new applications; Technical cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Patent already applied for
P201930047
https://www.ubu.es/otri-transferencia/propiedad-industrial-e-intelectual/patentes-y-modelos-de-utilidad-de-la-ubu/119-p201930047-panel-solar-hibrido
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The present invention relates to an inflatable rescue device for people, and method of use thereof, which can be used to evacuate the staff of high buildings in emergency situations, as it could be a fire , danger of imminent collapse, or other situations that prevent or advise the non- evacuation through the interior of the building.
New and innovative aspects
Currently existing devices for emergency evacuation in buildings mainly include controlled descent devices, escape chutes and different parachute systems, the latter based on the resistance that its components offer to air.
The innovative aspect of this life-saving device is in its design that uses an inflatable system based primarily on aerodynamic drag forces. The inflation gas is nitrogen which density is somewhat lower than air, so that the flotation effect is very small.Main advantages of its use
Main advantages of its use
- Can be used by adults. If there are children or elderly disabled, the device can be used in tandem accompanied by another person with normal faculties.
- It allows a controlled descent.
- It does not require that the user have prior knowledge as in the case of parachute, or make any control on the device.
- Its use does not require excessive high buildings.
Specifications
The device takes the form of hollow bell and the shape is achieved by the swelling inside with nitrogen from the ignition of pyrotechnic cartridges sodium azide, located in the backpack.
Due to the fact that the space is not empty, but is filled with air, it will present a resistance to be crossed, which causes the falling speed reaches a value of dynamic equilibrium between forces of Earth's gravity, aerodynamics resistence forces and buoyancy forces by density difference with air.
Applications
Device that can be part of the security system and evacuation of buildings in case of emergency. It could also be used for recreational and sporting purposes.
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P201200639
Current development status
Functional prototypes
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
The present technology relates to a new general procedure for the reduction of sulfoxides to sulfides using [MoO2Cl2(dmf)2] as catalyst and poliols (pinacol or glycerol) as reducing agent. The products are obtained in excellent yields. It is worth to note that this new procedure uses an easily available and non-toxic reducing agent, that generates non-toxic byproducts which are easily separated from the sufide synthesized.
New and innovative aspects
The main novelty of the present method is the use of poliols (pinacol o glycerol) as reducing agent, that implies several advantages over traditional methodologies for the reduction of sulfoxides to the corresponding sulfides. Thus, clasical reducing agents for this transformation encompass sulfur-containing compounds such as thiols, hydrogen sulfide; carbodithionic, thiophosphonic or thiophosphoric acids, sulfonyl or sulfinyl chloride, disulfides, elemental sulfur (S8) and thionyl chloride. However, this methods present certain disadvantages that make necessary the development of new alternatives.
Main advantages of its use
Main disadvantages of known methods are related to reaction conditions not compatible with the presence in the molecule of sensitive functional groups. Moreover, many methods generate byproducts that are difficult to separate from the final product, making neccesary tedious and costly purification stages to obtain pure products. Furthermore, most byproducts, reducing agents and solvents are toxic and environmentally harmfull.
Nevertheless, the procedure for the reduction of sulfoxides reported in the present invention is based in the use as reducing agent of pinacol or glycerol, an easily available and easy to handle compound which generates easily removable and enviromentally friendly byproducts and allows the isolation in high yields of high purity sulfides without the need of costly and tedious chromathographic purification procedures. Moreover no inert atmosphere or organic solvents are needed, with the consequent economic and enviromental benefits.
Specifications
The present invention relates to a procedure for the catalytic reduction of organic compounds that contain a sulfoxide functional group to sulfide compounds, that include a thioether functional group, by using pinacol (2,3-dimethyl-2,3-butanediol) or glycerol (propanotriol) as reducing agent in the presence of a Mo (VI) catalyst, in a solvent free reaction media, under atmospheric pressure and a temperature between 80-90 ºC using pinacol, or 170-200ºC using glycerol, generating as non-toxic and easily separable byproducts.
Applications
The technic allows the synthesis of compounds containing sulfur in their structure, that can show diverse already demonstrated propierties (drugs, pesticides, materials,…). Therefore, applications in pharmaceutical and agrochemical industries.
Intellectual property status
P201001413, P201200455
Current development status
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Polymeric material that responds colorimetrically to the presence of biogenic amines. The presence of biogenic amines is related to fish spoilage, becoming an indicator of freshness and quality for optimal consumption.
The material developed is able to determine biogenic amines in solution and in gaseous phase.
New and innovative aspects
This technology allows the design of smart tags that inform consumers of the quality and freshness of fish by a colour scale.
Labels can be applied as fabrics, fiber coatings, or films.
Regarding another innovative aspect in relation to other technologies is that the tags can be presented in different formats depending on the needs, allowing the coating of other polymeric and non-polymeric materials by conventional means, by printing, or other known methods.
Main advantages of its use
- Determination of quality and freshness of packaged fish through a simple colored scale
- Manufacture of the polymeric material is simple and very economical
- Versatility of manufacture in different shapes and sizes
Specifications
Polymeric material comprising a polymer with chemically anchored trinitrobenzene groups. The use of this material as a colorimetric sensor for amines.
This material, i.e., the sensor material, can be obtained or transformed into membranes, films, fibers or coatings by conventional means.
The polymer material changes its color if the medium contains primary and secondary or tertiary amines, both in solution and gas phase; the color development, or change, is clearly perceptible at the nake eye.
The application of these sensors can be for sensing both solutions and gaseous phases.
Applications
- Food quality and safety: Determining the quality of fish through color of labels incorporated into the package itself.
- Manufacture of smart textiles able to determine biogenic amines in work environments (prevention risk)
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent protection: P201400595
Current development status
In use, test results available
Desired business relationship
Trade Agreement, License Agreement, Technical cooperation: further development, Technical Cooperation: testing of new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Social and Economics concerns (6)
Summary of the technology
It is an application for mobile devices that allows health workers to evaluate home care.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
It is an application for mobile devices that improves the quality of assessments, the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare staff and modernises the information collection system in home care.
Main advantages of its use
- Practical and easy to use: forget about paper, all the assessment tests in a single application and for any mobile device.
- Facilitates the work of health professionals in their home visits.
- Improves the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare staff: the test result is available instantly. Allows the patient's history to be reviewed prior to the visit.
- It modernises the system for collecting information from healthcare workers in home care.
- Improves patient assessment: allows you to create notes on the visit and compare with previous results.
Specifications
The application brings together all the tests of the different patients in one place, saving time and money and making home care more efficient. This application improves the effectiveness and efficiency of healthcare staff as it allows them to obtain the results of the different tests carried out at the same time, as well as to review the patient's history before the visit. UBUnurse also improves patient assessment by allowing the creation of notes on the visit and comparison with previous results.
Applications
Possible applications are in the home nursing environment and in socio-health centres.
Intellectual property status
Protected by Intellectual property registration BU-102-17
Current development status
Device developed and validated for industrialisation. This application has an official website. There is also a YouTube account where there are explanatory videos (how to install the app and how to register in the app).
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Granted Patent
BU-102-17
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
It is a device to improve the rehabilitation process of people suffering from "claw hand".
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
At present, the devices intended for the rehabilitation of "claw hand" are not capable of autonomously rehabilitating, after programming, the fingers of the damaged hand, nor is there currently any motorized device to perform such a function. In addition, rehabilitation processes with current systems do not come close to what an adequate passive rehabilitation should be, which consists, fundamentally, of performing successive repetitions, maintaining the stretch for a short period of time. For this reason, rehabilitation treatment is currently performed by the therapist with his or her own hands during pre-set time sessions, which is why the currently existing devices can only be considered as a complement to the treatment performed by the physiotherapist.
The device described is autonomous and is in charge of carrying out the efforts by means of motors, controlled by a computer. The device allows better control of the effort exerted on the tendons of each joint in each patient's hand, as well as the loads and magnitudes achieved in each rehabilitation session. Furthermore, this invention allows the physiotherapist to do therapy with several patients at the same time, since the device is autonomous and works obeying the individual cycle marked.
Main advantages of its use
• Standalone device
• Allows the physiotherapist to do therapy with several patients at the same time
• The physical therapist schedules the exercises that the device will perform during each rehabilitation treatment session.
Specifications
The device for the rehabilitation of patients with "claw hand" pathology consists of a rigid splint made of thermosetting polymer where the patient must insert the forearm and the hand to be rehabilitated.
The device has five programmable stepper motors.
The device repeatedly performs the number of cycles at the tension stipulated by the therapist, in each of the fingers of the hand to be rehabilitated.
Applications
Possible applications are the rehabilitation of people suffering from "claw hand"
Intellectual property status
Protected by patent P201300328
Current development status
Device in concept stage
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs
Intellectual property status
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
It is a CD-Rom that includes the creation and development of a Program of physical and psycho-socio-stimulative activities that provides benefits on personal autonomy and physical function of institutionalized older people.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
It is a CD-Rom that includes the creation and development of a Program of physical and psycho-socio-stimulative activities (PESAMI) aimed at institutionalized elderly people. Continued participation in a program of physical and psycho-socio-stimulative activities produces benefits in the participants in their functional capacity (to develop basic and instrumental activities of daily life), cognitive, in their self-esteem and in their social relationships.
Main advantages of its use
- Benefits for the participants in their functional capacity (to develop basic and instrumental activities of daily life), cognitive, in their self-esteem and in their social relationships.
- Autonomy in daily life
- Personal development
- Healthy and active aging
Specifications
It is a CD-Rom that includes the creation and development of a Program of physical and psycho-socio-stimulative activities aimed at institutionalized elderly people.
Applications
The possible places of application are social-health centers such as residences for the elderly, day centers, specialized clinics, associations and hospitals.
Intellectual property status
Protected by: ISBN 978-84-92681-00-6
Current development status
Device already developed and validated for industrialization.
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Granted Patent
ISBN 978-84-92681-00-6
https://www.ubu.es/catalogo-de-publicaciones/programa-de-envejecimiento-saludable-activo-y-satisfactorio-con-mayores-institucionalizados-pesasmi
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
It is a computer program meant to improve rehabilitation of patients especially when it involves frequent repetition of exercises. It assists on the design of tracking protocols and on the management of rehabilitation exercises applied to recovery from injuries or shape maintenance.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The program fulfills the following requirements:
- Track patient’s evolution. Starting from the patient’s current state, a final report comprising the whole rehabilitation process has to be provided.
- Design exercises adapted to each patient’s condition.
- Grab patient’s attention using topics that match his or her age.
- The software has to be friendly enough to allow any person irrespectively to her computing knowledge, the use of the program.
Main advantages of its use
It is the easy use of this package what make it preferable over its competitors.
Specifications
Augmented reality involves the use of “markers”. They are barcodes that a webcam can that can be captured and displayed on the screen. The markers allow the webcam to to track patient’s movements in this case. Movements are recorded as a sign of patient’s progress in his therapy.
Applications
- The use of this tool is recommended to hospitals and rehabilitation centers in general.
- It could also be used by patients at home when they are prescribed long rehabilitation sessions.
- Improvement in the results of active aging programs.
Intellectual property status
Protected by intellectual property registration BU-8-12
Current development status
Working Prototype or Samples Ready for Testing
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Granted Patent
BU-8-12
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
Application to facilitate the use of the Nintendo Wii console for access to social networks and email. Intended for older people with difficulties in accessing information technologies.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
Simple and dynamic user interface. Use of low cost gaming technology for assitive purposes. No need for aditional hardware.
Main advantages of its use
Provides easy access to information technologies. The applications included can be started without any previous knowledge on the use of computers.
Specifications
Web application that can be executed both on a PC and on the game console. Client server architecture. Ease of use for non-expert users. Easy to install. Especially suitable for nursing homes and public meeting places.
Applications
Assists on active aging and enhances comunication between the elderly and with the rest of society.
Intellectual property status
Copyright - BU-159-12
Current development status
Working Prototype or Samples Ready for Testing
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Granted Patent
BU-159-12
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Summary of the technology
New teaching / learning method that allows blind or visually impaired people to learn Chinese. Since the essence of Chinese is found in its writing and its characters, a system has been devised so that blind people can easily learn and recognize the characters and write them.
Description of the technology
New and innovative aspects
The development of a device is proposed for a system for learning a language based on the use of pieces, for blind or visually impaired people. The device represents an innovative structure, with structural and constitutive characteristics unknown until now. This allows the learning of Chinese through the Western Braille System (six dots). In addition, the method includes a braille book, a tactile dictionary and a support for writing the characters.
Main advantages of its use
- Lets you apply a Chinese learning method for blind or visually impaired people.
- Enhances the senses of touch and hearing.
- The use of a system of pieces facilitates the learning of Chinese.
- The method is written in the Western Braille System, so there isn’t need for users to learn the Eastern Braille System.
Specifications
The device for a language learning system based on the use of a plurality of parts, for blind or visually impaired people, comprises a plurality of panels grouped together. Each one of the panels is configured to locate a plurality of pieces arranged in rows and columns. Additionally, a removable cover placed on top can be included.
Each one of the panels includes graphic inscriptions as numbers and / or letters of the alphabet, generating alphanumeric coordinates, so that it can facilitate the implementation of the learning method for the user.
Applications
- Device that allows applying a learning method for blind or visually impaired people to learn Chinese in a simple way.
- User can translate phrases from Western Braille to Mandarin Chinese.
Intellectual property status
Protected by Utility Model U202130050
Current development status
Device in conceptual phase
Desired business relationship
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Intellectual property status
Additional information (attached documents)
About UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS
The aim of the The Technology Transfer Office (TTO) of the Univesidad de Burgos is to promote Innovation technology through the reseach results transfer and the conexions between the University and the new needs and requirements of the society - we are the link between the University and the Industry. Contact person: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Portafolio de ofertas tecnológicas (132)
(9)
Resumen de la tecnología
El tratamiento de vinazas se ha realizado mediante tecnologías de separación con membranas. El uso combinado de ultrafiltración y nanofiltración ha permitido alcanzar grados de decoloración superiores al 99%. Las corrientes residuales de estos procesos con elevado contenido en compuestos coloreados fueron sometidas a un proceso híbrido de adsorción y ultrafiltración con grados de decoloración superiores al 90%.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Utilización de tecnologías de separación con membranas para la decoloración de vinazas como tecnologías limpias, con tratamiento del residuo final mediante un proceso híbrido de adsorción y ultrafiltración. Rendimientos superiores al 95%.
Características técnicas
Las vinazas son el residuo generado por las industrias basadas en la fermentación de melazas, principal subproducto de la producción de azúcar. Las vinazas presentan gran cantidad de sustancias coloreadas que dan color marrón y elevada carga orgánica a los efluentes. Los compuestos coloreados más abundantes en las vinazas son conocidos como melanoidinas, que son polímeros de elevado peso molecular formados por reacción de Maillard. Tras un tratamiento biológico, la mayoría de la carga orgánica es eliminada; sin embargo, el color marrón no desaparece y puede incluso aumentar debido a la re-polimerización de los compuestos coloreados. El tratamiento convencional anaerobio-aerobio de las vinazas suele alcanzar tan solo un 6% o 7% de degradación de melanoidinas. La eliminación de melanoidinas mediante tratamiento físico-químico requiere elevadas dosis de agentes químicos que generan un problema añadido medioambiental y económico.
Se utilizan tecnologías limpias de separación con membranas para eliminar el color de estos efluentes industriales y evitar problemas medioambientales en los ríos, como la reducción de la actividad fotosintética y la concentración de oxígeno disuelto.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Simplicidad de la instalación y de funcionamiento de la planta. Proceso continuo con bajos costes de operación. Incremento de los rendimientos de decoloración. Obtención de efluentes sin color que permiten el vertido directo.
Aplicaciones
Está orientado a empresas del sector azucarero, alcoholeras y plantas depuradoras para el tratamiento de efluentes con elevados contenidos en melanoidinas.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Resultados de pruebas en uso disponibles
Relación deseada
Cooperación técnica - ensayo de nuevas aplicaciones
Cooperación técnica - adaptación a necesidades específicas
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Técnicas de respuesta múltiple son todas aquéllas en las que se obtiene simultáneamente más de una respuesta sobre un mismo sistema o proceso químico. Habitualmente se utiliza la electroquímica como modo de control del estado de oxidación del material analizado, obteniéndose en la misma experiencia una o más informaciones espectroscópicas u otro tipo de señal, como la procedente de una balanza de alta precisión.
Modificaciones de color, cambios de estructura electrónica, cambios de estructura vibracional, variaciones de masa por oxidación o por depósito sobre un electrodo pueden ser estudiados con técnicas de respuesta múltiple. Nuestro grupo las ha utilizado con éxito en el estudio de diferentes materiales (nanotubos de carbono, polímeros conductores, nanopartículas metálicas, nanopartículas semiconductoras y materiales híbridos), si bien pueden proporcionar información cualitativa y cuantitativa de gran calidad sobre cualquier otro tipo de materiales.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Las técnicas desarrolladas en nuestro grupo todavía han sido comercializadas en instrumentos compactos en colaboración con la empresa Metrohm Dropsens, no obstante, las combinaciones más avanzadas todavía no están disponibles comercialmente. La modularidad de los componentes permite su combinación del modo adecuado para obtener los mejores resultados en función de cada problema planteado. Si bien los componentes utilizados son sobradamente conocidos, el ensamblaje de los mismos representa una tecnología punta en el contexto internacional.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Estas técnicas son relativamente económicas en relación con otro tipo de instrumentos y son capaces de suministrar gran información.
Características técnicas
Una de las técnicas desarrolladas en nuestro grupo, la Espectroscopía Bidimensional, se esquematiza en el apartado "3. imágenes". En ella se muestra un equipo para la medida simultánea de dos señales ópticas y una eléctrica. En este caso particular el equipo consta de una fuente luminosa cuya radiación llega mediante fibras ópticas hasta la cubeta que contiene el material estudiado. En la celda se introducen tres electrodos conectados al potenciostato. El portacubetas dispone de puntos de anclaje para fibras ópticas, con lentes que coliman el haz de luz incidente. Éste, tras atravesar el electrodo y/o la disolución en la que se está produciendo la reacción, disminuye o aumenta su intensidad en proporción a la cantidad de material o reactivos absorbentes presentes en la celda. La luz emergente es recogida por fibras ópticas que la conducen hacia el monocromador correspondiente, donde se dispersa en diferentes longitudes de onda sobre un detector de batería de diodos. La sincronización temporal del equipo electroquímico y el espectroscópico es clave, ya que pequeños errores en el registro de tiempo pueden conducir a grandes errores en los potenciales calculados. El control del experimento y el registro de los datos se realiza con dos ordenadores independientes.
Este esquema (ver figura 1) de dispositivo experimental es modificado en función de las técnicas analíticas utilizadas, pudiendo trabajar con diferentes rangos espectrales e incluso con fuentes láser que provoquen fenómenos ópticos como la dispersión Raman o la fluorescencia molecular. Nuestros dispositivos también permiten la obtención de espectros Raman simultáneamente con medidas en el espectro UV/Vis tanto en configuración normal como paralela. Además, se pueden emplear técnicas de fotoluminiscencia combinadas con la electroquímica y con otras técnicas espectroscópicas.
Actualmente, también se desarrollan sustratos SERS adecuados para la detección/determinación de moléculas de interés de modo particularizado, obteniendo una alta sensibilidad y selectividad con una buena reproducibilidad.
Aplicaciones
Nuestras tecnologías han sido aplicadas con éxito al estudio y caracterización de nuevos materiales:
1. Polímeros conductores
2. Nanopartículas metálicas
3. Nanopartículas semiconductoras
4. Nanotubos de carbono
5. Grafeno
6. Biomoléculas
Sin lugar a dudas pueden ser empleadas con materiales más “clásicos”, siempre que sean susceptibles de ser oxidados o reducidos o sufran algún tipo de transformación a lo largo del tiempo.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Fase de prototipo
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Los nuevos polímeros reticulados de aramida han demostrado propiedades mejoradas, en particular, de aislamiento eléctrico, térmicas, de estabilidad, y/o mecánicas mientras que mantienen la facilidad de procesamiento. Además, las propiedades que muestran las nuevas aramidas reticuladas hacen que el producto sea especialmente adecuado para aplicaciones tecnológicas avanzadas. La reticulación se puede llevar a cabo en los procesos industriales actuales de producción de fibra de aramida.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Reticulado de las fibras de poliamida aromática por procedimientos de producción convencional (hilado en seco y en húmedo). El reticulado de las fibras de aramida dará lugar a materiales con propiedades mecánicas, de resistencia al fuego, y de aislamiento eléctrico todavía mejores.
Características técnicas
La tecnología se refiere a un procedimiento para la preparación de un polímero de aramida reticulado que comprende la etapa de calentamiento de un polímero no reticulado que comprende la unidad repetitiva de fórmula (I), Figura 1 (ver documento adjunto), a una temperatura comprendida de desde 150 a 400 °C durante un período de tiempo comprendido de desde 1 segundo a 20 minutos, en la que A y B se seleccionan independientemente entre meta-fenileno, ver Figura 2 (ver documento adjunto) y R1 y R2 se seleccionan independientemente entre H y N3, con la condición de que al menos uno de R1 y R2 es N3, y R1 y R2 están unidos a cualquiera de las 5 posiciones 1, 2, 3 o 4 en para-fenileno y 1, 2, 3 en meta-fenileno. Se ha encontrado que la etapa de calentamiento de los polímeros no reticulados que comprenden la unidad repetitiva de fórmula (I) a una temperatura de desde 150 a 400°C produce el reticulado de los materiales poliméricos y da lugar a propiedades mecánicas y térmicas mejoradas, mientras que mantienen la facilidad de procesamiento. En particular, los polímeros reticulados de la invención han mostrado un Módulo de Young y una resistencia a la tracción mejorados en comparación con las aramidas no reticuladas, así como una constante dieléctrica menor.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
El reticulado de las fibras de aramida dará lugar a materiales con propiedades mecánicas, de resistencia al fuego, y de aislamiento eléctrico todavía mejores.
Aplicaciones
Empresas de producción de aramidas. DuPont, Teijin, Kolon industries, Hyosung, SRO Group, Yantai Sapndex co., Woongjin, Huvis, y Kermel.
Propiedad intelectual
Patente internacional PCT/EP2013/062824
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente concedida
PCT/EP2013/062824
https://www.ubu.es/otri/propiedad-industrial-e-intelectual/patentes-y-modelos-de-utilidad-de-la-ubu/61-cross-linked-aramid
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Planificación y diseño de estrategias y asesoramiento para lanzar un negocio online o móvil.
Estudios de mercado e identificación del público objetivo y segmentación del mercado.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Introducción en el campo de las nuevas tecnologías como ventaja competitiva para empresas de cualquier tamaño. El asesoramiento puede ser tanto para empresas nuevas que desean entrar en un mercado con bajo coste como de complemento para empresas ya posicionadas en el mercado
offline.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Ayuda a las empresas que deseen compatibilizar su negocio offline con uno online o móvil.
Características técnicas
Diseño de estudio de mercado, cuestionario, recogida de información primaria de consumidores o empresas, análisis estadísticos uni, bi y multivariantes y recomendaciones empresariales.
Aplicaciones
Desarrollo de un negocio online o móvil.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Se ha realizado el diseño, construcción y procedimiento de utilización de un sistema de tres electrodos (un electrodo de trabajo posteriormente modificado con la inmovilización de una enzima, uno de referencia y otro auxiliar) desechables serigrafiados en un soporte de poliéster (PET) cuya disposición espacial permita el rápido análisis “in situ” de pequeños volúmenes de muestra por técnicas electroquímicas.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La determinación de cocaína se ha llevado a cabo habitualmente utilizando técnicas cromatográficas muy costosas. Además es una técnica directa, rápida, sencilla y económica.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
El proceso de construcción por serigrafía implica, básicamente, tres etapas consistentes en la deposición secuencial de las diferentes tintas y sus posteriores curados. La primera etapa consiste en la deposición de la tinta de grafito (Electrodag 407A) sobre el sustrato de poliéster y su posterior curado a 120 ºC durante 30 min. Seguidamente se alinea adecuadamente el sustrato, que ya contiene los motivos impresos en tinta de grafito, y la pantalla que define el electrodo de referencia. Se deposita la tinta de Ag/AgCl (Electrodag 6037 SS), y se cura en las mismas condiciones.
Por último, y con el objeto de definir el área activa electroquímicamente de acuerdo con el diseño de la figura 1, una última capa de una tinta aislante se imprime con ayuda de un tercer patrón, dejando libre la parte superior de las bases conductoras de Ag para realizar las correspondientes conexiones eléctricas.
Características técnicas
Se ha construido un dispositivo conteniendo tres electrodos serigrafiados. Dos de los electrodos, serigrafiados con pasta de carbono, actuarán como electrodos de trabajo, otro serigrafiado con una tinta de Ag /AgCl, actuará como electrodo de referencia y el tercero, también de carbono, como contraelectrodo o auxiliar.
Figura 1.- Diseños realizados para la fabricación de los sensores serigráficos: electrodo auxiliar (negro), electrodo de referencia (gris), electrodo de trabajo (rojo)
Figura 2.- Imágenes de las pantallas utilizadas en la construcción de los electrodos serigráficos:
definición de las vías conductoras y los electrodos de trabajo y auxiliar en carbono (A), definición del electrodo de referencia en Ag/AgCl (B) y definición del material aislante (C).
Aplicaciones
De gran interés para la determinación de esta sustancia en controles rutinarios de muestras biológicas. Igualmente útil para determinar la pureza de las muestras de la droga.
Empresas relacionadas con el control del dopaje.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención P201000738
Estado actual de desarrollo
Desarrollado pero no comercializado.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
En las tareas de aprendizaje supervisado se dispone de un conjunto de datos, formado por varios ejemplos para los que se conoce los valores de ciertas variables y se trata de obtener un modelo que relacione las distintas variables con una de ellas que es la que interesa predecir. En función de que la variable a predecir sea nominal (o categórica) o numérica se habla de clasificación o predicción. En el método Rotation Forest las predicciones se obtienen mediante votación de varios árboles de decisión o regresión. Se ha utilizado con éxito en aplicaciones de muy diversa índole.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
En diversos ámbitos el método ha demostrado su robustez y buenos resultados, obteniendo menores errores en la predicción que las alternativas consideradas.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Las predicción, bien sean clasificación o regresión, es de utilidad en innumerables campos. Aplicaciones dónde ya se ha utilizado el método incluyen la diagnosis industrial, diagnosis médica, bioinformática, predicción de rendimientos (de
componentes industriales, estudiantes...)
Características técnicas
El método propuesto se basa en las técnicas de combinación de modelos (ensembles). Los modelos a combinar pueden ser de clasificación o de regresión. En concreto, en Rotation Forest los modelos combinados son árboles de decisión o regresión. Actualmente se acepta que es posible obtener mejores resultados combinando modelos que usando un único modelo, tanto por las propiedades teóricas de estas combinaciones como por el amplio número de aplicaciones donde se han demostrado útiles.
Aplicaciones
- Diagnosis industrial. Se ha utilizado el método para monitorizar la calidad de aceites lubricantes, ya que estos se degradan con el uso. Para determinar las relaciones entre las propiedades del suelo y el deterioro de tuberías mecánicas. Para establecer el estado de estructuras.
- Predicción de rendimientos. El método se ha utilizado para predecir la potencia generada por aerogeneradores.
- Diagnosis médica. El método se ha utilizado para analizar imágenes por resonancia magnética funcional (fMRI). Este tipo de imágenes se utilizan para localizar las funciones cerebrales. Otras aplicaciones son la diagnosis de enfermedades eritematoescamosas o de la epilepsia. También para la clasificación de cáncer a partir de microarrays.
- Bioinformática. Se ha utilizado para la clasificación de datos genómicos y proteómicos, para la anotación de genes promotores, para la predicción del pliegue de las proteínas e interacciones entre ellas, predicción de propiedades de drogas moleculares.
- Enseñanza. Se ha utilizado para identificar estudiantes con dificultades en el aprendizaje.
- Financieras. El método se ha aplicado en la predicción de quiebras y el riesgo de clientes; para la predicción de ingresos municipales.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial para procesado de datos y elaboración de informes técnicos.
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Programas formativos para desarrollar innovaciones tecnológicas con estructura pedagógica para su aplicación en diferentes contextos sociales al aprendizaje a lo largo de toda la vida como estrategia de envejecimiento activo y prevención de la dependencia.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
- Promoción de la autonomía de las personas
- Prevención de la dependencia
- Aprovechamiento del tiempo, de la lucidez y del disfrute lúdico de diversos aprendizajes
- Integración de recursos motivacionales en programas de atención individualizada
- Sistemas de seguimiento sobre el aprovechamiento, adaptación y mejora de los recursos, con la participación directa del usuario
- Conexión con la realidad actual y la promoción del uso de las TIC entre los mayores.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Partiendo del análisis de las necesidades concretas de cada colectivo, se fijan los objetivos de planificación en el diseño del programa formativo y de los recursos de aprendizaje.
Se toma como base motivadora partir de los conocimientos, valores y habilidades de los usuarios, contar con una adecuada integración de los medios utilizados, aprovechar la mayor simplicidad posible y los valores lúdicos en su aplicación practica por parte de los usuarios y llevar a cabo un seguimiento metódico de sus efectos y aprovechamiento para la consecución de una mejora continua en la calidad de sus procesos y resultados.
Características técnicas
Se trata de aplicaciones TIC y actividades vinculadas a las mismas a partir del conocimiento de las realidades y las necesidades específicas de sus destinatarios.
Se construyen a medida en función de la situación precisa que se trata de abordar, contando, en todo caso, con una estructura pedagógica común, para que puedan aplicarse dentro de actividades de formación específicas basadas en el aprender haciendo del envejecimiento activo y participativo.
Aplicaciones
Empresas, asociaciones e instituciones públicas y privadas, vinculadas a la formación, atención, estimulación y/o residencia de personas pertenecientes a los diferentes colectivos de mayores, bajo la adaptación a sus condiciones geográficas y personales, psíquicas y físicas, así como a las actividades propias que dichas entidades realizan en la prestación de sus servicios. Incluyendo programas de intervención "a distancia", por ejemplo, en el ámbito geográfico del medio rural y de su desarrollo local bajo la vertiente de la participación de los mayores.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Con los modelos desarrollados por este grupo, se puede visualizar en primer lugar y analizar posteriormente la estructura de conjuntos de datos de una alta dimensionalidad. Es decir, se permite un estudio de datos por ejemplo con un gran número de instancias (ejemplos) y además un gran número de variables para cada una de ellas.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Existen otros métodos de visualización de datos, pero la mayor parte de ellos no proporciona una forma sencilla e intuitiva para identificar la estructura y analizar el comportamiento de los datos.
De esta forma se reducen los tiempos de análisis y se obtienen resultados preliminares que pueden orientar posteriores análisis más exhaustivos.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Al ofrecer una proyección que preserva la mayor parte de información en los datos, maximizando la posibilidad de realzar la estructura de los datos, se permite un posterior análisis rápido de los mismos. En primer lugar se puede identificar la estructura general del conjunto de datos, detectando el agrupamiento de los mismos (diferentes tipos de clientes, grupos de productos, comportamientos de las máquinas analizadas, etapas o regiones de funcionamiento de los diferentes procesos...). Una vez conocida esta estructura general, se puede pasar a un análisis pormenorizado de cada uno de estos grupos, considerando la estructura interna de los mismos. Con todo esto, se puede fácilmente llevar a cabo un análisis de los datos, extrayendo conclusiones sobre los mismos al ser interpretados por un experto en la materia (factores que inciden en el comportamiento de los clientes, productos estrella o con menor éxito, valores óptimos de ajuste de una determinada máquina, comprensión de determinados procesos).
Características técnicas
Actualmente existe una cantidad de información tan elevada que no se puede procesar fácilmente para extraer conocimiento de ella. Un análisis exhaustivo, caso por caso, elevaría hasta límites inabordables el análisis de un gran número de datos que hoy en día son capturados. Estos pueden hacer referencia a estadísticas de compras de nuestros clientes, características de diferentes productos, registros de una determinada máquina o sistema, muestras de un determinado proceso industrial, etc. Los modelos proyeccionistas proponen una visualización de datos con estas características; un gran volumen y además una alta dimensionalidad (gran cantidad de información para cada uno de los clientes, productos, registros, muestras...).
Aplicaciones
Estos modelos pueden ser aplicados a cualquier conjuntos de datos que necesite ser
analizado, independientemente de la realidad a la que hagan referencia esos datos.
Algunos ejemplos de aplicación son los mencionados anteriormente: datos económicos, datos de producción, estadísticas de funcionamiento o de acceso, etc.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Nuestra tecnología permite la automatización de salas multisensoriales para que el terapeuta pueda programar la secuencia de actividades previamente y dedicar todo su tiempo al paciente. El software permite introducir anotaciones sobre la respuesta y evolución del paciente.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Programación flexible de las diferentes actividades a realizar en la sala junto con la música ambiente, control de iluminación, etc. Base de datos de pacientes. Aplicación portable para poder trabajar en cualquier ordenador sin necesidad de instalación.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Coste, flexibilidad.
Características técnicas
Incluye una tarjeta de control conectable a ordenador y una aplicación software portable. Hasta 8 estaciones pueden ser incluidas y configuradas.
Aplicaciones
Salas multisensoriales para muchos tipos de discapacidad.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Resultados de pruebas de uso disponibles
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Agricultura y Recursos Marinos (4)
Resumen de la tecnología
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos han desarrollado un polímero que es capaz de interaccionar con el cobre. En este contexto, se ha comprobado que, empleando este material, se puede determinar la concentración de cobre en muestras de mosto de forma rápida y sencilla.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Europa, liderada por Italia, Francia y España, es el mayor productor y exportador de vino del mundo. Esto se debe, en parte, a la gran calidad del producto final y al elevado número de controles que se llevan a cabo. Entre estos últimos destacan las medidas de pH, color, biomoléculas y metales. Dentro de este grupo se encuentra el cobre, y aunque se presenta en pequeñas cantidades, este elemento es esencial para que tenga lugar una correcta fermentación del mosto. En este contexto, los investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos han desarrollado un material polimérico que es capaz de interaccionar con el cobre y, mediante una simple fotografía, proporcionar la concentración de este metal de forma rápida y sencilla.
Es importante controlar los niveles de este elemento a lo largo de la fermentación del vino para evitar/detectar la "quiebra cúprica" que provoca la disminución de la calidad y seguridad del vino para los consumidores.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
El método de referencia para determinar la concentración de cobre en muestras de vino y mosto es la Espectroscopía de Absorción Atómica o la Espectrometría de Masa con Plasma Acoplaco Inductivamente. En comparación con estos métodos, el material desarrollado presenta una serie de ventajas:
- El polímero, al interaccionar con el cobre, genera un cambio de color y puede cuantificarse el valor de la concentración mediante una fotografía. Esto hace que este método sea sencillo y no requiere de personal altamente especializado para llevar a cabo la medición.
- El único equipamiento necesario es un smartphone para realizar la fotografía, mientras que los equipamientos de las técnicas de referencia son extraordinariamente costosos.
Características técnicas
El polímero se preparó mediante una reacción radicalaria partiendo del monómero previamente funcionalizado. El material se sintetizó en forma de film, y se comprobó que genera respuesta colorimétrica en presencia de cobre (I).
Pruebas realizadas en el laboratorio permitieron determinar que el límite de detección es de 0,08 ppm. El procedimiento de medida es el siguiente:
- Se introduce el film en la muestra junto con tampón a pH 5.
- Pasadas 12 horas, se retira el film y se realiza un lavado con agua.
- Se toma una fotografía junto con una carta de color y, mediante la aplicación de móvil registrada por este mismo grupo Colorimetric Titration, se obtiene el correspondiente valor de la concentración.
Aplicaciones
El material y el método de medida han demostrado ser adecuados para determinar los niveles de cobre en mostos de vino. La medida es más rápida, más barata y no requiere de equipamiento especializado.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente P202231015
Estado actual de desarrollo
Investigación o experimental
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La presente invención describe la obtención de un copolímero capaz de extraer de forma específica polifenoles en muestras alimentarias o soluciones acuosas de las mismas, en concreto, de muestras de miel. La eliminación de estos componentes de la muestra facilita, en gran medida, la determinación de la actividad de diferentes enzimas presentes en la miel, relacionadas con la calidad de este producto.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
El material polimérico objeto de la invención es capaz de interaccionar con polifenoles (al menos dos grupos -OH en posiciones contiguas) mediante reacciones de condensación.
La extracción de dichos polifenoles es de gran relevancia, ya que suponen un gran problema a la hora de determinar ciertos parámetros de calidad alimentaria, como la actividad de las enzimas catalasa y glucosa oxidasa en muestras de miel, debido a que actúan como interferentes en el análisis de la actividad de ambas enzimas.
Uno de los aspectos innovadores que presenta este método, a diferencia de varios de los procedimientos empleados con anterioridad, es que el copolímero únicamente interacciona con los polifenoles y permite su extracción de manera rápida y eficaz. Al eliminar estos compuestos de la muestra, la determinación de la actividad enzimática puede realizarse sin dichos interferentes. Esta determinación, en la actualidad, no se suele realizar por la complejidad de la misma.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Las principales ventajas que ofrece el método descrito por los investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos permite la retirada de polifenoles en 90 minutos, frente a las 24 horas del método anterior. Además, el volumen de reactivos para diluir la muestra pasa de 6 litros (actual proceso de diálisis de miel) a 12,5 mililitros, suponiendo una reducción de más del 99%.
El material descrito presenta un receptor capaz de interaccionar con derivados del catecol (1,2-dihidroxibenceno) y una matriz específica diseñada para eliminar o reducir interacciones con otros componentes de la miel.
Características técnicas
El copolímero esta formado por:
1) Un receptor basado en ácido fenilborónico para la interacción con estructuras derivadas del 1,2-dihidroxibenceno.
2) Una matriz específicamente diseñada para eliminar o reducir al máximo la interacción con otras estructuras con dos grupos -OH en carbonos adyacentes, como la fructosa y la glucosa.
El procedimiento para la extracción de los polifenoles aromáticos se basa en:
1) Dilución de la muestra con tampón fosfato pH 7 (reduciéndose más de un 99% del volumen del mismo en comparación con el procedimiento que se emplea en la actualidad).
2) Tras 90 minutos se retira el material y se puede realizar la medición de la actividad enzimática, reduciendo de esta forma el tiempo de extracción en más de un 93% (comparado con el actual proceso de diálisis de miel).
Aplicaciones
Determinación de la actividad de las enzimas glucosa oxidasa y catalasa en muestras de mieles. El copolímero desarrollado puede ser de aplicación en una amplia variedad de procesos industriales relacionados con la alimentación.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente P202230376
Estado actual de desarrollo
Investigación o experimental
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Esta tecnología está dirigida a la eliminación en la producción de aceitunas verdes de mesa del compuesto amargo oleuropeína el empleo de nuevos procedimientos biotecnológicos alternativos al uso de álcalis.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Utilización de biocatalizadores como alternativa a tratamientos químicos con sosa. El desamargado biotecnológico de las aceitunas es una alternativa muy interesante frente al proceso químico tradicional ya que aparte de las ventajas en cuanto a reducción de los tiempos de acondicionamiento, que supondría una reducción de los costos globales del proceso, se disminuiría también el impacto ambiental creado por la utilización de NaOH.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Se está desarrollando una tecnología, basada en la utilización de enzimas, dirigida a la eliminación del compuesto amargo oleuropeína, como alternativa al uso de álcalis en la producción de aceitunas verdes de mesa.
Características técnicas
El procesado de aceitunas de mesa implica un tratamiento con álcali (NaOH), lo que provoca la pérdida de constituyentes solubles y nutrientes responsables de las propiedades sensoriales de las aceitunas típicas de alta calidad. El objetivo de este proceso biotecnológico es aplicar la tecnología de enzimas para la eliminación de la amargura debido a la oleuropeína, evitando los cambios físicos y químicos que la adición de NaOH produce, y, por otra parte, reducir los tiempos de fermentación durante la etapa de acondicionamiento.
Aplicaciones
Esta técnica está orientada al sector de la Alimentación, especialmente para aquellas empresas productoras de aceitunas verdes de mesa.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
El grupo desarrolla sondas fluorogénicas selectivas para moléculas orgánicas de pequeño tamaño y alto impacto social y medioambiental. Las sondas fluorogénicas desarrolladas son capaces de mostrar grandes diferencias de fluorescencia en presencia de determinados analitos y están orientadas a la resolución de problemas de detección de contaminantes de alto impacto medioambiental para los que no existe una solución satisfactoria: agentes fosforilantes procedentes de armas químicas, metilmercurio, ión cianuro, substancias de dopaje y drogas de diseño. Mediante la incorporación de las sondas fluorogénicas a nanomateriales de sílica, el grupo genera nuevos materiales sensores luminiscentes de utilidad toxicológica o medioambiental.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Los sensores fluorogénicos han adquirido un enorme impacto social y económico, esto se debe a la importancia que pueden llegar a tener en la vida cotidiana. Los sensores químicos implican el diseño de moléculas aisladas o conjuntos de moléculas que reconozcan específicamente una especie en particular de manera reversible, en un rango apropiado de concentración, idealmente en cantidades traza. La necesidad de reversibilidad es un requisito esencial para la monitorización continua o “in vivo”, pero para medidas individuales aisladas no es necesaria. Por otro lado, en los últimos tiempos la detección de un analito aislado ha sido superada por nuevos sistemas que son capaces de detectar diversas clases o mezclas de compuestos químicos de forma similar a la que la naturaleza ha venido utilizando en el desarrollo del olfato humano y el sentido del gusto. En este caso, los requisitos para conseguir estos objetivos son muy complejos, por lo que la preparación de sistemas de señalización luminiscente así como de dispositivos luminiscentes resulta muy ventajosa ya que las medidas de fluorescencia suelen ser muy sensibles, de bajo coste, fáciles de realizar y extremadamente versátiles, consiguiendo sub -límites de detección micromolares. En consecuencia, los sensores químicos luminiscentes juegan un papel importante en campos clave como la detección industrial, el diagnóstico médico y terapéutico en ciencias de la salud y en la monitorización ambiental diversa. La nanotecnología es el marco natural de evolución y progresión de los sensores químicos, por lo que la combinación de la nanotecnología y la señalización luminiscente puede dar lugar a la preparación de materiales únicos en el camino hacia importantes desarrollos en diversas áreas técnicas, como sensores químicos ópticos y luminiscentes para analitos orgánicos de alto impacto ambiental y su implementación en estructuras más complejas para conseguir materiales capaces de amplificar la señal para ser incluidos en dispositivos de detección. Desde los sistemas programados de base supramolecular nos interesa el desarrollo de sondas fluorogénicas para su uso en sensores químicos donde el proceso de reconocimiento va unido a un proceso de señalización. Los sensores químicos para biomoléculas como neurotransmisores, glutamato y acetilcolina, glicina, aspartato y dopamina, NO y ATP, son de gran utilidad. En las ciencias ambientales, se sabe que los derivados del mercurio, en particular el metilmercurio, el plomo y el cadmio, son muy tóxicos para los organismos vivos y su detección en el medio ambiente es muy conveniente. Por otro lado, los sensores químicos de explosivos y agentes nerviosos están actualmente desarrollados para la detección de minas y armas químicas. Con la guerra al terrorismo, ha aumentado notablemente la necesidad de sensores químicos y biológicos fiables y precisos que funcionen en tiempo real. Existen muchos tipos de moléculas orgánicas de importancia crítica para las que no existen sensores químicos capaces de detectarlas, por lo que es importante ampliar el campo de analitos que pueden ser detectados y cuantificados, por lo que es necesario diseñar y desarrollar nuevos fluorogénicos específicos. La fluorescencia es uno de los mecanismos de transducción más potentes para informar un proceso de reconocimiento químico. La integración de sondas moleculares fluorescentes en dispositivos adecuados da lugar a sensores químicos. La investigación se ha centrado en la preparación de nuevos receptores pero existen muy pocas sondas fluorogénicas comerciales, por lo que las sondas moleculares desarrolladas por el grupo de investigación llenan un vacío tecnológico que existe en la actualidad.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Muchos problemas de biodetección o bioseguridad no han sido resueltos todavía. Por esto el grupo realiza el diseño de sensores fluorogénicos de contaminantes medioambientales orgánicos para los que no hay actualmente métodos fiables de detección, como los agentes fosforilantes en cantidades traza que pueden provenir de escapes tóxicos o de agentes de guerra química, el metilmercurio o el ión cianuro, y sensores fluorogénicos selectivos para biomoléculas de pequeño tamaño, especialmente metabolitos orgánicos de interés toxicológico o medioambiental. Para conseguirlo, el grupo de investigación ha puesto a punto una nueva familia de sondas fluorogénicas capaces de desarrollar grandes diferencias de fluorescencia en presencia de analitos específicos, que han dado lugar a sondas diferenciales entre series análogas de biomoléculas. La ventaja que ofrecen las nuevas sondas fluorogénicas que el grupo ha desarrollado es que su modo de acción difiere de las sondas conocidas, permitiendo la detección selectiva de especies para las que no existía ningún modo de acceso, por ejemplo, diferenciación entre suplementos deportivos o drogas de diseño. Así, el grupo desarrolla nuevas sondas fluorogénicas apropiadas para tipos de analitos de gran impacto social y medioambiental, y con ellas nuevos materiales sensores mediante su anclaje a nanomateriales de sílica, con el fin de generar nuevos dispositivos sensores de utilidad clínica o medioambiental.
Características técnicas
1.- Desarrollo de sondas fluorogénicas OFF-ON para procesos de reconocimiento fluorogénico de agentes fosforilantes, gases nerviosos o gases de guerra química.
Desarrollo de nuevos materiales sensores orientados a la detección de contaminantes orgánicos medioambientales de alto interés, y su aplicación a agentes fosforilantes, gases nerviosos o gases de guerra química.
2.- Desarrollo de sondas fluorogénicas para catión metilmercurio y su detección selectiva con respecto a mercurio(II).
Desarrollo de nuevos materiales sensores orientados a la detección y especiación de catión metilmercurio y mercurio(II).
3.- Preparación de sondas fluorogénicas OFF-ON para procesos de reconocimiento fluorogénico de contaminantes y metabolitos orgánicos, ión cianuro, y aminoácidos.
Desarrollo de nuevos materiales sensores orientados a la detección de contaminantes orgánicos de interés medioambiental y metabolitos orgánicos derivados de aminoácidos.
4.- Desarrollo de nuevos materiales sensores luminiscentes basados en nanomateriales de sílica para la detección de contaminantes y metabolitos orgánicos de alto impacto medioambiental.
Desarrollo de nuevos materiales sensores soportados en nanomateriales de sílica, orientados a la detección de contaminantes y metabolitos orgánicos de elevado interés medioambiental.
5.- Desarrollo de nuevos materiales sensores luminiscentes de respuesta múltiple, cromogénica, fluorogénica y en resonancia de spin paramagnético, para la detección de aminas biogénicas y sus análogos de alto impacto toxicológico y medioambiental.
Desarrollo de nuevos materiales sensores de respuesta múltiple, orientados a la detección de aminas biogénicas y sus análogos utilizados como fármacos o drogas de diseño.
Aplicaciones
- Empresas del ámbito farmacológico, alimentación y producción de compuestos químicos con interés medioambiental, detección toxicológica o medioambiental.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Investigación o Experimentación.
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Industria agroalimentaria (5)
Resumen de la tecnología
Se está desarrollando una tecnología de enzimas inmovilizadas para eliminar el amargor de los zumos cítricos sin alterar sus características organolépticas.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Los métodos convencionales, para reducir el amargor en los zumos de cítricos, implican no sólo la eliminación de los compuestos amargos (naringina y limonina), sino también componentes bioactivos (ácidos orgánicos, flavonoides, limonoides ...). En este sentido, los métodos biotecnológicos, bien enzimas aisladas o células microbianas, son una forma alternativa interesante para eliminar el amargor, sin afectar a las propiedades nutricionales y saludables (antioxidantes ...) del zumo procesado. Por otra parte, la tecnología de inmovilización de enzimas en soportes sólidos mejora la actividad catalítica y la resistencia a la desnaturalización y facilita la separación del biocatalizador de la mezcla de reacción.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
La aplicación de enzimas en el procesado de zumos cítricos presenta diversas ventajas tales como, la especificidad de reacción, condiciones suaves de operación, además se trata de una tecnología verde (no contaminante)… La inmovilización de la enzima en un soporte sólido permite su reutilización, aplicación de mayores concentraciones de enzimas y mayor estabilidad, prevención de la contaminación del producto procesado, modificación de las propiedades catalíticas, mejor control de las reacciones y el diseño de bioreactores que puedan fácilmente incorporarse en una línea de procesado en continuo.
Características técnicas
Las enzimas se pueden inmovilizar en varios soportes (intercambiadores iónicos, polímeros ...) o bien por adsorción, unión covalente o atrapamiento físico. La tecnología de inmovilización enzimática ofrece diversas ventajas tales como la facilidad de separación de una mezcla de reacción y la aplicación en procesos en contínuo, lo que permite un mayor control sobre los procesos catalíticos y la economía del proceso. Por otra parte, el uso de una enzima inmovilizada permite simplificar en gran medida el diseño del reactor y el control de la reacción.
Aplicaciones
Esta técnica está orientada al sector de la Alimentación, especialmente para aquellas empresas fabricantes de zumos.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La Universidad de Burgos ha desarrollado una tecnología de inmovilización de glucosa oxidasa que reduzca de manera controlada el contenido de glucosa en mosto para la obtención de vinos de menor contenido alcohólico.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Los procesos tecnológicos que se emplean para eliminar o reducir el alcohol en vino requieren prácticas intensivas y equipamientos que no están al alcance de todas las bodegas. En términos generales, son procesos que tienden a involucrar equipos costosos y, además, suelen conllevar una disminución en la calidad final del producto. Una alternativa biotecnológica a estos procesos es la aplicación de glucosa oxidasa (GOX) inmovilizada en soportes sólidos. Las técnicas de inmovilización pueden modificar las características cinéticas de la enzima, permitiendo su actuación a los pH ácidos del mosto. Además, mejoran la estabilidad operacional de las enzimas y permiten su reutilización y operación en continuo.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
El uso de enzimas solubles en la elaboración del vino presenta varias ventajas tales como la especificidad de la reacción, condiciones de funcionamiento suaves y sin efectos contaminantes (tecnología verde). Sin embargo, a pesar de los indudables ventajas, existen una serie de problemas prácticos en la utilización de la glucosa-oxidasa soluble en el mosto, tales como su inactivación a las condiciones de pH ácido o su alto costo. La inmovilización de la enzima sobre soportes sólidos permite la modificación de sus propiedades catalíticas (pH óptimo), una estabilidad más alta, la reutilización de la actividad catalítica, la prevención de la contaminación del producto procesado, y la posibilidad de procesamiento en continuo.
Características técnicas
La industria enológica ha desarrollado y evaluado diferentes estrategias para reducir el contenido de etanol en el vino evitando comprometer la calidad del producto final. Una alternativa biotecnológica es el tratamiento del mosto de uva con glucosa oxidasa para reducir su contenido en azúcares fermentables, lo cual permite reducir el contenido de etanol en el producto final de fermentación sin alterar sus parámetros de calidad.
No obstante, la glucosa oxidasa no es operativa a los valores de pH del mosto. En este sentido, se pretende la preparación de glucosa oxidasa inmovilizada activa y estable a valores de pH ácidos, con una buena estabilidad operacional, así como con unas propiedades mecánicas y químicas favorables que permitan su reutilización y aplicación en la elaboración de vinos de bajo contenido en alcohol.
Aplicaciones
Esta técnica está orientada al sector de la Alimentación, especialmente para aquellas empresas productoras de vinos.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Film polimérico que actúa como sensor colorimétrico para hierro en medios acuosos. La presencia o carencia de hierro presenta en la actualidad varios problemas como la proliferacion de Legionella spp. en torres de refrigeración, la clorosis férrica en frutales y vid, y su presencia en aguas de consumo.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
El material inteligente está diseñado para ahorrar costes y tiempo en reactivos, material de laboratorio y personal especializado. El material permite no solo la detección cualitativa sino también la cuantitativa. Esta cuantificación se puede obtener por medio de equipos convencionales de espectrofotometría o bien mediante la realización de un calibrado con los parámetros RGB de una fotografía digital de la membrana.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Análisis cualitativo y cuantitativo “IN SITU”.
- Cambio de color fácilmente diferenciable.
- Utilizable por personal no cualificado y bajo cualquier condición meteorológica (siempre y cuando el agua que vayamos a analizar esté en estado líquido).
- No requiere de cables ni baterías.
- Permite un análisis rápido a simple vista.
- Evita la utilización de equipos de espectrometría de elevado coste.
- No requiere reactivos para el análisis.
- En su condición de polímero orgánico la fecha de caducidad del producto es superior a 100 años
- Se transporta fácilmente en un sobre, sin necesidad de maletín o kit de análisis.
- Medida directa sin equipos complementarios.
- Actúa como detector de hierro, aluminio y mercurio independientemente. En presencia de hierro cambia a color verde oscuro, en presencia de mercurio cambia a color naranja intenso, y en presencia de aluminio pasa a ser fluorescente.
- Comportamiento de gel. Se hincha en agua permitiendo asi la detección de los elementos presentes en el medio en el que se sumerge.
- Gran selectividad hacia el hierro. La atracción con el hierro es muy fuerte (K=1040), lo que permite detectar hierro libre y hierro complejado en el caso de vinos y suero sanguíneo.
- Se puede almacenar en cualquier lugar que no suponga unas condiciones ambientales extremas
- No requiere de la utilizacion de medidas de protección (guantes, gafas, etc.)
Características técnicas
Membrana polimérica (film) basada en la polimerización de dos monómeros comerciales biocompatibles, un monómero sensor y un entrecruzante. El film presenta un aspecto casi incoloro. Al ser sumergido en medios acuosos con hierro, el film cambia bruscamente hacia un color verde oscuro. Si el medio está contaminado con mercurio o con aluminio, el film cambia a color naranja o a material fluorescente respectivamente. Además, tiene unas propiedades mecánicas excelentes, tanto en seco como en hinchado.
Aplicaciones
1. Torres de Refrigeración / Condensadores evaporativos. Legionella. La Legionella es una bacteria que genera problemas importantes de salud, incluso la muerte, a aquellos individuos que sufren su infección. El principal punto de crecimiento de estas bacterias se encuentra en los sistemas de refrigeración y de humidificación tanto industriales como particulares. Para ello hay que controlar la presencia de hierro en este tipo de sistemas ya que un exceso ayuda al crecimiento de la bacteria.
2. Siembra de Frutales y Vid. Clorosis férrica. La clorosis férrica es una enfermedad que afecta a las hojas debido a la deficiencia de hierro en el suelo de siembra. Con una simple medida pueden controlar que sus suelos son ricos en hierro; incluso pueden saber qué suelo es más idóneo para la siembra.
3. EDAR y ETAP. Anticoagulantes de Hierro y Aluminio. En las estaciones de depuración de aguas residuales y estaciones de tratamiento de agua potable se utilizan a diario y en grandes cantidades coagulantes basados en sales de hierro y de aluminio. Por lo tanto, existe un riesgo real de contaminación de aguas por estos metales. Este riesgo se puede eliminar con nuestro detector de film, ya que sabríamos al momento si están contaminadas.
4. Procesos industriales / tuberías de construcción. Corrosión. En todos aquellos sistemas que contengan tuberías con hierro existe el peligro de que se produzca corrosión y que contamine el agua que atraviesa estos circuitos. La formación de estas herrumbres provoca problemas en los procesos industriales que dependan directamente del agua suministrada por estas vías. Del mismo modo los sistemas de calderas o de circulación en los que este tipo de aguas queda almacenado terminan por desgastarse de tal modo las tuberías que tendrán que ser sustituidas.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente P201300575
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos han desarrollado un procedimiento para producir miel en polvo por liofilización o por desecación a vacío empleando maltodextrina como coadyuvante de deshidratación, de modo que se obtiene un sólido pulverulento fino y agradable que mantiene lo máximo posible las propiedades sensoriales y físico-químicas de la miel.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La miel contiene una elevada concentración de azúcares con bajas temperaturas de transición vítrea (Tg) lo que dificulta su desecación ya que durante la deshidratación se forma un producto extremadamente pegajoso, duro y muy difícil de manejar. La invención que se describe logra evitar estos inconvenientes mediante la desecación de la miel por liofilización empleando exclusivamente miel y maltodextrina de patata como coadyuvante para la deshidratación. El aspecto más innovador de la invención que se presenta con respecto a otros procedimientos descritos para la deshidratación de miel, es el relativo a las temperaturas de molienda del producto y de su conservación. La miel en polvo obtenida contiene un 75% (liofilización) o 60% (desecación a vacío) de sólidos de la miel y un 25% (liofilización) o 40% (desecación a vacío) de sólidos de la maltodextrina, siendo de textura fina y sedosa, con excelentes características sensoriales y físicoquímicas.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Obtención de miel en polvo con una concentración de sólidos totales de la miel del 75% (liofilización) o del 60% (desecación a vacío).
- Empleo de maltodextrina como único aditivo coadyuvante de la desecación en una concentración de sólidos totales del 25% (liofilización) o del 40% (desecación a vacío).
- Mayor rendimiento del proceso: 73,6%-96,4% (liofilización); 80,6%-97,9% (desecación a vacío).
- Mayor solubilidad y menor higroscopicidad en la miel en polvo obtenida.
- Mejores características físico-químicas y sensoriales de la miel en polvo.
- Posibilidad de comercializar la miel en polvo dentro de la demanda de “etiquetas limpias” (clean label) y la denominación “comida real” (real food), al contener tan sólo miel y maltodextrina.
Características técnicas
El procedimiento de liofilización y el de desecación a vacío descrito en esta invención logra la elaboración de miel en polvo con textura harinosa, empleando sólo un aditivo (maltodextrina de patata), con una mayor cantidad de miel en el producto sólido final, una mayor solubilidad, un mayor rendimiento y una menor higroscopicidad. Se comprobó que los mejores procedimientos de deshidratación de la miel eran los de desecación a vacío y liofilización, empleando maltodextrina como coadyuvante ya que presentaron los porcentajes de agua más bajos y fueron las mejor valoradas en los análisis sensoriales.
La miel en polvo obtenida presentó los valores más elevados de capacidad antioxidante frente al radical peroxilo y los resultados más altos para las actividades antiinflamatoria in vitro y antimicrobiana. La molienda y conservación del producto deben realizarse a temperaturas inferiores a la Tg de la miel en polvo obtenida, lo que mantiene óptimas las características de textura de este alimento sin necesidad de incorporar aditivos antiaglomerantes.
Aplicaciones
Las posibles aplicaciones de la miel en polvo es su utilización en postres de alta cocina como adorno, o elaboración de caramelos y productos de confitería, bollería, chocolate con miel o cosméticos con miel. Los sectores con potencial aplicación son:
- Alta cocina
- Industria galletera
- Industria panadera y pastelera
- Industria confitera
- Industria cosmética
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención P202130603 y P202130604
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Obtención de pasta de colágeno de uso alimentario a través del desengrasado de piel de cerdo mediante dióxido de carbono comprimido. Rendimientos superiores a 90%, mediante un procedimiento que no altera la naturaleza de la proteína contenida en la piel y que utiliza un disolvente inocuo (CO2), con el fin de obtener una materia prima adecuada.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Utilización de disolvente de extracción (CO2) inocuo que no altera la naturaleza de la proteína contenida en piel.
Alcanzados rendimientos superiores al 90% (en otras invenciones se describe que el rendimiento no puede alcanzar valores superiores al 60%).
Diversificación de la materia prima a partir de la cual se obtiene el colágeno de uso alimentario (habitualmente piel de vacuno).
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Revalorización de un producto (piel de cerdo) de escaso valor en la industria cárnica.
Incremento de los rendimientos en la producción de colágeno sin generación de residuos grasos, lo que le hace servible para uso alimentario.
Obtención de producto más puro sin grasa residual de difícil tratamiento.
Generación de nuevos subproductos de fácil comercialización.
Características técnicas
En este tratamiento, para eliminar la grasa de la piel de cerdo, se utilizan en primer lugar procedimientos mecánicos para separar la hipodermis de la dermis, que de esta forma queda prácticamente libre de grasa. Tanto la dermis como la hipodermis no eliminada mecánicamente se someten a un proceso de extracción con dióxido de carbono en condiciones supercríticas, en el que se realizan descompresiones rápidas del extractor Esta descompresión rápida va seguida de una compresión y circulación de disolvente para extraer la grasa que ha quedado accesible. Con sucesivas compresiones y descompresiones se reduce al mínimo la cantidad de grasa y de agua de la piel de cerdo, hasta un 1% de grasa en base seca, admisible por tanto para el procesado de la piel y su transformación en colágeno para uso alimentario.
Aplicaciones
Está orientado a empresas del sector cárnico, que en la actualidad estén gestionando las pieles de cerdo como un residuo, como subproducto alimentario de reducido valor, o que eliminen la grasa mediante disolventes convencionales para posterior aprovechamiento del colágeno. En esos sistemas convencionales el contenido en grasa del colágeno es muy elevado lo que hace difícil su gestión/eliminación, elevando su coste. El empleo de técnicas alternativas de extracción/eliminación de toda la grasa permite incrementar de manera muy importante los rendimientos en la posterior producción de colágeno sin generación, además, de residuos grasos.
El sector cosmético es otro sector de aplicación, incorporarían un incremento de valor por su característica “verde”, favoreciendo su introducción en productos comerciales finales. El mercado se beneficiaría de rendimientos más elevados, con un producto más puro, sin grasas residuales de difícil gestión o tratamiento, a costes competitivos.
Propiedad Intelectual
Patente P200400390
Estado actual de desarrollo
Muestras listas para pruebas
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Ciencias Biologicas (14)
Resumen de la tecnología
La invención describe un método para sintetizar un copolímero bifuncional diseñado para la detección y extracción de aniones específicos, como los nitratos en el agua de consumo. Este material puede regenerarse fácilmente, permitiendo su uso repetido en el tiempo, con el correspondiente ahorro en costes. Además, la síntesis del copolímero no requiere polímeros o disolventes orgánicos, lo que hace que el proceso sea más ecológico y eficiente. Su efectividad en el proceso de purificación es visible para el usuario gracias a una señal visual, como un cambio de color, que facilita el monitoreo del material de filtrado, garantizando el mantenimiento o la sustitución a tiempo.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
- El copolímero combina detección visual y eliminación de aniones, especialmente de nitratos, en el agua.
- A diferencia de las tecnologías existentes, este copolímero es reutilizable y más ecológico, ya que no requiere un consumo elevado de agua ni produce un flujo de desecho altamente concentrado.
- Permite que el usuario sea consciente del estado del purificador mediante una señal visual, haciendo más accesible el proceso de purificación.
- La invención presenta diferentes formatos versátiles como pastillas o láminas, de menor o mayor tamaño, para facilitar el uso en diferentes aplicaciones.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
El copolímero ofrece múltiples ventajas sobre las tecnologías de purificación de agua actualmente disponibles. En primer lugar, es un material reutilizable que puede regenerarse de manera sencilla, permitiendo así varios ciclos de uso sin perder su eficacia. Su diseño permite que el usuario detecte la presencia de aniones de nitrato a través de una señal visual, como un cambio de color o fluorescencia, lo cual facilita la observación y control del proceso de purificación sin necesidad de instrumentos adicionales. Además, al no generar un flujo de desecho concentrado ni consumir grandes volúmenes de agua durante su operación, es una alternativa sostenible y de bajo mantenimiento frente a tecnologías como la ósmosis inversa. Por último, al emplearse en dispositivos de uso cotidiano, promueve una mayor conciencia del usuario sobre la importancia de la calidad del agua. Otra ventaja destacable es su portabilidad y facilidad de uso, ya que su diseño práctico permite que pueda instalarse tanto en domicilios habituales como en residencias rurales o en áreas afectadas por problemas de acceso a agua potable. Además, gracias a su flexibilidad de aplicaciones y a sus múltiples formatos, este copolímero puede emplearse en contextos variados. Es adecuado para sistemas de filtración domésticos, como jarras individuales, depósitos de agua en entornos rurales, o incluso acuarios.
Características técnicas
El material inteligente es un copolímero diseñado para actuar como una resina de intercambio iónico con propiedades específicas para la absorción de nitratos, lo que lo hace especialmente eficaz en la purificación de agua. El tiempo de acción de este material depende en gran medida de la concentración inicial de nitratos en el agua, pero el sistema de alerta visual integrado elimina la necesidad de monitoreo constante. Este sistema inteligente alerta al usuario cuando el material ha alcanzado su saturación, asegurando un uso eficiente y conveniente del dispositivo sin necesidad de conocimientos técnicos especializados.
Aplicaciones
Este copolímero presenta un amplio rango de aplicaciones en el tratamiento y monitoreo de la calidad del agua. En el ámbito doméstico, puede integrarse en dispositivos de purificación de agua, como jarras o filtros, para eliminar contaminantes comunes en el agua de consumo, incluyendo nitratos y otros aniones. Además, gracias a su formato portátil, puede ser llevado a cualquier lugar, lo que resulta ideal para tratar agua durante viajes o actividades al aire libre, asegurando un acceso continuo a agua purificada.
A mayor escala, el copolímero también puede implementarse en sistemas comunitarios, como en comunidades de vecinos, debido a su versatilidad para adaptarse a diferentes formatos y volúmenes de tratamiento de agua.
En el sector de la acuicultura, el copolímero resulta útil para garantizar un entorno seguro en instalaciones comerciales, así como en acuarios domésticos. Muchas especies de peces son extremadamente sensibles a los niveles de nitratos, y esta tecnología proporciona una solución eficaz para mantener el agua en condiciones óptimas.
Estado actual de desarrollo
La fase de desarrollo está finalizada y ha sido validado para su uso en aplicaciones reales. Tecnología lista para ser implementada y comercializada.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, acuerdo de licencia o cooperación técnica (Mayor desarrollo, nuevas aplicaciones o adaptación a necesidades específicas).
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Sensor electroquímico capaz de realizar muestras in-situ para hallar concentraciones simultáneas de compuestos azufrados y 4-etilfenol
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Detección Simultánea: Uno de los aspectos más innovadores es la capacidad de detectar simultáneamente mercaptanos y 4-etilfenol en vinos. Esta funcionalidad es esencial para la evaluación completa de la calidad del vino, ya que ambos compuestos pueden afectar a sus características organolépticas.
Método sin Contacto: La tecnología permite la detección en fase gaseosa, evitando el contacto directo del sensor con la muestra líquida. Esta característica es crucial para mantener la integridad del producto, lo que es especialmente importante en la industria del vino.
Diagnósticos Preventivos: La capacidad de realizar análisis rutinarios e in situ facilita la detección temprana de problemas, lo que permite tomar medidas correctivas de manera preventiva y con un mínimo costo.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Mayor eficiencia en el análisis y sensibilidad: La capacidad de detectar simultáneamente mercaptanos y 4-etilfenol en vinos en fase gaseosa mejora significativamente la eficiencia del análisis. Al poder evaluar los dos compuestos críticos al mismo tiempo, se ahorra tiempo y recursos en comparación con los métodos tradicionales.
Calidad del producto preservada: La detección sin contacto directo con la muestra líquida es una ventaja clave, ya que garantiza que el vino no se vea afectado ni contaminado durante el proceso de análisis. Esto es esencial para preservar la calidad y la integridad del producto final.
Diagnóstico temprano de defectos: La capacidad de realizar análisis rutinarios e in situ permite la detección temprana de defectos en los vinos. Esto es fundamental para tomar medidas correctivas de manera preventiva y evitar problemas que puedan afectar la calidad del producto.
Costo eficiente: La capacidad de llevar a cabo diagnósticos preventivos con un costo mínimo es una ventaja significativa. Esto permite a las empresas vitivinícolas y agroalimentarias controlar la calidad de sus productos sin incurrir en gastos excesivos.
Facilidad de uso: La capacidad de realizar análisis in situ y la facilidad de uso de la tecnología hacen que sea accesible para un amplio rango de usuarios, desde pequeñas bodegas hasta grandes empresas de alimentos.
Características técnicas
Esta tecnología se basa en un sensor electroquímico diseñado para la detección
simultánea de mercaptanos y 4-etilfenol en vinos. El sensor utiliza dispositivos duales serigrafiados de carbono en los que los electrodos de trabajo se modifican con ftalocianina de cobalto (CoPh) y fullereno (C60). La modificación de los electrodos aumenta la conductividad, sensibilidad y selectividad del sensor.
El método de detección se realiza en fase gaseosa, evitando el contacto directo del sensor con la muestra de vino. Esto es fundamental para mantener la calidad del producto. Los cuatro electrodos (dos del trabajo, el auxiliar y el de referencia) están recubiertos con una película de polímero gelificado compuesta por una mezcla de fluoruro de polivinilideno, 1-metil-2-pirrolidona y hexafluorofosfato de 1-metil-3-octilimidazolio, que actúa como electrolito de soporte.
Una ventaja adicional de esta tecnología es su capacidad para llevar a cabo diagnósticos preventivos de compuestos críticos de manera eficiente y rentable, sin entrar en contacto directo con la muestra. Esto permite la detección temprana de defectos en el vino y la toma de medidas correctivas antes de que afecten significativamente a la calidad del producto, ofreciendo una solución innovadora y efectiva para la industria vitivinícola y agroalimentaria.
Aplicaciones
- En la industria Vitivinícola, permite garantizar la calidad y la consistencia de producto final, gracias a la detección de compuestos no deseados.
- Permite cumplir estándares y regulaciones específicas gracias a que se puede llevar un control de calidad exhaustivo.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente P202330838
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Herramienta software diseñada para ayudar en la detección temprana del Trastorno del Espectro Autista (TEA) en niños mediante el seguimiento visual de vídeos.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
- Tecnología de Seguimiento Visual: Utiliza seguimiento ocular para recopilar datos objetivos sobre cómo los niños interactúan visualmente con los videos.
- Inteligencia Artificial: Emplea modelos de redes neuronales para analizar patrones visuales, permitiendo una evaluación precisa y objetiva.
- Adaptabilidad Continua: Puede mejorar con nuevos datos, manteniendo su eficacia a lo largo del tiempo.
- Detección Temprana y Objetiva: Permite la identificación temprana del TEA de manera precisa, lo que es esencial para una intervención temprana y un mejor pronóstico.
- Reducción del Sesgo: Minimiza la influencia de la subjetividad en las evaluaciones, proporcionando resultados basados en datos visuales objetivos.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Ahorro de Tiempo y Recursos: En comparación con los métodos tradicionales, puede ahorrar tiempo y recursos en el proceso de diagnóstico.
- Potencial en Telemedicina: Facilita la evaluación remota de niños, lo que es especialmente relevante en situaciones donde las visitas presenciales pueden ser difíciles o costosas.
- Apoyo a la Investigación y Mejora continua: Contribuye a la investigación científica al proporcionar datos objetivos para estudios sobre el TEA y sus manifestaciones visuales, lo que permite a la herramienta adaptarse y mejorar con nuevos datos.
- Facilita la Toma de Decisiones Clínicas: Ayuda a los profesionales de la salud y psicólogos a tomar decisiones más informadas en el diagnóstico y la planificación de tratamientos.
Características técnicas
Esta herramienta innovadora se centra en recopilar datos del Trastorno del Espectro Autista (TEA) en niños mediante el seguimiento visual de vídeos. El proceso comienza al presentar una serie de vídeos especialmente diseñados a los niños. Durante la visualización de estos vídeos, se emplea tecnología de seguimiento visual para registrar y analizar en tiempo real hacia dónde dirigen su mirada los niños.
Los datos recopilados a partir de este seguimiento visual se traducen en un conjunto de variables, que se utilizan como entrada para modelos de redes neuronales artificiales. Estos modelos tienen la capacidad de aprender y detectar patrones complejos en los datos de seguimiento visual. Además, se incorporan técnicas de selección de variables para garantizar la robustez de los modelos y aumentar su precisión.
Por otro lado, esta herramienta tiene capacidad de adaptarse y mejorar con el tiempo a medida que se acumulan más datos. Esto asegura que el sistema pueda ajustarse continuamente y mantener una precisión constante en la detección del TEA.
La aplicación primordial de esta herramienta es proporcionar diagnósticos precisos de TEA en niños, incluso en edades tempranas. La identificación temprana del TEA es esencial, ya que permite una intervención oportuna y un inicio temprano de terapias y apoyo, lo que puede mejorar significativamente el pronóstico a largo plazo para los niños con TEA.
Además de su uso en la diagnosis clínica, esta herramienta también tiene implicaciones en la investigación del TEA, ya que puede ayudar a comprender mejor los patrones visuales asociados con el trastorno.
Aplicaciones
El software permite mejorar la detección y el diagnóstico del TEA, con el potencial de beneficiar a niños, familias y profesionales de la salud, así como a la investigación y el desarrollo de tratamientos más efectivos.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante software
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente concedida
software
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Investigadoras de la Universidad de Burgos han desarrollado un método capaz de detectar compuestos azufrados, en concreto mercaptanos, en vinos. Esta nueva metodología permite realizar los análisis de manera rápida y con una elevada sensibilidad. Además, el método electroquímico propuesto se caracteriza por su bajo coste y su portabilidad.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
España es el primer exportador mundial en volumen, con algo más de 2.300 millones de litros exportados en 2021 y es responsable del 25% de la producción de vino en Europa. La presencia de compuestos azufrados en el vino provoca la aparición de olores desagradables, como olor a huevos podridos. La formación de estos compuestos representa uno de los principales motivos de reclamación. Aunque durante los últimos años se han desarrollado métodos para la determinación de estos compuestos, el método desarrollado en la Universidad de Burgos se presenta como un referente dado que permite cuantificar mercaptanos de forma selectiva sin estar en contacto directo con la muestra.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Las principales ventajas que ofrece este método son las siguientes:
- Permite realizar el análisis en fase gaseosa, reduciéndose el número de especies interferentes e incrementándose la selectividad.
- El sensor no está en contacto directo con el vino, por lo que no altera el producto.
- No se requiere realizar un pretratamiento a la muestra.
- El método también se caracteriza por su alta sensibilidad, su bajo coste y, por su tamaño compacto, por su potabilidad.
Por todo ello, esta metodología se posiciona como una de las más idóneas para la determinación de mercaptanos.
Características técnicas
Las medidas electroquímicas se realizan utilizando un potenciostato al que se conecta el dispositivo serigrafiado modificado con CoPh, que previamente se ha sumergido en una disolución de electrolito de soporte de tal manera que queda precargado por adsorción. Las medidas amperométricas se realizan posteriormente en el espacio de cabeza de una celda sellada. Una vez que se registra una corriente constante, se agrega a la celda un volumen determinado de la disolución de EtSH o de vino, según corresponda, registrándose el incremento correspondiente en la corriente registrada debido al proceso de oxidación que tiene lugar en la superficie del electrodo. La corriente medida en la superficie del electrodo de trabajo depende de la concentración de EtSH en la celda.
La aplicabilidad del método desarrollado se ha validado mediante experimentos de veracidad, en los que se analizaron vinos tanto en su estado original como después de la adición de una cantidad conocida del analito.
Aplicaciones
La principal aplicación de los sensores desarrollados es en la industria vitivinícola como técnica para la determinación de mercaptanos. El análisis permitiría cuantificar estos compuestos durante todo el proceso de elaboración del vino.
Adicionalmente, esta metodología podría implantarse de forma generalizada en la industria agroalimentaria.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante una patente P202231013
Estado actual de desarrollo
Investigación o experimental
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos han desarrollado un procedimiento para concentrar virus a partir de muestras alimentarias y muestras clínicas. El nuevo procedimiento no solo es más económico y de fácil implantación, sino que es un método sostenible ya que no emplea disolventes orgánicos.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Los métodos actuales de detección de virus en alimentos presentan varias limitaciones, como poca representatividad de la muestra, dificultad en el aislamiento de los virus del interior celular y utilización de disolventes orgánicos perjudiciales para el medio ambiente y la salud.
Ante esta realidad se hace evidente desarrollar un método eficiente para la detección de virus.
El procedimiento descrito por investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos ha permitido superar estas limitaciones. Este método permite alcanzar una mayor eficacia en la concentración de los virus; posibilita la extracción de virus del interior de las células de la muestra; y es un método más respetuoso con el medio ambiente y seguro.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
• El método es capaz de extraer los virus que se encuentran tanto en la superficie de la muestra como en el interior celular. De esta forma se pueden cuantificar tanto los virus de la superficie como los del interior de las células del producto alimentario.
• Este método no utiliza disolventes orgánicos posicionándose como un método más sostenible a los actuales.
• Menor coste económico.
• Menor riesgo en el puesto de trabajo.
Características técnicas
• Los virus capaces de ser detectados mediante este método son virus causantes de enfermedades transmitadas por alimentos como, por ejemplo, el virus de la hepatitis E.
• La muestra se somete a una doble lisis haciendo que aumenta la cantidad de virus que se pueden aislar de una muestra lo que se traduce en un aumento de la sensibilidad de los pasos de extracción y detección posteriores.
• Método de fácil implantación en la rutina de un laboratorio ya que solo se requieren equipos rutinarios presentes en cualquier laboratorio.
Aplicaciones
- Empresas del sector alimentario.
- Sector sanitario tanto público como privado.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención P202230844
Estado actual de desarrollo
Investigación o experimental
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Un grupo de investigación de la Universidad de Burgos realiza estudios con compuestos bioactivos con propiedades saludables, presentes en alimentos o extractos de origen vegetal, con el objetivo de evaluar su efecto antioxidante y efecto sobre biomarcadores de enfermedades asociadas al estrés oxidativo (enfermedades cardiovasculares, cáncer), mediante ensayos "in vitro", "ex vivo" en cultivos celulares, e "in vivo" en animales de experimentación.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Son muchas las evidencias epidemiológicas que relacionan el consumo de frutas y verduras con una menor incidencia de enfermedades crónicas asociadas al estrés oxidativo, tales como enfermedades cardiovasculares, hipertensión, cáncer, etc. Este hecho, junto con la mayor preocupación de los consumidores por mantener un estado de salud adecuado, lleva a la búsqueda de compuestos bioactivos obtenidos a partir de antioxidantes naturales que puedan ser utilizados como componentes de los alimentos funcionales. Pero los beneficios de estos compuestos para la salud dependen de la ingesta y de la biodisponibilidad, que pueden variar ampliamente de unos a otros en función de factores como la matriz, el procesado, la interacción con otros compuestos, la estructura química, etc. Por ello es importante realizar estudios que conduzcan a la evaluación de los compuestos bioactivos y de sus efectos preventivos para la salud.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Evaluar el potencial efecto saludable de alimentos o extractos con capacidad antioxidante.
- Revalorización de residuos agroindustriales, para la obtención de antioxidantes naturales con aplicación en la industria alimentaria, cosmética y/o farmacéutica.
Características técnicas
- 1Determinación de la capacidad antioxidante y antirradical de alimentos, bebidas o extractos vegetales.
- Evaluación "in vitro" de biomarcadores de estrés oxidativo como indicadores del efecto protector de los compuestos bioactivos.
- Determinación de la viabilidad celular, citotoxicidad, genotoxicidad y producción de ROS.
- Evaluación de biomarcadores moleculares relacionados con el estrés oxidativo en modelos celulares y animales: malondialdehído, grupos carbonilo, 8-OHdG, NO, NOs, antioxidantes enzimáticos (superóxido dismutasa, catalasa y glutatión peroxidasa) y no enzimáticos (GSH (glutatión reducido)/GSSG (glutatión oxidado), tiorredoxina).
Aplicaciones
Esta tecnología va dirigida a la industria alimentaria, o farmacéutica, para el diseño de alimentos funcionales o la revalorización de un producto con propiedades saludables.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Investigación o experimental
Relación comercial deseada
Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Se pretende aplicar procedimientos biotecnológicos (lipasas), alternativos a los tratamientos químicos de transesterificación e hidrólisis, para la modificación de grasas y aceites. Las lipasas permiten llevar a cabo procesos enzimáticos para la formulación de productos nutricionales lipídicos "estructurados", formulados a medida para una función nutricional o tecnológica específica. Adicionalmente se evaluará la estabilidad oxidativa de los lípidos sintetizados.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Las lipasas (EC 3.1.1.3) constituyen un grupo muy versátil de enzimas debido a la gran cantidad de reacciones que catalizan, con la ventaja de su capacidad para actuar de forma selectiva sobre diferentes sustratos. Adicionalmente, la acción de las enzimas, en términos de eficiencia y de estabilidad, se puede mejorar mediante técnicas de inmovilización. Mediante esta tecnología, la enzima se fija a un soporte o se microencapsula, lo que generalmente permite incrementar su estabilidad y eficiencia catalítica al disminuir las posibilidades de modificación desnaturalizantes de su conformación tridimensional. Además, hay otras ventajas adicionales, tales como su reutilización, la posibilidad de uso de reactores en continuo, conclusión rápida de reacciones, formación de productos controlada, la mayor variedad de diseños de ingeniería y la mayor eficacia en reacciones con etapas sucesivas.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Con esta tecnología enzimática, es posible, por tanto, desarrollar grasas o aceites comestibles con propiedades nutricionales, organolépticas y de estabilidad térmica, para cada uso culinario. De esta forma se logra no solo obtener beneficios nutricionales en pacientes con requerimientos específicos, sino también prevenir el riesgo de morbilidad y mortalidad por algunas patologías de gran prevalencia, como es el caso de las enfermedades cardio-vasculares, a través del consumo de aceites diseñados con una estereoquímica específica.
Características técnicas
La industria de alimentos utiliza procedimientos de modificación química y enzimática de las grasas y aceites con el propósito de mejorar sus características organolépticas, nutricionales y/o estabilidad frente al procesado. Debido a que los procedimientos químicos presentan muchas limitaciones e inconvenientes, la aplicación de tecnologías que utilizan enzimas aparece como muy prometedora para el desarrollo de nuevos tipos de grasas y aceites. El uso de lipasas ha permitido mediante técnicas biotecnológicas, la obtención de lípidos estructurados con una estereoquímica establecida y constante.
Aplicaciones
Esta técnica está orientada al sector de la Alimentación, especialmente dirigido al diseño de alimentos funcionales.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Investigación o experimental
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La prohibición del uso en agricultura intensiva de fumigantes químicos como son los hidrocarburos halogenados, ha despertado el interés por nuevos métodos de control biológico de los patógenos vegetales que se encuentran en el suelo. Una de las metodologías más prometedoras es la biodesinfección de suelos consistente en procesos de solarización en la que se incorporan residuos orgánicos cuya descomposición produce gases de efecto fumigante y contribuye a restablecer la salud del suelo para posteriores cultivos.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La sustitución de productos químicos fumigantes como el bromuro de metilo y otros hidrocarburos halogenados se ha realizado buscando nuevos productos con similar efecto cuyo uso esté permitido como el metam sodio o el dazomet, productos cuya hidrólisis produce isotiocianatos volátiles, pero que se enfrentan a restricciones legales cada vez más extrictas dada su toxicidad y problemática ambiental.
Alternativamente se han utilizado diferentes procesos biológicos como los denominados biofumigación, en la que los restos de plantas de la familia de las brasicas, también producen isotiocianatos en su descomposición dado su alto contendio en glucosinolatos. Se trata de generalizar dichos procesos utilizando los residuos generados en la propia producción agrícola o en la actividad agroindustrial de la zona optimizándolos para su uso como biodesinfectantes de suelos.
Características técnicas
Las experiencias realizadas por el grupo UBUCOMP en laboratorio y en campo, demuestran que también es posible obtener dicho efecto biofumigante mediante la descomposición anaerobia de una adecuada mezcla de residuos orgánicos de origen agrario como purines, restos de cosecha, vinazas, melazas, alpechines, restos de champiñón, de algas, lignosulfonatos, etc en lo que se denomina de forma genérica biodesinfectación del suelo. La realización del proceso mediante técnicas de solarización en las que se sella el suelo y se incrementa su temperatura, se ha comprobado como un método eficaz en el control de hongos y nemátodos fitopatógenos.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
La técnica de la biodesinfección del suelo se está utilizando de forma creciente dadas las actuales restricciones legales al uso de fumigantes químicos y la necesidad de utilizar alternativas de menor impacto toxicológico y ambiental. Al mismo tiempo se consigue valorizar un residuo orgánico que dada su alta biodegradabilidad puede causar problemas de contaminación, el proceso global no deja residuos tóxicos en el suelo y es compatible con las prácticas de agricultura ecológica. Al mismo tiempo, se obtiene una activación de la actividad biológica del suelo, logrando una mejora de su salud y de su resistencia frente a plagas y enfermedades vegetales.
Aplicaciones
La técnica es de interés para productores agrícolas dedicados a la agricultura intensiva en invernaderos, horticultura intensiva a cielo abierto, agricultura ecológica, cultivos de fresa, cultivos extensivos de remolacha, maíz o patata donde tienen especial incidencia los nemátodos fitoparásitos. También para los productores de residuos orgánicos para la producción de enmiendas con carácter biodesinfectante de suelos.
Relación deseada
Cooperación técnica - mayor desarrollo
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Producto totalmente natural, derivado de masas de vinificación, que tiene potencial sazonador permitiendo reducir niveles de sal de los alimentos procesados haciéndolos más saludables (aptos para población hipertensa). Además tiene efecto conservante, lo que reduce/elimina el uso de conservantes (ej. sulfitos). El producto es aplicable en toda la industria alimentaria así como en restauración.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La gran novedad: el producto se obtiene por un procesado mínimo de las masas de vinificación, no se trata de un extracto, por tanto, es un producto totalmente natural que además del poder sazonador y conservante, es fuente de los mútiples componentes bioactivos presentes en las uvas como son polifenoles, fibra, potasio y otros minerales.
Características técnicas
Conservante natural y sustituto de la sal común con propiedades "funcionales".
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
El producto tiene un "per se" valor añadido por ser 100% "natural", obtenido por procesado mínimo con bajo consumo de energía y casi nulo de agua, contribuye a reducir huella de carbono de la elaboración de vinos, a reducir residuos generados, y por tanto aumentar la rentabilidad del proceso. Aporta valor añadido a los productos que adiciona gracias a los componentes bioactivos y la riqueza de potasio.
Aplicaciones
Industria alimentaria en general, en especial a aquella que necesite reducir los niveles de sal en sus productos sin perder estabilidad o poner en riego la conservación. Además, el producto es apto para ser aplicado en restauración, en la elaboración de platos, tapas, etc...
Posible limitación: productos que admitan la incorporación de productos sólidos "coloreados".
Propiedad intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención P201300555
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos han descrito un procedimiento de síntesis de derivados de hidroxialquilamidas a partir de los correspondientes N,N-dietilcarbamatos de O-arilo y un epóxido, lo que les ha permitido preparar varias series de nuevos compuestos quirales con aplicaciones potenciales en la industria farmacéutica.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Los compuestos orgánicos quirales con grupos hidroxilo son importantes precursores sintéticos de aminoácidos, alcaloides, carbohidratos y otros compuestos quirales con posible actividad biológica y/o farmacológica. Es por eso que uno de los principales retos de la química orgánica actual es la búsqueda de nuevos procedimientos de síntesis, eficientes y limpios, que permita acceder a compuestos quirales. El novedoso procedimiento descrito por los investigadores de la UBU permite obtener una nueva familia de derivados de (6-hidroxifenil)-N,N-dietil-3-hidroxialquilamidas, que no se encuentran descritos en bibliografía y que se obtienen como un único diastereoisómero. La relevancia farmacológica tanto de los compuestos orgánicos quirales como de los epóxidos se demuestra por el hecho de encontrarlos o ser precursores de numerosos compuestos biológicamente activos o productos naturales.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- El procedimiento que permite obtener una nueva familia de derivados de (6-hidroxifenil)-N,N-dietil-3-hidroxialquilamidas es novedoso.
- Los compuestos no se encuentran descritos en bibliografía y se obtienen como un único diastereoisómero.
- También se puede llevar a cabo el procedimiento empleando epóxidos quirales, pudiéndose así obtener los productos finales de forma enantioespecífica.
Características técnicas
El procedimiento descrito permite la síntesis de nuevos compuestos derivados de (6-hidroxifenil)-N,N-dietil-3-hidroxialquilamidas a partir de N,N-dietilcarbamatos de O-arilo como sustratos de partida, pudiendo presentar grupos de diferente naturaleza química en el anillo aromático, tales como halógenos, grupos metoxilo, o no sustituidos. Asimismo, se requiere del empleo de sec-butil-litio o diisopropilamiduro de litio, en tetrahidrofurano, a –78 ºC, a presión atmosférica y en atmósfera inerte de nitrógeno gas, para la reacción de orto-litiación de los carbamatos de partida. La posterior adición de 2,2,6,6-tetrametilpiperiduro de litio y la adición de un epóxido terminal, pudiendo ser alquílico o con un grupo funcional, tanto racémicos como enantioméricamente puros, da lugar al reagrupamiento homólogo de Snieckus–Fries 1,4-O→C del grupo carbamoílo por la evolución de la reacción a temperatura ambiente durante 3 horas.
Aplicaciones
La potencial aplicación del procedimiento descrito es la síntesis de compuestos orgánicos aromáticos quirales que contienen grupos alcohol en su estructura, así como halógenos y otros grupos funcionales, por lo que se postulan como intermedios sintéticos altamente versátiles con gran aplicabilidad en la industria farmacéutica, agroquímica, química, etc.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención P202130635
Estado actual de desarrollo
Procedimiento testado en laboratorio.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos, la Universidad de Barcelona y la Spin-off Nostrum Biodiscovery, han descrito el uso en medicina de la asenapina o las posibles combinaciones de esta con otros agentes anticancerígenos, así como a composiciones farmacéuticas y kits que los contienen, en particular como agentes anticancerosos.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La survivina es una diana terapéutica para tratar el cáncer. La asenapina es un antipsicótico atípico vendido en la forma de su sal de maleato bajo la marca SAPHRIS. Se cree que el papel de la asenapina en el tratamiento del cáncer podría estar relacionado con su capacidad para inhibir la survivina. Las principales funciones establecidas de la survivina son la regulación de la mitosis celular y la inhibición de la apoptosis. Hasta el momento, no se han encontrado datos experimentales que apoyen el uso de asenapina contra el cáncer.
Los investigadores de la UBU, UB y Nostrum han encontrado que la asenapina se puede utilizar de forma eficaz en el tratamiento del cáncer ya que no solo es capaz de mostrar una actividad cancerígena moderada contra varias líneas de células cancerosas in vitro, sino que también ha mostrado efectos antitumorales in vivo.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
La acción inhibidora de la survivina que ejerce la asenapina permitiría:
- inducir la apoptosis en células tumorales
- inhibir el ciclo celular
- sensibilizar las células tumorales a agentes quimioterapéuticos estándar u otros agentes anticancerosos , sin ser tóxicos para las células sanas.
Características técnicas
En los ensayos realizados la asenapina redujo la viabilidad celular en adenocarcinoma de pulmón (A549) y de colon (SW620), y no resultó citotóxico para las células sanas. La asenapina también mostró in vitro efectos anticancerígeno contra el neuroblastoma pediátrico (LAN-1), sarcoma pediátrico (RD), y glioblastoma (U87) en el mismo rango de eficacia como otros agentes quimioterapéuticos tales como cisplatino.
Aplicaciones
Gracias a su capacidad para cruzar la barrera hematoencefálica (BHE), la asenapina puede ser de especial interés en el tratamiento de tumores cerebrales, incluidos tumores cerebrales primarios o cánceres con metástasis cerebrales. También se ha observado su potencial en adenocarcinoma de pulmón, adenocarcinoma de colon, neuroblastoma pediátrico, sarcoma pediátrica y glioblastoma.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención EP21382721
Estado actual de desarrollo
Procedimiento testado en laboratorio
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La Universidad de Burgos, en cotitularidad con la Universidad Complutense de Madrid, ha registrado un nuevo accesorio que permite controlar la postura visual y corporal de quién lo porte, incluyendo un sensor de vibración como sistema avisador.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
El sistema de control postural consiste en un accesorio simple, sin conexiones a otros dispositivos, que permite controlar la postura visual y corporal. Este sistema incluye acelerómetros para el cálculo de la posición del cuerpo y sensores de vibración como sistema avisador.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Permite medir en tres ejes diferentes su posición real
- Posee sensores de vibración como sistema avisador
- Se encuentra en una caja hermética cerrada junto con el chip informático
Características técnicas
La caja del dispositivo se coloca cerca de la piel del usuario para percibir los movimientos que realiza. Esta caja es de material plástico elástico y puede ser personalizable. Los acelerómetros miden en los tres ejes y esos datos son comparados con los datos de posición correcta acotados previamente. Si los resultados salen fuera de estas cotas, el sistema avisador se activa para que el usuario corrija su postura visual y/o corporal.
Aplicaciones
- Control de postura corporal
- Control de postura visual
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención P202130256
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo en vía de desarrollo.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos han patentado un proceso sintético para la obtención de complejos catiónicos de Iridio(III) con fórmula (I). Además, se ha desarrollado un procedimiento de tipo one-pot para la síntesis regioselectiva de 3-tiocianato indoles (II) a partir de sus correspondientes indolinas utilizando los citados complejos de Ir(III) como fotocatalizadores. Por otro lado, en dicha patente también se protege el uso de los complejos de Ir(III) como fotosensibilizadores terapéuticos y más en particular su uso en terapia fotodinámica antitumoral.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Los complejos de Iridio(III) descritos poseen una serie de características que los diferencian de los complejos conocidos hasta el momento. Presentan una importante actividad como fotocatalizadores o fotosensibilizadores, absorbiendo energía proveniente de la luz y transfiriéndosela al oxígeno para formar especies de oxígeno reactivas (ROS) que actúan como oxidantes muy eficaces y medioambientalmente sostenibles. Además, la síntesis de los complejos de Iridio(III) se lleva a cabo en condiciones suaves y proporciona buenos rendimientos de reacción.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Alta estabilidad de los complejos de Iridio(III) en disolución.
- Presentan fotoestabilidad bajo diferentes fuentes de luz, aumentando considerablemente su rango de aplicaciones posibles.
- Como fotocatalizadores, el uso de luz de menos energía implica un menor riesgo de reacciones secundarias en fotocatálisis y por lo tanto procesos más selectivos.
- En la síntesis regioselectiva de 3-thiocianato indoles a partir de indolinas, el proceso se lleva a cabo en un solo paso, por lo que es más económico dado que se evitan etapas de aislamiento y purificación de los productos intermedios.
- En aplicaciones terapéuticas, los complejos diseñados presentan un elevado índice de fotocitotoxicidad (PI = IC50,dark/IC50,light).
Características técnicas
Los complejos de Iridio(III) catiónicos de fórmula (Mn+)(X-)n se caracterizan porque el átomo de Iridio se encuentra coordinado a dos ligandos 2-fenilpiridinato, a través del átomo de nitrógeno del anillo piridina y uno de los átomos de carbono del grupo fenilo; y a un ligando derivado de β-carbolina, a través de dos átomos de nitrógeno. Estos complejos pueden ser empleados como fotocatalizadores en síntesis orgánica o como fotosensibizadores en terapia fotodinámica.
En síntesis orgánica, estos complejos permiten llevar a cabo la síntesis regioselectiva de 3-tiocianato indoles, en la posición C-3, mediante un procedimiento de tipo one-pot partir de las correspondientes indolinas. En primer lugar, se produce una deshidrogenación de la indolina y, posteriormente, la tiocianación de los respectivos indoles. Ambos pasos de reacción implican la utilización de oxígeno en presencia de luz y el uso de los complejos de Iridio(III) como fotocatalizadores.
Aplicaciones
Las potenciales aplicaciones de los nuevos complejos de Ir(III) son las siguientes:
- Reacciones de fotooxidación en síntesis orgánica.
- Empleo como fotocatalizadores en reacciones de tiocianación de índoles e indolinas.
- Uso como fotosensibilizadores en terapia fotodinámica en el tratamiento del cáncer.
- Elaboración de un medicamento para el tratamiento del cáncer, en combinación con radioterapia, es decir, en donde dicho medicamento se administra junto con, o antes de, la administración de radioterapia.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención P202031190
Estado actual de desarrollo
La tecnología relativa al método de sintesis esta desarrollada.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La invención proporciona nuevos copolímeros reticulados derivados de la ninhidirina, y su uso, en forma de película, membrana o gel, como sensores cromogénicos en presencia de aminoácidos, proteínas pequeñas o péptidos presentes en muestras acuosas, heridas, exudados de heridas, muestras biológicas y muestras médicas.
Presenta
La capacidad de cambio de color de los nuevos sensores en presencia de parámetros de cicatrización permite monitorizar la evolución de las heridas crónicas mediante parámetros RGB de una fotografía digital, anticipando el diagnóstico y tratamiento de los pacientes.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Las dificultades de cicatrización de heridas cutáneas, es un problema de primera magnitud que afecta aproximadamente al 1-2% de la población y genera gran sufrimiento a los pacientes, a la vez que supone un enorme coste económico.
El proceso de cicatrización es complejo y el diagnóstico y tratamiento de las heridas crónicas es un desafío. El personal médico, realiza estas valoraciones mediante inspecciones visuales para establecer tratamientos que pueden prolongarse durante largos períodos de tiempo.
Esa tecnología de monitorización basado en la detección cuantitativa de parámetros de cicatrización es un gran avance permitiendo realizar diagnósticos preventivos, control de infecciones en tiempo real, reduciendo considerablemente el tiempo de respuesta además del coste económico sanitario.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Su principal ventaja es la capacidad de detección de marcadores de cicatrización como es la proteasa, aminoácidos, proteínas pequeñas o pépticos presentes en medios acuosos y/o biológicos, mediante un simple cambio de color de manera rápida, sin manipulación previa, y sin interferentes.
Características técnicas
La síntesis de la estructura (I) derivada de ninhidrina dentro del propio material polimérico, mediante modificación directamente en las cadenas poliméricas, permite obtener un material estable durante años sin ningún tipo de almacenaje ni tratamiento especial.
Aplicaciones
Este desarrollo permite la detección, cuantificación y monitorización de heridas crónicas mediante la utilización de los parámetros RGB de una fotografía digital. El dispositivo de monitorización de heridas crónicas puede reducir el número de infecciones de los pacientes, disminuir las hospitalizaciones prolongadas, seguir la evolución de los pacientes después de recibir el alta hospitalaria y reducir las pruebas de laboratorio asociadas al diagnóstico de heridas crónicas.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención P202030077
Estado actual de desarrollo
La tecnología relativa al método de sintesis esta desarrollada.
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Electrónica, Informática y Telecomunicaciones (24)
Resumen de la tecnología
Aplicación móvil que permite anticiparse a la situación de riesgo para incrementar la atención del conductor durante el tramo de coincidencia con un vehículo frágil.
Esta aplicación recoge datos de geolocalización de los sujetos y los almacena de manera que las principales empresas que ofrecen servicios de GPS puedan utilizarlos para incluir una referencia en sus mapas.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Esta invención permite abordar un vacío existente en las aplicaciones de geolocalización y prevención de accidentes con vehículos frágiles, como ciclistas, en vías urbanas e interurbanas. DEVECA introduce la capacidad de comunicar la presencia de ciclistas, mejorando conciencia y seguridad vial.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Prevención de Accidentes: Anticipa situaciones de riesgo, permitiendo a los conductores aumentar su atención al aproximarse a lso ciclistas, lo que reduce la posibilidad de accidentes.
- Inclusividad: No requiere de infraestructuras adicionales, ya que funciona en dispositivos móviles estándar.
- Simplicidad: Es intuitiva para los ciclistas y conductores, permitiendo una curva de aprendizaje rápida.
Características técnicas
El software presenta el enfoque de un modelo de comunicación "publicador-suscriptor". En este esquema, la aplicación móvil actúa como el "publicador", notificando la ubicación de vehículos frágiles, como ciclistas, a otros dispositivos GPS en la vía. Esta comunicación se apoya en la utilización eficiente de la memoria, batería y sistema de geolocalización estándar presentes en los teléfonos inteligentes de los usuarios emisores.
La aplicación se distingue por su capacidad para integrarse con plataformas de geolocalización, las cuales poseen una extensa base de usuarios global. Este tipo de colaboraciónes amplía significativamente el alcance de la información sobre la presencia de ciclistas en las carreteras, ya que la aplicación móvil DEVECA puede recoger datos de geolocalización de los sujetos y almacenarlos de manera que utilicen como referencia en sus mapas. Este enfoque técnico no solo simplifica la implementación al no requerir infraestructuras adicionales, insumos o maquinaria, sino que también permite que tanto la aplicación publicadora como la consumidora de información se ejecuten de manera efectiva en dispositivos móviles estándar, facilitando su adopción por parte de los usuarios.
Además, la invención sugiere futuras aplicaciones, como la detección de otros vehículos en situaciones de riesgo y su potencial uso en el desarrollo de vehículos autónomos.
Aplicaciones
El software permite mejorar la seguridad vial al permitir que ciclistas compartan su posición en carreteras nacionales y locales. Su aplicación se extiende tanto a vías urbanas como interurbanas, enfocándose en prevenir accidentes causados por la falta de atención o el desconocimiento de la presencia de vehículos frágiles.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante sofware
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente concedida
software
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Herramienta de soporte a la toma de decisiones en la flexibilidad (volumen y mix) de producción (en particular, el PQ Problem de Goldratt extendido) basada en simulación híbrida (simulación discreta y simulación basada en agentes inteligentes).
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
En contraste con los enfoques tradicionales que utilizan métodos deterministas o heurísticos para la optimización de los sistemas de fabricación y producción, el enfoque innovador con el que cuenta PQ Problem Extended es el de abordar la complejidad intrínseca del PQ Problem y extenderlo con incertidumbre tanto en el volumen como en el mix mediante técnicas de modelado y simulación. Estos métodos permiten capturar tanto las interacciones internas del sistema de producción como las incertidumbres externas, lo que puede llevar a soluciones más realistas y efectivas. Al considerar situaciones estocásticas y aplicar enfoques de simulación basados en simulación discreta y agentes inteligentes, se supera la limitación de simplificación en los enfoques tradicionales y se logra una toma de decisiones más informada y eficiente en sistemas de producción complejos.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Permite identificar los problemas actuales y las potenciales mejoras en la secuenciación de los sistemas de fabricación y producción.
- Considera fuentes de incertidumbre, tanto en el volumen como en el mix de producción, lo que aumenta la utilidad práctica de las soluciones propuestas.
- Facilita la experimentación antes de implantar la toma de decisiones en sistemas de fabricación y producción reales.
Características técnicas
En líneas generales, el simulador PQ Problem Extended es una herramienta que permite experimentar con el conocido sistema de producción PQ Problem de Goldratt. Además, para ofrecer mayor realismo y cercanía a un sistema de producción real, el PQ Problem Extended ha sido extendido con incertidumbre tanto en el volumen como en el mix de producción. De esta manera, el PQ Problem Extended ofrece un adecuado marco de trabajo para analizar el comportamiento de los gestores y el impacto de sus decisiones sobre la flexibilidad de los sistemas de fabricación.
Para implementar este PQ Problem Extended, se han utilizado técnicas de modelado y simulación híbrida. El modelado se ha realizado a través de Redes de Petri, una alternativa común para modelar el dinamismo de sistemas basados en agentes, las cuales representan la operación del sistema de producción a lo largo del tiempo. Respecto a la simulación, por una parte, se ha utilizado simulación discreta para implementar una lista de eventos futuros, la cual es necesaria para avanzar el reloj de la simulación y gestionar la secuencia de eventos discretos que despliegan acciones. Por otra parte, se ha utilizado simulación basada en agentes inteligentes, ya que esta aproximación descentralizada se considera muy adecuada para analizar el complejo comportamiento de las sistemas de fabricación flexibles que son fuertemente construidos sobre interdependencias en entornos variables. Los sistemas son creados desde la interacción de sus unidades básicas, agentes, de manera que el sistema global se modela como un sistema multi-agente, donde los agentes individuales interactúan en un entorno cambiante y cooperan para alcanzar objetivos colectivos. No dude en ponerse en contacto con la Universidad de Burgos para ampliar la información sobre las características técnicas de este software.
Aplicaciones
Esta herramienta de simulación permite analizar el comportamiento de un sistema de fabricación teniendo en cuenta diferentes niveles de incertidumbre en el volumen de producción y en el mix de productos fabricados. Mediante la experimentación, es posible prever los resultados antes de realizar cambios en sistemas de producción reales. La herramienta ayuda en la toma de decisiones al identificar cómo estas fuentes de incertidumbre pueden afectar el desempeño económico del sistema. Además, proporciona a los administradores una visión del comportamiento del sistema a lo largo del tiempo.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante software
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente concedida
Software
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Herramienta software diseñada para ayudar la toma de decisiones y con ello mejorar la cadena de suministro basada en la simulación híbrida, simulando un comportamiento detallado de manera colaborativa y no colaborativa, a diferentes niveles de ruido.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La herramienta extiende el Beer Game de manera que permite la configuración tanto de diferentes niveles de incertidumbre como de la filosofía de trabajo de la cadena de suministro (colaborativa y no colaborativa). A través de la simulación, pueden experimentarse diferentes alternativas de las ofrecidas para facilitar la toma de decisiones.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Permite identificar los problemas actuales y las potenciales mejoras de una determinada cadena de suministro.
- Favorece el cambio de paradigma desde un enfoque no colaborativo hasta un enfoque colaborativo.
- Facilita la experimentación antes de implantar la toma de decisiones en cadenas de suministro reales.
Características técnicas
En líneas generales, el simulador Beer Game Extended es una herramienta que permite experimentar con el conocido sistema de producción y distribución Beer Game. Además de las dos clásicas fuentes de incertidumbre consideradas en el Beer Game, la demanda del consumidor y la distorsión causada por los tiempos de espera (producción y envíos) fijados, para ofrecer mayor realismo y cercanía a una cadena de suministro real, el Beer Game Extended ha sido extendido con diferentes fuentes de ruido: tasa de productos defectuosos, restricciones de capacidad de producción y de capacidad de transporte, costes de producción, costes de envío y costes de almacenamiento. De esta manera, el Beer Game Extended ofrece un adecuado marco de trabajo para analizar el comportamiento de los gestores y el impacto de sus decisiones sobre la dinámica de la cadena de suministro. Para implementar este Beer Game Extended, se han utilizado técnicas de modelado y simulación híbrida. Por una parte, se ha utilizado simulación discreta para implementar una lista de eventos futuros, la cual es necesaria para avanzar el reloj de la simulación y gestionar la secuencia de eventos discretos que despliegan acciones. Por otra parte, se ha utilizado simulación basada en agentes inteligentes, ya que esta aproximación descentralizada se considera muy adecuada para analizar el complejo comportamiento de las cadenas de suministro. De esta manera, la cadena de suministro ha sido modelada como un sistema multi-agente, donde los agentes individuales interactúan en un entorno y cooperan para alcanzar objetivos colectivos. No dude en ponerse en contacto con la Universidad de Burgos para ampliar la información sobre las características técnicas de este software.
Aplicaciones
El software permite ayudar a los gestores en el proceso de comprensión de los efectos subyacente a la hora de la toma de decisiones en todos aquellos sectores que contengan una cadena de suministros.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante software
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente concedida
Software
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Es una herramienta educativa de realidad virtual cuyo objetivo es aumentar el éxito en el aprendizaje de conceptos de informática básica.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
En las clases de informática básica, normalmente, no se realizan ejercicios prácticos sobre los componentes de un ordenador (montaje-desmontaje), debido al coste que supone. Este hecho podría traducirse en una carencia de conocimientos básicos (función y características principales de los componentes de un ordenador). Para cubrir esta necesidad se ha creado la herramienta PC Virtual LAB que pretende que los alumnos de titulaciones técnicas comprendan mejor la función y características principales de los componentes de un ordenador, y de esta forma, aumentar el éxito en el aprendizaje de la informática básica en un número muy amplio de alumnos.
Abrir un ordenador, extraer componentes o sustituirlos por otros supone un elevado coste. Por lo que esta herramienta resulta de gran valor ya que proporciona al alumno un medio para profundizar en estos conocimientos dentro y fuera del aula de manera autónoma.
Los resultados de la validación de este juego educativo muestran estadísticamente la mejora del rendimiento en el aprendizaje cuando se utiliza esta aplicación, comparando su uso con otras metodologías de aprendizaje más tradicional (visualización en pantallas planas de la misma aplicación o una clase tradicional en la que sólo el profesor tiene acceso al interior de un ordenador).
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
• Permite aumentar el éxito en el aprendizaje de conceptos de informática básica.
• Permite profundizar en estos conocimientos básicos fuera del aula de manera autónoma.
• Proporciona una formación básica de conocimientos informáticos.
• Permite comprender mejor la función y características principales de los componentes de un ordenador.
• Genera en el alumnado un mayor interés y compromiso en comparación con los entornos de aprendizaje convencionales.
Características técnicas
La principal novedad de esta herramienta es que se puede visualizar tanto en pantallas de ordenador como en entornos de Realidad Virtual. Esta herramienta educativa de realidad virtual permite "hacer" en lugar de limitarse a observar. Los estudiantes pueden aprender de forma experimental y avanzar de manera autónoma, convirtiéndose en los protagonistas de su propio aprendizaje. Además, el uso de la realidad virtual provoca un mayor interés y compromiso en comparación con los entornos de aprendizaje convencionales.
Aplicaciones
La herramienta esta específicamente desarrollado para estudiantes de informática básica, que mayoritariamente es un público joven. Si bien el principal público objetivo serían profesores de informática que quieran usar este juego educativo en clases o para que les recomienden a sus alumnos usarlo como complemento a lo visto en clase. En segundo lugar, estarían los alumnos que deseen aprender más sobre conceptos de informática y finalmente, entusiastas de la informática con inquietudes sobre los últimos avances de la informática. Respecto a entidades, la herramienta también está destinada a instituciones educativas para que decidan incorporar este juego junto a su metodología docente dentro de los programas de informática básica. Finalmente, existe otro objetivo más secundario que son las empresas tecnológicas de desarrollo de hardware y software que quieran cooperar en el desarrollo y la mejora de este simulador a cambio de que sus marcas aparezcan dentro de la aplicación.
Estado actual de desarrollo
El videojuego se encuentra de forma temporal disponible para su descarga gratuita en Steam con el nombre "PC Virtual LAB"
(https://store.steampowered.com/app/1825460/PC_Virtual_LAB/).
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ceQjUx9PMyc
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente solicitada
Sotware
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
El cáncer es una de las principales causas de muerte en el mundo. Por lo tanto, se necesitan nuevos agentes quimioterapéuticos mejorados. Los tambjamines son una clase de alcaloides marinos, con propiedades farmacológicas interesantes, incluyendo la actividad antitumoral. Inspirado en la estructura de estos compuestos hemos sintetizado una familia de análogos sintéticos que muestran una interesante actividad antitumoral "in vitro", promocionando la apoptosis en varias líneas celulares de cáncer.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Los compuestos descritos en esta invención exponen una interesante actividad antitumoral "in vitro" que muestran baja toxicidad contra las células normales. Su mecanismo de acción propuesto es su actividad ionofórica. Estos compuestos pueden funcionar como portadores de aniones alterando el equilibrio iónico de las células. Ellos son citotóxicos y a través de la actividad thios inducen a la apoptosis a indiferentes líneas de cáncer celular.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
El mecanismo de acción de estos compuestos les permite ser utilizados en líneas celulares resistentes contra las quimioterapias convencionales.
Características técnicas
Los compuestos descritos en esta invención se inspiran en la estructura de los alcaloides marinos que lleven una unidad de 4-methoxybipyrrol. La sustitución de esta parte por diferentes grupos examinados produce derivados activos. Estos compuestos pueden promover el transporte transmembrana de aniones tales como cloruro de una actividad ionofórica bicarbonate.La actividad ionofórica de estos compuestos cambia el pH intracelular de las células tratadas. Utilizando ensayos vitales tintados como el naranja de acridina (colorante) revelaron la desacidificación de los organelos ácidos como los lisosomas. Se sabe que este proceso desencadena la apoptosis y los valores de IC50 en el intervalo micromolar, los cuales se calcularon para estos compuestos en diferentes líneas celulares de cáncer.
Aplicaciones
Estos compuestos son de interés para empresas farmacéuticas que deseen llevar a cabo estudios preclínicos para evaluar su potencial en la clínica. Se pueden utilizar para el tratamiento de diferentes condiciones de cáncer.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente P201201039
Estado actual de desarrollo
Investigación o experimental
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Modelización eléctrica y topológica de redes de distribución eléctrica para su visualización en Google Earth y posteriores estudios de optimización y cálculos de flujos de cargas y capacidades de conexión de generadores eléctricos según RDC/DE/001/21 de la Comisión Nacional de los Mercados y la Competencia. Exportación del modelo a software a formato PTI RAW y Powerworld.
Software desarrollado para procesar los archivos de los distribuidores eléctricos y obtener un formato de archivos para software de cálculo de flujo de potencias.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Se automatiza el modelado de redes de distribución a partir de archivos que todos los distribuidores eléctricos de España tienen obligación de informar a la CNMC. Al ser de texto plano provenientes del GIS de cada distribuidor se unifica el formato de salida para visualizarlo en un software universal y gratuito (Google Earth).
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Permite visualizar de forma geolocalizada la corrección y consistencia de los datos numéricos de las redes de distribución.
- Se obtiene un modelo de red para su estudio en software de flujo de cargas que de otra manera sea muy laborioso obtener.
Características técnicas
El software, de sarrollado en Visual Basic NET, procesa las tablas de archivos de texto plano para generar los modelos de las redes y exportarlos en formato KML o de otro proveedor de software.
Aplicaciones
Procesado de archivos de los Distribuidores de Energía Eléctrica de España para visualización y posteriores cálculos de explotación.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Software desarrollado y validado para su uso.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial para procesado de datos y elaboración de informes técnicos.
Intellectual property status
Patente concedida
Software
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La aplicación permite obtener al usuario una ruta turística sobre una determinada población, propuesta según unas preferencias determinadas por él mismo. El usuario define las horas de comienzo y fin de la visita y qué características de la ciudad prefiere visitar (monumentos,
restaurantes, parques y jardines…). La aplicación devuelve una ruta calculada de forma personalizada teniendo en cuenta las preferencias y restricciones del usuario. Para ello, emplea información pública, actualizada periódicamente, a cerca de la población a visitar obtenida desde una BD; que se complementa con otra información obtenida por medio de los sensores del dispositivo en el que se ejecuta (S.O. Android).
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Existen en el mercado para dispositivos móviles numerosas aplicaciones que permiten principalmente dos cosas diferentes:
- (a) el cálculo de la ruta más rápida para alcanzar un único destino solicitado por el usuario (a modo de dispositivo GPS)
- (b) aplicaciones turísticas que proporcionan al usuario información a cerca de los lugares y actividades más destacadas de una población (a modo de guía de viajes).
Sin embargo, no existe ninguna aplicación que permita la recomendación de una ruta de interés turístico al usuario, que generalmente se compone de varios puntos geográficos de interés a visitar y que facilite un camino entre esos puntos.
La aplicación propuesta proporciona varias ventajas al usuario: no tiene que preocuparse por decidir por qué ruta o en qué orden alcanzar los puntos que se le sugieren; se asegura de que visitará los lugares más interesantes dentro del limite temporal que ha fijado; la ruta que se le proporciona no incluye puntos / actividades que difieran de sus gustos…
La aplicación se completa con características que facilitan su uso en el momento de realizar la ruta: indicando en que punto de la misma se encuentra en cada momento, almacenando las preferencias para futuras rutas o mostrando opiniones de otros usuarios a cerca de los puntos a visitar.
A todo esto se le añade la comodidad de poder consultar toda esta información desde un dispositivo móvil de su elección.
Características técnicas
La aplicación está construida empleando una arquitectura de cliente-servidor. El cliente consiste en una aplicación para el S.O. Android (empleado en una gran gama de dispositivos portátiles). Se emplea para que el usuario acceda a la aplicación, bien solicitando información o visualizando la que se ofrece. El servidor incluye una aplicación escrita en leguaje Java (altamente extendido y fácilmente portable entre S.O.)
junto con una B.D. MySQL que almacena y procesa datos geo-localizados provinienes del proyecto libre Open Street Maps. Esta parte se encarga de resolver las peticiones de los usuarios y transmitirlas a los dispositivos de consulta.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Se pretende que la aplicación se pueda considerar como complementaria a la información que pueda facilitar un trabajador en una oficina de turismo de cualquier población, con las ventajas añadidas de conocer por anticipado los gustos del usuario y poder consultarse en cualquier momento y lugar ya sea antes, durante o después de la visita.La aplicación pretende el facilitar la visita turística de cualquier población: - Por medio de la selección de preferencias, se permite que la ruta incluya siempre los lugares de la localidad a visitar que más puedan interesar al usuario, obviando el resto. El sistema es lo suficientemente flexible como para permitir un "grado de preferencia" por cada una de las grandes agrupaciones de puntos de interés (cultura, ocio, gastronomía y naturaleza) e incluso filtrar o no tipos de lugares sobre esas agrupaciones (p.ej. incluir "restaurantes", pero no "terrazas" dentro de "gastronomía").
Por medio de la clasificación de puntos obtenida de los datos de OpenStreetMap, junto con la valoración de puntos realizada por otros usuarios y la restricción de tiempo que proporciona el usuario actual, el sistema permite ofrecerle la visita de aquellos puntos más interesantes que puedan ser alcanzados en el tiempo de que dispone para la visita. Es decir, se maximiza el interés de la visita sin exceder un límite de tiempo establecido.- El calculo automático de la ruta permite al usuario despreocuparse de muchos detalles de la planificación de su visita: buscar mapas o guías de viaje, revisarlas, planificar una ruta o llevarlas consigo durante la visita… Dicha ruta se ofrece al usuario en el momento en que la solicita, utilizando además como base la información actual de su localización y la hora en que se solicita ésta.- Puede funcionar de manera similar con cualquier población del mundo, siempre que se dispongan de datos sobre la misma en el proyecto OpenStreetMap.
Aplicaciones
Puesto que la aplicación pretende la facilitación y mejora de la satisfacción en la visita turística a una población, uno de los principales beneficiarios puede ser el Ayuntamiento, Oficina de Turismo o cualquier otra entidad interesada en la promoción del turismo en la localidad.La aplicación funciona de manera genérica con cualquier población del mundo, siempre que se dispongan de datos sobre la misma en el proyecto Open Street Maps.Aunque en principio la aplicación está desarrollada para la visita de una única localidad, se puede adaptar al calculo de rutas entre varias localidades.Ya que las rutas pueden incluir locales de restauración, ocio u otras atracciones y se guarda información a cerca de cada uno en la B.D., se contempla la posibilidad de que dichos locales se promocionen a sus potenciales clientes por medio de la aplicación. De esta forma, siempre que el usuario final de la aplicación solicite incluir en su ruta puntos asociados a la categoría correspondiente, se pueden incluir con mayor preeminencia en la ruta aquellos negocios que se encuentren suscritos a este servicio. Esta forma de publicidad cuenta con la ventaja de ser muy poco intrusiva y en teoría más eficaz, ya que se presenta al potencial cliente en el momento en que demanda de ese servicio/actividad.
Propiedad intelectual
Registro de Software realizado en la Oficina Provincial del registro Central de la Propiedad Intelectual de Burgos (solicitud BU-143-13)
Estado actual de desarrollo
Software desarrollado
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente concedida
BU-143-13
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La Universidad de Burgos cuenta con equipo de Tomografía axial computarizada (TAC) de alta resolución 3D para realizar digitalizaciones rápidas y precisas de pequeños objetos. Así mismo cuenta con un sofisticado equipo para Fabricación rápida de réplicas de alta precisión mediante Sinterizado Láser de polvo de poliamida que además permite reproducir en un solo paso partes externas e internas, mecanismos, etc. Son moldes de poliamida de alta resolución creados a partir de modelos digitales 3D generados por cualquier técnica (TAC, CAD, escáner…).
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
1. Se trata de TÉCNICAS DE ANÁLISIS NO DESTRUCTIVAS.
2. Con el TAC se puede visualizar el interior de los objetos.
3. El modelo digital 3D del objeto permite reconstruir partes perdidas, permite al observador interactuar activamente con el objeto, sirve para intercambiar rápidamente información muy precisa entre especialistas.
4. El modelo 3D permite obtener sin manipular el original y de manera rápida y exacta, réplicas tridimensionales de alta resolución a partir de los diseños que han sido generados mediante otras aplicaciones como CAD, el TAC o el escáner 3D de superficie.
5. Almacenamiento de información estructural y morfológica muy precisa de objetos del Patrimonio Cultural.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Potente herramienta no destructiva para el estudio y análisis de la estructura externa e interna de objetos. Aplicable a muy diversos materiales (hueso, plástico, metal, piedra …). Permite abordar aspectos como la densidad, el volumen, la porosidad, fracturación etc. Muy potente en contextos paleontológicos, arqueológicos, industriales y patrimoniales.
Características técnicas
Potente herramienta no destructiva para el estudio y análisis de la estructura externa e interna de objetos. Aplicable a muy diversos materiales (hueso, plástico, metal, piedra). Permite abordar aspectos como la densidad, el volumen, la porosidad, fracturación etc… Muy potente en contextos paleontológicos, arqueológicos, industriales y patrimoniales.
Digitalización 3D de superficies sin contacto mediante Escáner Láser de alta precisión: Digitalizar con gran precisión la superficie de cualquier objeto para generar modelos virtuales 3D que pueden ser utilizados en múltiples ámbitos de investigación, docencia o difusión del conocimiento. Para pequeñas superficies del K-Scan Krypton K-610 de la casa Metrics.
Nubes de puntos e imágenes 3D: Los escáner láser 3D generan nubes de puntos de la superficie de un objeto que deben ser convertidas en superficies continuas (reconstrucción) a fin de generar modelos virtuales e imágenes 3D optimizadas para su posterior uso en diversos campos (investigación, difusión…)
Producción rápida de réplicas de alta precisión en plástico de poliamida mediante Sinterizado Láser: Producción de moldes de poliamida de alta resolución a partir de modelos digitales 3D generados por cualquier técnica (TAC, CAD, escáner…). Permite reproducir en un solo paso partes externas e internas, mecanismos, etc… Aplicable a las más diversas áreas industriales, científicas o culturales (automoción, aeronáutica restauración, educación, medicina, arqueología, paleontología, arquitectura …). Las piezas son resistentes, flexibles, duraderas y mecanizables.
Aplicaciones
Aplicables a las más diversas áreas industriales, científicas o culturales (automoción, aeronáutica restauración, educación, medicina, arqueología, paleontología, arquitectura, etc.). Los modelos digitales son muy exactos y las reproducciones físicas son resistentes, flexibles, duraderas y mecanizables. Estas técnicas son imprescindibles para la conservación del Patrimonio, ya que una pérdida de cualquier objeto de cultura material es una pérdida irreparable. Gracias a las digitalizaciones y fabricación de réplicas, podemos tener, tanto de manera virtual como física, réplicas exactas de estos objetos y poder exponerlos a toda la humanidad, sin que sufran ningún deterioro. Así mismo, es de gran importancia el que todas las piezas de los museos estén digitalizadas a modo de prevención, así como para una buena documentación y difusión de las mismas.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Disponibles resultados de pruebas
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Aplicación diseñada para resolver problemas de desplazamiento urbano y aparcamiento, destinada a personas con discapacidad o movilidad reducida.
El funcionamiento se basa en un intercambio de información sobre la disponibilidad de plazas reservadas a personas con movilidad reducida o discapacidad en un entorno determinado, como puede ser una ciudad, un municipio, etc.
El usuario deja su posición marcando la plaza como en uso para que otros usuarios conozcan que se encuentra ocupada y cuáles son las plazas alternativas más cercanas.
Actualmente la información de ocupación la introducen los propios usuarios pero cabe la posibilidad de ampliarlo con sensores u otras formas de incorporar la información sobre el uso y ocupación de un aparcamiento.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Esta aplicación aprovecha las posibilidades de los teléfonos móviles para fijar, fundamentalmente mediante satélite, la posición del usuario y se benefician de la información del entorno.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Conocimiento previo por parte del usuario, personas con discapacidad o movilidad reducida, de la disponiblidad de plazas para el estacionamiento, evitando el traslado o desplazamiento en caso de ocupación total.
Características técnicas
Aplicación cliente servidor para dispositivos móviles Android cuyo objetivo es conocer la disponibilidad de plazas reservadas a personas con movilidad reducida o discapacidad en un entorno determinado facilitando de esta forma su día a día.
Aplicaciones
Se puede utilizar en cualquier población o municipio que disponga de plazas de aparcamiento para personas con alguna discapacidad.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Prototipo funcional o muestras listas para pruebas
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente concedida
APP
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La visita virtual o interactiva consiste en recrear mediante un ordenador un elemento real como puede ser un paisaje, un entorno urbano, el interior de un establecimiento..., permitiendo al observador desplazarse a través de dicho entorno y obtener información de los diferentes elementos incluidos en él, como por ejemplo, datos históricos, características de un producto, nombre de una tienda y precio de los productos.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
El acceso a estas visitas es, generalmente, a través de la web, lo que permite el acceso universal a los lugares visitados y también permite poner a disposición del visitante información complementaria pero integrada en la visita, como son recursos de audio, vídeo y otros.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
La principal ventaja que ofrecemos es la realización de todas las fases de la actividad agrupadas, frente a la multiplicidad de empresas que son necesarias en otros casos: fotografía, diseño, informática... Esto supone un claro ahorro, tanto de tiempo como de dinero.
El hecho de poder contar, en el mismo grupo de investigación, con personas procedentes de diferentes campos de actividad, dota de valor añadido a nuestra oferta ya que posibilita la solución de problemas que, de otro modo, harían necesario el recurso a terceras personas o empresas con el consiguiente aumento del precio y del tiempo invertido.
Otra ventaja es la rápida incorporación a nuestros mecanismos de trabajo de los resultados obtenidos en sus investigaciones por los miembros de nuestro grupo, lo cual redunda en una mayor calidad y mejor servicio al cliente.
Características técnicas
A través de tomas fotográficas, mediante el software, se generan las visitas virtuales. A las imágenes se las aplica una serie de correcciones iniciales, tras lo cual pasan a ser tratadas mediante el software correspondiente, que permite correcciones en la proyección y enlazado de las fotos. Tras verificar la correcta calidad de la fusión de la imagen final se procede a su renderizado y a una nueva fase de control que permite eliminar detalles que hubiesen pasado inadvertidos en etapas anteriores.
La imagen final, así preparada es adaptada al visor utilizado por el cliente, generalmente de tipo Flash debido a su universalidad y su independencia de plataformas y versiones.
En esta adaptación se incluyen referencias añadidas en la foto así como hipervínculos que permiten saltar de unos puntos a otros del panorama o proporcionar información suplementaria documental o multimedia.
En la actualidad, y en proceso de desarrollo, estamos añadiendo la posibilidad de efectuar la conexión entre las imágenes y bases de datos para proporcionar valor añadido a las visitas virtuales.
Aplicaciones
La principal utilidad de las guías virtuales y/o interactivas radica en la puesta a disposición de un público prácticamente universal de aquellos elementos visuales propios de cada negocio que quieran ser difundidos y estén interesados por dar a conocer su territorio o sus instalaciones de forma interactiva para el usuario. El poder controlar la cantidad y la calidad de la información que complementa la información visual es muy importante.
Las empresas y organismos a quienes van dirigidos estas guías son muy variados cubriendo desde la pequeña empresa, que a través de su implantación en Internet quiere darse a conocer físicamente, hasta la gran empresa u organismo que quiere poner en conocimiento del público aquellas partes de sus instalaciones y técnicas de trabajo que considere oportunas.
Las empresas, particularmente aquellas que se dedican a la hostelería, venta de viviendas, actividades recreativas, residencias, etc. son destinatarias de las visitas virtuales, sobre todo si se ven acompañadas de la posibilidad de hacerse con datos valiosos ya sean multimedia, ya procedan de una base de datos.
También lo son aquellas administraciones públicas como ayuntamientos, diputaciones, museos, etc. que deseen dar a conocer su patrimonio o sus instalaciones de forma virtual y atractiva a posibles futuros visitantes.
Para ello cuentan con estas tecnologías como herramienta de primer orden para dar a conocer al gran público el objeto de su trabajo de forma pormenorizada.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Debido a la naturaleza híbrida de la mayoría de los problemas de la vida real, se deben aplicar tanto los datos como el conocimiento para encontrar una solución adecuada. De acuerdo con esta idea, los sistemas inteligentes híbridos combinan diferentes técnicas y paradigmas (simbólicos y sub-simbólicos) de inteligencia artificial para construir modelos de resolución de problemas más robustos y confiables.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Los Sistemas Inteligentes Artificiales Híbridos (HAIS) demostraron superar las propuestas anteriores cuando se trata de problemas complejos y de la vida real. Este nuevo paradigma del campo de la IA (inteligencia artificial) permite la aplicación exitosa de técnicas y modelos combinados para tratar problemas complejos.
Los HAIS se han aplicado a muchos problemas diferentes, obteniendo buenos resultados de rendimiento.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Mediante la combinación de diferentes tecnologías de IA, se superan las limitaciones de modelos y paradigmas individuales.
Características técnicas
El grupo de investigación cuenta con una amplia experiencia en el diseño, desarrollo y despliegue de este tipo de sistemas inteligentes, para resolver problemas prácticos de muy diversas aplicaciones: ajuste de parámetros de máquinas-herramienta, seguridad de redes, gestión del conocimiento, etc.
Requiere elegir las técnicas adecuadas (Redes Neuronales Artificiales, modelos de aprendizaje automático, técnicas de aprendizaje evolutivo, mecanismos de optimización, etc.) y combinarlas para cada uno de los problemas, ajustándose a la naturaleza específica del problema.
Aplicaciones
Problemas de carácter híbrido, cuya solución requiere la combinación de diferentes técnicas.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Resultados de pruebas disponibles
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Se trata de un conjunto de software socio-comunicativo que ha sido diseñado para ser utilizado por personas con Trastornos del Espectro del Autismo o por aquellas personas que tengan dificultades para desenvolverse en situaciones sociales con diversos niveles de dificultad, como pueden ser personas con daño cerebral, fobia social, trastorno de aprendizaje no verbal, trastorno específico del lenguaje entre otros. Su fin es facilitar la comprensión de circunstancias complejas a estas personas.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La mayoría de los trabajos relacionados solo están destinados a plataformas iOS (iPhone y iPad). Estos dispositivos tienen un alto costo. En cambio Socio-Ruta, al estar desarrollado para plataformas Android tiene la ventaja de poder funcionar en tablets Android de bajo coste (hasta 10 veces inferior que un iPad). De esta manera Socio-Ruta puede llegar a más gente y a un precio mucho mas reducido.
• Se pueden crear guiones personalizados, ofreciendo de esta manera la opción de poder crear un guión para cada caso distinto.
• La aplicación resultante puede ser reutilizable para otros usos que no fuesen el original.
• Mediante la edición de grafos se pueden construir por ejemplo test de cualquier tipo y con cualquier finalidad.
• Se podría contemplar la opción de realizar una aplicación de escritorio para el usuario final, para poder llegar a un público más amplio.
• No existe a día de hoy ninguna herramienta de este tipo en castellano.
Características técnicas
Software basado en ordenador de sobremesa para la creación de guiones sociales y Android para su visualización por parte de las personas con TEA.
Para ayudar a las personas con TEA, los tutores disponen de una aplicación Java de escritorio con la cual pueden generar complejos guiones mientras que los usuarios finales disponen de una aplicación Android para tablets, en la cual pueden acceder a un conjunto de guiones sociales que responden a diversos entornos (escuela, trabajo, calle, encuentros en el hogar, centro de día…) y a diversas situaciones o relaciones sociales qué frecuentemente se desarrollan en esos entornos o suponen un problema para la persona con el déficit social. Estos guiones representan la fragmentación estructurada paso a paso del desarrollo de situaciones sociales que pueden representar diferentes niveles de complejidad.
Es totalmente modelable a las necesidades individuales, se pueden añadir nuevos guiones de forma sencilla por los educadores, familiares o por la propia persona, teniendo en cuenta sus situaciones sociales particulares, su edad, sus preferencias y la complejidad que pueda manejar el niño o adulto que lo vaya a utilizar. Así, se pueden escoger los contenidos que presenta (imágenes, vídeos o audios) y también su nivel de complejidad en función de si el niño puede o no manejar categorías y componer frases. Este software también se podría readaptar para entornos educativos a todos los niveles para complementar el método tradicional de enseñanza con nuevas tecnologías.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
• Producto específico.
• Idioma castellano.
• Personalización de guiones.
• Posibilidad de expansión mediante traducción.
Aplicaciones
Además de los centros de autismo, puede ser útil para formación en ámbito doméstico y así complementar la educación de dichos centros. También puede ser aplicable a otros tipos de centros educativos como colegios, institutos o universidades.
Propiedad Intelectual
Programa de Ordendor con Copyright - BU-144-13
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente concedida
BU-144-13
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La tecnología desarrollada es una aplicación que permite de manera transparente al usuario utilizar todas las funciones del ordenador mediante un teclado y ratón virtual de barrido.
La aplicación ha sido diseñada para facilitar el manejo de ordenadores a personas con diferentes niveles de discapacidad, así como deficiencias motoras o visuales. Permite realizar todas las acciones que se pueden hacer con un teclado y ratón tradicionales, a través de una interfaz visual (teclado y ratón virtual de barrido). Se trata de una aplicación sencilla, atractiva y altamente configurable.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Cada uno de los usuarios puede guardar sus opciones de configuración y trasladarlas de un ordenador a otro. Arranque automático del interfaz para la siguiente sesión dando autonomía a cada usuario.
Que la aplicación sea transparente al usuario y al resto del sistema le permite ser usado en cualquier tipo de entorno y aplicación que necesite el uso combinado de teclado y ratón, como son los editores de texto, calculadoras, navegadores web o aplicaciones gráficas como programas de retoque fotográfico.
Permite la asociación personalizada de sonidos (o fonemas) a cada uno de los caracteres en el momento de su selección facilitando y reforzando el aprendizaje.
Existe una página web (http://www.interfazenpantalla.com ) donde pueden verse los aspectos relacionados con el proyecto y descargarse los manuales. Se incluyen videos mostrando su uso por parte de usuarios en aplicaciones reales.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Analizando las características de los productos similares que se encuentran actualmente en el mercado, nos encontramos con que las principales ventajas son que no es absolutamente necesaria la utilización de un ratón físico, y que el programa puede ser configurado en relación a las necesidades del usuario (incluidas personas con deficiencias visuales). La selección de colores para cada una de las letras del teclado es indicada para su uso con niños en etapas de aprendizaje.
Características técnicas
Resuelve para las personas con discapacidades físicas relacionadas con problemas motores el acceso a los entornos informáticos y que normalmente se realiza con dispositivos como teclados y ratones convencionales o adaptados.
Funciona mediante una interfaz gráfica configurable que representa un teclado y un ratón en la pantalla del ordenador, a través de la cual, realizando un barrido por las diferentes opciones, se selecciona la tecla/botón/función deseada.
Presenta la característica de permitir configurar varias opciones tanto visuales, como auditivas y también de velocidad, de forma que se adapta a las diferentes necesidades de un mismo usuario.
En algunos casos se facilita la interacción con el ordenador y en otros, se mejora la destreza en el manejo.
Aplicaciones
- Según datos estadísticos, el número de personas en España con discapacidad alcanza los 3,8 millones, lo que supone casi el 9% de la población. De ellos, 120.000 tienen parálisis cerebral. Los grados de intensidad de la misma varían: hay personas con una parálisis apenas apreciable y otras, que necesitan a terceras personas para desenvolverse y desarrollar su vida diaria. La aplicación podría ser utilizada por el porcentaje de población indicado, pero el acceso a los usuarios puede ser por distintas vías:
- Particulares: Puede ser utilizado tanto por hombres como por mujeres, sin límite de edad que dispongan de un ordenador en su domicilio.
- Asociaciones, fundaciones, servicios sociales.
- Colegios públicos o privados: Aquellos que presentan programas de integración para discapacitados.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante registro propiedad intelectual BU-157-12
Estado actual de desarrollo
Disponibles resultados de pruebas
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente concedida
BU-157-12
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Juego de fichas basado en realidad virtual para discapacitados. Una herramienta donde niños con parálisis cerebral interactúan con el ordenador mediante el uso de fichas debidamente diseñadas que pueden ser reconocidas por una cámara web y, acto seguido, mostrar por pantalla, en el lugar donde estaría la ficha, una frase, imagen en 2D o 3D, según corresponda con la combinación de dichas fichas.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La técnica del visionado de las fichas mediante la cámara y la posterior representación en pantalla del concepto que representan las mismas recibe el nombre de realidad aumentada. Este proceso se ha realizado con la colaboración de la Asociación de Parálisis Cerebral de Burgos (APACE).
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Nos encontramos ante la dificultad que puede encontrar al manejar un ordenador una persona con parálisis cerebral y mucho más si se trata de un niño. Además de que se trata de unas personas que al tener grandes problemas motores, al utilizar las herramientas de aprendizaje tales como puzles, aunque muy sencillos, les provoca mucha frustración ya que por la enfermedad son muchas veces incapaces de interactuar correctamente con ellos. Apoyándonos en el uso de la cámara web y en la realidad aumentada conseguimos un entorno muy visual y atractivo para ellos ya que ven el lugar en el que se encuentran en pantalla, combinado con gráficos o textos que cambian de posición al mismo tiempo que ellos mueven las fichas que se les proporciona. Pretendemos el acercamiento de estos usuarios al manejo del ordenador, que les sea útil y estimulante, aunque no manejen las aplicaciones y programas típicos de una computadora.
Características técnicas
La aplicación está escrita en el lenguaje orientado a objetos Action Script (similar a Java) desarrollado por ADOBE y que es de libre distribución. Las librerías necesarias para el funcionamiento del proyecto son:
- Papervision 3D que se usa para hacer un soporte gráfico para la aplicación y que es software libre. Programada en Action Script.
- FLARToolKit que se usa para el tratamiento de las fichas de realidad aumentada, la cámara web y las imágenes en 3D. En este caso tiene una licencia GNU que consiste en que no hay que pagar una licencia si la aplicación que realizamos no se utiliza con fines comerciales, en caso contrario, habría que pagar para poder desarrollar y hacer rentable la idea. Programada en Action Script.
Los modelos en 3D están diseñados en el programa de libre distribución Blender.
Aplicaciones
Esta herramienta, aunque esté destinada al aprendizaje y estimulación de las personas con parálisis cerebral, es para uso y apoyo de los psicólogos y terapeutas y en ningún caso la utilizará el paciente/alumno en solitario. En otras palabras, es una herramienta didáctica para el uso de docentes de educación especial. Se puede decir que el desarrollo de aplicaciones en el campo de la realidad aumentada está bastante avanzado y cubre bastantes campos como pueden ser los videojuegos, el marketing de empresas, telefonía móvil… En cambio, en el sector en el que nos vamos a mover nosotros no tenemos constancia de que exista ninguna herramienta parecida y dirigida a este colectivo con este tipo de problemas.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Prototipo de trabajo o muestras listas para pruebas
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente solicitada
En trámite
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La Universidad de Burgos ha desarrollado una aplicación web, accesible desde un navegador, que implementa una herramienta para el análisis de tráfico. Para ello, utiliza datos GPS de vehículos que se están desplazando y estos datos sirven para obtener una muestra del tráfico durante sus desplazamientos. El uso de tecnología Big Data en la monitorización y análisis de actividades de transporte en el mundo físico (mercancías o pasajeros) permitirá a las empresas contratantes, tanto la extracción de conclusiones a cerca de los procesos de transporte o logística que tienen actualmente implantados, como la predicción de las condiciones de los desplazamientos en el futuro próximo, pudiendo planificar o adelantarse a diferentes situaciones y permitiendo, por tanto, una optimización de sus actividades. Este tipo de servicio puede resultar muy provechoso a empresas de mensajería, logística de transporte, transporte de pasajeros (taxis o autobuses), administraciones públicas o ayuntamientos, etc.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Existen diversas soluciones de software comercial dedicadas al análisis del tráfico. Estas empresas realizan el análisis utilizando datos geoespaciales y cámaras de tráfico principalmente. El software TraVisAna se basa en el análisis de trayectorias GPS lo que abarata en coste en infraestructuras ya que solamente es necesario un dispositivo con GPS y, a día de hoy, casi todos los vehículos públicos y privados cuentan con uno. Al igual que estas soluciones se necesita una aplicación que se ejecute en un servidor y en estos dispositivos para poder recoger las rutas y analizarlas.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- El tratamiento de los datos generados permite identificar los segmentos de tráfico en que se puede dividir la actividad de transporte y analizar e incluso predecir, la dirección y velocidad del tráfico.
- Solamente es necesario un dispositivo con GPS.
- Es configurable y de fácil manejo.
- No se depende en exceso de los datos geoespaciales, haciendo la aplicación adaptable a cualquier ciudad, lo que ahorra costes en software de este tipo.
- La app también puede recabar información de peatones, bicicletas o patinetes.
- Dividiendo los datos se puede hacer análisis más pormenorizados por barrios, sectores, horas o días concretos.
- El coste es mucho más reducido que otras soluciones existentes, ya que solo se incurre en gastos de alquiler o compra del servidor y el mantenimiento de la aplicación; lo que hace el servicio asequible para PYMES o empresas de menor tamaño, que pueden obtener información relevante en su área de negocio.
Características técnicas
El prototipo se basa en la tecnología de Big Data y en la “Aplicación de análisis del tráfico mediante rutas de geoposición (AATRG)”. Aunando ambas tecnologías, es posible construir, a partir de los datos en bruto recabados a través de los dispositivos GPS de los usuarios, un modelo del estado del tráfico. Mediante esta tecnología se puede procesar grandes cantidades de datos en bruto y enriquecer esos datos con información de otras fuentes. Mediante el procesado de los datos enriquecidos se genera un modelo que permite describir y analizar la información contenida en esos datos.
El modelo generado en el prototipo es un grafo dirigido que describe el tráfico entre diferentes localizaciones de la ciudad. Este grafo lleva asociada información adicional en sus relaciones tales como velocidad media y densidad del tráfico. Representando este grafo de forma gráfica sobre un mapa, permite de forma visual comprender el estado del tráfico. Además, es posible realizar predicciones de días y horas concretas, para que las empresas puedan adaptar su logística a las condiciones diarias. Esto permitiría a las empresas de transporte y logísticas adaptarse a los cambios diarios en el tráfico con el fin de optimizar sus recursos lo cual mejoraría su competitividad.
Aplicaciones
- Proporcionar tanto servicios de consultoría y análisis personalizados como aplicaciones a medida que permitan el análisis a la propia empresa.
- Empresas de transporte y reparto de paquetería o mercancías, que les permitiría ir un paso más allá en la optimización de las rutas planificadas
- Administraciones públicas, ayuntamientos y aquellas empresas subcontratadas por estos, ya que permite un análisis del tráfico que resulta clave para el desarrollo de estrategias conocidas como Smart Cities o el de Destinos Turísticos Inteligentes.
- Administraciones públicas ya que permite tomar decisiones informadas para la regulación de semáforos, planificación del sistema público de transporte urbano, planificación de sistemas de emergencias (ambulancias, evacuación por emergencias), planes urbanísticos y en general todo tipo de decisiones que puedan afectar al tráfico.
- Usuarios particulares que bien son trabajadores autónomos cuya actividad comercial depende del transporte urbano, bien son desarrolladores de otras aplicaciones que pueden emplear los datos de tráfico procesados para su propio funcionamiento o bien simplemente desean conocer el estado del tráfico en su ciudad para planificar sus propios desplazamientos.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante registro de software BU-121-20
Estado actual de desarrollo
Software desarrollado y en constante mejora.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente concedida
BU-121-20
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La herramienta desarrollada permite la automatización, registro y evaluación de la “Escala de detección de Habilidades Funcionales en niños de 0-6 años” (e-EarlyCare) y la elaboración de programas personalizados a través de una aplicación web. Esta aplicación está destinada a profesionales de centros de Atención Temprana, específicos de Educación Especial y otros centros que realicen intervenciones en edades tempranas. Asimismo, se puede aplicar en otros centros como Residencias de mayores, Centros de rehabilitación de lesiones modulares, etc.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
El objetivo de la aplicación es la automatización, registro y evaluación de la Escala de detección de Habilidades Funcionales en usuarios con edades de desarrollo evolutivo de 0-6 años y, como resultado de la evaluación, la concreción de las áreas funcionales prioritarias para la intervención terapéutica, a través de una aplicación web (eEarlyCare Therapeutic Program).
Esta aplicación permite la corrección e interpretación del desarrollo del usuario en las 11 dimensiones de análisis funcional que mide la Escala: Autonomía en la alimentación, Cuidado e higiene personal, Autonomía de vestido y desvestido, Control de esfínteres, Movilidad funcional, Comunicación y Lenguaje, Habilidades de interacción social, Juego interactivo y simbólico, Rutinas de la vida diaria, Conducta adaptativa y Atención.
Además, facilita un programa de intervención personalizado para cada usuario que abarca las distintas áreas funcionales en las que se ha detectado afectación.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Permite la automatización del registro y de la interpretación, lo que va a facilitar su uso a profesionales de centros de Atención Temprana, Centros Específicos de Educación Especial y otros centros que realicen intervenciones en estas edades ya sean dependientes de Ayuntamientos, Diputaciones o Comunidades Autónomas.
- La interpretación de los resultados se produce prácticamente en tiempo real para conocer el desarrollo funcional del usuario.
- Permite el seguimiento individualizado de un usuario y la comparativa del desarrollo en las habilidades funcionales de distintos usuarios de un mismo centro.
- Las tecnologías utilizadas para el desarrollo de la aplicación web facilitan visualizaciones e interactividad de gran calidad y permite el almacenamiento de los datos en bases en ficheros o en la nube.
- La tecnología posibilita la realización de análisis estadísticos más complejos con aplicación de técnicas de Machine Learning supervisado (clasificación y/o regresión) y no supervisado (Clustering) a través de la exportación de los ficheros a paquetes estadísticos más potentes. En concreto las técnicas de clasificación son de gran utilidad para la propuesta de aprendizaje personalizado.
- Su uso permite potenciar la eficacia y la rentabilización de los recursos del centro donde se implementa.
- La aplicación está orientada a un entorno de escritorio por su facilidad de instalación y recursos necesarios.
- La ampliación permite elaborar programas personalizados de intervención terapéutica en las áreas en las que se han detectado afectación.
Características técnicas
La aplicación diseñada consiste en una escala de desarrollo en habilidades funcionales (EHFI), un algoritmo para la corrección e interpretación a través de gráficas de visualización y un software (eEarlyCare Therapeutic Program) de registro, interpretación y visualización de los resultados de la evaluación del usuario para edades de 0-6 años en habilidades funcionales. Este software permite al profesional de la intervención la realización de evaluaciones trimestrales sobre el desarrollo de los usuarios tanto a nivel individual como grupal. Toda esta información se representa en gráficas que pueden ser exportadas a formato png y/o pdf. También, admite la exportación de los registros de la evaluación a hojas Excel. Asimismo, la aplicación se ofrece en formato bilingüe español-inglés.
Aplicaciones
Las potenciales aplicaciones del software desarrollado son las siguientes:
- La automatización de la medición de las habilidades funcionales en usuarios con edades de desarrollo evolutivo 0-6 años.
- Concreción de las áreas funcionales prioritarias para la intervención terapéutica en el usuario.
- Seguimiento individualizado de evaluación en la adquisición de dichas habilidades funcionales en un usuario y/o un grupo de usuarios en centros de educación o de terapia en edades de desarrollo 0-6 años.
- La edad cronológica puede ser mayor por lo que se amplía el radio de intervención también a personas con patologías involutivas como demencias seniles, preseniles o afectaciones en las áreas de autonomía.
- Su uso sería aplicable también en Residencias de mayores o centros de rehabilitación de lesiones medulares, con el objetivo de estudiar la evolución de estas habilidades funcionales en patologías como demencias preseniles y seniles (Alzheimer…), ictus, ACV, lesiones medulares, etc.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante registro de propiedad intelectual BU-120-20
Estado actual de desarrollo
Software desarrollado y en constante mejora.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente solicitada
BU-120-20
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Se describe fotocatalizadores de rutenio (II) de fórmula (M+)nXn-, en el que Xn- es un anión y M+ es un complejo catiónico de fórmula (la) que comprenden un ligando 8-arilsulfonamidoquinolina, así como su procedimiento de obtención. También se describe el uso de dichos fotocatalizadores de rutenio (II) en la síntesis de iminas mediante fotooxidación de aminas en presencia de oxígeno y mediante la utilización de luz visible.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
El procedimiento de síntesis de complejos monocatiónicos de Ru (II) de tipo polipiridínico descrito, presenta actividad como fotocatalizadores a pesar de no ser considerados como buenos candidatos para fotocatálisis según el estado de la técnica. En concreto, los complejos de Ru (II) de la invención, presentan una estabilidad superior a los fotocatalizadores equivalentes conocidos en el estado de la técnica, como los complejos de rutenio (II) del tipo, [Ru(bipi)3]2+ .
Además, los complejos de rutenio (II) de la invención proporcionan un elevado rendimiento para la conversión de aminas en iminas (mayores del 90 %), con muy buena selectividad y sin producir productos secundarios no deseados. Este procedimiento de síntesis de iminas se realiza en presencia de O2 irradiando con luz visible a temperatura ambiente, entre 20-30 oC.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Conversiones de bencilamina a imina con rendimientos superiores al 90 % y sin aditivos, a temperatura ambiente y con el uso de oxígeno o aire como agente oxidante.
- La utilización de la luz visible, permite llevar a cabo la síntesis con sustratos más sensibles a la sobreoxidacion o la degradación de sus productos por fotoactivación de enlaces, evitando la formación de productos secundarios no deseados.
- Presentar una fotoestabilidad igual o superior a la de los complejos análogos del estado de la técnica de rutenio (II) de fórmula [Ru(bipi)3]2+.
- Procedimiento más selectivo y con óptimos rendimientos.
Características técnicas
Diseño de nuevos fotosensibilizadores de Ru (II) que contienen 8-arilsulfonamidoquinolinas y la evaluación exitosa de sus propiedades fotocatalíticas, en un nuevo método de oxidación suave y selectiva de bencilaminas primarias y secundarias utilizando O2 como oxidante.
En este método propuesto, deben destacarse tres características clave: la capacidad de fotosensibilización de los complejos Ru (II) que promueve la producción de O2; La naturaleza electrofílica del O2 que facilita su reacción con las aminas nucleofílicas y el carácter ácido débil del H2O2 generado in situ que ayuda a la activación catalítica de la aldimina primaria.
Aplicaciones
- Síntesis de nuevos fármacos y realización de diagnósticos debido a su interacción con el ADN.
- Actuación como luminóforos en técnicas de Bioimaging (visualización celular).
- Terapia fotodinámica (Photodynamic Therapy, PDT). Algunos de estos complejos de Ru(II) son conocidos por su actividad citotóxica tras su irradiación con luz, generándose oxígeno singlete altamente reactivo que provoca la muerte celular.
- Fotocatálisis actuando como fotosensibilizadores (PS) en reacciones orgánicas sintéticas o en producción de hidrógeno.
- Dispositivos electroluminiscentes como diodos de emisión LED, incluyendo también los de tipo OLED (Organic Light Emiting Diodes).
- Obtención de Sulfóxidos a partir de la oxidación de sulfuros de aplicación en la obtención de distintos fármacos.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención P202030245
Estado actual de desarrollo
La tecnología relativa al método de sintesis esta desarrollada.
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Dispositivo inteligente enfocado a la gestión total del agua en tiempo real. Aplicable tanto en aguas destinadas al consumo como industriales y residuales, los parametros que monitoriza abarcan desde cationes (Hierro, Mercurio, Aluminio, etc.), oxidantes (Cloro, peróxidos, nitritos,etc.), aminas biógenas, explosivos nitroderivados, ph, turbidez, conductividad etc.
La tecnología desarrollada integra una serie de sensores, biochips que ,al entrar en contacto con el analito de interés, experimentan un cambio de color. Esta modificación es recogida por una cámara digital y transmitida a un centro de control a través de conexión Wifi, dónde se analiza y registra. Existe la posibilidad de emitir un informe y/o avisar al usuario en tiempo real.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Los biochips utilizados en este dispositivo, en comparación con otras patentes relacionadas, no requieren del uso de reactivos químicos y son menos complejos, lo que permite diseñar y desarrollar sensores a la carta para problemas determinados.
Además, al proporcionar resultados en tiempo real, permite una actuación rápida en caso de detección de contaminantes perjudiciales para la salud y/o el medioambiente.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Facilidad de instalación y de mantenimiento, tanto del dispositvo como de los biochips.
- Conectividad inteligente.
- Capacidad multianálisis de analitos de interés.
- Análisis cualitativo y cuantitativo “in situ”.
- Utilizable por personal no especializado, sin necesidad de emplear EPI´s, bajo cualquier condición meteorológica.
- No requiere de ninguna calibración ni reactivos químicos.
- Base de datos online.
Características técnicas
El dispositivo es una solución creada en el marco del Internet de las Cosas (IoT) que integra varias tecnologías con el fin de obtener un producto final capaz de dar una respuesta integral al control de calidad en aguas y otros medios acuosos.
Los biochips, los cuales se pueden presentar en forma de discos de 8 mm de diametro o en cuadrados de 5 mm de lado, cuentan un espesor de entre 100 y 200 micras. Estos sensores se colocan en un soporte, que puede ser un disco o un cartucho, fungibles de bajo coste. El cartucho, a diferencia, del disco, no presenta limitaciones en cuanto al número de biochips a incorporar. Existe la posibilidad de combinar distintos biochips para monitorizar varias especies.
Respecto al límite de detección, este varia en función del analito, siendo inferior a 1 ppm en el caso del Hierro e inferior a 2 ppb para el Mercurio.
Aplicaciones
- Laboratorios de calidad y seguridad en tratamiento de aguas.
- EDAP y EDAR de municipios para su control de aguas.
- Industrias alimentarias.
- Industrias extractivas.
- Control medioambiental de residuos y contaminantes.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegido mediante patente P201830631
Estado de desarrollo actual
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Tipo de acuerdo deseado
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Socio para industrialización.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La presente tecnología patentada se centra en el desarrollo de un sensor para la detección y determinación del contenido de ión cloruro en muestras líquidas. Esta determinación es de interés en el diagnóstico de enfermedades, como por ejemplo la fibrosis quística, y en el análisis de muestras, tanto alimentarias, farmaceuticas y ambientales.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Esta nueva tecnología permite realizar la medida de cloruros sin necesidad de adicionar reactivo alguno, sin producir interferencias y aumentando el rango de sus posibles aplicaciones, como son: diagnóstico de fibrosis quística, análisis de muestras alimentarias, farmacéuticas, etc.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
El sensor desarrollado, que soluciona las desventajas de los sensores ya conocidos (compleja preparación y límite de aplicación), se caracteriza por ser muy simple, fácil de usar, económico y con mayor sensibilidad y versatilidad. Al presentar un bajo coste es posible utilizarlo tanto una sola vez como también ser reutilizado más de 100 veces sin afectar a su funcionamiento.
Respecto a los sensores basados en métodos potenciométricos, el sensor desarrollado en esta patente requiere menor tiempo de reacción, tan solo 20 segundos. Puede ser utilizado en mayor número de matrices y de mayor complejidad. Tampoco es necesaria la adicción de electrolitos, proceso que requiere más preparativa en el análisis.
Características técnicas
El sensor está formado por tres electrodos, producidos mediante serigrafía, sobre una lámina plástica, de una tinta conductora de platino (para los tramos conductores, el contraelectrodo y el electrodo de trabajo), frente a las basadas en carbono utilizadas habitualmente, y con una tinta de Ag/AgCl (para el electrodo de referencia). El procedimiento comprende una etapa de activación, una etapa de calibración y una de medida. La reacción electroquímica, que se produce en la superficie de platino, genera señales que se registran en un voltamperograma.
Aplicaciones
Presenta una alta capacidad de respuesta en:
- Diagnóstico de enfermedades relacionadas con concentraciones bajas o altas de ion cloruro en los distintos fluidos biológicos, como la fibrosis quítica, etc.
- Industria alimentaria, como por ejemplo la determinación de cloruro de sodio (sal común).
- Industria farmaceutica.
- Medioambiente, como por ejemplo en estudios de contaminación de aguas.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegido mediante patente P201830271.
Estado actual de desarrollo
El sensor se encuentra desarrollado y está listo para ser usado cuando se conecta a un potenciostato.
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Diseño de entornos y visitas virtuales para la industria, el turismo y la cultura. Se pueden recrear elementos reales como paisajes o interiores, añadiendo información histórica, características de un producto, nombre de un espacio o el precio de los productos.
El acceso para dichas visitas virtuales es a través de la web, permitiendo el acceso desde cualquier lugar del mundo. Se integran en la visita recursos de audio, vídeo y otros.
Empresas y organismos pueden darse a conocer de esta forma a través de internet, permitiendo el acceso de forma virtual y atractiva a posibles visitantes.
Accesibilidad
Se realizan todas las fases de la actividad agrupadas, incluidas las tareas de fotografía, diseño digital y la programación. Para más información y ejemplos pueden visitar: http://3dubu.es/
Persona de contacto:
- Andrés Bustillo Iglesias, grupo de Advanced Data Mining Research and Bioinformatics Learning (ADMIRABLE).
- E-mail: abustillo@ubu.es
- http://www.ubu.es/otri-transferencia/oferta-cientifico-tecnologica/centro-de-creacion-digital-de-la-universidad-de-burgos-digiubu
Breve descripción sobre su utilización
Se crea desde el contenido audiovisual hasta la creación del entorno web que permite el acceso a la visita digital, de acuerdo a las preferencias y necesidades de la organización o empresa. El uso de las visitas virtuales es una herramienta para darse a conocer y mostrar las instalaciones, atrayendo de esta forma a potenciales clientes o visitantes.
Comisiones
Las guías y visitas que se crean son altamente personalizadas y se pueden incluir multitud de servicios audiovisuales. En general, la aplicación web puesta en marcha acarrea un coste que puede oscilar entre los 2.000 y los 30.000€, si bien los potenciales creativo y técnico del grupo permiten servicios que pueden implicar una mayor necesidad de tiempo y económica.
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Sistema de visión artificial y captura de datos para contar personas en condiciones ambientales adversas. Estos datos recolectados en tiempo real, sirven para analizar ocupación o afluencia de personas de forma fiable, convirtiéndose en una herramienta para mejorar la toma de decisiones con mayor eficiencia.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Los sistemas de conteo de personas con información en tiempo real, permiten tomar decisiones en múltiples sectores como los comercios, el transporte público, museos u otros espacios públicos.
Los datos obtenidos, pueden servir para analizar con detalle la afluencia, la concentración en zonas, los hábitos de compra, la influencia de campañas publicitarias u optimizar los recursos materiales y humanos propios.
Garantizar su funcionamiento en condiciones de luminosidad adversas, garantizando la operatividad y la seguridad en la toma de datos, posicionando al sistema como una alternativa fiable para el control de personas en un recinto.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Aporta información en tiempo real de la afluencia y concurrencia en comercios, transporte público, museos, etc.
- Permite análisis automático mediante cámaras de video de entrada y salida de personas.
- Facilita el control de aforo y la toma de decisiones en recintos o vehículos.
- Funcionamiento garantizado en condiciones de luminosidad adversas.
Características técnicas
Sistema de visión artificial para detectar y contar personas que transitan una zona delimitada. Las imágenes se captan mediante cámaras y son analizadas de forma automática por visión por computador.
Dichas soluciones requieren de elevadas cargas de cálculo, si bien el sistema es capaz de seleccionar las imágenes de una secuencia de video suficientemente estables. Con dichas imágenes, se realizan aproximaciones mediante rectángulos en las zonas donde se han detectado movimiento y un filtro se encarga de discernir si se trata de una persona.
El sistema también realiza un seguimiento en la entrada y salida de personas en un establecimiento o recinto, analizando el movimiento como se expresa en el párrafo anterior. Esto permite que la toma de decisiones puedan ser también automáticas, por ejemplo avisando si se sobrepasa el aforo o el tránsito.
Aplicaciones
- Control de acceso y afluencia en establecimientos: Comercios, museos, transporte público y otros recintos.
- Análisis de efectividad de campañas de marketing y otros datos de influencia en el comprador.
- Optimización de recursos según la presencia de clientes o asistentes.
Propiedad Intelectual
Registro de la propiedad intelectual BU-43-17.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Prueba de Concepto. Fase de evaluación de resultados.
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Nuevo dispositivo para la detección “in situ” de ácido ascórbico en distintos tipos de muestras líquidas, como por ejemplo muestras biológicas o productos alimentarios.
El equipo está constituido por un sistema electródico formado por tres electrodos desechables, obtenidos mediante serigrafía.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Los métodos empleados habitualmente presentan una serie de problemas como una pobre selectividad y un deterioro progresivo de la sensibilidad del electrodo al ser utilizados en matrices complejas.
Este nuevo dispositivo solventa estos problemas al emplear electrodos desechables que permiten la determinación de ácido ascórbico con una mayor sensibilidad en distintos tipos de muestras, por ejemplo, en muestras biológicas y alimentarias.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Este método electroquímico de bajo coste, aplicado al análisis quimico, simplifica las técnicas empleadas habitualmente, pudiendo ser utilizado por personal no cualificado, con un corto tiempo de análisis, permitiendo la detección “in situ” del analito.
Características técnicas
El análisis se basa en la oxidación del ácido ascórbico a ácido dehidroascórbico.
El dispositivo desarrollado es de naturaleza electródica, caracterizado porque comprende tres electrodos desechables: un electrodo de trabajo, uno auxiliar o contraelectrodo, y otro de referencia. Cada uno de ellos consta de: un contacto o borne, un tramo y un área activa. Todos los electrodos han sido fabricados mediante serigrafía con una tinta de materiales conductores sobre una lámina plástica de poliéster (PET). Cada electrodo presenta una forma concreta, para adaptarse mejor a sus respectivas funciones.
Los bornes y los tramos se han impreso con una tinta a base de Ag. Las superficies activas del contraelectrodo y del electrodo de trabajo se han impreso con una tinta conductora de C, y la del electrodo de referencia con una tinta de Ag/AgCl. A su vez, el área activa del electrodo de trabajo esta modificada con nanopartículas de oro.
Aplicaciones
Presenta una alta capacidad de respuesta en sectores como: salud, alimentación y bebidas.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegido mediante patente P201631238
Estado actual de desarrollo
Actualmente, el dispositivo se encuentra en fase de prototipo validado en laboratorio
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial; Acuerdo de licencia; Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo; Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La Universidad de Burgos ha desarrollado un nuevo material polimérico conductor eléctrico sólido a partir de polímeros no conductores que se puede presentar preferentemente en forma de película o recubrimiento. Este material se puede utilizar en la elaboración de sensores resistivos o conductivos para sustancias de interés, tanto en fase gas como en disolución, o para su uso en sistemas eléctricos y electrónicos.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
El procedimiento de obtención del material polimérico conductor permite adquirir una serie de propiedades “a la carta” en función del uso final que se quiere dar a dicho material. Esto es posible en función de los monómeros seleccionados que conforman la estructura inicial no conductora que puede presentar características tales como flexibilidad, rigidez, resistencia química, resistencia térmica, hidrofilia, hidrofobia, por nombrar alguna propiedad relevante en el campo de las aplicaciones de los materiales poliméricos, donde la conductividad puede jugar un papel especial en aplicaciones innovadoras
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Su principal ventaja es la facilidad con la que se puede producir este material polimérico y el hecho de que existen uniones químicas entre el material acrílico de partida y las cadenas de polímero conductor, de esta manera, se consiguen materiales homogéneos en forma de membranas sólidas de fácil manejo y con buenas propiedades mecánicas al mismo tiempo que presentan valores de conductividad propias de un material semiconductor e incluso de un metal.
Características técnicas
La invención se refiere a polímeros conductores basados en secuencias de polianilina y, por tanto, se engloba en el campo de los materiales conductores y semiconductores.
Más concretamente, la invención proporciona materiales poliméricos conductores y semiconductores eléctricos preparados mediante crecimiento de cadenas laterales de polianilina a partir de polímeros no conductores con grupos laterales aminofenilo en su estructura, en forma de películas o recubrimientos.
Aplicaciones
- Se pueden emplear como semiconductores en electrónica, como sustitutos de conductores metálicos, en la preparación de células fotovoltaicas. Se puede utilizar como conductor en circuitos electrónicos y también en el aligeramiento de piezas que han de conducir la electricidad (sustituto de metales), en sensores de especies químicas, etc.
- En campos como la automoción y aeronautica por ejemplo se puede emplear principalmente como material con propiedades antiestáticas en pinturas, tintas, tejidos y adhesivos.
- Al tratarse de un material que puede cambiar de color en función del estado de oxidación, puede utilizarse en la fabricación de dispositivos electrocrómicos, ventanas inteligentes y papeles electrónicos.
- Aplicación en el campo de la Bioingeniería.
- Aplicación en el campo de la Nanotecnología.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegido mediante patente de invención P201631147
Estado actual de desarrollo
En uso, resultados de pruebas disponibles.
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Dispositivo electródico capaz de detectar ácido láctico en sudor, en tiempo real, a través de electrodos serigrafiados. El dispositivo incluye un biosensor enzimático capaz de medir la actividad específica de la enzima lactato oxidasa sobre el ácido láctico, sustancia que se genera durante el esfuerzo físico y en parte excretada a través del sudor.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Actualmente no se conoce ningún dispositivo capaz de medir ácido láctico en sudor.
El lactato es un buen indicador de los niveles de esfuerzo físico de una persona, y juega un papel importante en medicina deportiva, donde su determinación es útil para el seguimiento de insuficiencia respiratoria, choques, insuficiencia cardiaca y trastornos metabólicos.
Dispositivo autónomo y portable, incluye todos los elementos eléctricos y electrónicos necesarios para efectuar la medida sin necesidad de conectarse a un equipo externo.
El dispositivo incluye un potenciostato miniaturizado y el biosensor, desechable, de único uso, y recambiable para cada medida.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Medidas sencillas, simplemente a través del contacto del sudor con el electrodo.
- Medidas no invasivas, a diferencia de las que pueden realizarse a través del lactato en sangre, que requieren de mucho tiempo y de procedimientos complejos.
- Medidas en tiempo real.
- Se requiere una pequeña cantidad de sudor, una gota, para realizar la medida, consumiendo un bajo voltaje.
- La medida obtenida se transforma en señal digital y se transmite al usuario.
Características técnicas
El biosensor es un sistema desechable compuesto por tres electrodos serigrafiados en un soporte textil flexible. Tiene la capacidad de extraer información del sistema biológico y cuantificar la señal en corriente eléctrica. En contacto con el sudor, la señal eléctrica se verá modificada de forma proporcional a la concentración de ácido láctico, permitiendo medidas cuantitativas del mismo. Para el funcionamiento del biosensor se requiere de la aplicación de un potencial que será generado por un potenciostato.
Aplicaciones
Equipamiento de deporte y salud.
Propiedad Intelectual
Patente P201630518.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Prototipo.
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Tecnología de Energía (11)
Resumen de la tecnología
La patente se basa en la creación de hormigón sostenible utilizando residuos de palas de aerogeneradores, áridos de hormigón reciclados y componentes tradicionales. El proceso de elaboración garantiza una buena trabajabilidad del hormigón y su transporte eficiente. El residuo de pala, compuesto por fibras, madera y poliuretano, se integra en el hormigón, ofreciendo ventajas como resistencia mejorada a la flexión y contribuyendo a la economía circular al reducir el vertido de residuos y disminuir el consumo de recursos naturales. La tecnología busca un equilibrio entre la sostenibilidad, la eficiencia estructural y la minimización del impacto ambiental.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
- Uso de Residuos de Palas de Aerogeneradores compatibles con el árido de hormigón reciclado: Este enfoque contribuye a la reutilización de residuos industriales y a la reducción de su impacto ambiental, además de resolver la problemática del complejo reciclaje de las palas de aerogenerador.
- Uso de árido de hormigón reciclado: Integrando estos componentes, optimiza la reutilización de materiales reciclados y ayuda a mitigar la demanda de recursos naturales.
- Contribución a la economía circular: Al minimizar el vertido de residuos de aerogeneradores y reducir la necesidad de producción de nuevos materiales, se alinea con los principios de la economía circular.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Adecuada trabajabilidad: A pesar de la presencia de árido de hormigón reciclado y residuo de pala de aerogenerador, se obtienen un hormigón que presenta una adecuada capacidad de bombeo.
- Propiedades estructurales mejoradas: La presencia de los componentes usados en esta patente, otorga una mayor resistencia a la flexión, post-fisuración y post-rotura, mejorando las propiedades mecánicas y aumentando la seguridad de las estructuras.
- Reducción de emisiones de C02: Disminuye la producción de clínker de cemento, reduciendo las emisiones de dióxido de carbono asociadas.
Características técnicas
Este novedoso hormigón se caracteriza por integrar eficazmente residuos de palas de aerogeneradores y áridos reciclados, destacando su contribución a la sostenibilidad y la economía circular. Presenta propiedades frescas con consistencia fluida y baja densidad. A los 28 días, exhibe resistencia a compresión de 26,8-42,6 MPa, resistencia a flexión de 4,9-6,4 MPa y propiedades mecánicas mejoradas gracias a la inclusión de fibras de vidrio y poliuretano en el residuo. Este hormigón versátil se adapta a diversas aplicaciones en la construcción, consolidándose como una opción técnica y ambientalmente avanzada.
Aplicaciones
Este hormigón sostenible, compuesto por árido de hormigón reciclado y residuo de palas de aerogeneradores, encuentra aplicaciones en una variedad de campos de construcción. Desde elementos estructurales como vigas y columnas hasta pavimentos, tubos y prefabricados, este material versátil se adapta a diversas necesidades constructivas. Su resistencia mejorada, gracias a la inclusión de fibras de GFRP y poliuretano en el residuo, lo convierte en una elección adecuada para proyectos que buscan tanto eficiencia estructural como sostenibilidad ambiental.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente P202430081
Estado actual de desarrollo
La patente ha sido sometida a pruebas en el laboratorio, obteniendo resultados satisfactorios, y se encuentra preparada para su fase de producción.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Dispositivo de cierre del tiro de una chimenea que comprende un soporte configurado para ser fijado en la pared de la chimenea.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Automatización y Control Remoto: Gracias a los sensores integrados, Implementar una funcionalidad de automatización y control remoto del dispositivo podría ser una innovación significativa en entornos industriales. Esto permitiría ajustes y monitoreo eficientes del cierre del tiro de la chimenea, optimizando el proceso sin requerir intervención física.
Materiales Avanzados y Recubrimientos Especiales: Utilización de materiales avanzados y recubrimientos especiales para los álabes permiten mejorar la resistencia a la corrosión, la durabilidad y la capacidad para soportar altas temperaturas.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Gestión Energética: Este sistema permitiría una coordinación más efectiva de los recursos y una optimización global del consumo energético en contraposición a los sistemas de tiro natural actuales.
Escalabilidad y Adaptabilidad: El dispositivo es escalable y adaptable a diferentes tamaños de chimeneas industriales. Esto permite su implementación en una variedad de contextos industriales, desde plantas de producción hasta instalaciones de procesamiento.
Eficiencia en Grandes Escalas: Se consigue un cierre efectivo del paso de un fluido, en este caso el humo de la combustión, con una muy reducida pérdida de carga.
Características técnicas
El dispositivo de cierre para chimeneas presenta características técnicas innovadoras diseñadas para optimizar su funcionamiento. Con conjuntos de álabes desplegables controlados por ejes motrices, logra un cierre sincronizado y eficaz del tiro de la chimenea. La elección de materiales avanzados, como teflón o poliéster, en algunos álabes asegura resistencia a la corrosión y estabilidad dimensional, incluso en entornos con altas temperaturas. Además, la implementación de un sistema de engranajes planetarios en la transmisión de movimiento permite un despliegue suave y controlado, minimizando las pérdidas de carga. Opcionalmente, la inclusión de funciones de automatización y control remoto proporciona flexibilidad y facilidad de ajuste en entornos industriales. Estas características combinadas posicionan al dispositivo como una solución técnica robusta y versátil para el cierre eficiente de chimeneas en diversos contextos.
Aplicaciones
Esta patente permite el cierre de del tiro de chimeneas en todo tipo de entornos, incluidas grandes instalaciones industriales, su implementación permite controlar de manera eficiente el flujo de humos y gases de combustión, mejorando la eficiencia energética, alargando la vida de las instalaciones y de los equipos (tanto calderas pirotubulares, como acuotubulares ) y reduciendo las emisiones no deseadas al medio ambiente.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente P202331051
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
En la búsqueda de compuestos orgánicos para baterías de flujo redox, investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos han desarrollado un procedimiento sintético que permite la obtención de un viológeno, 3,3'-([4,4'-bipiridin]-1,1'-diio-1,1'-diil)bis(butano-1-sulfonato), de forma sencilla, selectiva y en escala multigramo. Esta molécula puede reemplazar a metales como el vanadio, dando como resultado baterías más económicas y ecológicas, entre otras ventajas. Además, en comparación con otros viológenos, las baterías construidas con el compuesto desarrollado en la UBU poseen una mayor estabilidad.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Los viológenos son un tipo de compuesto orgánico catiónicos que se caracterizan por presentar estructuras rígidas deficientes en electrones π y excelentes propiedades redox reversibles. Los investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos han sido capaces de poner a punto una nueva metodología para la síntesis de una nueva estructura orgánica de manera sencilla (un único paso de reacción), eficaz (rendimientos superiores al 90%) y en cantidades multigramo. Este nuevo viológeno de 3-butilsulfonato ha sido utilizado como molécula electroactiva para el anolito de baterías de flujo redox orgánicas.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Al emplear la metodología descrita por los autores se obtiene el compuesto orgánico deseado a partir de productos de partida accesibles y en un único paso de reacción.
- El viológeno se aísla con un rendimiento superior al 90% y en cantidades superiores a un gramo.
- Las baterías de flujo construidas empleando esta molécula como anolito, presentan una mayor estabilidad.
- Permite sustituir al vanadio, posicionándose como una alternativa más económica y ecológica.
Características técnicas
El método patentado describe la obtención del viológeno de 3-butilsulfonato a partir de la 4,4'-bipiridina y la 1,3-butano sultona. Mediante una doble alquilación de los átomos de nitrógeno de la bipiridina se logra acceder al compuesto final (1,61 gramos, 93% de rendimiento) empleando dimetilformamida como disolvente y calentamiento térmico. La batería de flujo construidas utilizando este compuesto orgánico da como resultado una menor perdida de capacidad obtenida (0,15% h-1) que la correspondiente batería que contiene el viológeno de propilsulfonato (0,49 % h-1).
Aplicaciones
Entre las diversas aplicaciones del viológeno de 3-butilsulfonato, se encuentra su uso como molécula electroactiva para el anolito de baterías de flujo (almacenamiento de energía).
La metodología desarrollada puede ser aplicada en la síntesis de otros viológenos de interés.
Por otro lado, el viológeno descrito por los investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos podría tener otras aplicaciones propias de los viológenos (herbicidas, elementos electrocrómicos, etc.).
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente P202230676
Estado actual de desarrollo
Prototipo disponible para demostración.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Proceso que permite la valorización energética de los aceites y grasas presentes en las aguas residuales de las industrias alimentarias, mediante reactores avanzados de membranas AnMBR. Es conocido que la presencia de grasas a bajas concentraciones provoca a largo plazo importantes alteraciones en los procesos de tratamiento anaerobio convencionales y, para reducir problemas de ensuciamiento de MBR aerobios, se recomienda el predesengrasado. Sin embargo, la Combinación de las ventajas del proceso anaerobio y la separación con membranas resulta competitiva ante aguas residuales con grasas.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Tratamiento directo de aguas residuales con elevado contenido en aceites y grasas sin necesidad de procesos de coagulación-floculación-flotación de pretratamiento para la separación de grasas. Al prescindir del pretratamiento fisicoquímico reducen los costes de coagulantes y floculantes y gestión de los fangos de flotación. De acuerdo con su composición química los aceites y grasas tienen un elevado potencial metanogénico, con lo que el aprovechamiento energético es óptimo.
Características técnicas
El reactor anaerobio de membranas AnMBR emplea módulos de fibras huecas sumergidas. El reactor está descompuesto en dos etapas: reactor anaerobio de fango en suspensión y de flujo ascendente y tanque de filtración que se encuentran en serie con recirculación. El agua residual se introduce por la parte inferior del reactor anaerobio. Una bomba recircula continuamente fangos del reactor a la unidad de filtración de la que, por rebose retornan al reactor. En el tanque de filtración se encuentran sumergidos los módulos de filtración de fibras huecas que permiten separar el agua tratada, microfiltrada, de los fangos anaerobios que permanecen en el sistema. La agitación de las fibras huecas se realiza mediante burbujeo de biogás. Tanto el reactor como el tanque de filtración cuentan con salidas en su parte superior para la recogida de biogás.
La separación de las dos etapas evita el contacto directo de las grasas que contiene el agua con las membranas de filtración y facilita las operaciones de limpieza dado que permite realizar tareas de mantenimiento en el tanque de membranas sin necesidad de abrir el reactor anaerobio.
La retención de biomasa por filtración evita problemas de pérdida de fango característicos de los procesos anaerobios de basados en la separación gravitatoria, cuando tratan aguas residuales con elevado contenido en aceites y grasas.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
La adsorción de ácidos grasos de cadena larga a los agregados microbianos reduce la capacidad de desgasificación de los flóculos bacterianos impidiendo su separación por gravedad en los procesos convencionales. La tecnología que se propone está basada en cultivos suspendidos con la particularidad de que su retención tiene lugar mediante una membrana de micro o ultrafiltración con capacidad de retención cuantitativa de microorganismos, incluso dispersos, con independencia de su densidad.
Aplicaciones
Tratamiento aguas residuales con elevado contenido en aceites y grasas en la Industria Alimentaria.
Propiedad intelectual
Protegida mediante P200201891, U200501010 y P200703231.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente concedida
P200201891
https://www.ubu.es/otri/propiedad-industrial-e-intelectual/patentes-y-modelos-de-utilidad-de-la-ubu/6-reactor-biologico-integrado-de-lecho-fijo-ordenado
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Según la norma UNE correspondiente, los ensayos de este tipo tienen que corregir sus resultados por rendimiento energético. Para ello se ha diseñado un dispositivo mediante unos sensores de instrumentación y unos acondicionadores de señal y equipo de adquisición. En España, a fecha de hoy, se trata de un dispositivo singular.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Si no se corrigen los resultados de los ensayos de penetración por rendimiento energético, los valores de penetración que se consiguen están demasiado del lado de la seguridad. Esto implica que los elementos que se dimensionen, de acuerdo a los parámetros del suelo así deducidos, van a estar sobredimensionados, con el sobrecoste que esto implica para las obras.
En algunas ocasiones, dado el mayor rendimiento energético de los equipos actuales, se reducen los coeficientes de seguridad en los dimensionamientos estructurales aumentando el golpeo de los ensayos de penetración, para tener en cuenta este exceso de seguridad. En la mayor parte de las ocasiones, esta reducción del coeficiente de seguridad se realiza sin unas medidas reales de rendimiento energético, sino con unas medidas estimadas. Esto algunas veces puede ser por defecto generando sobrecostes. En otras ocasiones será por exceso, generando reducciones no admisibles de coeficientes de seguridad de elementos estructurales. Por todo ello, es necesario medir dicho rendimiento con el dispositivo diseñado.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
La ventaja principal es de ahorro económico debido a que los elementos normalmente se dimensionan ya que los ensayos se tienen que corregir por rendimiento energético, de acuerdo a los parámetros del suelo que se deduzcan por lo que van a estar sobredimensionados, con el sobrecoste que esto implica para las obras.
Características técnicas
Barra instrumentada para medir energía real en ensayos de penetración dinámica de registro continuo, empleada en ensayos geotécnicos “in-situ” de caracterización, identificación, determinación de resistencia y/o deformabilidad de suelos. Esta barra posibilita a los sensores de los equipos de medida adosados a ella, acceder a la toma de datos estáticos y dinámicos, que posteriormente permitan calcular la energía real que atraviesa el varillaje de un equipo de penetración dinámica de registro continuo durante un golpe de ensayo sobre un terreno.
Aplicaciones
Esta tecnología puede ser utilizada en cualquier empresa que disponga de equipos de penetración dinámica.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante registro modelo de utilidad U200900809
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo disponible para comercializar
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Un grupo de investigación de la Universidad de Burgos (UBU) ha desarrollado nuevos modelos de poliamidas aromáticas (aramidas) y materiales poliméricos reforzados con nanocargas de carbono dispersas, previamente funcionalizadas químicamente con dichos modelos de poliamida, constituyendo materiales con excepcionales propiedades mecánicas y térmicas.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Estas nuevas aramidas y/o polímeros reforzados con nanocargas de carbono pueden preparase en forma de membrana porosa, membrana densa, recubrimiento, fibra, etc., constituyendo materiales con excepcionales propiedades mecánicas y térmicas. Los materiales nano y microporosos se elaboran por adición de un líquido iónico en el proceso de preparación y su posterior eliminación en un disolvente, produciendo materiales de altas prestaciones con una densidad reducida.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Sencillez del proceso de fabricación. El proceso de generación de la porosidad es más simple, rápido y homogéneo que otras técnicas tales como la inversión de fase o el uso de CO2 supercrítico.
- Versatilidad, ya que puede ser aplicado tanto a membranas como a materiales de mayor espesor (hasta varios mm).
- Es posible controlar los parámetros la porosidad a partir de condiciones de proceso (cantidad y tipo de líquido iónico empleado, fundamentalmente).
- La funcionalización de las nanocargas permite una óptima dispersión en el polímero.
- La estructura porosa mejora notablemente las propiedades mecánicas respecto a polímeros densos (sin porosidad). Estas propiedades específicas (valores relativos a la densidad) son superiores en los materiales porosos frente a los materiales densos.
Características técnicas
Las aramidas reforzadas con nanocargas se preparan por dispersión de la nanocarga funcionalizada en una disolución de la aramida, y posterior eliminación del disolvente. Estos polímeros se pueden preparar en forma de membrana porosa, membrana densa, recubrimiento, fibra etc. obteniéndose materiales con excepcionales propiedades mecánicas y térmicas. Los materiales nano y microporosos se elaboran por adición de un líquido iónico en el proceso de preparación y su posterior eliminación en un disolvente, produciendo materiales de altas prestaciones con densidad reducida.
Aplicaciones
Estos materiales pueden emplearse como polímeros de altas prestaciones en diferentes aplicaciones, tales como:
- Refuerzo en diferentes estructuras
- Fibras textiles de alta resistencia
- Materiales conductores flexibles
- Elementos de almacenamiento de energía en aplicaciones electroquímicas
- Membranas de filtración y depuración de aguas.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención P202030044
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La Universidad de Burgos (UBU) ha desarrollado una nueva tecnología dirigida a obtener extractos de jara con alta capacidad antioxidante por sus niveles en polifenoles y flavonoides, mediante el empleo de fluidos en condiciones inferiores a su punto crítico (condiciones subcríticas).
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La jara (Cistus ladanifer, especie más común) al igual que otras especies de plantas, contiene aceites esenciales y compuestos bioactivos (polifenoles, flavonoides) de alta capacidad antioxidante que pueden ser utilizados en la elaboración de cosméticos, preparados farmacéuticos y como ingredientes en productos de alimentación humana.
Para la obtención de compuestos bioactivos de las plantas, las técnicas convencionales de extracción suelen requerir altos tiempos de reacción/extracción (del orden de horas) y el empleo de disolventes orgánicos (como etanol, acetona, etc). El producto final obtenido mediante técnicas que empleen disolventes orgánicos obliga a la realización de un proceso de purificación.
La tecnología desarrollada por la UBU se refiere a una tecnología verde conocida como extracción con líquidos presurizados en la que el líquido empleado para la extracción es agua. La ventaja que ofrece el agua como disolvente es la nula toxicidad ambiental y humana en comparación con los disolventes orgánicos, por lo que no supone riesgo de contaminación durante su uso, así como no hace necesario la purificación del producto final, además de ser un disolvente abundante y fácilmente disponible.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- El proceso patentado permite trabajar en régimen semicontinuo y discontinuo.
- El proceso incorpora una línea llamada de "bypass" que permite que el disolvente adquiera las condiciones óptimas de extracción previas a su paso al extractor sin estar en contacto con la materia prima, evitando que la composición de la materia prima se vea modificada.
- Sistema de control basado en hardware de programación "friendly" y abierta, reduciendo el coste en automatización.
- Se puede emplear agua como disolvente o mezcla de agua con disolventes orgánicos (etanol).
- Los biocompuestos disueltos en el disolvente se separan del mismo mediante técnicas de secado en la que se utilizan fluidos recuperables y que no dejan residuos en el producto final.
- El sistema de calefacción puede ser una resistencia eléctrica tipo abrazadera, que requiere menos espacio que un horno.
- No se utilizan disolventes orgánicos para extraer compuestos de la materia prima, reduciendo la toxicidad total y provocando un ahorro económico en el proceso.
- El empleo de un disolvente "verde" como es el agua no deja residuos tóxicos en el producto final, por lo que no es necesario purificarlo.
- Los tiempos de reacción para que se produzca la extracción son inferiores cuando se emplean líquidos sobrecalentados como disolventes (de horas a minutos). A nivel industrial es un factor importante.
- Al modificar uno de los dos parámetros de operación, temperatura o presión, o ambos, se puede lograr extraer el compuesto de interés.
Características técnicas
La técnica propuesta en la presente invención se basa en el empleo de un disolvente inocuo y presente en grandes cantidades y fácilmente adquirible, como es el agua, que modificando sus propiedades físicas y químicas mediante cambios en la temperatura y/ o presión, adquiere propiedades similares a los disolventes orgánicos pudiéndose emplear para la misma finalidad, eliminando los riesgos tóxicos y el tratamiento posterior del producto extraído.
La instalación para la obtención de extractos de jara, consistente en la entrada de un disolvente, agua principalmente, que es bombeado hasta un flujo de trabajo por el sistema de bombeo mientras alcanza la presión de trabajo. Este disolvente o fluido atravesará un dispositivo de calentamiento. Un bypass divide el sistema de líneas en dos vías: una vía permite al fluido llegar al extractor que albergará la materia prima que contenga el compuesto a extraer, y la segunda vía deriva la corriente del fluido hacia la salida del sistema. El cambio de una vía a otra del bypass se realiza mediante un dispositivo de corte de flujo como una válvula. El disolvente que atraviese el extractor y la materia prima y contenga los compuestos de interés, o el disolvente que proceda de la otra línea del bypass. Este procedimiento permite la operación en régimen semicontinuo o en discontinuo.
Aplicaciones
- Obtención de compuestos bioactivos a partir de la jara que pueden ser empleados en fórmulas magistrales de farmacia, cosméticos e ingredientes en productos alimentarios.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención P202130306
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos han desarrollado una instalación para la depuración de aguas residuales en pequeños núcleos de población, ofreciendo una solución económica y medioambiental, con múltiples ventajas. En España, el 47% de los municipios cuenta con menos de 500 habitantes, los posibles beneficiarios de esta tecnología.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La instalación para el tratamiento de aguas residuales puede adaptarse a la problemática que enfrentan los pequeños núcleos de población del territorio nacional. Es de sencilla construcción y facilidad de operación, no necesita consumo eléctrico para su funcionamiento; y presenta muy bajos costes de mantenimiento. Además, ofrece la posibilidad del aprovechamiento del biogás generado. En particular, la instalación multi-etapa consistente en cuatro etapas sucesivas conectadas en serie, que permite una mejora considerable de la calidad físico-química del agua tratada en dicha instalación.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Esta instalación de tratamiento de aguas residuales potencia la actividad biológica de los microorganismos logrando mayores porcentajes de reducción de materia orgánica, además de retener sólidos no sedimentables.
- En comparación con los sistemas aerobios, el ritmo de crecimiento de los microorganismos anaerobios es menor que el ritmo de crecimiento de los microorganismos aerobios, lo que se traduce en una menor producción de fangos, prolongando el periodo de funcionamiento de la instalación sin necesidad de purgar fangos o lodos.
- El empleo de digestión anaerobia evita la necesidad de airear el agua con soplantes o bombas de aire.
- La digestión anaerobia permite convertir la materia orgánica en biogás, una fuente de energía renovable que puede emplearse para generar energía en forma de calor o electricidad.
- Sencillez de construcción.
- No es necesario un sistema de bombeo para hacer circular el agua de una etapa a otra, sino que se aprovecha el desnivel natural del terreno.
Características técnicas
La instalación de tratamiento de aguas residuales está basada en la utilización de reactores anaerobios híbridos multietapa conformada por cuatro etapas sucesivas conectadas en serie, donde las primeras tres de estas etapas sucesivas están configuradas como un reactor anaerobio híbrido, funcionando la última etapa como un decantador que favorece la retención de partículas que puedan escapar de las primeras tres etapas, mejorando la calidad del agua tratada. Además de las ventajas mencionadas, permite obtener un sistema eficiente de depuración de aguas residuales, con altos rendimientos de la calidad físico –química del agua tratada y muy poca producción de fangos.
Aplicaciones
Las potenciales aplicaciones de la instalación son las siguientes:
- Tratamiento de aguas residuales en pequeños núcleos de población.
- Tratamiento de aguas residuales económicamente eficiente.
- Alta calidad físico –química del agua tratada.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención P202031093.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
En la actualidad y desde la implantación de parques de aerogeneradores de gran altura, es difícil hacer la limpieza exterior de las torres y de las palas de los aerogeneradores, con los sistemas tradicionales.
Por motivos de las tareas típicas de mantenimiento, se suelen producir derrames de líquidos y lubricantes de las transmisiones de la maquinaria de transformación de la energía cinética del viento en la energía eléctrica que se envía a la red. Estos fluidos al derramarse ensucian la torre del aerogenerador.
Es preciso por otro lado proceder periódicamente a la limpieza de las palas del aerogenerador porque sobre ellas quedan restos de insectos que chocan contra las palas. Estos restos hacen que la pala vaya perdiendo su eficacia.
Por otro lado es preciso una revisión periódica debido a la fatiga a la que están sometidas las palas del aerogenerador obligando a realizar inspecciones visuales periódicas para evitar la rotura de las mismas y por lo tanto la parada del aerogenerador.
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos han desarrollado una solución con la que realizar dichas tareas sin que para ello sea necesario que los operarios deban trepar por la torre del aerogenerador.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
En general los sistemas empleados en la actualidad para hacer limpieza exterior de torres de aerogeneradores y de sus palas suelen emplear sistemas similares al de limpieza de cristaleras en fachadas de edificios. Es decir mediante operarios que se cuelgan de la góndola y del buje del aerogenerador y manualmente limpian tanto la pala como la torre.
El sistema que se ha patentado, es un sistema trepador con los utillajes necesarios para limpieza y aclarado de las torres y de las palas, así como la recogida del agua jabonosa como fluido residual tras la limpieza. La ubicación de minicámaras en el mecanismo permite la inspección visual en detalle de la totalidad de las palas como de las soldaduras de las torres.
No es necesario que ningún operador tenga que elevarse con el sistema trepador para realizar las funciones de limpieza.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- La principal ventaja que presenta el sistema es que no requiere de personal que haga las propias tareas de limpieza, por lo que se elimina la necesidad de que haya personas expuestas a trabajos en alturas y sus posibles riesgos de caída.
- El personal que realiza las operaciones de mantenimiento e inspección del aerogenerador se limita al montaje del mecanismo en tierra así como el gobierno y control posterior del automatismo que gobierna los mecanismos de limpieza e inspección.
Características técnicas
El mecanismo está pensado para torres y palas de aerogeneradores de gran potencia que requieren de palas de gran tamaño y torres de elevada altura.
El movimiento de apertura y cierre de ambos cinturones del mecanismo trepador, admite su uso para distintos rangos de diametros máximo/mínimo de torre, pudiendose incrementar el tamaño del mecanismo aumentando el tamaño de los lados que componen ambos cinturones superior e inferior o bien incrementando el número de lados del polígono que conforman ambos cinturones.
Aplicaciones
Empresas de mantenimiento de grandes aerogeneradores ( limpieza, pintado e inspección de torres y palas)
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegido mediante patente P2011 00665
Estado actual de desarrollo
No se ha desarrollado un prototipo a escala real del mecanismo.
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La tecnología consiste en una máquina que soporta módulos de captación de energía solar para el seguimiento del sol con objeto de incrementar el rendimiento de módulos solares fotovoltaicos o térmicos.
La principal característica de ambos seguidores es la simplicidad del equipo y su estructura basada en cinemática paralela, que permite un mejor reparto de cargas y una gran modularidad. De esta forma, se consigue que los seguidores se adapten mejor a las restricciones geométricas de inclinación y orientación, así como a las restricciones de tamaño y peso admisibles por la infraestructura sobre la que se instalen.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La tecnología viene a solventar uno de los principales problemas existentes en el diseño de la estructura de los seguidores solares para edificios, la cual tiene relación con el tamaño y peso requerido para la instalación de los mismos. Habitualmente estas estructuras se caracterizan por ser complejos montajes que por lo general están diseñados para superficies planas y pensadas para un uso en huertos solares, pero no para espacios pequeños y desiguales como una azotea o cubiertas de casas y edificios.
Con el objetivo de solucionar este problema, se han desarrollado dos tecnologías que se caracterizan por tener una estructura robusta y un soporte de volumen reducido que cuenta con gran modularidad y una mayor distribución de los esfuerzos. Junto con ello, es capaz de integrar las restricciones geométricas (inclinación y orientación de las cubiertas), mecánicas (tamaño y peso de la estructura) y económicas (compuestos por materiales económicos y accionamientos simples). No obstante, la cinemática para el seguidor solar del invento es aplicable a cualquier sistema que necesite un seguimiento con dos grados de libertad.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Este tipo de sistema aumenta la eficiencia energética de los módulos respecto a los sistemas fijos, pues la tecnología puede adaptarse a múltiples superficies por pequeña e inclinada que ésta sea y puede orientarse según la posición geográfica que tenga la edificación con menos restricciones que los sistemas convencionales. Su fabricación no requiere un alto costo debido a su geometría y sencillez de elementos actuadores.
Características técnicas
Los seguidores solares, están formados por una construcción modular de cinemática paralela, siendo uno de ellos de accionamiento en línea y el otro de accionamiento individual (véase las figuras 1 y 2), los cuales cuentan con un soporte fijo y una plataforma móvil que sostienen los módulos de captación de energía a través de cuatro barras de longitud definida y que permiten realizar el seguimiento del sol en su recorrido en la bóveda celeste. Adicionalmente, el seguidor se adapta a las plataformas rectangulares de paneles solares que existen en el mercado.
Otras características generales en ambas tecnologías son:
- Eje de seguimiento: 2 ejes, horizontal y vertical.
- Potencia energética: Se estima que el diseño del seguidor en capaz de incrementar la producción de energía solar fotovoltaica entre un 24% y 26% respecto de un sistema fijo.
- Adaptabilidad: Adaptable a cualquier forma de paneles.
- Diseño: Se diseña un seguidor para cada proyecto, adaptado a medida dependiendo de las características físicas del lugar de instalación ya sea en viviendas o en parques solares.
Aplicaciones
Las tecnologías de seguimiento solar se aplican al campo de la energía solar térmica y solar fotovoltaica. Estas aplicaciones se centran en dos sectores con dinámicas diferentes: construcción (generación de energía para uso doméstico) y las grandes empresas que generan energía a gran escala.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegidas por patentes de invención P200901628 y P200901629.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Prueba de Concepto
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Dispositivo que permite la medición de la radiación difusa de forma simultánea en cualquier inclinación (60º-90º) y en las cuatro direcciones (norte, sur, este y oeste). Con este dispositivo de medida se puede modelar la radiación difusa sobre cualquier edificio o cubierta.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
En los dispositivos actuales las medidas de la radiación difusa se realizan usualmente mediante un sensor de radiación, un piranómetro, que permite obtener el valor de radiación difusa gracias a un elemento blocante de la radiación directa. Estas soluciones conocidas solamente permiten la proyección de sombra sobre un único sensor, el cual debe estar posicionado en un plano con una inclinación con orientación sur o en un plano horizontal paralelo a la superficie terrestre.
El dispositivo diseñado y patentado por la Universidad de Burgos, permite superar estas limitaciones realizando la medida de radiación difusa simultánea con varios sensores y con posibilidad de que dichos sensores estén en las 4 orientaciones, norte, sur, este y oeste, en planos perpendiculares a la superficie terrestre, y con diferentes inclinaciones.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
El mayor beneficio es el ahorro de tiempo, ya que hasta ahora las medidas se hacen independientemente, lo que hace imprescindible tener 4 estructuras, una para cada sensor y con este sistema se pueden hacer simultáneamente en una única estructura. Además el dispositivo dispone de un sistema para el cálculo de la corrección de las medidas de radiación difusa, en función de las características del anillo del dispositivo.
Características técnicas
Dispositivo de medida de radiación difusa que comprende, una estructura y 4 sensores de radiación, fijados a la misma, además un anillo lobular fijado al marco, con un lóbulo por cada sensor de manera, que cada lóbulo proyecta una sombra a un sensor correspondiente, proporcionando el anillo lobular sombra de manera simultánea a todos los sensores. De esta forma se puede realizar la medida de radiación difusa con varios sensores a la vez y con posibilidad de que dichos sensores estén en orientaciones diferentes entre sí, y con diferentes inclinaciones.
Aplicaciones
Fabricantes y comercializadores de dispositivos que miden variables climáticas y en concreto radiación solar e iluminancia, especialmente por las ventajas de uso del mismo:
- Aplicación de los datos obtenidos a la eficiencia energética de edificios
- Dimensionamiento de instalaciones energéticas sobre fachadas y cubiertas
- Diseño y disponibilidad energética lúminica en fachadas de edificios. El conocimiento del recurso solar a través de los datos de radiación difusa permite el diseño de iluminación en edificios
- Optimización de climatización de edificios mediante la estimación de cargas térmicas por radiacción a través de las paredes
El Grupo de Investigación puede ofrecer un servicio especializado basada en la preparación de informes técnicos y la interpretación de datos para empresas de servicios / auditoría energética, ingeniería y consultoría energía.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegido por patente P201400714
Estado actual de desarrollo
Prototipo funcional o muestras listas para pruebas
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Tecnología Industrial (9)
Resumen de la tecnología
Nuevos conceptos estructurales más económicos que los utilizados en la actualidad pudiendo realizarse estimaciones de la capacidad mecánica residual y de la vida útil con elementos a escala 1:1. Esto es posible tanto a las instalaciones como al equipamiento que se dispone.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La ventaja fundamental es económica utilizándose menos cantidad de material a partir de los nuevos diseños conceptuales que el grupo de investigación es capaz de analizar para distintos tipos estructurales. Esto es especialmente importante en el sector industrial, en el que, por su naturaleza, tiene tendencia a ejecutar multitud de unidades iguales.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Para el caso del hormigón estructural, por su naturaleza, los ensayos a escala reducida son poco significativos, siendo necesario llevar a cabo ensayos a escala real.
En el Laboratorio de Grandes Estructuras de la Universidad de Burgos, se dispone de instalaciones adecuadas para llevar a cabo ensayos a escala 1:1 de elementos de hormigón de hasta 30 metros de longitud y de hasta 40 toneladas de peso.
Optimizar las soluciones estructurales es fundamental, (especialmente en el sector industrial, en el que el número de unidades a ejecutar puede ser muy elevado), pues esto puede proporcionar al cliente una ventaja competitiva de su producto frente al de la competencia.
Características técnicas
Existen cada vez más situaciones estructurales en las que los elementos de hormigón se ven sometidos a estados de carga de naturaleza dinámica. Cabe destacar, por ejemplo, las estructuras situadas en las líneas de Alta Velocidad Ferroviaria, así como torres y cimentaciones de aerogeneradores, losas de cimentación de maquinaria pesada.
La optimización de las soluciones estructurales a utilizar en estos casos pasa necesariamente por conocer, de forma precisa, su respuesta estructural, tanto bajo solicitaciones estáticas como solicitaciones dinámicas.
Para esta última situación, es importante conocer cómo evoluciona la capacidad mecánica (y, en consecuencia, el factor de seguridad estructural) con el número de ciclos; y, a partir de ello, determinar, de modo más exacto, la vida útil de nuestro elemento.
En base a modelos numéricos únicamente no es posible, en la actualidad, conocer este dato y se hace necesario apoyar los necesarios cálculos numéricos con campañas de ensayos experimentales.
Para el caso del hormigón estructural, por su naturaleza, los ensayos a escala reducida son poco significativos, siendo necesario llevar a cabo ensayos a escala real.
En el Laboratorio de Grandes Estructuras de la Universidad de Burgos, se dispone de instalaciones adecuadas para llevar a cabo ensayos a escala 1:1 de elementos de hormigón de hasta 30 metros de longitud y de hasta 40 toneladas de peso.
Aplicaciones
Empresas del sector de la Ingeniería Civil que trabajen con grandes estructuras.
Empresas del sector energético, especialmente vinculadas a la aerogeneración, ya que especialmente los nuevos prototipos incluyen elementos de hormigón (cimentación y torres).
Relación comercial deseada
Commercial Agreement, License Agreement, Technical Cooperation: further development; Technical Cooperation: testing new applications; Technical Cooperation: adaptation to specific needs.
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Pueden llevarse a cabo ensayos a gran escala en nuestro laboratorio. El campo principal es la ingeniería civil, pero también se pueden desarrollar trabajos para otros sectores industriales, como el sector energético, aeroespacial, del automovil, etc.
Se pueden llevar a cabo ensayos estáticos y dinámicos, incluidos largos ensayos cíclicos, ensayos sísmicos, etc.
Nuestros servicios incluyen el diseño del ensayo (tanto conceptual como diseño detallado), desarrollo de modelos de elementos finitos, análisis de resultados, propuestas de mejora de los diseños iniciales proporcionados por el cliente, etc.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La integración de tecnologías de simulación numérica y capacidades de ensayo, permite una mejor en los diseños iniciales, haciéndolos óptimos para los propósitos deseados. Utilizando protocolos propios, es posible realizar ensayos a escala 1:1 de partes de una estructura. A través del desarrollo de modelos de elementos finitos de los ensayos, es posible comparar los modos de fallo de las probetas de ensayo con los de la estructura completa. Utilizando los factores de seguridad obtenidos en los ensayos, es posible determinar de forma precisa los factores de seguridad real de toda la estructura.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Los ensayos a gran escala permiten optimizar los diseños, minimizando costes. Esto es especialmente útil en el sector industrial, en el que se fabrican un gran número de piezas iguales. En este caso, la optimización del diseño permite una reducción significativa de los costes.
Características técnicas
El nuevo Laboratorio de Grandes Estructuras de Obra Civil está ubicado en el ala oeste del nuevo edificio de ingeniería civil de la Universidad de Burgos (Burgos - España).
El laboratorio consiste en un edificio de 200x300 m2. Incluye una losa de reacción de 12x24 metros con 4 metros de espesor y puntos de anclaje de 1 MN de capacidad, en una cuadrícula de 0.80x0.80 metros. Está dotado de los muros de 3.5x3.5 metros y 3.5x4.5 metros y 0.80 metros de espesor, y puntos de anclaje de 1 MN de capacidad en una cuadrícula de 0.80x0.80 metros.
Para mover grandes piezas de ensayo dentro del laboratorio, éste dispone de dos puentes-grúa de 16 ton de capacidad y 18 metros de luz cada uno. Dichos puentes-grúa van dispuestos sobre dos vigas carrileras de 26 metros de longitud.
Asimismo se dispone de un pórtico de acero de 7.5 metros de altura y 8 MN de capacidad y de otro pórtico de 4.5 metros de altura y 1 MN de capacidad. Esto permite realizar ensayos simultáneos de diferentes elementos.
El laboratorio está dotado de un grupo oleo-hidráulico de 200 litros / minuto, un actuador hidráulico servocontrolado de 5 MN y 4 actuadores de 2 MN (modelo ENERPAC), un actuador de 1 MN, un actuador de 500 kN y un actuador de 100 kN tensión / compresión, específico para ensayos de fatiga, con un rango de 25 mm (modelo MTS), un sistema de control computerizado para hasta 4 actuadores simultáneos, una cadena de medida con capacidad para hasta 96 canales y otras tres cadenas de medida con capacidad para hasta 36 canales cada una (modelo HBM), así como un elevado número de sensores para la medida estática y dinámica de componentes estructurales completos y sistemas.
Aplicaciones
Las empresas a las que va dirigida esta tecnología son, fundamentalmente, empresas de obra civil, y también empresas de sector industrial, preferentemente, energía, aeronautica, aeroespacial, automoción, etc. Las aplicaciones fundamentales son el desarrollo de un producto nuevo, la optimización de un producto existente, el análisis de las propiedades de un producto más alla de su vida de servicio, etc.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención P200801660
Estado actual de desarrollo
Comercialmente disponible
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La Universidad de Burgos ha patentado una metodología para la síntesis de derivados de perileno diimidas (PDI), para los cuales no existía ningún procedimiento de obtención, y su uso en diferentes aplicaciones como bioimagen o biomarcador.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La gran versatilidad de la metodología desarrollada permite obtener compuestos con dos posiciones de funcionalización, permitiendo interaccionar con distintas dianas y así controlar la especificidad biológica (qué se va a detectar y a qué partes de la célula irá), y, en las posiciones bahía, seleccionar el color de emisión para modular la emisión fluorescente.
La bioconjugación, estrategia química de formación de enlaces estables entre diferentes biomoléculas, presenta algún inconveniente, resueltos empleando esta nueva metodología propuesta. Además, se evita tener que desarrollar sistemas específicos para cada aplicación, lo que supone un gran ahorro de costes y amplía su campo de acción en múltiples sectores.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Las alternativas disponibles en el mercado muestran bajas fotoestabilidades, son muy sensibles al pH o fuerza iónica y sus intensidades de emisión fluorescentes son bajas. Además, suelen presentar longitudes de onda de emisión bajas, por lo que pueden tener lugar fenómenos no deseados como autoabsorción de energía o scattering.
Las perileno diimidas (PDI) obtenidas mediante la presente invención poseen muchas características deseables que solventan las deficiencias del mercado, como: gran fluorescencia, alta estabilidad química y óptica, estabilidad frente a la radiación, diferentes longitudes de onda de emisión fluorescente en función de los sustituyentes en dichas posiciones y la posibilidad de una fácil funcionalización en las posiciones N y N'. Además, exhiben rendimientos cuánticos elevados, que pueden incluso llegar a la unidad.
Características técnicas
Las modificaciones realizadas en los sustituyentes de las moléculas orgánicas conocidas como perileno diimidas (PDI) o perileno bisimidas (PBI) alteran su solubilidad, haciéndolas versátiles en distintos medios, tanto orgánicos como acuosos. Las variaciones en los sustituyentes de las posiciones imida no afectan significativamente a sus propiedades fluorescentes, permitiendo la inclusión de biomoléculas bioconjugables, mientras que en los sustituyentes de las posiciones bahía, modifican sus propiedades luminiscentes, permitiendo modular las longitudes de onda de emisión del fluoróforo resultante.
Gracias a la bioconjugación se obtienen sistemas novedosos con características únicas, como, por ejemplo, la emisión fluorescente. En este caso, se considera la posibilidad de su uso como biomarcador específico en campos como bioimagen, terapia y diagnóstico.
Aplicaciones
El mercado potencial es relativamente amplio debido a la versatilidad de esta tecnología. Sus posibles aplicaciones se encuentran en múltiples sectores, como, por ejemplo: medicina, ciencia de materiales e industria agroalimentaria. Como aplicaciones más concretas se pueden citar:
- Realización de kits particulares para bioconjugación, específicamente marcadores fluorescentes en el campo de medicina que permiten la realización de diagnósticos y seguimiento de tratamientos específicos.
- Detección de especies contaminantes biológicas de gran interés en la industria alimentaria como son las enterotoxinas o la avidina (sistemas PDI-Biotina)
- Estudio de células epiteliales (sistemas PDI-mupirocina).
- Marcado, rastreo o determinación de la biodistribución de proteínas.
- Seguimiento de eventos celulares como administración de fármacos a células diana y estudio de funciones enzimáticas entre otros.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida por patente de invención P201830029.
Estado actual de desarrollo
La tecnología relativa al método de sintesis esta desarrollada.
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La gran mayoría de los productos metálicos a nivel industrial se obtienen mediante conformado de chapas, los cuales son empleados en diversidad de aplicaciones, desde carrocerías de automóviles, electrodomésticos y aviones hasta envases de bebidas.
Para definir el diseño y estructura final de un componente estampado existen dos etapas fundamentales: el proceso de fabricación para realizar la pieza y la simulación estructural para la superación de las exigencias del cuaderno de cargas establecido.
La Universidad de Burgos ha patentado un procedimiento de diseño y fabricación de componentes metálicos estampados en frío que establece una interconexión entre la simulación de proceso y la simulación estructural durante el desarrollo de los componentes estampados, de modo que las propiedades mecánicas del material se modifiquen en función del nivel de predeformación alcanzado en cada zona del componente.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La metodología desarrollada mejora las correlaciones numérico –experimentales obtenidos con los programas de simulación estructurales empleados actualmente, disminuyendo la discrepancia entre los datos de la simulación y los elementos fabricados. La aplicación de la metodología, supone una optimización tanto en el tiempo de puesta a punto del proceso de fabricación de nuevos componentes, como en materiales empleados para la fabricación de piezas.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Los programas que actualmente se comercializan no tienen en cuenta el grado de afectación que sufren las propiedades mecánicas en función del nivel de predeformación alcanzado durante la estampación del componente.
La principal ventaja es que este procedimiento controla y define la manera óptima de transferir los resultados de la deformación, producida durante la simulación del proceso de estampado, hacia los programas de simulación estructural para poder así tenerla en cuenta al realizar las simulaciones de los casos de carga a que esté sometido ese componente estampado. Se define también una metodología de trabajo, aplicable a nivel industrial, con la que enfrentarse a la estimación mediante simulación de la rigidez estructural de componentes estampados.
Características técnicas
El producto es una metodología que incorpora un software de tratamiento de datos aplicado fundamentalmente al desarrollo de productos metálicos obtenidos por estampación en frío.
Aplicaciones
Indicar que la gran mayoría de los productos metálicos a nivel industrial se obtienen mediante conformado de chapas, los cuales son empleados en diversidad de aplicaciones.
Destacan: carrocerías de automóviles, electrodomésticos; aviones, envases de bebidas etc..
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegido mediante patente de invención P201630414
Estado actual de desarrollo
En uso, resultados de pruebas disponibles
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Un grupo de investigación de la Universidad de Burgos ha patentado diferentes materiales cuya base es el cemento y que disponen propiedades mejoradas para la construcción e ingeniería civil, en especial para la utilización de los mismos como revestimiento interior/exterior, como relleno de suelos y rejuntado de fábricas. La característica en común a todos ellos es que se utilizan diferentes residuos para los cuales se fijan los criterios de su utilización y dosificaciones básicas que garanticen su resistencia y durabilidad, así como un alto grado de prestación y puesta en obra.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Los nuevos morteros ligeros tienen propiedades iguales o en algunos casos mejoradas, además ofrecen una forma innovadora de reciclar los residuos del tipo de los polímeros. Además de la ventaja del reciclado de residuos, el uso de estos en morteros de albañilería permite la obtención de propiedades mecánicas mejoradas que pueden aplicarse incluso en la sustitución del 100% de los morteros convencionales con una densidad más baja.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Las ventajas fundamentales son del tipo medioambiental y económico así como de mejoras de las prestaciones de producto. Para la obtención de estos materiales se reciclan y reutilizan materiales de muy diversa índole, normalmente muy difíciles de degradar por métodos no mecánicos, debido a su estabilidad química.
Características técnicas
Los materiales que se disponen y que están patentados por la universidad de Burgos son:
Composite ligero cemento-polímero para la construcción obtenido a partir del reciclado de espumas rígidas de poliuretano:
Material compuesto de cemento y polímero de peso ligero obtenido a partir de espumas rígidas de poliuretano reciclado, útil como un nuevo material de construcción que sustituye a los morteros daligerados tradicionales, reemplazando los agregados expansivoso arenas utilizados en la fabricación de estos productos por diferentes porcentajes de espumas rígidas de poliuretano residuos de la industria.
Morteros aligerados con poliamida en polvo reciclada utilizada como árido:
Material ligero a partir de polvo de poliamida reciclada como agregado en morteros de albañilería, donde cantidades variables de arena se sustituyen por polímero para fabricar estos productos.
Mortero elaborado con melamina reticulada:
Mortero de albañilería que incluye conglomerante, agregados y agua con diferente sustitución de áridos por melamina en polvo (polímero urea-formaldehído o melamina-formaldehído). La invención se basa en la obtención de un material de construcción con propiedades mejoradas como mayor adherencia y menor porosidad abierta.
Mortero seco de cemento y cemento y cal para la construcción, realizado con residuos de pizarra:
Morteros de cal y cemento de albañilería reciclado con pizarras desechos, que se trituran y tratan para evitar las reacciones árido-álcali.
Aplicaciones
Empresas del sector de la Construcción Civil y Construcción. Materiales en base cemento y su utilización del mismo como revestimiento interior/exterior y como relleno de suelos y rejuntado de fábricas.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegidas por patentes de invención P200902028, P201100664 , P201300297 y P201531132.
Estado actual de desarrollo
En uso, resultados de prueba disponibles.
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente concedida
P200902028
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Un grupo de investigación de la Universidad de Burgos ha patentado diferentes materiales cuya base es la cal y que disponen propiedades mejoradas para la construcción, en especial para la utilización de los mismos como revestimientos utilizados en Patrimonio Artístico. La característica en común a todos ellos es que se utilizan diferentes residuos para los cuales se fijan los criterios de su utilización y dosificaciones básicas que garanticen su resistencia y durabilidad, así como un alto grado de prestación y puesta en obra.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Se consiguen materiales ligeros con propiedades mejoradas respecto de las mezclas convencionales (por ejemplo optimizando algunas de las propiedades básicas como son la trabajabilidad, la permeabilidad y el comportamiento reológico frente a cargas de fuerza) y con un buen comportamiento en régimen de prestación.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Las ventajas fundamentales son del tipo medioambiental y económico así como de mejoras de las prestaciones de producto. Para la obtención de estos materiales se reciclan y reutilizan materiales de muy diversa índole, normalmente muy difíciles de degradar por métodos no mecánicos, debido a su estabilidad química.
Los resultados obtenidos para estas patentes nos llevan a afirmar que los diseños de mortero de cal presentan propiedades físicas y mecánicas equivalentes a las de los materiales tradicionales, con suficiente adherencia, permeabilidad adecuado al vapor de agua y cumpliendo con los requisitos reglamentarios y de pruebas de durabilidad.
Características técnicas
Los materiales que se disponen y que están patentados por la universidad de Burgos son:
- Obtención de morteros de cal con residuo de poliamida en polvo
Nuevo material consistente en morteros de cal para restauración, con la mejora de algunas de las propiedades básicas tales como la trabajabilidad, la adsorción y la resistencia a la adherencia.
- Mortero de cal para construcción y rehabilitación fabricado con residuos siderúrgicos
Morteros de cal aérea e hidráulica como conglomerantes, dosificados con subproductos industriales como son las escorias blancas y negras que son residuos de la fabricación de acero.
Aplicaciones
Empresas del sector de la Construcción. Utilización de los materiales para rehabilitación del Patrimonio Histórico.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegidas por patentes de invención P201300847, P201400382.
Estado actual de desarrollo
En uso, resultados de prueba disponibles.
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Dispositivo telescópico intramedular para el alargamiento de huesos largos, principalmente para pacientes de acondroplasia (1 de cada 25.000 niños nacidos vivos), que dispone de un mecanismo motorizado hermético que incrementa su longitud a voluntad del paciente y sin ningún tipo de conexión física con el dispositivo. Por su carácter autoportante el paciente puede caminar mientras se produce el efecto de alargamiento y endurecimiento del hueso.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Los procedimientos quirúrgicos empleados actualmente para corregir los efectos por esta enfermedad o por otras causas son por lo general traumáticos y de larga duración, haciendo que el paciente tenga que estar largos periodos de tiempo en reposo con una baja calidad de vida.
El dispositivo propuesto por el contrario permite una prótesis progresiva, autoportante, autónoma (incorpora un micromotor reductor en el interior del cilindro fijo y movido por la energía acumulada en la batería anexa al motor), limita el riesgo de infecciones y permite una alta capacidad de control de la distancia elongada.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
-El paciente solo sufre una operación quirúrgica por cada hueso
-El paciente no necesita estar sentado o en cama durante largos meses, sino que tiene capacidad de locomoción sobre sus propias piernas que están en proceso de elongación.
-Facilidad de manejo del mecanismo de recrecimiento por el propio paciente
Características técnicas
El dispositivo comprende dos elementos tubulares cilíndricos coaxiales con una entalla longitudinal, de forma tal que el cilindro exterior se une fijamente mediante tornillos a una de las dos partes del hueso a alargar, y el tubo deslizante interior se une por el otro extremo mediante tornillos a la otra parte del hueso. El tubo externo lleva en su interior en su extremo, un acumulador de energía eléctrica o batería que se recarga a través de inducción eléctrica.
El material elegido es de aleación de Titanio Ti6Al4V-ELI, material bioinerte, de gran resistencia a la corrosión y alta resistencia mecánica. Permite la adhesión del hueso sobre la capa de óxido que lo recubre y un recubrimiento de “hidroxiapatito”, para mejorar y acelerar el anclaje del hueso.
Aplicaciones
La aplicación de esta prótesis progresiva se centra exclusivamente al sector sanitario u hospitalario y dentro de este, a la sección de traumatología.
Propiedad Intelectual
P201530996
Estado actual de desarrollo
Prototipos funcionales
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Es conocida la elevada toxicidad de los explosivos nitroderivados, como por ejemplo el TNT, que se absorben fácilmente por la piel y el tracto intestinal y también es conocida la presencia de este compuesto tanto en zonas contaminadas civiles, en el caso de restos de atentados, como militares, en antiguas instalaciones. Esto hace que se generen problemas que son necesarios abordar, tanto de salud como de tipo medioambiental.
Con el objetivo de cubrir esta necesidad se han desarrollado nuevos sensores colorimétricos, simples, rápidos y de bajo coste para la detección in situ de trazas de TNT por parte de personal no especializado y mediante técnicas convencionales (sustituyendo a las comúnmente conocidas IMS, GC, HPLC..).
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Se trata de sustratos sensores sólidos que se pueden manejar con facilidad, tanto en seco como en húmedo. Por otra parte, la posibilidad de recubrir fibras convencionales con este tipo de materiales poliméricos sensores tendría la ventaja de preparar tejidos inteligentes capaces de indicar la presencia de moléculas de interés mediante cambios de color, en el caso de materiales cromogénicos. Además, sería ventajoso el uso de disoluciones acuosas de los materiales poliméricos sensores en aplicaciones forenses o de detección de contaminación por pulverización in situ sobre la zona a valorar.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Permite la detección colorimétrica visual de trazas de TNT por parte de personal no especializado, in situ, en tiempo real, y con un coste mínimo. Se puede detectar TNT directamente sobre superficies, o medir la concentración en aguas y efluentes, suelos, etc. La cuantificación se puede llevar a cabo mediante una fotografía tomada con una cámara digital o con un teléfono móvil.
Características técnicas
Los detectores visuales de TNT son nuevos materiales poliméricos basados en monómeros sensores. La polimerización de estos monómeros permite obtener polímeros lineales solubles en agua, películas o membranas densas, así como fibras inteligentes, por copolimerización de estos monómeros con otros, entre los que se incluyen monómeros polifuncionales, proporcionando materiales poliméricos con buenas propiedades mecánicas, tanto en seco como en hinchado, que se comportan como sensores colorimétricos de TNT en agua y/o medios acuosos.
Los materiales poliméricos cambian de color cuando hay trazas de TNT presentes en el medio. Este comportamiento específico permite la detección de TNT por cambios en el espectro visible de color, de manera que además de con un espectrofotómetro, también se puede valorar a simple vista. Por otra parte, la cuantificación se puede llevar a cabo utilizando los parámetros digitales (RGB) de una fotografía tomada a los materiales con una cámara o mediante un teléfono móvil inteligente.
Aplicaciones
Puede ser de interés para empresas que utilizan este tipo de explosivos. Detección de explosivos en atentados (química forense). Gobiernos que necesitan establecer el grado de contaminación por este compuesto debido a acciones como pueden viejas instalaciones militares, atentados, enfrentamientos armados etc.. Canteras y minas. Empresas cuya área es la fabricación de explosivos y armamento. Empresas que utilizan TNT para hacer demoliciones. Empresas de gestión ambiental y tratamiento de áreas contaminadas.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegido por patente P201301187.
Estado actual de desarrollo
En uso, resultados de pruebas disponibles.
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Se ha patentado un nuevo procedimiento para la oxidación de un grupo sulfóxido a un grupo sulfona que consiste en la oxidación del sulfóxido con aire en presencia de un compuesto de molibdeno como catalizador, preferentemente bis(acetilacetonato) de dioxomolibdeno(VI) o los derivados dinucleares procedentes de su hidrólisis parcial.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La principal novedad del presente método es el uso de aire como agente oxidante, mientras que los procedimientos clásicos emplean peróxido de hidrógeno, problemático en su almacenamiento y uso debido a sus propiedades corrosivas y el carácter explosivo de sus vapores.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Este nuevo procedimiento ha demostrado ser más eficaz que los diversos procedimientos descritos para este proceso. Por otro lado, el aire destaca por ser el agente oxidante más barato, accesible, fácil de manipular y seguro. Además, los catalizadores de molibdeno son menos tóxicos que los comúnmente utilizados, y resistentes a la degradación en las condiciones de reacción. Por último, no se observa la formación de subproductos y la sulfona resulta fácilmente aislable. En conjunto, el procedimiento es eficiente, sencillo, barato y medioambientalmente más beneficioso que los descritos con anterioridad
Características técnicas
Mediante esta invención se ha desarrollado un procedimiento para la oxidación de sulfóxidos a sulfonas empleando el oxígeno del aire como agente oxidante, en presencia de un complejo de molibdeno como catalizador, preferentemente bis(acetilacetonato) de dioxomolibdeno(VI) o los derivados dinucleares procedentes de su hidrólisis parcial en presencia de dimetilsulfóxido, dimetilformamida u óxido de trifenilfosfina. La cantidad de catalizador varía entre un 1 mol% y un 10 mol%. La síntesis se lleva a cabo a presión atmosférica y la temperatura de reacción varía entre 15-50 ºC. El disolvente empleado es un éter de bajo peso molecular. Los productos se obtienen con rendimientos excelentes y no se detectan otros productos secundarios en la reacción.
Aplicaciones
Síntesis de sulfonas, que pueden presentar diversas propiedades (fármacos, pesticidas, materiales...) ya demostradas. Por tanto, aplicabilidad en la industria farmacéutica, agroquímica, etc.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegido por patente P200703331
Estado actual de desarrollo
En uso, resultados de pruebas disponibles
Relación deseada
Acuerdo Comercial
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Fabricación industrial, materiales y tecnologías de transporte (24)
Resumen de la tecnología
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos han desarrollado unos polímeros que son capaces de detectar los compuestos que liberan ciertos alimentos en descomposición.
Mediante esta tecnología, se puede conocer de forma rápida y segura si los alimentos envasados, en concreto los pescados, siguen siendo adecuados para su consumo. Estos materiales pueden presentarse en forma de films, membranas porosas e integrados en otros tejidos, como por ejemplo fibras de algodón.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Hasta ahora, la fecha de caducidad (o fecha de consumo preferente) es la única información a disposición del consumidor para conocer la vida útil de un alimento. Los polímeros desarrollados por la Universidad de Burgos permiten determinar la presencia de las aminas biógenas que un alimento libera durante su putrefacción. Aplicando esta tecnología, se puede determinar la presencia, por ejemplo, de putrescina y cadaverina (dos de las aminas más habituales) de forma rápida y eficiente. Esta técnica se posiciona como una alternativa viable a la determinación de estos compuestos por técnicas más complejas.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Las principales ventajas de este material y su uso en la determinación de los compuestos químicos de interés son:
- Sencillo y económico. No requiere manipular reactivos ni realizar un tratamiento previo.
- Específico. La detección de aminas en fase gas no tiene interferentes.
- Tiempo de Respuesta. El análisis es prácticamente inmediato (cambio de color y fluorescencia).
- Versátil. El polímero puede presentarse como un film, una membrana o recubierto por fibras, como por ejemplo algodón.
Características técnicas
Las poliamidas aromáticas sintetizadas (figura 1), que contienen ancladas en la cadena principal estructuras derivadas de 1,8-naftalimida, se obtienen por reacción de policondensación de los monómeros iniciales. Estas estructuras, al interaccionar con aminas y aminas biógenas, sufren un cambio de color y/o fluorescencia. En concreto:
Cambio de color: B-etilendiamina, cadaverina, trimetilamina, morfolina y putrescina.
Cambio de fluorescencia: B-etilendiamina, cadaverina, morfolina y putrescina.
El material final puede obtenerse como un film o, mediante un espumado, como una membrana porosa. Adicionalmente, estos polímeros pueden integrarse dentro de otros tejidos, como fibras de algodón.
Aplicaciones
El material desarrollado puede aplicarse en la industria de la alimentación a modo de etiqueta inteligente para dar cuenta de la frescura de los alimentos envasados con atmósfera controlada como el pescado envasado.
Un uso más general consistiría en su aplicación como sensor frente a la presencia de una gran variedad de aminas en fase gas.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente P201730765
Estado actual de desarrollo
Investigación o experimental
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Un grupo de investigación de la Universidad de Burgos ha desarrollado un procedimiento para la fabricación de hormigón utilizando residuo de pala de aerogeneradores. El hormigón objeto de la invención no solo cuenta con buenas prestaciones en estado fresco y endurecido, sino que representa una solución viable para el reciclado de las palas de los aerogeneradores, contribuyendo de esta forma a la economía circular y posicionándose como una alternativa a los hormigones tradicionales.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
En España, se estima que el 40% de los aerogeneradores tendrá que ser reciclado para el año 2030. Ante esta realidad, se hace evidente la necesidad de buscar métodos para el reciclado de los mismos. En bibliografía son pocas las opciones que se encuentran para el aprovechamiento de estos residuos, y, la gran mayoría, pasa por la separación de parte de sus componentes (fibras de vidrio y de carbono, resinas poliméricas, espuma de poliuretano, madera de balsa y resinas de poliéster) mediante procesos de pirólisis, solvólisis o gasificación. El procedimiento descrito por investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos ha permitido la elaboración de hormigón sostenible empleando el residuo triturado de las palas de aerogeneradores sin haberle realizado previamente una separación de los diferentes componentes, lo cual supone un ahorro económico y energético, con el consiguiente beneficio en términos de reducción de huella de carbono.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Obtener un hormigón con buenas características técnicas, poniéndose de manifiesto la viabilidad de estos residuos para su uso en elementos estructurales.
- Reducción de costes al emplear el residuo en bruto (no es necesario la separación de sus componentes) reduciendo los tiempos de producción y no siendo necesario la contratación de personal especializado.
- Dar salida al residuo bruto procedente del triturado de pala de aerogenerador como fibra reciclada para empleo en hormigón. Contribuyendo a la minimización del cambio climático, favoreciéndose al mismo tiempo una economía más circular.
Características técnicas
- El método desarrollado permite la utilización de hasta un 6% en volumen de residuos procedentes de las palas de los aerogeneradores.
- El hormigón formado conserva la resistencia a flexión del hormigón tradicional a pesar de contener un menor porcentaje en volumen de cemento y cuenta con resistencia tras la fisuración, proporcionando una mayor seguridad. Su buena trabajabilidad le convierte en una alternativa válida para su utilización en cualquier tipo de elemento estructural según la normativa actual de aplicación.
- La optimización llevada a cabo por los investigadores ha permitido la creación de un procedimiento con una baja dificultad técnica y un coste económico bajo.
Aplicaciones
- Empresas del sector de la construcción y la construcción civil.
- Empresas relacionadas con la construcción, mantenimiento y/o retirado de aerogeneradores interesadas en el reciclaje de los mismos.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente P202230623
Estado actual de desarrollo
Investigación o experimental
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos han desarrollado un procedimiento para producir productos en polvo por liofilización o por desecación a vacío a partir de productos siruposos (PS) empleando opcionalmente maltodextrina como coadyuvante de deshidratación, de modo que se obtienen sólidos pulverulentos finos y agradables que mantienen lo máximo posible las propiedades sensoriales y físico-químicas de los productos de partida.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Los PS (jarabes, siropes y productos alimentarios de consistencia densa), contienen una elevada concentración de azúcares con bajas temperaturas de transición vítrea (Tg) lo que dificulta su desecación ya que durante la deshidratación se forma un producto extremadamente pegajoso, duro y muy difícil de manejar. La invención que se describe logra evitar estos inconvenientes mediante la desecación de los PS por liofilización y además se ha conseguido realizar el proceso sin la necesidad de añadir coadyuvantes para la deshidratación. El aspecto más innovador de la invención que se presenta con respecto a otros procedimientos descritos, es el relativo a las temperaturas de molienda del producto y de su conservación. Se obtienen elevados rendimientos de hasta el 96 % mediante liofilización y de hasta el 94% por desecación a vacío. El PS en polvo obtenido puede contener hasta un 100% de sólidos del PS, siendo necesaria la adición de maltodextrina de patata en algunos PS para obtener el producto en polvo (25% en liofilización o 40% en desecación a vacío). La textura final es fina y con excelentes características sensoriales y físico-químicas.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Obtención de un PS en polvo con una concentración de sólidos totales de PS de hasta el 100%.
- Obtención de un producto en polvo sin la necesidad de añadir aditivos.
- Elevado rendimiento del proceso: 80% -96% (liofilización); 80%-94% (desecación a vacío).
- Buena solubilidad y baja higroscopicidad en el PS en polvo obtenido.
- Buenas características físico-químicas y sensoriales del PS en polvo.
- Posibilidad de comercializar el PS en polvo dentro de la demanda de “etiquetas limpias” (clean label) y la denominación “comida real” (real food), al contener tan sólo PS y opcionalmente, maltodextrina de patata.
Características técnicas
El procedimiento de liofilización y el de desecación a vacío descrito en esta invención logra la elaboración de un PS en polvo con textura fina y agradable, empleando opcionalmente maltodextrina de patata, con una elevada cantidad de PS en el producto sólido final, una buena solubilidad, un elevado rendimiento y una baja higroscopicidad. La molienda y conservación del producto deben realizarse a temperaturas inferiores a la Tg del PS en polvo obtenido, lo que mantiene óptimas las características de textura de este alimento sin necesidad de incorporar aditivos antiaglomerantes.
Aplicaciones
Las posibles aplicaciones del PS en polvo es su utilización en productos destinados a la alimentación humana o animal. Los sectores con potencial aplicación son:
- Alta cocina
- Industria galletera
- Industria panadera y pastelera
- Industria confitera
- Industria cosmética
- Industria farmacéutica: elaboración de medicamentos
- Producción de alimentos enriquecidos con prebióticos
- Producción de piensos enriquecidos con prebióticos
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención P202230308 and P202230309
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
El dimetil sulfóxido utilizado como agente oxidante en este procedimiento es un reactivo fácilmente accesible, de bajo coste y que genera como único subproducto dimetil sulfuro, fácilmente eliminable del medio de reacción por tratarse de un compuesto volátil, permitiendo un sencillo aislamiento del aldehído o cetona obtenido como producto final sin necesidad de emplear cromatografía de columna.
Description of the technology
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Se trata de un método eficiente para la obtención de aldehídos y cetonas a partir de dioles, que emplea un oxidante fácilmente accesible y medioambientalmente benigno. Además, la reacción se lleva a cabo al aire (no hay necesidad de emplear atmósfera inerte) y sin el uso de disolventes orgánicos (ventajas económicas y medioambientales) y los aldehídos y cetonas se aíslan con pureza analítica sin necesidad de cromatografía de columna.
Características técnicas
Se trata de la utilización del dimetil sulfóxido como agente oxidante para la ruptura oxidante de 1,2-dioles a compuestos tipo carbonilo que incluyen un grupo funcional aldehído o cetona en presencia de un catalizador de molibdeno (VI), en un disolvente orgánico o en un medio libre de disolventes orgánicos, bajo presión atmosférica y a una temperatura entre 100-180 ºC o, alternativamente, por irradiación en un horno microondas monomodo a una potencia máxima de 300 W y a una temperatura comprendida entre 120 ºC y 180 ºC.
Aplicaciones
Síntesis de compuestos que contengan un aldehído o cetona en su estructura, intermedios sintéticos altamente versátiles. Por tanto, aplicabilidad en la industria farmacéutica, agroquímica, etc. Fabricación de esmaltes en la Industria Cosmética. En la Industria Alimenticia, como producto intermediario para dar olor y sabor a los alimentos. Industria del plástico, resinas, pinturas, solventes. Fabricantes de explosivos
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención P201301117
Estado actual de desarrollo
Procedimiento testado en laboratorio
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos han desarrollado una APP que permite medir sustancias de interés (biocompuestos, contaminantes, etc.) con solo una fotografía.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Actualmente la técnica de referencia para la determinación de la concentración de especies diana mediante sensores colorimétricos es la espectroscopia ultravioleta visible (UV-vis). Este tipo de técnicas requieren de personal especializado que maneje este tipo de equipos, además de un procedimiento experimental largo y tedioso que requiere de un calibrado previo que permita calcular la concentración de la especie de interés en una muestra problema.
La aplicación descrita permitiría medir la concentración de un analito de forma rápida, sencilla y eficiente con una simple fotografía digital. Para llevar a cabo las medidas es necesario fotografiar las muestras del calibrado y las muestras problema.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Rápido, sencillo y eficiente
- Solo se necesita un smartphone
- No requiere de personal, ni de equipos especializados
- Gran abanico de campos de aplicación como química analítica, laboratorios de calidad, aguas industriales, control de calidad, etc.
Características técnicas
Esta aplicación permite la determinación de la concentración de analitos objetivo o especies químicas de interés, realizando un análisis de color tanto de las muestras de calibración (procedimiento de valoración) como de las muestras problema. Para ello, se debe tomar una fotografía tanto de las diferentes muestras de calibración como de las muestras problema. A continuación, se debe colocar el selector circular sobre cada muestra para el análisis de color, y finalmente la aplicación mostrará la representación gráfica de la concentración frente a diferentes parámetros de color (R, G, B, H, S, V, RGB, ΔRGB). La curva de mejor ajuste (lineal o cuadrática), es decir, la curva de ajuste con el parámetro R2 más alto, aparecerá en la primera posición, y la aplicación muestra las concentraciones calculadas de las muestras de problema. El aspecto más innovador es la rapidez, sencillez, y eficiencia a la hora de realizar una analítica de concentraciones.
Aplicaciones
Las posibles aplicaciones son el análisis de sustancias de interés en química analítica, laboratorios de calidad, aguas industriales, control de calidad, etc.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante registro propiedad intelectual BU-122-20
Estado actual de desarrollo
La aplicación se encuentra de forma temporal disponible para su descarga gratuita en Google Play Store y Apple Store con el nombre Colorimetric Titration.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente concedida
BU-122-20
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos han descrito un nuevo material polimérico que posee capacidad biocida (tanto capacidad bactericida como virucida) contra bacterias de origen alimentario o ambiental, así como para virus presentes en los alimentos o de trasmisión respiratoria.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
El material polimérico descrito en la invención interacciona con bacterias y virus, y en particular bacterias alterantes y patógenas de origen alimentario o ambiental y virus entéricos o de otro tipo alimentarios, así como virus de trasmisión respiratoria. Como resultado se produce una inhibición de la propagación de estos microorganismos, lo que permite el empleo de estos materiales en la preparación o fabricación de materiales biocidas orientados al uso como como absorbentes bactericidas en envases alimentarios, y en recubrimientos de fibras textiles para la fabricación de mascarillas.
De forma adicional, los absorbentes bactericidas también pueden disolverse en un disolvente orgánico para que no supongan un residuo plástico, y puedan gestionarse como residuos líquidos.
Además, los copolímeros de la presente invención son totalmente reutilizables, de modo que, si dicho copolímero se lava con agua y etanol, una vez utilizados como absorbentes bactericidas en envases alimentarios, o en recubrimientos de fibras textiles o material biosanitario, vuelve a ser totalmente operativo.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Inhibición de la propagación de microorganismos.
- Los copolímeros son totalmente reutilizables
- Los copolímeros pueden disolverse en un disolvente orgánico para que no supongan un residuo plástico, y puedan gestionarse como residuos líquidos.
- No existe migración o liberación de sustancias desde el material
Características técnicas
El método de inhibición del crecimiento y propagación de bacterias y virus, así como la inhibición de la formación de biopelículas bacterianas, descrito en la patente se basa, por tanto, en la capacidad de dichos copolímeros de interaccionar con bacterias y virus. El monómero (I), presente en los copolímeros desarrollados, es un grupo derivado de vainillina unido a la cadena polimérica por un enlace diazo.
Aplicaciones
Las potenciales aplicaciones son:
- Absorbentes bactericidas en envases alimentarios.
- Recubrimientos de fibras textiles o material biosanitario para la fabricación de mascarillas con capacidad biocida o tubos o sondas de drenaje
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención P202130734
Estado actual de desarrollo
Procedimiento testado en laboratorio
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos, en colaboración con otros centros de investigación, han descrito una nueva invención que consiste en la definición geométrica de una probeta para la realización de los ensayos de caracterización de la resistencia a tracción del hormigón y otros materiales conglomerantes secundarios, específica para el ensayo de tracción directa.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Los ensayos de caracterización a tracción del hormigón y otros materiales conglomerantes secundarios se realizan, fundamentalmente, mediante ensayos de tracción indirecta, que son más sencillos desde el punto de vista de su ejecución, pero menos fiables. Los ensayos de tracción directa, al ser más complejos, son menos habituales. No existe una geometría de probeta normalizada para estos ensayos, y se han utilizado probetas con muy diversas geometrías. El diseño geométrico de la probeta de ensayo es esencial para realizar con éxito el ensayo de tracción directa.
La solución que proponen los investigadores permite determinar geométricamente una probeta de ensayo que garantice que la rotura se va a producir, en la proporción más alta posible, en la zona central y que ésta no se vea afectada por los efectos locales derivados del sistema de anclaje de la probeta al sistema de aplicación de cargas.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Esta probeta pretende servir de base para la realización, de una forma más fiable, de los ensayos de tracción directa en el hormigón y otros materiales conglomerantes secundarios, de tal forma que todas las probetas muestren una rotura por la zona central y, por lo tanto, todos los ensayos de tracción directa puedan alcanzar la condición de “válidos”.
Características técnicas
La geometría de la probeta descrita por los investigadores por la presente invención comprende un cuerpo de revolución conformado por un tramo recto central, unos primer y segundo tramos rectos extremos, y sendos primer y segundo tramos curvos de transición, que están dispuestos entre el tramo recto central y los primer y segundo tramos recto extremo respectivamente. Esta probeta propuesta logra reducir sustancialmente el cociente entre la máxima tensión en la probeta y la máxima tensión en el tramo recto central de la misma, aproximándose a la unidad. Para ello, se han calculado los campos de tensiones principales máximas de tracción que aparecen en diferentes ejemplos de probetas, todas ellas, con geometría de revolución, sometidas a una carga de tracción uniforme, de tal modo que la máxima tensión principal en la zona del tramo recto central sea la unidad.
Aplicaciones
Esta probeta es de gran interés para los laboratorios de caracterización de materiales conglomerantes hidráulicos (como los hormigones, los morteros de cemento, los morteros de cal o los morteros de yeso entre otros). También es de interés para los centros de investigación en los que se investigue en propiedades mecánicas de los hormigones y los materiales conglomerantes secundarios.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención P202130588
Estado actual de desarrollo
Desarrollado en el laboratorio exclusivamente y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos (UBU) han desarrollado un prefabricado de cemento resistente al fuego aligerado con residuos industriales de origen polimérico, procedente de techos de vehículos reciclados, elaborado en forma de bloque para la construcción de muros o estructura similar.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores / New and innovative aspects
La novedad de la invención se basa en la utilización de los residuos de los techos generados en la industria del automóvil valorizados como materia prima con valor añadido para su incorporación a la industria del prefabricado del Sector de la Construcción. El porcentaje de residuo presente en el material final depende de las propiedades requeridas del producto final, obteniéndose propiedades en estado endurecido suficientes para poder aplicar la legislación vigente.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización / Main advantages of its use
- Sustitución de parte del árido fino y grueso del prefabricado de mortero por residuos de techos completos provenientes de la industria del automóvil.
- Los aditivos a la carta, de naturaleza polimérica, que se añaden, mantienen e incluso mejoran las resistencias mecánicas dentro de los valores necesarios de referencia exigidos por normativa europea. Supone un ahorro de estructura de base y una mayor trabajabilidad.
- Mayor aislamiento térmico de la envolvente final, así como un buen comportamiento frente a la temperatura y frente al fuego (no combustibilidad).
- Reciclado de residuos para la construcción de materiales, pasando de desechos a nuevas materias primas, con la reducción del impacto ambiental que conlleva.
- Reducción del peso del material sin que afecte a sus propiedades.
Características técnicas / Specifications
Las características y naturaleza propias de los materiales de construcción, en base cemento, hace posible valorizar espumas que provengan de paneles aislantes de poliuretano con restos de otros materiales (adhesivos, óxidos metálicos, restos de pintura y/o enlucidos, etc.). El cemento es del tipo Cemento Portland con una composición en masa de un 95-100% de clínker y un 0-5% de componentes minoritarios. Esta alteración en los componentes del prefabricado de cemento objeto de la invención, ayuda a mantener las resistencias mecánicas del mismo, obteniendo materiales reciclados con capacidades ciertamente estructurales, pero al mismo tiempo, con una baja densidad con respecto a los morteros ligeros convencionales. Este prefabricado de cemento aligerado con residuos de matriz polimérica aporta mejoras en las características físicas del prefabricado, con reducciones de peso de hasta un 70%.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante Modelo de Utilidad U202131039
Estado actual de desarrollo
Desarrollado en el laboratorio exclusivamente y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos (UBU) han desarrollado un hormigón de alta resistencia (HPC) y retracción mejorada, elaborado con árido reciclado de hormigón (RCA) y óxido de magnesio reactivo (MgO). El hormigón desarrollado presenta una elevada trabajabilidad, que permite una puesta en obra sencilla y económica, y una elevada resistencia, por lo que es válido para su utilización en cualquier tipo de elemento estructural según la normativa actual de aplicación. El empleo de óxido de magnesio permite reducir la retracción, muy elevada en el HPC por su elevado contenido de cemento, reduciendo la fisuración causada por este fenómeno y mejorando la durabilidad de los elementos estructurales.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
El hormigón de alta resistencia es un tipo de hormigón con una elevada resistencia y durabilidad gracias a su elevado contenido de cemento, pero este elevado contenido también implica que presente un elevado calor de hidratación durante el fraguado y una elevada retracción, además de una baja trabajabilidad. El árido reciclado de hormigón es un residuo de la industria de la prefabricación de hormigón que se caracteriza por presentar una absorción de agua muy elevada. El óxido de magnesio (MgO) es un producto químico que presenta propiedades expansivas al ser mezclado con agua. Además, esta expansión se produce durante el proceso de fraguado del hormigón y generándose un 70% menos de emisiones de CO2 que durante la fabricación del cemento Portland ordinario.
La solución propuesta por los investigadores se centra en solventar los problemas existentes en la fabricación tradicional de hormigón. La invención persigue, por tanto, el aprovechamiento del árido reciclado de hormigón y del óxido de magnesio para la elaboración de un hormigón sostenible de alta resistencia óptimo para uso estructural desde el punto de vista de la puesta en obra (alta trabajabilidad), desde el punto de vista de la resistencia (alta resistencia) y en relación con la retracción (disminución de la retracción).
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Se consigue una maximización de la sostenibilidad del hormigón de alta resistencia mediante la adición conjunta de árido reciclado de hormigón y óxido de magnesio reactivo, como segundo conglomerante
- Se disminuye el vertido de residuos, del consumo de clínker y de las emisiones de CO2, con la consecuente reducción del cambio climático.
- Se consigue maximizar simultáneamente la trabajabilidad y la resistencia del hormigón de alta resistencia elaborado con árido reciclado de hormigón y óxido de magnesio reactivo simultáneamente.
- Se consigue minimizar la retracción (acortamiento) del hormigón de alta resistencia y la fisuración asociada a este fenómeno mediante la adición de óxido de magnesio reactivo con características expansiva.
Características técnicas
Los hormigones de alta resistencia diseñados se componen de cemento tipo I (cemento Portland ordinario) como primer conglomerante y óxido de magnesio reactivo como segundo conglomerante en un contenido entre el 10% y el 15% de la masa de conglomerante total del hormigón de alta resistencia. La fracción gruesa de árido y la fracción fina de árido está compuesta exclusivamente por árido reciclado de hormigón. Además de estos componentes, los hormigones diseñados también incorporan agua y un aditivo superplastificante para aumentar la trabajabilidad del hormigón.
Aplicaciones
Las potenciales aplicaciones son las siguientes:
- Sector de la construcción y la ingeniería civil
- Sector de nuevos materiales válidos para aplicaciones estructurales
- Sector técnico del reciclado y aprovechamiento de desechos procedentes de la industria de la prefabricación
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención P202130466
Estado actual de desarrollo
Desarrollado en el laboratorio exclusivamente y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos (UBU) han desarrollado un prefabricado de cemento resistente al fuego aligerado con residuos industriales de origen polimérico, procedente de techos de vehículos reciclados, elaborado en forma de bloque para la construcción de muros o estructura similar.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La novedad de la invención se basa en la utilización de los residuos de los techos generados en la industria del automóvil valorizados como materia prima con valor añadido para su incorporación a la industria del prefabricado del Sector de la Construcción. El porcentaje de residuo presente en el material final depende de las propiedades requeridas del producto final, obteniéndose propiedades en estado endurecido suficientes para poder aplicar la legislación vigente.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Sustitución de parte del árido fino y grueso del prefabricado de mortero por residuos de techos completos provenientes de la industria del automóvil.
- Los aditivos a la carta, de naturaleza polimérica, que se añaden, mantienen e incluso mejoran las resistencias mecánicas dentro de los valores necesarios de referencia exigidos por normativa europea. Supone un ahorro de estructura de base y una mayor trabajabilidad.
- Mayor aislamiento térmico de la envolvente final, así como un buen comportamiento frente a la temperatura y frente al fuego (no combustibilidad).
- Reciclado de residuos para la construcción de materiales, pasando de desechos a nuevas materias primas, con la reducción del impacto ambiental que conlleva.
- Reducción del peso del material sin que afecte a sus propiedades.
Características técnicas
Las características y naturaleza propias de los materiales de construcción, en base cemento, hace posible valorizar espumas que provengan de paneles aislantes de poliuretano con restos de otros materiales (adhesivos, óxidos metálicos, restos de pintura y/o enlucidos, etc.). El cemento es del tipo Cemento Portland con una composición en masa de un 95-100% de clínker y un 0-5% de componentes minoritarios. Esta alteración en los componentes del prefabricado de cemento objeto de la invención, ayuda a mantener las resistencias mecánicas del mismo, obteniendo materiales reciclados con capacidades ciertamente estructurales, pero al mismo tiempo, con una baja densidad con respecto a los morteros ligeros convencionales. Este prefabricado de cemento aligerado con residuos de matriz polimérica aporta mejoras en las características físicas del prefabricado, con reducciones de peso de hasta un 70%.
Aplicaciones
Las potenciales aplicaciones del depósito son las siguientes:
- Bloques de cemento compacto que se instalan uniendo hiladas con mortero y se trabajan de forma similar al ladrillo.
- Dinteles para instalar encima de los marcos de carpintería donde los ladrillos quedan sin sujeción.
- Paneles, placas y cimentación para edificaciones, naves industriales, etc.
- Arquetas para redes de saneamiento o redes eléctricas usadas en urbanizaciones.
- Pavimentos y adoquines de hormigón para calzadas peatonales, zonas ajardinadas y viales de poco tránsito.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante Modelo de Utilidad U202131039
Estado actual de desarrollo
Desarrollado en el laboratorio exclusivamente y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos ha patentado un nuevo material en base yeso que dispone de propiedades mejoradas para la construcción, en especial para la utilización como revestimientos en los que se necesite alta resistencia al fuego. Este material está formado por residuos procedentes de la industria siderometalúrgica para los cuales se fijan los criterios de su utilización y dosificaciones básicas que garanticen su resistencia y durabilidad, así como un alto grado de prestación y puesta en obra, además de la resistencia al fuego.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La solución presentada permite la obtención de un material con elevada densidad con propiedades mejoradas respecto de las mezclas convencionales (por ejemplo, optimizando algunas de las propiedades básicas) y con un buen comportamiento en régimen de prestación en relación a la resistencia y a la reacción al fuego.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Mejora de las propiedades de no combustibilidad de los yesos convencionales.
- Incremento de aplicaciones de los materiales en base yeso en atmósferas especiales.
Características técnicas
Se trata de una ecoplaca de yeso prefabricada de alta resistencia al fuego, estando la placa constituida por una matriz de yeso que incluye residuos siderúrgicos procedentes de la industria del acero, dichos residuos esencialmente compuestos por CaO, SiO2, Al2O3 y MgO.
Aplicaciones
Las potenciales aplicaciones son:
- Empresas del sector de la construcción.
- Utilización en revestimientos en masa como materiales con alta resistencia y reacción al fuego.
- Prefabricados de uso en tabiques de edificios o protección en áreas industriales que requieran protección frente al fuego.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante Modelo de Utilidad U201930281
Estado actual de desarrollo
En uso y validado.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
El hormigón sostenible seco compactado con rodillo comprende cemento Portland como primer conglomerante, áridos, agua y aditivos. Caracteriza al hormigón el que comprende fibras metálicas y/o plásticas, escoria siderúrgica granulada molida como segundo conglomerante y escoria blanca de horno de cuchara como tercer conglomerante, los áridos comprenden árido reciclado de hormigón.
El hormigón siderúrgico seco compactado con rodillo comprende cemento Portland como primer conglomerante, áridos, agua y aditivos. Caracteriza al hormigón el que comprende fibras metálicas y/o plásticas, escoria siderúrgica granulada molida como segundo conglomerante y escoria blanca de horno de cuchara como tercer conglomerante, los áridos comprenden escoria de horno de arco eléctrico.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Los hormigones con consistencia seca, también denominados hormigones secos, y con componentes recuperados, provenientes de otros procesos o sustancias, como deshechos de la industria del acero (hormigón siderúrigoco) o deshechos de la industria de la prefabricación del hormigón (hormigón sostenible), haciéndolos sostenibles.
El aprovechamiento de residuos propios de la construcción junto con los residuos de la industria siderúrgica confiere a estos hormigones un proceso innovador de puesta en obra consiguiendo las mismas características técnicas que los hormigones autocompactantes cuya composición se basa en la utilización de fracciones con áridos naturales con ventajas técnicas y económicas adicionales.
La dosificación del hormigón siderúrgico de consistencia seca se muestra en la Tabla 1:
|
Componentes (kg/m3) |
RCC-E-M |
RCC-E-P |
|
Cemento Portland ordinario (CEM I 52.5 R) |
140 |
140 |
|
Escoria siderúrgica granulada molida |
115 |
115 |
|
Escoria blanca de horno de cuchara |
40 |
40 |
|
Agua |
115 |
115 |
|
Escoria de horno de arco eléctrico: fracción gruesa |
390 |
390 |
|
Escoria de horno de arco eléctrico: fracción media |
700 |
700 |
|
Escoria de horno de arco eléctrico: fracción fina |
535 |
535 |
|
Arena caliza: fracción polvo |
485 |
485 |
|
Arena silícea: fracción polvo |
245 |
245 |
|
Aditivo plastificante |
5,0 |
5,0 |
|
Fibras (M, metálicas; P, plásticas) |
55 (M) |
6,5 (P) |
Tabla 1. Dosificación de las mezclas del hormigón siderúrgico seco (kg/m3)
(M: fibras metálicas; P: fibras plásticas)
La dosificación del hormigón sostenible de consistencia seca se muestra en la Tabla 2:
|
Componentes (kg/m3) |
RCC-AH-M |
RCC-AH-P |
|
Cemento Portland ordinario (CEM I 52.5 R) |
140 |
140 |
|
Escoria siderúrgica granulada molida |
115 |
115 |
|
Escoria blanca de horno de cuchara |
40 |
40 |
|
Agua |
130 |
130 |
|
Árido reciclado de hormigón: fracción gruesa |
275 |
275 |
|
Árido reciclado de hormigón: fracción media |
495 |
495 |
|
Árido reciclado de hormigón: fracción fina |
375 |
375 |
|
Arena caliza: fracción polvo |
485 |
485 |
|
Arena silícea: fracción polvo |
245 |
245 |
|
Aditivo plastificante |
5,0 |
5,0 |
|
Fibras (M, metálicas; P, plásticas) |
55 (M) |
6,5 (M) |
Tabla 2. Dosificación de las mezclas del hormigón sostenible seco (kg/m3)
(M: fibras metálicas; P: fibras plásticas)
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Hormigón compactado con rodillo de fácil trabajabilidad, fácilmente bombeable y gran autocompactabilidad.
- Reducción en las etapas de elaboración minimizando el consumo de energía y aumentando los rendimientos en su puesta en obra.
- Eliminación del proceso de vibrado reduciendo el consumo de combustible y la emisión de CO2.
- Reciclado de escorias de horno de arco eléctrico en el caso del hormigón siderúrgico seco.
- Reciclado de árido de hormigón en el caso del hormigón sostenible seco.
- Elevada resistencia a la fisuración por la inclusión de fibras metálicas y/o plásticas junto con la escoria de horno de arco eléctrico.
- Hormigón sostenible.
Características técnicas
Los novedosos hormigones secos compactados con rodillos cumplen las especificaciones internacionales EN 206 y recomendaciones de la EFNARC.
Las propiedades en estado fresco de las diferentes mezclas del hormigón siderúrgico de consistencia seca se muetran en la tabla 3:
|
Propiedad |
RCC-E-M |
RCC-E-P |
|
Tiempo de vibrado consistómetro Vebe (s) |
7,5 |
6,5 |
|
Asiento consistómetro Vebe (cm) |
4,0 |
4,5 |
|
Densidad consistómetro Vebe (Mg/m3) |
2,68 |
2,63 |
Tabla 3. Propiedades en estado fresco del hormigón siderúrgico seco
Las propiedades en estado fresco de las diferentes mezclas del hormigón sostenible de consistencia seca se muetran en la tabla 4:
|
Propiedad |
RCC-AH-M |
RCC-AH-P |
|
Tiempo de vibrado consistómetro Vebe (s) |
6,0 |
5,5 |
|
Asiento consistómetro Vebe (cm) |
4,5 |
5,0 |
|
Densidad consistómetro Vebe (Mg/m3) |
2,27 |
2,22 |
Tabla 4. Propiedades en estado fresco del hormigón sostenible seco
Las propiedades en estado endurecido de las diferentes mezclas del hormigón siderúrgico de consistencia seca se muetran en la tabla 5:
|
Propiedad |
Edad (días) |
RCC-E-M |
RCC-E-P |
|
Densidad endurecida (Mg/m3) |
28 |
2,59 |
2,54 |
|
Resistencia compresión (MPa) |
1 |
46,9 |
41,4 |
|
28 |
59,6 |
56,9 |
Tabla 5. Propiedades en estado endurecido del hormigón siderúrgico seco
Las propiedades en estado endurecido de las diferentes mezclas del hormigón sostenible de consistencia seca se muetran en la tabla 6:
|
Propiedad |
Edad (días) |
RCC-AH-M |
RCC-AH-P |
|
Densidad endurecida (Mg/m3) |
28 |
2,19 |
2,16 |
|
Resistencia compresión (MPa) |
1 |
12,5 |
43,1 |
|
28 |
53,4 |
51,8 |
Tabla 6. Propiedades en estado endurecido del hormigón sostenible seco
Aplicaciones
- Elementos estructurales sometidas a cargas muy elevadas; vigas, columnas, forjados o muros.
- Pavimentos.
- Muros de grandes dimensiones y presas de cualquier tipología, como, por ejemplo, presas de gravedad, arco o bóveda.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención P202030878 y P202030881
Estado actual de desarrollo
Desarrollado en el laboratorio exclusivamente y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
El hormigón autocompactante con escoria de horno de arco eléctrico en todas las fracciones está compuesto por cemento Portland como primer conglomerante, escoria siderúrgica granulada molida como segundo conglomerante y escoria blanca de horno cuchara como tercer conglomerante, además de áridos, agua y aditivos, fibras metálicas y/o plásticas. Por su innovadora composición y procedimiento de puesta en obra consigue excelentes resultados de durabilidad, sostenibilidad y estética.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
El aprovechamiento de residuos propios de la construcción junto con los residuos de la industria siderúrgica confiere a estos hormigones un proceso innovador de puesta en obra consiguiendo las mismas características técnicas que los hormigones autocompactantes cuya composición se basa en la utilización de fracciones con áridos naturales con ventajas técnicas y económicas adicionales.
Su dosificación se muestra en la Tabla 1:
|
Componentes (kg/m3) |
T |
M |
P |
|
Cemento Portland ordinario (CEM I 52.5 R) |
215 |
215 |
215 |
|
Escoria siderúrgica granulada molida |
115 |
115 |
115 |
|
Agua |
170 |
180 |
185 |
|
Escoria de horno de arco eléctrico: fracción gruesa |
750 |
750 |
750 |
|
Escoria de horno de arco eléctrico: fracción fina |
550 |
550 |
550 |
|
Arena caliza (< 0.50 mm) |
950 |
950 |
950 |
|
Aditivo plastificante |
5,5 |
5,5 |
5,5 |
|
Fibras (M, metálicas; P, plásticas) |
20 (M) |
40 (M) |
4,5 (P) |
Tabla 1. Dosificación de las mezclas (kg/m3)
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Hormigón autocompactante de fácil trabajabilidad, fácilmente bombeable y gran autocompactabilidad.
- Reducción en las etapas de elaboración minimizando el consumo de energía y aumentando los rendimientos en su puesta en obra.
- Eliminación del proceso de vibrado reduciendo el consumo de combustible y la emisión de CO2.
- Reciclado de escorias de horno de arco eléctrico.
- Elevada resistencia a la fisuración por la inclusión de fibras metálicas y/o plásticas junto con la escoria de horno de arco eléctrico.
- Hormigón sostenible.
Características técnicas
Los novedosos hormigones autocompactantes, cumplen las especificaciones internacionales EN 206 y recomendaciones de la EFNARC.
Las propiedades en estado fresco de las diferentes mezclas se recogen en la tabla 2:
|
Propiedad |
T: fibras metálicas 0,25% volumen hormigón |
M: fibras metálicas 0,5% volumen hormigón |
P: fibras plásticas 0,5% volumen hormigón |
|
Escurrimiento (mm) |
720 (SF2) |
650 (SF1) |
620 (SF1) |
|
Densidad fresca (Mg/m3) |
2,71 |
2,67 |
2,60 |
|
Aire ocluido (%) |
2,2 |
2,0 |
1,9 |
|
Retracción de secado (mm/m) |
1,1 |
0,9 |
1,0 |
Tabla 2. Propiedades en estado fresco
SF: clase de escurrimiento
Las propiedades en estado endurecido de las diferentes mezclas pre-fisuración se recogen en la tabla 3. Entre paréntesis, la desviación estándar.
|
Edad (días) |
T |
M |
P |
|
|
Densidad endurecida (Mg/m3) |
90 |
2,63 (0,3) |
2,57 (0,3) |
2,54 (0,2) |
|
Resistencia a compresión (MPa) |
7 |
47,1 (1,5) |
38,2 (0,4) |
33,3 (0,1) |
|
28 |
59,7 (5,7) |
53,1 (1,5) |
46,1 (1,0) |
|
|
90 |
75,3 (4,1) |
63,6 (3,6) |
56,8 (5,3) |
|
|
180 |
76,1 (3,5) |
65,2 (3,5) |
59,1 (3,2) |
|
|
360 |
77,9 (0,2) |
68,8 (5,3) |
60,5 (2,7) |
|
|
Módulo de elasticidad (GPa) |
90 |
40,1 (0,7) |
34,7 (1,5) |
31,6 (0,9) |
|
Coeficiente de Poisson (ν) |
90 |
0,23 (0,1) |
0,22 (0,1) |
0,22 (0,1) |
|
Resistencia a flexión (MPa) |
90 |
7,93 (2,3) |
5,97 (1,1) |
5,04 (0,3) |
|
Resistencia a tracción indirecta (MPa) |
90 |
5,11 (0,4) |
4,84 (0,6) |
4,35 (0,4) |
|
Resistencia a tracción directa (MPa) |
160 |
4,25 (0,2) |
3,77 (0,4) |
3,66 (0,4) |
|
Módulo de elasticidad a tracción (GPa) |
160 |
38,5 (1,0) |
37,9 (2,8) |
35,5 (0,3) |
|
Altura máxima de penetración de agua (mm) |
90 |
16 (6,1) |
19 (5,4) |
20 (4,7) |
|
Altura media de penetración de agua (mm) |
90 |
10 (4,5) |
12 (4,8) |
12 (5,1) |
Tabla 3. Propiedades en estado endurecido pre-fisuración
Las propiedades en estado endurecido de las diferentes mezclas post-fisuración se recogen en la tabla 4. Entre paréntesis, la desviación estándar.
|
Ensayo |
Propiedad |
T |
M |
P |
|
Ensayo de flexión sobre cuatro puntos |
Tenacidad a la fractura por flexión (N·m) |
8,61 |
21,38 |
11,72 |
|
Resistencia a primera fisura (MPa) |
7,59 (2,1) |
4,89 (1,4) |
4,13 (0,5) |
|
|
Energía de fractura (N/mm) |
0,749 |
2,153 |
1,190 |
|
|
Ensayo de flexión sobre tres puntos en probetas entalladas |
Límite de proporcionalidad (MPa) |
5,20 |
5,98 |
3,66 |
|
Resistencia residual (MPa) |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
Apertura de entalla: 0.5 mm |
5,50 |
6,52 |
1,21 |
|
|
Apertura de entalla: 1.5 mm |
4,80 |
5,70 |
1,17 |
|
|
Apertura de entalla: 2.5 mm |
3,65 |
3,96 |
1,29 |
|
|
Apertura de entalla: 3.5 mm |
3,93 |
3,01 |
1,31 |
|
|
Energía de fractura (N/mm) |
1,124 |
2,235 |
0,598 |
|
|
Energía de fractura según la apertura de entalla (N/mm) |
1,133 |
2,637 |
0,707 |
Tabla 4. Propiedades en estado endurecido post-fisuración
Aplicaciones
- Elementos estructurales sometidas a cargas muy elevadas; vigas, columnas, forjados o muros.
- Aplicaciones de hormigón armado como pretensado tanto in situ como prefabricado.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegido mediante patente P202030750
Estado actual de desarrollo
Desarrollado, validado y listo para su utilización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
El hormigón autocompactante con árido reciclado de hormigón en todas las fracciones, se caracteriza por su composición basada en cemento Portland como primer conglomerante y escoria siderúrgica granulada molida como segundo conglomerante. Su innovadora composición y procedimiento de puesta en obra consigue excelentes resultados de durabilidad, sostenibilidad y estética.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
El aprovechamiento de residuos propios de la construcción junto con los residuos de la industria siderúrgica confiere a estos hormigones un proceso innovador de puesta en obra consiguiendo las mismas características técnicas que los hormigones autocompactantes cuya composición se basa en la utilización de fracciones con áridos naturales con ventajas técnicas y económicas adicionales.
Las tres mezclas son adecuadas para su puesta en obra, aunque la mezcla MIX50 proporciona adecuado equilibrio entre el comportamiento de material y la sostenibilidad del producto.
Su dosificación se muestra en la Tabla 1:
|
Material/Mix |
MIX0 |
MIX50 |
MIX100 |
|
CEM I 52.5 R |
208 |
||
|
Escoria siderúrgica granulada molida |
208 |
||
|
Árido reciclado de hormigón fracción polvo |
305 |
||
|
Agua |
225 |
280 |
335 |
|
Árido reciclado de hormigón fracción gruesa |
405 |
||
|
Árido reciclado de hormigón fracción fina |
0 |
430 |
865 |
|
Arena silícea |
935 |
470 |
0 |
|
Regulador de fraguado |
2,30 |
||
|
Plastificante |
4,50 |
Tabla 1. Dosificación de las mezclas (kg/m3)
Aprovechamiento de residuos para la elaboración de hormigón sostenible autocompactante óptimo para uso estructural.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Gran fluidez y facilidad de relleno de moldes para estructuras con formas complicadas.
- Eliminación de la etapa de presaturación en los áridos reciclados empleados.
- Alta autocompactabilidad del hormigón. Compactación sin necesidad de vibrado.
- Acabados homogéneos sin imperfecciones.
- Puesta en obra económica y sostenible por la utilización de residuos de la industria de la prefabricación de hormigón y de subproductos de la industria siderúrgica conocido como escoria.
- Reducción del consumo de energía en su puesta en obra.
- Excelentes propiedades físicas y mecánicas.
Características técnicas
Las características técnicas para la mezcla MIX50 son las que aquí se muestran:
|
Escurrimiento |
820 mm |
|
Resistencia a compresión a 28 días |
39,6 MPa |
|
Resistencia a tracción indirecta a 28 días |
2,4 MPa |
|
Resistencia a flexión a 28 días |
4,5 MPa |
|
Densidad |
2,08 Mg/m3 |
|
Tamaño máximo de árido |
12,5 mm |
Los novedosos hormigones autocompactantes, cumplen las especificaciones internacionales EN 206 y recomendaciones de la EFNARC.
|
Propiedad |
Tiempo desde el amasado (min) |
MIX0 |
MIX50 |
MIX100 |
|
Escurrimiento (mm) |
0 |
800 (SF3) |
820 (SF3) |
830 (SF3) |
|
15 |
770 (SF3) |
780 (SF3) |
780 (SF3) |
|
|
30 |
715 (SF2) |
700 (SF2) |
705 (SF2) |
|
|
60 |
570 (SF1) |
560 (SF1) |
555 (SF1) |
|
|
T500 (s) |
0 |
2,4 (VS2) |
3 (VS2) |
3,6 (VS2) |
|
15 |
3,4 (VS2) |
4,6 (VS2) |
5,8 (VS2) |
|
|
30 |
5,6 (VS2) |
6,8 (VS2) |
8,4 (VS2) |
|
|
60 |
8,6 (VS2) |
11,2 (VS2) |
12,8 (VS2) |
|
|
Tiempo de vaciado del embudo en V (s) |
15 |
10,6 (VF2) |
19,2 (VF2) |
24,8 (VF2) |
|
Cociente de alturas en la caja en L |
15 |
0,80 (PA1) |
0,82 (PA1) |
0,86 (PA1) |
|
Resistencia a la segregación (%) |
30 |
1,86 (SR2) |
1,67 (SR2) |
1,31 (SR2) |
|
Densidad en estado fresco (Mg/m3) |
- |
2,22 |
2,16 |
1,96 |
|
Aire ocluido (%) |
- |
4,5 |
5,3 |
5,9 |
Tabla 2. Propiedades en estado fresco
SF: clase de escurrimiento, VS: viscosidad en escurrimiento, VF; viscosidad en el ensayo de embudo en V, PA; habilidad de paso y SR; segregación
|
Edad (días) |
MIX0 |
MIX50 |
MIX100 |
|
|
Resistencia a compresión sobre probeta cúbica (MPa) |
1 |
12,5 |
9,9 |
5,2 |
|
7 |
36,4 |
32,1 |
22,3 |
|
|
28 |
45,9 |
39,6 |
31,8 |
|
|
90 |
47,8 |
43,3 |
35,5 |
|
|
Resistencia a compresión sobre probeta cilíndrica (MPa) |
7 |
29,5 |
25,1 |
16,7 |
|
28 |
41,8 |
34,5 |
27,3 |
|
|
Densidad endurecida (Mg/m3) |
28 |
2,15 |
2,08 |
1,81* |
|
Módulo de elasticidad (GPa) |
7 |
26,6 |
24,5 |
13,9 |
|
28 |
29,3 |
27,1 |
16,1 |
|
|
Resistencia a tracción indirecta (MPa) |
7 |
2,7 |
2,1 |
1,4 |
|
28 |
3,2 |
2,4 |
1,8 |
|
|
Resistencia a flexión (MPa) |
7 |
4,1 |
3,8 |
2,9 |
|
28 |
4,9 |
4,5 |
3,3 |
|
|
Índice de rebote (adimensional) |
1 |
11 |
10 |
10 |
|
7 |
28 |
26 |
20 |
|
|
28 |
31 |
28 |
26 |
|
|
90 |
32 |
30 |
27 |
|
|
Velocidad de impulso ultrasónico (km/s) |
1 |
2,82 |
2,77 |
2,43 |
|
7 |
3,83 |
3,75 |
3,21 |
|
|
28 |
4,03 |
3,93 |
3,68 |
|
|
90 |
4,07 |
4,01 |
3,89 |
Tabla 3. Propiedades en estado endurecido
Aplicaciones
- Aplicación en obra mediente vertido, bombeo o inyección.
- Fabricación de piezas de hormigón con formas complicadas con altos requerimientos estéticos.
- Cimentaciones y estructuras.
- Estructuras fuertemente armadas.
- Construcción de grandes infraestructuras como puentes o túneles donde la compactación es complicada.
- Obras de dificil acceso y edificios de gran altura.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegido mediante patente P202030746
Estado actual de desarrollo
Desarrollado, validado y listo para su utilización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
El hormigón autocompactante con árido reciclado de hormigón y de baja retracción, se caracteriza porque está formado por cemento Portland como primer conglomerante, escoria siderúrgica granulada molida como segundo conglomerante y escoria blanca de horno de cuchara como tercer conglomerante. Su innovadora composición y procedimiento de puesta en obra, consigue excelentes resultados de durabilidad, sostenibilidad y estética.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
El aprovechamiento de residuos propios de la construcción junto con los residuos de la industria siderúrgica confiere a estos hormigones un proceso innovador de puesta en obra consiguiendo las mismas características técnicas que los hormigones autocompactantes cuya composición se basa en la utilización de fracciones con áridos naturales con ventajas técnicas y económicas adicionales.
Su dosificación se muestra en la Tabla 1:
|
Material/L |
L0 |
L5 |
L10 |
|
CEM I 52.5 R |
210 |
190 |
170 |
|
Escoria blanca de horno de cuchara |
0 |
20 |
40 |
|
Escoria siderúrgica granulada molida |
210 |
||
|
Árido reciclado de hormigón fracción polvo |
305 |
||
|
Agua |
335 |
||
|
Árido reciclado de hormigón fracción gruesa |
405 |
||
|
Árido reciclado de hormigón fracción fina |
865 |
||
|
Regulador de fraguado |
2,3 |
||
|
Plastificante |
4,5 |
Tabla 1. Dosificación de las mezclas (kg/m3)
Aprovechamiento de residuos para la elaboración de hormigón sostenible autocompactante óptimo para uso estructural.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Gran fluidez y facilidad de relleno de moldes para estructuras con formas complicadas.
- Eliminación de la etapa de presaturación en los áridos reciclados empleados.
- Alta autocompactabilidad del hormigón. Compactación sin necesidad de vibrado.
- Acabados homogéneos sin imperfecciones.
- Puesta en obra económica y sostenible por la utilización de residuos de la industria de la prefabricación de hormigón y de subproductos de la industria siderúrgica conocido como escoria.
- Reducción del consumo de energía en su puesta en obra.
- Excelentes propiedades físicas y mecánicas.
Características técnicas
Los novedosos hormigones autocompactantes, cumplen las especificaciones internacionales EN 206 y recomendaciones de la EFNARC.
|
Propiedad |
Tiempo desde el amasado (min) |
L0 |
L5 |
L10 |
|
Escurrimiento (mm) |
0 |
830 (SF3) |
825 (SF3) |
810 (SF3) |
|
15 |
780 (SF3) |
770 (SF3) |
755 (SF3) |
|
|
30 |
705 (SF2) |
700 (SF2) |
675 (SF2) |
|
|
60 |
555 (SF1) |
550 (SF1) |
550 (SF1) |
|
|
T500 (s) |
0 |
3,6 (VS2) |
4,0 (VS2) |
4,4 (VS2) |
|
15 |
5,8 (VS2) |
6,0 (VS2) |
6,6 (VS2) |
|
|
30 |
8,4 (VS2) |
9,0 (VS2) |
9,8 (VS2) |
|
|
60 |
12,8 (VS2) |
13,8 (VS2) |
15,2 (VS2) |
|
|
Tiempo de vaciado del embudo en V (s) |
15 |
24,8 (VF2) |
25,6 (VF2) |
26,2 (VF2) |
|
Cociente de alturas en la caja en L |
15 |
0,86 (PA1) |
0,85 (PA1) |
0,82 (PA1) |
|
Resistencia a la segregación (%) |
30 |
1,31 (SR2) |
1,26 (SR2) |
1,19 (SR2) |
|
Densidad en estado fresco (Mg/m3) |
- |
1,96 |
1,97 |
2,01 |
|
Aire ocluido (%) |
- |
5,9 |
5,7 |
5,4 |
Tabla 2. Propiedades en estado fresco
SF: clase de escurrimiento, VS: viscosidad en escurrimiento, VF; viscosidad en el ensayo de embudo en V, PA; habilidad de paso y SR; segregación
|
Edad (días) |
L0 |
L5 |
L10 |
|
|
Resistencia a compresión sobre probeta cúbica (MPa) |
7 |
22,3 |
21,8 |
20,5 |
|
28 |
31,8 |
32,6 |
34,5 |
|
|
Densidad endurecida (Mg/m3) |
28 |
1,81 |
1,86 |
1,89 |
|
Módulo de elasticidad (GPa) |
7 |
13,9 |
13,4 |
13,3 |
|
28 |
16,1 |
16,3 |
16,8 |
|
|
Retracción de secado (mm/m) |
2 |
0,65 |
0,51 |
0,63 |
|
Retracción a largo plazo (mm/m) |
180 |
1,30 |
1,08 |
0,83 |
Tabla 3. Propiedades en estado endurecido
Aplicaciones
- Aplicación en obra mediante vertido, bombeo o inyección.
- Fabricación de piezas de hormigón con formas complicadas con altos requerimientos estéticos.
- Cimentaciones y estructuras.
- Estructuras fuertemente armadas.
- Construcción de grandes infraestructuras como puentes o túneles donde la compactación es complicada.
- Obras de dificil acceso y edificios de gran altura.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegido mediante patente P202030748
Estado actual de desarrollo
Desarrollado, validado y listo para su utilización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos han desarrollado un nuevo depósito para células de medición de presión de compresión, de aplicación geotécnica, lo que supone una importante mejora respecto a los dispositivos existentes en el mercado hasta el momento al facilitarse su proceso de fabricación, reduciendo el coste por pieza.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La solución propuesta se centra en solventar el problema técnico de configurar un dispositivo para que sea más sencillo y menos costoso que los depósitos conocidos de chapa metal. La tecnología desarrollada se caracteriza por el empleo de un material termoplástico para la fabricación de depósitos de tamaño reducido. Este material permite emplear técnicas habituales para la fabricación de piezas con materiales termoplásticos, como la fabricación por adición de material o impresión 3D o el rotomoldeo, con lo que el coste por pieza es menor. Además, es posible desarrollar células de presión total especiales, específicas para soluciones concretas.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- El poliuretano termoplástico presenta resistencia mecánica combinada con cierta flexibilidad y resistencia química a los aceites.
- Es posible mejorar la impermeabilidad con una lámina de material impermeable látex o similar.
- Diámetro de entre 30 mm y 150 mm, inferior a la de los depósitos conocidos que suelen empezar en un diámetro mínimo de 200 mm.
- Altura máxima de entre 5 mm y 30 mm.
- Espesor de pared de entre 0,5 mm y 3 mm.
- Proceso de fabricación más barato al emplear un material termoplástico.
- Es más sencillo y económico desarrollar células de presión total especiales, específicas para soluciones concretas, sin un incremento de coste significativo.
Características técnicas
Una célula de presión total (o simplemente célula de presión) es un dispositivo con un sensor que sirve para medir presiones de compresión en el interior de un medio material en una determinada dirección. Se utiliza habitualmente para conocer las presiones de compresión que se ejercen en un punto del interior del terreno o en el interior de los revestimientos definitivos en túneles. El dispositivo incluye un depósito. Existe una relación directa entre el tamaño del depósito y la precisión de la medida de la presión, de forma que cuanto más pequeña sea una célula de presión total, más precisa será. El proceso tradicional de fabricación del depósito metálico es laborioso, lo que encarece el producto final. Además, la demanda de este tipo de sensores es baja y, en consecuencia, su proceso de fabricación está poco mecanizado.
El problema técnico a resolver es configurar el depósito para que sea más sencillo y menos costoso que los depósitos conocidos de chapa de metal. El material empleado es un poliuretano termoplástico, adecuado para este tipo de aplicaciones, por su resistencia mecánica combinada con cierta flexibilidad y resistencia química a los aceites. Tanto el diámetro como la altura del depósito, así como el espesor de las paredes, son considerablemente inferiores a los de los depósitos conocidos en chapa. Existe la opción de mejorar la impermeabilidad, disponiendo en el interior una lámina de material impermeable látex o similar.
Aplicaciones
Las potenciales aplicaciones del depósito son las siguientes:
- En instrumentación geotécnica para conocer las presiones de compresión que se ejercen en un punto del interior del terreno en una determinada dirección o bien en el interior de los revestimientos definitivos en túneles, o bien entre éstos y el terreno.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante modelo de utilidad U202031698
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Un grupo de investigación de la Universidad de Burgos ha patentado diferentes materiales cuya base es el yeso y que disponen propiedades mejoradas para la construcción, en especial para la utilización de los mismos como revestimientos en masa o para prefabricados para interiores. La característica en común a todos ellos es que se utilizan diferentes residuos para los cuales se fijan los criterios de su utilización y dosificaciones básicas que garanticen su resistencia y durabilidad, así como un alto grado de prestación y puesta en obra.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Obtención de materiales ligeros con propiedades mejoradas respecto de las mezclas convencionales (por ejemplo optimizando algunas de las propiedades básicas como son la trabajibilidad , la permeabilidad y el comportamiento reológico frente a cargas de fuerza) y con un buen comportamiento en régimen de prestación.
Los valores obtenidos son similares a otros materiales de construcción utilizados para el aislamiento térmico, lo que sugiere que el yeso con los mismos residuos de polímeros podría ser una alternativa a estos productos como un material con propiedades térmicas mejoradas.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Las ventajas fundamentales son del tipo medioambiental y económico así como de mejoras de las prestaciones de producto. Para la obtención de estos materiales se reciclan y reutilizan materiales de muy diversa índole, normalmente muy difíciles de degradar por métodos no mecánicos, debido a su estabilidad química.
Características técnicas
Los materiales que se disponen y que están patentados por la universidad de Burgos son:
- Yeso aligerado con residuos de poliuretano espumado. Nuevo material de yeso ligero para uso en la construcción, incorporando en la matriz los residuos de espuma de poliuretano rígidas industriales. Se emplean diferentes tamaños granulométricos dependiendo del uso final.
- Yeso aligerado con residuo de poliamida en polvo. Nuevo material en base yeso que utiliza residuos de polvo de poliamida para producir un nuevo derivado de yeso ligero, con propiedades térmicas mejoradas para aplicaciones industriales de acuerdo con las normas de construcción.
- Yeso de construcción con residuo de escorias blancas de horno. Este material deriva del yeso modificado con diferentes proporciones de escoria horno de cuchara utilizado como agregado mineral. El producto de invención se aditiva para mejorar sus propiedades de adherencia y de absorción y permeabilidad de agua. Los resultados físicos y mecánicos confirman la viabilidad de emplear escoria horno de cuchara como un agregado mineral, lo que induce un aumento de la densidad, de la permeabilidad de vapor y de la porosidad
- Yeso de construcción con fracciones de rechazo de piedra artificial tipo cuarzo triturado. Material obtenido a partir de cluster de yeso con agregados de cuarzo industriales rechazados para su uso en la construcción, consiguiendo diferentes texturas, colores y diseño con mejores propiedades frente al fuego en comparación con los productos de referencia
- Placas de yeso laminado aligeradas con residuo de espuma de poliuretano. Proceso para la produción placas de yeso de peso ligero para uso en las paredes interiores de una manera simple. El material permiteplacas de diferentes dimensiones y espesores dependiendo de la aplicación. El ensayo de incombustibilidad confirma que los residuos de poliuretano se puede utilizar en la fabricación de placas de yeso ecumpliendo las especificacionesnormalizadas
- Placas de yeso laminado con residuo de poliamida en polvo. Material en el que se muestra que el aumento de la cantidad de residuos de polímero implica reducciones importantes en su dureza y resistencia mecánica de la superficie, al tiempo que mejora su resistividad térmica
Aplicaciones
Empresas del sector de la Construcción Civil. Utilización en revestimientos en masa o prefabricados para interiores.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegidas por patentes de invención P201001011, P201100886, P201200092, P201300296, P201300464 y P201300846.
Estado actual de desarrollo
En uso, resultados de prueba disponibles.
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente concedida
P201001011, P201100886, P201200092, P201300296, P201300464,P201300846
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Ensayo de componentes sometidos a alta presión (tuberías y elementos de conducción), que permite:
1. Evaluar la Integridad estructural y análisis de fallos.
2. Reproducir el ciclo de trabajo (0-6000bar-0).
3. Conocer el comportamiento de nuevos componentes sometidos a alta presión.
4. Determinar la fatiga del componente real bajo la presión de trabajo.
5. Realizar ensayos de fractura y fatiga hidráulica hasta 6.000 bares.
Accesibiliad
Personal de contacto: - Isidoro Iván Cuesta Segura y Jesús Manuel Alegre Calderón, Grupo de Investigación de Integridad Estructural (GIE) E-mail: iicuesta@ubu.es; jalegre@ubu.es ; http://www.ubu.es/integridad-estructural-gie
Breve descripción sobre su utilización
Se podrán verificar de manera rápida y sencilla nuevos componentes sometidos a alta presión interna conociendo su comportamiento a fractura y fatiga (vida a fatiga), permitiendo realizar un mantenimiento preventivo de los equipos.
Comisiones
Solicitar oferta, el coste es variable en función del tipo de ensayo a realizar (fractura, fatiga de bajo número de ciclos, fatiga de alto número de ciclos, …).
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Dispositivo para ensayo de componentes sometidos a alta presión (tuberías y elementos de conducción sometidos a altas presiones), pudiéndose acoplar en cualquier máquina universal de ensayos dinámicos para reproducir los ciclos de trabajo (0-6000bar-0) de los diferentes componentes a analizar. Gracias a este nuevo equipo se podrán verificar de manera rápida y sencilla nuevos componentes sometidos a alta presión conociendo sus correspondientes vidas a fatiga, permitiendo realizar un mantenimiento preventivo de los equipos.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La mayoría de los componentes industriales sometidos a alta presión únicamente pasan pruebas estáticas de presión para su validación, en las que la presión se eleva hasta 1.5 veces la presión de trabajo.
Actualmente, no existen dispositivos comerciales que permitan efectuar ensayos para determinar la fatiga del componente real bajo la presión de trabajo, lo que implica que algunos de los componentes fallen por fatiga aun habiendo superado la prueba de presión.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
El dispositivo Integra la tecnología (HPP, High Pressure Processing) que se podrá acoplar en cualquier máquina universal de ensayos dinámicos para reproducir los ciclos de trabajo a alta presión de cualquier componente industrial. De esta forma se podrán realizar Ensayos de componentes sometidos a alta presión (tuberías y elementos de conducción), que permiten:
- Evaluar la Integridad estructural y análisis de fallos.
- Reproducir el ciclo de trabajo (0-6000bar-0).
- Conocer el comportamiento de nuevos componentes sometidos a alta presión.
- Determinar la fatiga del componente real bajo la presión de trabajo.
- Realizar ensayos de fractura y fatiga hidráulica hasta 6.000 bares.
Características técnicas
Dispositivo para ensayo de componentes sometidos a alta presión en una máquina de tracción-compresión que permite evaluarlos bajo esfuerzos estáticos y a fatiga, comprende:
- Un intensificador de presión con un cilindro por cuyo interior discurre un vástago,
- Dos mordazas comprendidas en la máquina de tracción-compresión,
- Un tubo portante alberga el intensificador de presión,
- Un tubo probeta,
Así, un fluido dispuesto en la cámara puede ser comprimido mediante el movimiento del vástago en el interior del tubo probeta.
Aplicaciones
Fabricantes de maquinaria para El procesado de alimentos por alta presión (HPP, High Pressure Processing) , Fabricantes de tuberías y elementos de conducción sometidos a alta presión, y empresas que centran sus actividades en el diseño, desarrollo, construcción, montaje, y puesta en marcha de maquinaria de alta presión.
Estado actual de desarrollo
El dispositivo esta disponible para Demostración. Probado en laboratorio.
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Sistema intercambiador de calor con medios internos de almacenamiento de energía, que incorpora diversos elementos que permite detectar alteraciones en el funcionamiento y tomar decisiones sobre la eficiencia energética del sistema, ahorrando energía y pérdidas económicas.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Los intercambiadores de calor incluyen mecanismos que almacenan la energía obtenida de fuentes renovables para satisfacer la demanda cuando las fuentes no están disponibles (por ejemplo, la energía solar durante la noche). Para este almacenaje hay un material (PCM) que absorbe o cede energía térmica y sufre cambios de comportamiento que actualmente no son detectables, provocando un innecesario aumento del consumo energético.
Este nuevo sistema permite detectar estas alteraciones y la consiguiente toma de decisiones o/y gestión automatizada para un mayor ahorro energético.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Almacenamiento de energía con sensores de temperatura para conocer el estado y el funcionamiento energético del intercambiador de calor.
- Permite tomar decisiones sobre la eficiencia energética de los medios de almacenamiento.
Características técnicas
Equipo intercambiador automatizado con medios de almacenamiento de energía, combinable con energías renovables intermitentes o con energías convencionales de bajo coste.
El intercambiador está compuesto por una cavidad interior que contiene un material de cambio de fase (PCM) como medio del almacenamiento de energía. Dispone además de conductos de entrada de fluidos fríos y calientes para absorber o ceder energía térmica.
Adicionalmente, se incluyen sensores de temperatura del material PCM, así como en los fluidos de los conductos frío y caliente, tanto en la cavidad interior y en la entrada y salida de sus respectivos conductos.
La medición de temperatura, permite una gestión automatizada de la energía, por ejemplo, en una instalación de climatización que incluya el intercambiador de calor, pudiendo evaluar continuamente la eficiencia energética y el estado del intercambiador.
Aplicaciones
Sistemas de climatización que incorporen intercambiadores de calor con acumulación de energía (renovables y convencionales)
Aplicable en instalaciones en edificación
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida por patente de invención P201730420.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Prototipo
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Rotor de polos curvos constituido por imanes permanentes aglomerados para emplear en motor trifásico síncrono, incrementando el par motor y el rendimiento más de un 20% respecto a motores de polos rectangulares.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
En el nuevo rotor, la disposición de los imanes permanentes en forma de arco de segmento circular mejora la componente reluctante del par motor, conformando una doble capa magnética.
Se emplean además imanes aglomerados de polvo de aleación de elementos de tierras raras (elementos como cerio, itrio o neodimio) con los que se obtienen valores de energía similares a los que se obtienen actualmente con imanes sinterizad
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Uso de imanes aglomerados de polvo de aleación de elementos de tierras raras, presentan un mejor comportamiento ante aumentos de temperatura respecto a imanes sinterizados.
- Obtención de un 20% más de par motor que otro con la misma cantidad de imanes rectangulares.
- Reducción de costes por empleo inferior de materiales de tierras raras, peso reducido y mejora de la eficiencia eléctrica.
Características técnicas
Rotor de imanes permanentes para usar en motores trifásicos síncronos para vehículos híbridos. Este rotor está constituido por dos capas concéntricas con forma de arco circular con magnitudes optimizadas geométricamente para conseguir aumentar el par reluctante lo que permite, junto con el par magnético, obtener un par total mayor.
Para conformar sendas capas magnéticas, se emplean imanes aglomerados de polvo de aleación de elementos de tierras raras, en lugar de sinterizados, permitiendo geometrías distintas a las rectangulares favorecedoras del par reluctante. Dichos imanes aglomerados, con las nuevas tecnologías de fabricación, obtienen valores energía aproximados a los sinterizados, que son los utilizados actualmente.
Mediante la combinación de la doble capa y las características mejoradas de los nuevos imanes se obtiene un par motor un 20% superior respecto a los motores eléctricos con los rotores actuales. Asimismo, se reduce el peso, el coste y las pérdidas energéticas del motor eléctrico.
Aplicaciones
Motores eléctricos para vehículos eléctricos puros e híbridos.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida por patente de invención P20173042.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Prototipo
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Plataforma de trabajo elevable como apero acoplable a tripuntal de tractor agrícola constituido por un mecanismo articulado que dispone de una plataforma elevable con forma de jaula para elevar personas y realizar tareas agrícolas en altura con seguridad.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
No existe un utillaje específico pensado para las distintas tareas en altura en el mundo rural y agrícola-ganadero.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Permite el movimiento telescópico vertical, longitudinal y transversal para realizar trabajos de altura con total seguridad en el mundo agrícola-ganadero.
- Puede nutrirse de la energía eléctrica procedente de la batería del tractor, permitiendo la eliminación de ruidos y ahorro de combustible.
Características técnicas
Plataforma elevable como apero, acoplable a tripuntal delantero o trasero de un tractor agrícola, no autopropulsada. El suministro de aceite a los cilindros oleohidráulicos se realiza mediante centralita activada por electrobomba, cuya energía eléctrica es tomada de la batería del tractor.
Dispone de varios dispositivos de seguridad:
1. Un interruptor de emergencia que desconecta todo el sistema eléctrico de la máquina de la batería del tractor.
2. Un inclinómetro de tipo eléctrico ubicado en la plataforma de trabajo orientado verticalmente.
3. Un sensor de nivel de tipo eléctrico ubicado en la base de la plataforma de trabajo con orientación longitudinal a esta.
Aplicaciones
Usuarios del sector maquinaria agrícola para la realización de tareas en altura en el mundo rural y agrícola-ganadera, como el podado e injertado de árboles, recogida de fruta de árboles frutales y cualquier trabajo de altura con seguridad.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida por patente de invención P201630499.
Estado actual de desarrollo
El dispositivo se encuentra en fase de validación de mercado.
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Software desarrollado para la optimización de rutas a medida destinado a empresas y entidades interesadas en resolver sus problemas de planificación de transporte (entrega a clientes o delegaciones, recogida de proveedores, etc.).
El objetivo del uso de este sistema es ayudar a la obtención de soluciones más económicas, rutas más cómodas, seguras y equilibradas (según los objetivos que se consideren) y que se ajusten a las restricciones de cada situación.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
El aspecto novedoso y que le da el valor añadido al producto con respecto a otras soluciones comerciales es el algoritmo de optimización utilizado que es donde realmente reside la innovación del software desarrollado. Este algoritmo es fruto de un trabajo extenso y profundo, ya que no todos los métodos son igual de buenos y por tanto el desarrollo de un algoritmo adecuado es crítico a la hora de obtener buenas soluciones.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Entre otras el uso de este sistema conlleva las siguientes ventajas:
- Facilidad de uso
- Rapidez de cálculo
- Reducción de costes
- Reducción emisión de CO2 y Sostenibilidad
- Mejora en el nivel de servicio a clientes (con la consiguiente mejora de imagen)
- Adaptación a diferentes objetivos, condiciones y/o restricciones
- Ayuda a la toma de decisiones
Características técnicas
El sistema desarrollado ofrece un entorno visual amigable al usuario, fácilmente manejable. Básicamente se gestionan los siguientes elementos:
- La entrada de datos, que se puede realizar por fichero o interactivamente
- Algoritmos de optimización para sugerir las soluciones más adecuadas
- La salida de datos: Hojas de rutas completas con toda la información.
- Un GIS (Sistema de Información Geográfica) para visualizar más cómodamente las localizaciones (almacenes, clientes, proveedores, etc.), carreteras, y las rutas obtenidas
Aplicaciones
Este software tiene aplicación en el campo de la optimización de rutas a medida en las empresas o entidades interesadas en resolver sus problemas de planificación de transporte (entrega a clientes o delegaciones, recogida de proveedores, etc.). Un área de especial interés es el correspondiente a la Industria Logística, y en concreto en el sector de los Operadores Logísticos que son unos actores de gran importancia en ésta industria.
Propiedad Intelectual
Programa de Ordenador con número de solicitud BU-117-15.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Software disponible para su comercialización. Se dispone de Demo.
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
En los materiales compuestos es conocida la correlación entre la orientación de las fibras y sus propiedades meá¡nicas y/o físicas. Conociendo las orientaciones reales de las fibras dentro de un material compuesto se puede optimizar el diseño y el proceso de fabricación.
Un material compuesto contiene materiales de diferentes densidades (material fibroso y matrices), y estos tienen diferentes capacidades de absorción de los rayos generando diferentes niveles de intensidad en el color de las imágenes escaneadas. Esto permite la posterior identificación y separación por tomografía computarizada (TAC), una técnica no destructiva que proporciona imágenes escaneadas con las orientaciones de los componentes fibrosos o filamentosos contenidas dentro de un material compuesto, y por lo tanto sus propiedades mecánicas y / o físicas. Sin embargo, la interpretación de estas imágenes depende del criterio de los técnicos, al ser una opinión subjetiva.
Esta interpretación subjetiva se transforma en objetiva cuando nos basamos en una valoración numérica de las orientaciones de las fibras o filamentos en el interior del compuesto. El resultado final es un uso más eficiente de la fibra, y por lo tanto un diseño óptimo, desde el punto de vista tanto estructural como económico.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La tecnología ofrece:
- Una orientación real y exacta de las fibras dentro de la matriz
- Una valoración numérica objetiva de los datos obtenidos
- Una interpretación global y local. Es posible obtener parámetros desde diferentes partes del compuesto (bordes, centro, etc ..)
- Una medición no destructiva y económica, los testeos mediante tomografía computarizada son más baratos que los testeos mecánicas
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Nuestro procedimiento está practicamente automatizado. La ruta marcada es fácil de seguir, es extremadamente preciso y los resultados se pueden obtener en un corto período de tiemo. El nivel de error sobre las orientaciones de las fibras es muy bajo.
Esta tecnología puede garantizar a las pequeñas y medianas empresas un salto cualitativo en cuanto a su productividad y competitividad. Mejoras en la calidad del producto, tener una información más objetiva de los procesos en tiempo real para el análisis y toma de decisiones, la mejora de los ciclos de inspección, diseño mejorado de productos, fabricación, etc.
Características técnicas
Utilizando un único algoritmo implementado en un software de análisis matemático (MATLAB, OCTAVE, SCILAB o similar) todos los procesos de post-procesamiento de las exploraciones tomográficas son automatizados. La segmentación de las fibras es más preciso porque este método utiliza una técnica de detección predictivo que agrupa la puntos espaciales en diferentes fibras para obtener posteriormente las orientaciones de las fibras en el espacio.
El hecho de utilizar una técnica de predicción, es decir, predecir la posición del grupo de puntos que están en la misma fibra, hace que sea posible separar los puntos que pertenecen a diferentes fibras, incluso si hay una pequeña distancia entre ellos. La agrupación de los puntos que pertenecen a una sola fibra, la orientación dominante de cada una de estas fibras se puede determinar automáticamente mediante la interpolación de una línea de puntos. El proceso completo se agrupa en un único algoritmo. Criterios de tolerancia se introducen como un valor de entrada y por lo tanto la exactitud del protocolo de análisis.
Aplicaciones
- Esta tecnología es útil para todas las empresas industriales relacionadas con la utilización de material compuesto reforzado con fibras, cuando estas muestran un valor diferente de la densidad en comparación con la matriz. Por lo tanto, es posible identificar de forma separada las fibras de la matriz, por ejemplo en las empresas de automoción, aeronáuticas, y las empresas de construcción que utilizan hormigones reforzados con fibra.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegido por patente PCT/EP2013/067219
Estado actual de desarrollo
En uso, resultados de pruebas disponibles
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Lightweight (2)
Resumen de la tecnología
En las últimas décadas han sido muchos los investigadores que han utilizado el ensayo miniatura de punzonado con el fin de obtener las propiedades mecánicas y de fractura de un material, en los casos que no se dispone de material suficiente para poder llevar a cabo ensayos normalizados, como por ejemplo en el caso de soldaduras o material irradiado. En este sentido, se ha desarrollado un procedimiento para evaluar la tenacidad a fractura empleando probetas miniatura de punzonado prefisuradas.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Se propone un nuevo procedimiento de ensayo, que permita obtener las propiedades a fractura del material, en los casos que no se dispone de una cantidad suficiente de material para poder realizar ensayos normalizados.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
La metodología desarrollada pretende convertirse en un nuevo procedimiento de ensayo, que permita obtener las propiedades a fractura del material, en los casos que no se dispone de una cantidad suficiente de material para poder realizar ensayos normalizados. La generación de la fisura inicial en las probetas SPT, previa al ensayo, se ha realizado a través de microfisuración por láser. Tras una calibración inicial, el láser es aplicado longitudinalmente a partir de la cara inferior, desde el centro de un lado de la probeta hacia el centro del lado opuesto.
Características técnicas
El ensayo miniatura de punzonado o “Small Punch Test” (SPT) consiste básicamente en un punzonado sobre una probeta cuadrada o circular de reducidas dimensiones, mediante un punzón de gran rigidez, estando la periferia de la probeta empotrada por dos matrices (ver apartado imagen).
Por otro lado, el diagrama FAD (failure assessment diagrames) un procedimiento para la evaluación de la integridad estructural de cualquier componente fisurado. Dicho diagrama considera el efecto de la fisura, geometría y propiedades del material como la tenacidad a fractura teniendo en cuenta el comportamiento plástico del mismo. Se asume que el fallo del componente o probeta se produce en el momento en el que se alcanza la línea de fallo definida por el diagrama FAD, la cuál se puede definir mediante diferentes niveles de análisis, en función de las propiedades del material disponible.
Se ha establecido un procedimiento integrado entre el ensayo de probetas SPT prefisuradas y el diagrama FAD, apoyándose el estudio en la simulación numérica, con el objetivo de estimar y determinar cuantitativamente la tenacidad a fractura de aceros. A partir de una porción de material del tamaño de una moneda de céntimo, el trabajo desarrollado permite estimar las propiedades más importantes desde el punto de vista resistente y de fractura.
Aplicaciones
El ensayo miniatura de punzonado podría ser aplicado en la caracterización de soldaduras. También sería valido para estudiar el material degradado de las centrales térmicas y nucleares dentro de sus programas de inspección.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La detección de explosivos en fase gas es crucial tanto en el ámbito de la seguridad civil como en química forense, en la determinación del explosivo utilizado en ataques terroristas.
En este ámbito se enmarca esta tecnología, que describe el uso desarrollo y uso de una matriz de tres sensores fluorogénicos sólidos para la detección selectiva de explosivos nitrados en fase gaseosa. El tratamiento estadístico de la información obtenida de la espectroscopía de fluorescencia de tres membranas en contacto con la atmósfera que contiene trazas de explosivos permite la diferenciación de no solo los explosivos de otra serie de compuestos similares, tales como 1-cloro-4-nitrobenzeno (ClNB), 2-nitro-m-xileno (NX), 1,3-dinitrobenzeno (1,3-DNB), 2-nitrotolueno (2-NT), 4-nitrotolueno (4-NT) y 2,4-dinitrotolueno (2,4-DNT), sino también la diferenciación inequívoca del explosivo entre los ensayados, tales como TNT (2,4,6-trinitrotolueno), ciclotrimetilentrinitramina (RDX) y tetranitrato de pentaeritritol (PETN).
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Se trata de materiales poliméricos sólidos novedosos que permiten la detección y diferenciación de compuestos nitroderivados no-explosivos de explosivos (TNT, RDX y PETN) mediante el tratamiento matemático de los cambios en los espectros de fluorescencia debidos a la presencia de vapores de estos compuestos.
Con respecto a otras soluciones conocidas representa un gran salto en cuanto a economía de uso y facilidad de aplicación debido a que las técnicas existentes en la actualidad aunque también son muy precisas (espectrometría de movilidad de iones (IMS) y cromatografía de gases (GC)), por ejemplo, requieren de un equipamiento muy caro y de mantenimiento costoso.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Tecnología barata para la detección de vapores de explosivos. Se basa en un sistema de filmes sensores cuya fluorescencia cambia ante la presencia de vapores de explosivos. Además, permite no sólo la detección de explosivos sino también su diferenciación y la discriminación de compuestos similares no explosivos.
Características técnicas
Se trata de materiales poliméricos sólidos para la detección fluorogénica de explosivos nitroderivados basados en nuevos monómeros vinílicos.
Mediante la polimerización de estos monómeros se obtienen películas o membranas densas, por copolimerización de estos monómeros con otros, entre los que se incluyen monómeros polifuncionales, para proporcionar materiales con buenas propiedades mecánicas, tanto en seco como en hinchado, que se comportan como sensores fluorogénicos sólidos de vapores de compuestos nitroderivados, TNT, RDX y PETN. Además, la utilización conjunta de estos sensores en forma de matriz de sensores y el tratamiento estadístico de los datos obtenidos a partir de su utilización permite la detección selectiva de estos compuestos y su diferenciación de otros interferentes similares.
Aplicaciones
- Puede ser de interés para empresas que utilizan este tipo de explosivos.
- Detección de explosivos en atentados (química forense).
- Seguridad civil en espacios cerrados de uso masivo (aeropuertos, estadios, estaciones, etc.).
- Canteras y minas.
- Empresas cuya área es la fabricación de explosivos y armamento.
- Empresas que utilizan explosivos para hacer demoliciones.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante P201400073.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Prototipo funcional o muestras listas para pruebas
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Medidas y estándares (3)
Resumen de la tecnología
Las máquinas de fatiga por flexión rotativa son esenciales para testar las propiedades de los materiales. Es habitual enfrentar las muestras de los distintos materiales a condiciones que difieren de las habituales, como por ejemplo a ambientes corrosivos, para evaluar su comportamiento.
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos han desarrollado un dispositivo que permite llevar a cabo este tipo de análisis permitiendo, a diferencia de muchos de los métodos actuales, que el material a analizar este en contacto directo con el electrolito responsable de generar condiciones distintas a las habituales. Adicionalmente, el diseño del dispositivo hace que pueda ser empleado en más de un experimento.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
En la actualidad existen dispositivos que permiten acoplar celdas electroquímica a las máquinas de fatiga y, de este modo, llevar a cabo estas mediciones, pero no todas permiten controlar el volumen de electrolito que está en contacto con la probeta (material). La invención de los investigadores de la UBU no solo permite que la probeta esté en contacto continuo con el electrolito, sino que el dispositivo puede acoplarse y desacoplarse de la máquina de fatiga sin realizar modificaciones en la misma.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Las principales ventajas de esta tecnología son las siguientes:
- El dispositivo permite que la probeta este en contacto con el electrolito a lo largo de todo el ensayo, manteniéndose un volumen constante del mismo y controlando la superficie del material que esta en contacto con el electrolito.
- La tecnología permite la renovación del electrolito durante el análisis.
- La celda electroquímica objeto de la invención puede utilizarse sin la necesidad de realizar modificaciones en la máquina de fatiga.
- El material puede someterse a distintos ambientes susceptibles de alterar el comportamiento a fatiga de forma sencilla y eficiente.
- La facilidad de implementación hace que el coste por ensayo sea muy competitivo.
Características técnicas
El dispositivo se trata de una minicelda o caja desmontable que se dispondría rodeando la probeta sin llegar a tener contacto con la misma. El dispositivo cuenta con una entrada y una salida parta el electrolito con unas medidas que permiten controlar el volumen contenido por el mismo. Mediante una serie de elementos, la celda se dispone, sin amarres, sobre la máquina de fatiga. Al finalizar el experimento, cuando la probeta se rompe, el diseño de la celda permite la recuperación de la misma, pudiendo ser utilizada de nuevo para llevar a cabo más ensayos.
Aplicaciones
Esta tecnología presenta un elevado interés para determinar las propiedades físicas de distintos materiales. Siendo de utilidad en el sector de la construcción, energético, petroquímico y la industria del metal, entre otros.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente P202330236
Estado actual de desarrollo
Prototipo disponible para demostración.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La Universidad de Burgos, a través del grupo de investigación AUSINCO (Auscultación, Instrumentación y Control de Estructuras), pone a disposición del sector de la obra civil (empresas constructoras, empresas de control de calidad, centros de investigación, Administraciones Públicas, etc.) e industria en general, una tecnología basada en la tecnología de sensor láser para la monitorización de movimientos en estructuras.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La posibilidad de monitorizar movimientos en estructuras de grandes dimensiones, como puentes para tráfico rodado y/o ferroviario, entre otros, es fundamental para conocer su estado y definir de forma más eficiente y económica las acciones de mantenimiento a desarrollar que permitan salvaguardar los niveles máximos de seguridad frente a los procesos de envejecimiento estructural con un consumo óptimo de recursos. El problema técnico a resolver es cómo lograr la medición, de manera precisa y económica, de los movimientos que experimenta una estructura constructiva.
La solución propuesta, más eficiente y de menor coste que lo presente actualmente en el mercado, permite obtener información muy útil sobre el estado de estructuras, con el objetivo de poder diseñar de forma más eficiente las labores de mantenimiento estructural y evitar así daños catastróficos en las mismas.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Monitorización continua de los movimientos en el tiempo.
- Elevada precisión de la medición de desplazamientos.
- Bajo coste de producción e instalación.
- Sensores ubicados de manera que las condiciones ambientales y lumínicas son favorables.
- Análisis de los datos en tiempo real.
Características técnicas
El medidor de desplazamientos consta de un conjunto de medición con una referencia fija y otro con una referencia móvil. Cada uno de dichos conjuntos de medición incluye al menos un elemento de diana y un transductor de desplazamiento láser apuntado hacia dicho elemento de diana. El transductor de desplazamiento láser está adaptado para medir variaciones de distancia respecto al correspondiente elemento de diana, donde, dichas variaciones de distancia son generadas por movimientos verticales en la estructura a monitorizar. El dispositivo se caracteriza porque el elemento de diana y el transductor de desplazamiento láser están dispuestos sobre la estructura, donde, el elemento de diana es la referencia fija y el transductor de desplazamiento láser es la referencia móvil.
La instalación de los sensores es llevada a cabo por personal especializado, en colaboración con el personal implicado en estas funciones de la empresa contratante. La realización de los ensayos y la monitorización tienen lugar in situ, desplazándose hasta el lugar el personal especializado de la Universidad de Burgos encargado de llevar a cabo todo el proceso.
Aplicaciones
- Estructuras de obra civil de grandes dimensiones, como puentes para tráfico rodado y/o ferroviario.
- Estructuras industriales.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención P201830539
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
El desarrollo de nuevos sensores colorimétricos simples, rápidos y baratos para la detección de trazas de hierro, aluminio y mercurio por parte de personal no especializado y mediante técnicas no convencionales se ha convertido en un importante reto, debido principalmente a que la presencia o ausencia de estos compuestos puede dar lugar a diferentes problemas de contaminación o de otra índole.
Como consecuencia de las necesidades anteriormente descritas se ha desarrollado y patentado un nuevo material polimérico de bajo coste y rápida aplicación que permite la detección colorimétrica (visual) y la cuantificación de hierro, aluminio y mercurio, utilizando el material sensor y la cámara de un teléfono móvil.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Estos nuevos materiales tienen la ventaja de proporcionar buenas propiedades físicas y facilitar la detección de los elementos indicados en fluidos a simple vista, o de cuantificar su presencia a través de los parámetros de color de fotografías digitales convencionales. Otro aspecto diferenciador es que se puede utilizar un teléfono móvil para conocer de forma directa la concentración de estos componentes mediante la calibración de una fotografía digital de una membrana.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- El film polimérico cambia de color fácilmente y de una forma totalmente distinguible permitiendo por lo tanto la realización de análisis cualitativo y cuantitativo "in situ"
- Se puede usar por personal no cualificado y bajo cualquier condición climática (siempre y cuando lo que se va a analizar esté en fase líquida) – Se permite realizar rápidos testeos sin necesidad de tener acoplado ningún equipo o fuente energética
- Se evita el uso de equipos de espectrometría caros así como los reactivos necesarios y requeridos para el análisis
- Como se trata de un polímero orgánico la fecha de caducidad del producto es superior a 100 años
- Se puede transportar fácilmente sin la necesidad de un kit adicional
- El material puede detectar el hierro en forma libre o bien en forma compleja, este caso sería por ejemplo cuando está disuelto en vino y en suero sanguíneo
- Se puede almacenar en cualquier lugar que no implique condiciones ambientales extremas
- No requiere el uso de medidas de protección (guantes, gafas, etc.)
Características técnicas
Membrana polimérica reticulada basada en dos monómeros comerciales de biocompatibles, un monómero sensor y una película. El film presenta una característica casi incolora.
Actúa como detector de hierro, aluminio y mercurio de forma separada. Como detector de hierro el cambio de color se vuelve verde oscuro, en la presencia de mercurio el cambio de color es naranja profundo, y en la presencia de aluminio se convierte fluorescente.
Por otra parte, la cuantificación se puede llevar a cabo utilizando los parámetros digitales (RGB) de una fotografía tomada a los materiales con una cámara o mediante un teléfono móvil inteligente.
Adicionalmente a esto, el material presenta excelentes propiedades mecánicas tanto en seco como en mojado.
Aplicaciones
- Detección de Legionella en torres de refrigeración y condensadores evaporativos.
- Clorosis férrica en plantaciones de árboles frutales y de la vid. Con una simple medición puede conocer si los suelos son ricos en hierro o no, siendo este parámetro fundamental para conocer si el suelo es apto para la siembra.
- EDAR and ETAP: En las plantas de tratamiento de aguas residuales y agua potable se utilizan a diario grandes cantidades de coagulantes como son las sales de hierro y aluminio. Por lo tanto, hay un riesgo real de contaminación del agua por estos componentes. Este riesgo puede ser eliminado mediante el uso de este detector.
- Proceso de construcción de canalizaciones en la Industria. En todos los sistemas que contienen tubos de hierro existe el peligro de que la corrosión se produzca y contamine el agua que fluye a través de estos circuitos. La formación de estos óxidos causa problemas en los procesos industriales que dependen directamente del agua que circula por estas canalizaciones. Del mismo modo, los sistemas de calderas debido a esta problemática se desgastan y oxidan provocando que finalmente los tubos y otras partes de la caldera tienen que ser reemplazados.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegido por patente P201300575
Estado actual de desarrollo
En uso, resultados de pruebas disponibles
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Physical Sciences and Exact Sciences (7)
Resumen de la tecnología
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos han desarrollado un dispositivo que se acopla al varillaje de los ensayos de penetración dinámica (DP) para medir in situ la resistividad eléctrica del terreno. Permite obtener valores de resistividad a diferentes profundidades y se ajusta al varillaje estándar. Esta invención ofrece una solución práctica y eficiente para la medición de la resistividad eléctrica del terreno durante los ensayos de penetración.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
El dispositivo presenta varios aspectos nuevos e innovadores en el campo de la medición de resistividad eléctrica del terreno durante los ensayos de penetración dinámica. Estos aspectos incluyen la integración del dispositivo con el varillaje estándar de los ensayos de penetración, el uso de un cilindro de material plástico aislante con electrodos metálicos en forma de anillo, la conexión al resistivímetro mediante un cable multifilar y la utilización de la propia batería del resistivímetro como fuente de energía. Estas características permiten una medición precisa y eficiente de la resistividad eléctrica a diferentes profundidades, mejorando así la caracterización del terreno en este tipo de ensayos.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Las principales ventajas de este dispositivo son:
- Integración sin problemas: El dispositivo se acopla fácilmente al varillaje estándar de los ensayos de penetración dinámica, lo que facilita su implementación en los equipos existentes sin necesidad de modificaciones adicionales.
- Medición in situ: Permite obtener mediciones de resistividad eléctrica en el mismo lugar donde se realiza el ensayo de penetración dinámica, lo que proporciona una evaluación directa y en tiempo real de las propiedades eléctricas del terreno.
- Precisión y profundidad ajustable: El dispositivo permite realizar mediciones a diferentes profundidades al ajustar el varillaje. Esto proporciona una caracterización más detallada del terreno a lo largo del perfil de penetración.
- Ahorro de tiempo y costos: Al realizar las mediciones durante el ensayo de penetración dinámica, se reduce la necesidad de realizar pruebas adicionales y se optimiza el uso del equipo, lo que resulta en ahorros significativos de tiempo y costos.
- Compatibilidad con diferentes configuraciones: El dispositivo puede adaptarse a diferentes configuraciones de electrodos, como la configuración Wenner o Dipolo-dipolo, lo que brinda flexibilidad al operador para elegir la configuración más adecuada según los requisitos del estudio.
Características técnicas
El dispositivo para medir la conductividad eléctrica se caracteriza por su construcción robusta con una camisa de material plástico aislante, electrodos metálicos embebidos, conexión al resistivímetro mediante un cable multifilar, adaptabilidad al varillaje estándar y fijación segura con cinta adhesiva. Estas características aseguran un funcionamiento confiable y una integración sin problemas con los equipos de penetración dinámica, permitiendo mediciones precisas de la conductividad eléctrica del terreno.
Aplicaciones
Las principales aplicaciones de este dispositivo son:
- Identificación de las propiedades físicas del suelo e índices de humedad.
- Localización de niveles arcillosos en terrenos granulares.
- Localización del nivel freático en el terreno.
- Medida de la resistividad para el diseño, verificación y mantenimiento de redes de puesta a tierra de instalaciones eléctricas.
Por lo que es de especial interes en sectores como la geotecnia y exploración del subsuelo, la ingeniería civil y la construcción, la hidrogeología y la geofísica.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente P202330366
Estado actual de desarrollo
Prototipo disponible para demostración.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Un grupo de investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos, en colaboración con la Universitat de Barcelona e IDIBELL, ha patentado una familia de moléculas que tiene la capacidad de transportar lactato en células vivas. La capacidad de estas moléculas para alterar la concentración de lactato de las células puede tener un impacto significativo en terapia oncológica, ya que se ha observado que altos niveles de lactato en el microambiente tumoral están relacionados con la progresión y resistencia al tratamiento en algunos casos de cáncer. Esta tecnología representa un nuevo avance en la búsqueda de estrategias terapéuticas contra el cáncer.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Esta investigación pionera llevada a cabo por un grupo de científicos de la Universidad de Burgos en colaboración con la Universitat de Barcelona ha logrado un descubrimiento innovador al identificar y desarrollar las primeras moléculas capaces de transportar de manera efectiva el lactato a través de las membranas biológicas. A modo de ejemplo, una de las moléculas sintetizadas (AS37) es capaz de interaccionar con el lactato formando un complejo que, a diferencia del lactato, es capaz de atravesar la membrana celular. Esto permite alterar las concentraciones de lactato en células, teniendo el lactato un papel relevante en el metabolismo característico de células cancerosas. Los estudios in vitro han demostrado que estos compuestos son capaces de hacer más sensibles a células cancerosas frente a otros fármacos utilizados en quimioterapia, por lo que presentan potenciales aplicaciones en este campo.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Las principales ventajas de esta tecnología son las siguientes:
- Se trata de la primera familia de moléculas capaces de facilitar el transporte de lactato a través de membranas biológicas.
- Estas moléculas transportan el lactato de forma independiente a los mecanismos de transporte propios de la célula, los transportadores de monocarboxilatos (MCTs).
- La molécula AS37 es capaz de alterar las concentraciones intra y extracelulares de lactato en presencia de un inhibidor de MCTs.
- Se ha demostrado la capacidad de este compuesto de actuar de forma sinérgica con agentes ampliamente utilizados en quimioterapia como el cis-platino en experimentos in vitro con células tumorales.
Características técnicas
Las moléculas descritas son capaces de interaccionar mediante enlaces de hidrógeno con los aniones lactato, formando un complejo supramolecular que es capaz de difundir a través de las membranas lipídicas. De esta forma es posible facilitar el paso del lactato en membranas celulares de forma independiente de los mecanismos celulares encargados de este proceso, proteínas transmembrana denominadas transportadores de monocarboxilato (MCTs). Este mecanismo puede demostrarse mediante la utilización de un inhibidor de este tipo de proteínas MCT, la sirosingopina. En presencia de sirosingopina las moléculas son capaces de alterar la concentración intra y extracelular de lactato en células cancerosas de acuerdo a los resultados in vitro obtenidos. Se ha demostrado en este modelo in vitro que esta estrategia consigue sensibilizar a las células tumorales frente a agentes empleados en quimioterapia como el cis-platino. Esta actividad sinérgica abre la puerta a la exploración de la utilidad de estas moléculas en el desarrollo de nuevas terapias para el tratamiento del cáncer.
Aplicaciones
El compuesto descrito permite alterar la permeabilidad y homeostasis del lactato in vitro. Al ser el lactato una diana terapéutica en el tratamiento del cáncer se abre la posibilidad de desarrollar compuestos con aplicación como agentes terapéuticos para el tratamiento de esta enfermedad. Los compuestos señalados pueden servir como herramientas de investigación bioquímica y de biología celular en este contexto, utilizándolos solos o en combinación con inhibidores de MCTs.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente P202330370
Estado actual de desarrollo
Pruebas realizadas in vitro.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La presente invención describe un procedimiento para la síntesis de p-cimeno a partir de monoterpenos o mezclas de estos, utilizando dimetilsulfóxido como agente oxidante y disolvente, en presencia de un catalizador de molibdeno. Esta ruta sostenible y económicamente competitiva para la síntesis de p-cimeno a partir de fuentes renovables procedentes de la biomasa, representa una alternativa viable a los procedimientos que se están empleando en la actualidad. Este procedimiento presenta ventajas en términos de selectividad, baja toxicidad, disponibilidad de materias primas y facilidad de purificación.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La invención propone un nuevo método para la síntesis de p-cimeno a partir de monoterpenos o mezclas de los mismos, procedentes de la biomasa utilizando dimetilsulfóxido como agente oxidante y un catalizador de dioxomolibdeno(VI). Este enfoque innovador evita los problemas de las técnicas anteriores, como la generación de mezclas de isómeros, la sensibilidad al azufre presente de forma habitual en algunos de los materiales de partida y el uso de productos tóxicos. Además, el procedimiento es más eficiente, seguro y sostenible, ofreciendo una alternativa prometedora para la producción de p-cimeno puro y de alta calidad.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Obtención de p-cimeno puro: El método permite la síntesis de p-cimeno isoméricamente puro tras un sencillo proceso de destilación.
- Utilización de monoterpenos procedentes de la biomasa: Se emplean materias de partida renovables y de bajo costo, como el sulfato de trementina crudo y el aceite de cítricos generados como residuos o subproductos en la industria del papel y los zumos cítricos.
- Agente oxidante de baja toxicidad: Se emplea dimetilsulfóxido, un agente oxidante biodegradable y fácilmente eliminable del medio de reacción.
- Catalizador resistente al azufre: El catalizador utilizado es resistente a la presencia de azufre o sus derivados en el sulfato de trementina crudo de partida.
- Condiciones de reacción suaves: La síntesis se realiza a presión atmosférica y a una temperatura moderada de 150 ºC.
- Aspectos económicos y de seguridad: El método es económico, sencillo de operar y no requiere productos químicos tóxicos ni atmósfera inerte en las reacciones.
Características técnicas
- Material de partida: Monoterpenos o mezclas de estos procedentes de la biomasa.
- Agente oxidante: Se emplea dimetilsulfóxido (DMSO) como agente oxidante estequiométrico y disolvente en la reacción.
- Catalizador: Se utiliza un catalizador de dioxomolibdeno(VI), específicamente bis-(dimetilformamido)diclorodioxomolibdeno(VI), MoO2Cl2(dmf)2, en cantidades de 3-5 mol%.
- Condiciones de reacción: La reacción se lleva a cabo a presión atmosférica, a una temperatura de 150 ºC y en un tiempo de reacción de 24 horas.
- Purificación del producto: El p-cimeno obtenido se purifica mediante extracción con distintos disolventes y destilación fraccionada.
Aplicaciones
El método de síntesis de p-cimeno descrito por científicos de la Universidad de Burgos presenta una alternativa económicamente sostenible al método empleado actualmente a partir del tolueno, procedente de recursos petroquímicos y por tanto, no renovables.
El p-cimeno sintetizado tiene diversas aplicaciones en la industria, incluyendo la perfumería, farmacéutica, herbicidas, tintes, polímeros y productos químicos de alto valor añadido. La nueva metodología proporciona una forma más eficiente, empleando residuos industriales y/o recursos renovables procedentes de la biomasa, de obtener p-cimeno puro, lo que beneficia a estas industrias en términos de calidad, disminución de costos y sostenibilidad.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente P202330367
Estado actual de desarrollo
Prototipo disponible para demostración.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos han desarrollado una metodología para la desoxigenación de compuestos azufrados (sulfóxidos). Para llevar a cabo esta transformación, se emplean compuestos naturales procedentes de la biomasa y un catalizador de molibdeno. Los productos se obtienen con elevados rendimientos y una gran pureza.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La reducción de sulfóxidos (1) a los correspondientes sulfuros (2) es una transformación de gran utilidad tanto en la industria química, como en la industria farmacéutica.
Existen varios métodos para llevar a cabo esta transformación, sin embargo, el procedimiento patentado por la Universidad de Burgos permite obtener estos compuestos de forma rápida y eficaz, empleando un agente reductor novedoso y un catalizador de molibdeno. Las condiciones de reacción hacen que la purificación de los compuestos finales sea extremadamente sencilla.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Las principales ventajas de este método son las siguientes:
- Empleo de reductores naturales, monoterpenos procedentes de la biomasa, medioambientalmente benignos y sostenibles.
- Los monoterpenos actúan como disolvente, reduciendo los costes y sus subproductos pueden eliminarse con elevada facilidad.
- Los productos se obtienen con rendimientos superiores al 75% y una elevada pureza.
- La transformación no requiere de atmósfera inerte y se completa en dos horas calentando a 160 ºC.
- Elevada tolerancia de grupos funcionales.
Características técnicas
Los monoterpenos obtenidos de la biomasa se emplean en cantidades equimolares, actuando como agentes reductores y sustituyendo al disolvente. El compuesto de dioxomolibdeno (VI), MoO2Cl2(dmf)2, se añade en cantidades catalíticas (5 mol%) y es el encargado de acelerar y facilitar el proceso.
Los subproductos obtenidos en la reacción son p-cimeno y agua, lo cual permite la purificación del producto desoxigenado de forma rápida y sencilla, sin la necesidad de recurrir a técnicas de separación complejas.
La baja toxicidad de los reactivos utilizados permite llevar a cabo la reacción con un mayor grado de seguridad y desde un punto de vista medioambientalmente más respetuoso.
Aplicaciones
Esta tecnología tiene aplicación directa en la industria química y en la industria farmacéutica.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente P202330200
Estado actual de desarrollo
Prototipo disponible para demostración.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Un grupo de investigación de la Universidad de burgos ha puesto a punto un nuevo procedimiento que permite transformar grupos nitro (1) a aminas (2) en tiempos cortos y con rendimientos que alcanzan el 95%. La clave de esta transformación reside en el catalizador de molibdeno utilizado y el agente reductor.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
En bibliografía, existen una gran variedad de métodos que permiten la transformación del grupo nitro (1) a amina (2). Dada la importancia que tienen estos últimos compuestos en la industria farmacéutica y la industria química, la metodología descrita por los investigadores de la Universidad de burgos representa una forma rápida, sencilla y económica de obtener aminas. Por otro lado, las condiciones de reacción son compatibles con una gran variedad de grupos funcionales, incluso aquellos susceptibles de ser reducidos. Otro de los aspectos innovadores de esta estrategia sintética es la utilización de γ-terpineno como agente reductor y un catalizador de dioxomolibdeno (VI).
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Las principales ventajas derivadas de la utilización de esta metodología son:
- Obtención de los compuestos finales con rendimientos que van desde el 50 hasta el 95%.
- Elevada tolerancia a otros grupos funcionales como grupos carbonilos, nitrilos, cadenas insaturadas, etc.
- El γ-terpineno es un producto natural procedente de la biomasa. Cuando se emplea como agente reductor, en presencia del catalizador de dioxomolibdeno (VI), se consigue la reducción del grupo nitro a amina, formándose subproductos de reacción fácilmente separables.
- La transformación no necesita de atmósfera inerte ni presiones elevadas, lo que supone una ventaja desde el punto de vista económico, medioambiental y de seguridad.
Características técnicas
El γ-terpineno actúa como reductor, en cantidades equimolares, y como disolvente se emplea la dimetilacetamida. El compuesto de dioxomolibdeno (VI), MoO2Cl2(dmf)2, se añade en cantidades catalíticas (5 mol%) y puede prepararse fácilmente a partir de reactivos comerciales.
Empleando calentamiento por microondas, la reacción se completa en 60 minutos. Además, la transformación puede llevarse a cabo en ausencia de disolvente.
Los subproductos obtenidos en la reacción son el p-cimeno y agua, lo cual permite la purificación del producto desoxigenado de manera sencilla y rápida, sin la necesidad de recurrir a técnicas de separación complejas.
Aplicaciones
Esta tecnología tiene aplicación directa en la industria química y en la industria farmacéutica.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente P202330202
Estado actual de desarrollo
Prototipo disponible para demostración.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
nvestigadores de la Universidad de Burgos han diseñado un método para sintetizar un compuesto extremadamente útil en la detección de explosivos, como por ejemplo el triperóxido de triacetona. Este explosivo resulta muy sencillo de preparar y extremadamente difícil de detectar. El proyecto ha sido subvencionado por la OTAN y, dado el potencial de la molécula, se ha solicitado la patente para proteger y comercializar la misma.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Los artefactos explosivos improvisados (IEDs) suponen una gran amenaza para la sociedad, por lo que, durante los últimos años se han desarrolado métodos para la detección de los mismos. Sin embargo, explosivos como el triperóxido de triacetona (TATP) resulta extremadamente complicado de detectar y, dada la facilidad con la que puede obtenerse, es imperativo disponer de métodos sencillos, robustos y con la suficiente sensibilidad para detectar estos compuestos. La tecnología desarrollada por la Universidad de Burgos nace para dar respuesta a estas demandas y posicionarse como un método eficaz, asequible y de fácil utilización.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
La molécula patentada ha demostrado ser perfecta para usarse como elemento activo en la preparación de sensores fluorogénicos.
La principal ventaja de esta tecnología es que permite detectar trazas de TATP en el aire sin el empleo de grades y costosos equipos de forma selectiva y ultrasensible.
El límite de detección es significativamente bajo, llegando a detectar concentraciones inferiores a 60 pM.
Para dar un mayor valor a esta tecnología, este método resulta útil para detectar una gran variedad de moléculas oxidantes.
Características técnicas
Las naftalimidas que se describen en la presente invención, al interaccionar con una molécula oxidante, experimentan una modificación de su fluorescencia que está directamente relacionada con la concentración de analito oxidante.
La molécula sintetizada se absorberse en distintos materiales (anatasa, sílice, etc.) y, una vez absorbido, la interracción con las moléculas de interes se realiza en su superficie. Se ha comprobado que el límite de detección de TATP es de hasta 13 ng.
Aplicaciones
Detección ultrasensible de triperóxido de triacetona, TATP, (muy difícil de detectar y frecuentemente utilizado en artefactos explosivos improvisados) en el aire en tiempo real.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente P202330107
Estado actual de desarrollo
Prototipo disponible para demostración.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Análisis de dentaduras mediante software para obtener información sobre restos paleontológicos a partir del tratamiento de imágenes semiautomático. Se reduce de esta forma el error por factor humano en el trabajo repetitivo. También puede emplearse en odontología forense.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Es posible obtener información relevante acerca del modo de vida de los antecesores de la humanidad mediante análisis de imágenes obtenidas de su mandíbula. Principalmente se puede estimar su edad, los problemas alimenticios durante el crecimiento y estimar su dieta. De esta forma se puede reconstruir su vida, comportamiento y entorno.
En el nuevo método de análisis, se emplean diversos módulos de tratamiento de las imágenes. Se evitan de esta forma, minimizar los fallos que a menudo se cometen en este tipo de análisis por el fallo humano en un proceso repetitivo.
En cada uno de los módulos, se identifican de forma semi-automática las principales marcas e indicadores de la alimentación o los problemas de crecimiento, a diferencia del tratamiento de imágenes actual y posterior identificación de dichas marcas y análisis.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Análisis semi-automático de imágenes de la superficie de restos dentales.
- Aumento de la velocidad en los análisis odontológicos.
- Disminución de errores en el análisis.
- Reducción de tiempos de análisis.
Es importante remarcar que este análisis no sustituye al profesional de la materia, imprescindibles para los resultados, sino que elimina los errores por el factor humano en ciertas tareas repetitivas.
Características técnicas
Software semi-automático que dispone de diversos módulos para obtener información dentro de un análisis odontológico:
- Estimación de la edad. Se efectúa, en primer lugar una reconstrucción de la imagen global de la muestra, que se compone de diversas tomas de un microscopio.
En segundo lugar, se realiza un análisis de las diversas marcas del crecimiento, obteniendo lo que se conoce como anillos perikymata. El grosor de estos anillos, permiten distinguir la especie de homínido a la que corresponde la muestra y aportan información acerca de la edad o posibles problemas durante el crecimiento.
- Estimación de problemas alimenticios. En este caso se efectúa una selección de la zona correspondiente a la mandíbula inferior y superior sobre una radiografía de la misma, mediante el cálculo de una recta curva que las separa. Por procesado de la imagen se localizan las separaciones entre dientes para distinguirlos y poder detectar marcas y realizar su posterior análisis.
- Estimación de la dieta. En este caso, tras el tratamiento de la imagen, se trazan aquellas líneas relevantes para la detección de marcas que sirvan para estimar la dieta de los homínidos.
Aplicaciones
Análisis paleontológico de mandíbulas. También podrían emplearse los diversos módulos en odontología forense, si bien requeriría de un número mayor de datos.
Propiedad Intelectual
Registro de la propiedad intelectual BU-75-17, BU-76-17 y BU-77-17.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Software desarrollado en constante mejora.
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Protección al hombre y al medio ambiente (12)
Resumen de la tecnología
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos han diseñado un dispositivo innovador para la instalación vertical de mangueras utilizado por los cuerpos de bomberos, con el objetivo de mejorar las condiciones laborales y reducir los riesgos durante las intervenciones. El dispositivo resuelve las deficiencias y limitaciones de los dispositivos existentes en el mercado. Entre sus ventajas, destaca la capacidad de ofrecer un anclaje seguro en diversas ubicaciones, se ajusta a diferentes anchuras, evita el colapso de las mangueras y reduce el peso para facilitar el transporte y la colocación.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
- Anclaje seguro y adaptable: El dispositivo ofrece un anclaje seguro y adaptable en diferentes ubicaciones para una instalación versátil.
- Doble apertura sin bifurcación: El dispositivo tiene dos salidas integradas que permiten conectar dos mangueras sin necesidad de una bifurcación adicional, reduciendo volumen y peso.
- Llaves de bola independientes: El dispositivo cuenta con llaves de bola independientes para regular el caudal de agua en cada manguera, brindando control individualizado.
- Integración de elementos de sujeción y freno: El dispositivo incorpora elementos de sujeción y un freno para mejorar el anclaje y estabilidad durante su uso.
- Fabricación aditiva: El dispositivo se fabrica utilizando tecnología de fabricación aditiva, permitiendo flexibilidad en el diseño y producción.
- Mejora de las condiciones laborales: La patente busca mejorar las condiciones laborales al reducir riesgos como roturas de mangueras, caídas y limitaciones de caudal, brindando mayor seguridad y eficiencia en las intervenciones.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
El dispositivo de sujeción de doble apertura ofrece las siguientes ventajas:
- Anclaje seguro en diferentes ubicaciones.
- Adaptabilidad en anchura para una instalación versátil.
- Conexión directa de dos mangueras sin bifurcación adicional.
- Control independiente del caudal de agua mediante llaves de bola.
- Mejora de la estabilidad con elementos de sujeción y freno integrados.
- Fabricación eficiente y flexible mediante tecnología aditiva.
- Reducción de riesgos laborales, como roturas de mangueras y caídas, mejorando la seguridad de los bomberos.
Características técnicas
El dispositivo cuenta con anclajes seguros, adaptabilidad en anchura, control independiente del caudal de agua, elementos de sujeción y freno integrados, fabricación mediante tecnología aditiva, y ofrece mejoras en la estabilidad y reducción de riesgos laborales.
Aplicaciones
Este dispositivo, por sus características técnicas y las ventajas que presenta, podría ser empleado en los siguientes en/por:
- Cuerpos de Bomberos
- Servicios de emergencia
- Edificios de gran altura
- Industria naval
- Industria petroquímica
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente P202330365
Estado actual de desarrollo
Prototipo disponible para demostración.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Se trata de un elemento conector acodado para mangueras de incendios que permite mejorar las condiciones laborales de los cuerpos de bomberos y sus actuaciones durante una intervención.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
A la hora de combatir un incendio los bomberos cuentan con un dispositivo para la sujeción de una instalación vertical de mangueras la cual presenta una serie de carencias o deficiencias, que pueden llegar a comprometer su actuación. En respuesta a esta necesidad se ha desarrollado un dispositivo de sujeción para la instalación vertical de mangueras mediante fabricación aditiva. Este dispositivo permite reducir los riesgos laborales de los efectivos y mejorar su actuación durante una intervención.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
• El dispositivo se instala de forma rápida y sencilla.
• Permite mejorar las condiciones laborales de los bomberos.
• Se puede anclar de forma segura en las diferentes ubicaciones que se pueden encontrar los bomberos en un edificio (barandillas, muros, alfeizares, etc.). De esta forma se reduce el riesgo de producirse cualquier incidente o accidente por caída del tendido vertical y arrastre de los bomberos que se encuentran trabajando en la extinción del incendio.
• Se adapta o ajusta en anchura en función del punto donde se tenga que ubicar.
• Evita que las mangueras colapsen o se plieguen contra el suelo, de esta forma se evita limitar el caudal para afrontar el incendio.
• Se ha optimizado el peso del dispositivo mediante fabricación aditiva.
• Se evita trabajar con presiones de trabajo elevadas, lo que se traduce en una reducción del riesgo de rotura en las mangueras y por consiguiente se reduce el riesgo para los efectivos.
Características técnicas
El dispositivo desarrollado integra un codo con dos racores tipo Barcelona junto con los elementos de unión de un sargento de sujeción.
Se evitan los posibles accidentes (caídas, torceduras, etc.) que puedan producirse por las escaleras de los edificios siniestrados ya que los tramos de dichas escaleras quedarían libres de obstáculos. El uso del dispositivo de anclaje permitiría una instalación vertical por el hueco de escalera o por fachada dejando la escalera como un recurso libre y seguro en caso de ser utilizado para realizar evacuaciones, rescates y movilizar recursos humanos y materiales durante la intervención.
Se evita que no se consiga el caudal necesario para contrarrestar la potencia calorífica del incendio en edificios de gran altura (EGAs) ya que con el dispositivo desarrollado se consigue reducir pérdidas de carga al utilizar de forma segura un tendido vertical de mangueras y así establecer un caudal disponible suficiente.
Aplicaciones
El dispositivo desarrollado puede ser empleado en la instalación vertical de mangueras durante las actuaciones de los cuerpos de bomberos en edificios de gran altura.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante modelo de utilidad U202231148
Estado actual de desarrollo
Se han realizado pruebas en laboratorio.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Este software permite una interacción entre rehabilitadores, pacientes y sus familias de manera que resulte sencilla, motivadora y efectiva la terapia realizada.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Este software permite una interacción entre pacientes, rehabilitadores y sus familias de manera que resulte sencillo, motivador y efectivo el trabajo realizado. Consta de varios módulos: gestor de valoraciones y resultados, gestor de ejercicios cognitivos, gestor de ejercicios físicos (fichas de ejercicios con dibujos y explicación de la forma correcta a la hora de realizarlos, videos y fotografías), gestor agenda (sesiones, tratamiento, medicación, coordinación entre diferentes profesionales y familiares), gestor aplicación de productos de apoyo. Este software permite realizar programas individualizados dirigidos a la prevención y mantenimiento de capacidades físicas y psicosociales de una persona según su nivel de dependencia.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Permite la elaboración de programas individualizados
- Permite la prevención y mantenimiento de capacidades físicas y psicosociales en personas dependientes
- Permite la interacción entre pacientes, rehabilitadores y sus familias
- Sencillo, motivador y efectivo
Características técnicas
El gestor consta de varios módulos, todos ellos integrados y actualmente en aplicación.
- Gestor de Valoraciones y resultados.
- Gestor de Ejercicios Cognitivos.
- Gestor de Ejercicios Físicos (fichas de ejercicios, videos y fotografías).
- Gestor Agenda: sesiones, tratamiento, medicación, coordinación entre diferentes profesionales y familiares. El gestor, permite a los familiares llevar un continuo seguimiento del tratamiento sobre el paciente con una continua comunicación con el terapeuta.
- Gestor aplicación de productos de apoyo. Permite realizar un seguimiento de aquellos pacientes que realicen el tratamiento en domicilio.
Aplicaciones
Los posibles lugares de aplicación son centros socio-sanitarios como centros de día, clínicas especializadas, asociaciones y hospitales.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante Registro propiedad intelectual BU-49-17
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente concedida
BU-49-17
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Un grupo de investigación de la Universidad de Burgos ha desarrollado un procedimiento para la fabricación de un prefabricado de yeso utilizando residuos de espuma de poliuretano (de origen industrial). El coste del prefabricado sostenible es menor respecto al tradicional y además presenta mejoras en cuanto a reducción de peso, aumento en la capacidad aislante y representa una solución viable para el reciclado de la espumas de poiluretano. De esta forma contribuye a la economía circular, posicionándose como una alternativa a los prefabricados de yeso tradicionales.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Uno de los mayores desafíos ambientales del siglo XXI es la reducción, reutilización y reciclaje de plásticos. Ante esta realidad se hace evidente la necesidad de buscar alternativas de valorización y reciclado de los residuos de plástico generados. El procedimiento descrito por investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos ha permitido la elaboración de un prefabricado de yeso sostenible empleando el residuo de espuma de poliuretano, lo cual supone un ahorro económico y energético, con el consiguiente beneficio en términos de reducción de huella de carbono.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Reducción de costes. El coste final del material obtenido es un 12% menor respecto a un prefabricado de yeso tradicional.
- Mejora en las características físicas del prefabricado.
- Reducción de peso de hasta un 25% respecto a las placas estándar.
- Aumento en la capacidad aislante del material elaborado.
- Aumento de las tasas de reciclaje de este residuo.
Características técnicas
- La procedencia de los residuos de espuma de poliuretano es variada: industria de la refrigeración, industria de la construcción e industria del automóvil. Se ha realizado la caracterización (física, química y microscópica) de estos residuos, con el objetivo de establecer un procedimiento estándar de fabricación.
- Presenta fibras de refuerzo, que mejoran las propiedades mecánicas del prefabricado.
- Presenta aditivos de diversa naturaleza, que aportan mejoras en las prestaciones del producto.
Aplicaciones
- Empresas el sector de la edificación, construcción y rehabilitación.
- Empresas relacionadas con la industria de la refrigeración y del automóvil interesadas en el reciclaje de residuos de espumas de poliuretano.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante modelo de utilidad U201931952
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La reutilización de los lodos de depuradora para su uso agrícola tiene como principal condicionante la presencia en ellos de metales pesados. El proceso que se propone optimiza su disolución mediante una combinación adecuada de extractantes ácidos y agentes complejantes para luego mediante procesos de separación en membrana e intercambio iónico, recuperar fracciones metálicas enriquecidas donde la recuperación de los diferentes metales es posible.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Diferentes procesos han sido utilizados eficazmente para la desmetalización de los lodos de depuradora: la extracción química, la biolixiviación, los procesos electrocinéticos y la extracción con fluidos supercríticos. De todas ellas, es la extracción química la que ha conseguido los mejores resultados de aplicación, si bien dada la alta variabilidad en la naturaleza y estado de los lodos, su elevado volumen de tratamiento y el coste asociado es indispensable lograr la máxima recuperación metálica en el mínimo coste operativo, lo que se consigue optimizando el agente extractivo y con una adecuada combinación de procesos de separación con membranas y resinas de intercambio catiónico.
Características técnicas
Las experiencias realizadas por el grupo UBUCOMP en laboratorio , demuestran que es posible lograr un descenso significativo en el contenido metálico de lodos de depuradora, tanto si son procedentes de tratamiento primario, secundario o tras un proceso de digestión anaerobia. El escalado a planta piloto es factible desde el punto de vista operacional y de costes, siendo una opción interesante para la obtención de un lodo final desmetalizado de potencial uso como fertilizante orgánico.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
La reducción de la carga metálica de los lodos de depuradora en un proceso in situ a desarrollar en la planta de tratamiento, es una opción factible desde el punto de vista técnico y económico que se puede incorporar a la propia gestión de los lodos. La mejora del proceso permitiría la recuperación de fracciones metálicas y un producto final cuya carga orgánica y contenido de nutrientes pueden constituir la base para la formulación de un fertilizante orgánico.
Aplicaciones
La técnica puede ser de interés para gestores de lodos de depuradora, de plantas EDAR, de vertederos de residuos o de plantas industriales que generen efluentes con elevada carga orgánica y metálica.
Estado actual de desarrollo
Investigación o Experimental
Relación deseada
Cooperación técnica - mayor desarrollo
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos han desarrollado una instalación de tratamiento de aguas residuales basada en biorreactores de membrana. Esta instalación permite mantener elevadas concentraciones de biomasa activa en las etapas de reacción y una baja concentración de sólidos suspendidos en el tanque de filtración, reduciéndose el ensuciamiento de las membranas de filtrado de la instalación y mejorando con ello el rendimiento y la efectividad de dicha instalación.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La presente instalación para el tratamiento de aguas residuales está basada en biorreactores de membrana y constituida por cuatro etapas, de las que tres son de tratamiento biológico (un biorreactor de cultivo suspendido y dos biorreactores de cultivo adherido), y una etapa de filtración.
El biorreactor de cultivo suspendido del tipo “manto de lodos” es un tanque en el que se desarrollan microrganismos que biodegradan el material orgánico presente en el agua residual a tratar se agregan formando gránulos o flóculos. Los biorreactores de “cultivo adherido” son aquellos donde el agua a tratar entra en contacto con películas de microorganismos adheridas, en este caso a las superficies de los materiales de relleno desordenados.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Permite mantener elevadas concentraciones de biomasa activa.
- Mantiene una baja concentración de sólidos suspendidos en el tanque de filtración.
- Se reduce el ensuciamiento de las membranas de filtrado de la instalación.
- Emplea un volumen reducido de material de relleno.
- Se mejora el rendimiento y la efectividad de la instalación.
Características técnicas
La instalación para el tratamiento de aguas residuales caracterizada por estar conformada por cuatro etapas, tres de tratamiento biológico (1, 2, 3) y una de filtración. La primera etapa de tratamiento biológico (1) aloja en su interior un material de relleno inerte desordenado donde se adhieren los microorganismos encargados del tratamiento biológico del agua residual. La segunda etapa de tratamiento biológico (2) incluye un cultivo suspendido del tipo manto de lodos donde se acumulan los microorganismos encargados del tratamiento biológico del agua residual procedente de la etapa (1), y permite mantener una elevada concentración de biomasa activa con un mínimo coste de construcción. La tercera etapa de tratamiento biológico (3) posee en su interior un material de relleno inerte desordenado para la retención de los microorganismos que abandonan la etapa (2). Esta etapa tiene una función protectora de las membranas del tanque de filtración y permite agregar los flóculos de microorganismos arrastrados por el flujo ascendente del agua y defectos de desgasificación del biorreactor principal. La etapa de filtración (4) aloja en su interior módulos de membrana de ultrafiltración sumergidos. Este tanque de filtración presenta además un sistema de agitación por inyección de burbujas de gas.
Aplicaciones
Las potenciales aplicaciones de la instalación son las siguientes:
- Tratamiento de aguas residuales industriales
- Tratamiento de aguas residuales urbanas
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención P202130509
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Investigadores de la Universidad de Burgos han patentado un nuevo panel solar híbrido, que permite optimizar el proceso de generación conjunta de energías eléctrica y térmica consiguiendo un mayor rendimiento y mejor almacenamiento de calor en condiciones de baja energía lumínica mediante un aprovechamiento óptimo del espacio.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Los aspectos innovadores que presenta son:
- Dispone de una acumulación de calor integrada mediante la utilización de materiales de cambio de fase PCM.
- El concepto patentado hace posible que el diseño fácilmente sea escalable y adaptable, a diferencia de otros paneles.
- El material de cambio de fase se calienta tanto por la radiación transmitida desde el panel fotovoltaico como por la del caloducto (heat pipe), esto supone una transmisión de calor optimizada.
- Utilización de materiales no contaminantes.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Las principales ventajas de su utilización
- Permite la generación simultánea de calor y electricidad. También permite el almacenamiento de la energía térmica generada.
- Permite incrementar el valor de energía térmica generada, pudiendo variar la relación calor/electricidad ajustándola a las necesidades de cada aplicación concreta.
- Permite poder utilizar el calor cuando sea necesario, aunque la radiación solar sea reducida.
- El panel solar permite una eficiencia energética mejorada frente a otros paneles conocidos, gracias a la refrigeración extra que se aporta al panel fotovoltaico, con el material de cambio de fase.
- El diseño permite que la energía residual en forma de calor se aproveche para calentar el fluido y el material de cambio de fase, logrando una eficiencia global muy elevada, hasta el 60-70%, o incluso superior.
- Permite generar dos recursos energéticos mediante el mismo dispositivo no siendo necesaria la instalación de dos paneles (fotovoltaico y térmico) para generar la energía. La necesidad de utilizar menos estructuras de anclaje hace que el coste de la instalación se vea reducido
A efectos prácticos la utilización de este panel supone:
- Un aumento de la energía eléctrica: +15%
- Generación de agua caliente (o aire)
- Ahorro de espacio (2x1)
- Optimización y un gran rendimiento global del panel
- Ahorro costes: estructura, colector, combustible
- No tiene mantenimiento
Características técnicas
Panel solar híbrido diseñado para conseguir un mejor almacenamiento de calor en condiciones de baja energía lumínica, que comprende un panel fotovoltaico, un colector térmico dispuesto en la cara del panel fotovoltaico, opuesta a la radiación solar y un material de cambio de fase. El colector térmico se encuentra embebido en el material de cambio de fase, dicho colector térmico se dispone en correspondencia con la cara del panel fotovoltaico, opuesta a la que recibe la radiación solar. Un caloducto, cerrado en ambos extremos, en correspondencia con la cara del colector térmico opuesta al panel fotovoltaico, permite la evaporación y la condensación del fluido que alberga en su interior. Al menos una porción del caloducto está en contacto con el material de cambio de fase y otra porción del caloducto recibe la radiación solar.
Aplicaciones
El Kit Solar Hibrido de puede ser utilizado de forma general en:
- Hoteles
- Residencias de ancianos
- Polideportivos
- Granjas
- Industria
- Hospitales
- Edificios residenciales
- Viviendas unifamiliares.
Además las ventajas y la tecnología de este panel hace que sea adecuado para ser instalado en lugares reducidos como:
- Autocaravanas.
- Barcos,
- Casetas de obra,
- Oficinas portátiles
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención P201930047
Estado actual de desarrollo
Se disponen de varios prototipos así como una instalación que permite realizar pruebas con diferentes condiciones de funcionamiento.
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Dispositivo para ser acoplado a las sillas de ruedas con objeto de dar protección a los usuarios de las mismas frente a las condiciones climáticas adversas tales como las precipitaciones de lluvia, nieve o granizo o frente al viento, así como la protección frente a la radiación solar directa.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Se trata de una capota rígida que da estabilidad al conjunto de la silla y aumenta el grado de protección ante la lluvia y el viento.
Dispone de un mecanismo que se acciona de forma automática por lo que el usuario de la misma no tiene ningún impedimento de accionarla sin ayuda de otra persona.
Dispone de protección solar, así como paredes laterales que protegen ante las inclemencias cuando las ráfagas viento o lluvia son laterales.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Protección del usuario ante las inclemencias del tiempo en cualquier época del año.
- Mayor autonomía del usuario de la silla en cualquier circunstancia, haciendo que las condiciones meteorológicas adversas no sean impedimento en la vida diaria.
- Dispone de zona opaca y translucida por lo que también protege de las radiaciones solares.
Características técnicas
Se trata de una capota retráctil para sillas de ruedas motorizadas que comprende una cubierta superior rígida compuesta, un eje motriz que se conecta a un motor eléctrico solidario al cuerpo de la capota, dos cuadriláteros articulados de barras a ambos lados de la capota se encargan de transmitir el movimiento de plegado y desplegado a la cubierta. Por último dispone de unas placas laterales con forma de sector circular que se abren y cierran de forma secuencial a ambos lados de la silla de ruedas y que ofrecen protección lateral al usuario.
Aplicaciones
De cara al usuario:
Mejora de la autonomía y calidad de vida al disponer un modelo de silla de ruedas que se acciona de forma automática y que permite ser utilizado en cualquier estación del año.
De cara al fabricante:
Implantar una solución que permitiría a la empresa comercializadora disponer una silla de ruedas que sería una novedad frente a la competencia y disponer por tanto de un producto diferenciado.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegido mediante patente P201201037
Estado actual de desarrollo
Esta desarrollado a nivel de diseño y protegido mediante patente.
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La presente invención se refiere a un dispositivo inflable de salvamento para personas, y el procedimiento de utilización del mismo, que permite ser empleado para poder evacuar el personal de edificios altos en situaciones de emergencia, como pudiera ser un incendio, peligro de colapso inminente del mismo, u otras situaciones que impidan o aconsejen la no evacuación por su interior.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Actualmente los dispositivos existentes de evacuación en caso de emergencia en edificios incluyen principalmente dispositivos del tipo montacargas, toboganes de escape y diversos sistemas de paracaídas, estos últimos basados en la resistencia que sus componentes ofrecen al aire.
El aspecto innovador de este dispositivo de salvamento se encuentra en su diseño que emplea un sistema inflable basado fundamentalmente en las fuerzas de resistencia aerodinámica. El gas de inflado es nitrógeno, cuya densidad es algo menor a la del aire, por lo que el efecto de flotación es muy pequeño.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
* Puede ser empleado por personas adultas. En caso de la existencia de niños o de mayores discapacitados el dispositivo puede utilizarse en tándem acompañados de otra persona con facultades normales
* Permite un descenso controlado
* No exige que el usuario tenga que tener conocimientos previos como en el caso de paracaídas, o hacer ningún tipo de control en el dispositivo
* Su utilización no requiere edificios de excesiva altura
Características técnicas
El dispositivo adquiere forma de campana hueca y la forma se consigue por inflado en su interior con nitrógeno procedente de la ignición de cartuchos pirotécnicos de azida de sodio, situados en la mochila.
Dado que el espacio no es vacío, sino que esta relleno de aire, éste presentará una resistencia al ser atravesado, que hace que velocidad de caída alcance un valor de equilibrio dinámico entre fuerzas de atracción terrestre, fuerzas de resistencia aerodinámica y fuerzas de flotación por diferencia de densidad con el aire.
Aplicaciones
Dispositivo que puede formar parte del sistema de seguridad y evacuación de edificios en caso de emergencia. También podría emplearse con fines lúdicos y deportivos.
Propiedad Intelectual
Patentado P201200639
Estado actual de desarrollo
Prototipos funcionales
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La presente tecnología se refiere a un nuevo procedimiento general para la reducción de sulfóxidos a sulfuros empleando [MoO2Cl2(dmf)2] como catalizador y polioles (pinacol o glicerol) como reductor. Los productos se obtienen con rendimientos excelentes. Este nuevo procedimiento destaca por utilizar un agente reductor fácilmente accesible, no tóxico y que genera subproductos igualmente no tóxicos y fácilmente separables del sulfuro sintetizado.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La principal novedad del presente método es el empleo de polioles (pinacol o glicerol) como agente reductor, lo que implica una serie de ventajas sobre los métodos tradicionalmente empleados para la reducción de sulfóxidos a sus correspondientes sulfuros. Así, se han venido utilizando compuestos que contienen azufre, tales como tioles, sulfuro de hidrógeno, ácidos carboditiónicos, tiofosfónicos o tiofosfóricos, cloruro de sulfonilo o de sulfinilo, disulfuros, azufre elemental (S8) y cloruro de tionilo. Sin embargo, estos métodos presentan ciertas desventajas, haciendo necesario el desarrollo de nuevas alternativas.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Entre las desventajas de muchos de los métodos conocidos para la reducción de sulfóxidos a sulfuros se encuentran las condiciones de reacción que resultan incompatibles con la presencia de grupos funcionales sensibles en la molécula. Igualmente, muchos de estos métodos conocidos dan lugar a subproductos difícilmente separables del producto final, que hacen necesarias tediosas y costosas etapas de purificación para obtener el producto puro. Muchos de los subproductos, reductores y disolventes empleados en las reacciones según los métodos anteriores son tóxicos y medioambientalmente problemáticos.
Sin embargo, el procedimiento para la reducción de sulfóxidos de la presente invención se basa en la utilización de pinacol o glicerol, como agentea reductores, compuestos fácilmente accesibles y manejables; genera subproductos fácilmente separables y medioambientalmente inocuos y permite la obtención de sulfuros de elevada pureza con un alto rendimiento sin necesidad de costosos procedimientos de separación cromatográficos. El procedimiento de la invención tiene además la ventaja de no necesitar atmósfera inerte ni disolventes orgánicos, con las consecuentes beneficios económicos y medioambientales.
Características técnicas
La presente invención se refiere a un procedimiento para la reducción catalítica de compuestos orgánicos que incluyen un grupo funcional sulfóxido a compuestos tipo sulfuro, que incluyen un grupo funcional tioéter, mediante la utilización de polioles (pinacol (2,3-dimetil-2,3-butanodiol) o glicerol (propano-1,2,3-triol) como agente reductor en presencia de un catalizador de molibdeno (VI), en un medio libre de disolventes orgánicos, bajo presión atmosférica y a una temperatura entre 80-90 ºC, en el caso del pinacol, y entre 170 ºC y 200ºC, en el caso del glicerol, generando subproductos no tóxicos y facilmente separables.
Aplicaciones
La técnica permite la síntesis de compuestos que contengan un sulfuro en su estructura, que pueden presentar diversas propiedades (fármacos, pesticidas, materiales...) ya demostradas. Por tanto, aplicabilidad en la industria farmacéutica, agroquímica, etc.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegido por patente.
Número de solicitud: P201001413
Número de solicitud: P201200455
Estado actual de desarrollo
Investigación o experimental
Relación deseada
Acuerdo Comercial
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
La invención se refiere a un nuevo procedimiento general para la reducción de nitroarenos a anilinas empleando un catalizador de Mo (VI) y pinacol como agente reductor. Los productos que se obtienen presentan rendimientos excelentes. Este nuevo procedimiento destaca por utilizar un agente reductor fácilmente accesible, no tóxico y que genera subproductos igualmente no tóxicos y fácilmente separables de la amina sintetizada.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
La principal novedad de la presente invención es el uso de pinacol como agente reductor, lo que conlleva una serie de ventajas indiscutibles sobre los métodos clásicos de reducción de nitrocompuestos, que se engloban en dos grupos: (a) hidrogenación catalítica empleando hidrógeno molecular, y (b) reducción química, habitualmente con un metal en medio ácido.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Las ventajas de la nueva metodología respecto a las clásicas son:
- Frente a la hidrogenación catalítica: La reacción es más selectiva, no produciéndose la reducción de otros grupos como olefinas, carbonilos, nitrilos o halógenos. El nuevo proceso no implica el manejo y almacenamiento de hidrógeno gas, todos los reactivos son sólidos o líquidos fácilmente manipulables.
- Frente a la reducción con metales en medio ácido: El nuevo proceso es más selectivo, permite la reducción de compuestos con grupos funcionales sensibles al medio ácido y emplea cantidades catalíticas del complejo metálico (no siempre posible en las reducciones en medio ácido).
- Frente a ambas metodologías clásicas: El nuevo proceso tiene lugar generalmente en tiempos de reacción más cortos y en condiciones más suaves. La reacción se lleva a cabo al aire, no hay necesidad de emplear atmosfera inerte. Los subproductos generados son fundamentalmente agua y acetona, medioambientalmente benignos y fácilmente separables del medio de reacción. Aislamiento de las aminas con pureza analítica sin necesidad de cromatografía de columna (ventajas económicas y medioambientales)
Características técnicas
La presente invención se refiere a un procedimiento para la reducción catalítica de compuestos orgánicos que incluyen un grupo funcional nitro a compuestos que incluyen un grupo funcional amino mediante la utilización de pinacol (2,3-dimetil-2,3-butanodiol) como agente reductor en presencia de un catalizador de molibdeno (VI), en un disolvente orgánico, a presión atmosférica o superior y a una temperatura entre 110-150 ºC, generando como principales subproductos agua y acetona.
Aplicaciones
Síntesis de aminas aromáticas, que pueden presentar diversas propiedades (fármacos, pesticidas, materiales...) ya demostradas. Por tanto, aplicabilidad en la industria farmacéutica, agroquímica, etc.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegido por patente P201100596. Fecha de concesión: 05/07/2013
Estado actual de desarrollo
En fase de Investigación y fase experimental
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Material polimérico que en presencia de aminas biógenas volátiles presenta propiedades colorimétricas. La presencia de aminas biógenas se relaciona con el deterioro del pescado convirtiéndose en un indicador de frescura y calidad para su óptimo consumo.
El material desarrollado es capaz de determinar aminas biógenas tanto en disolución como en fase gaseosa.
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Esta tecnología permite el diseño y realización de etiquetas inteligentes que mediante una escala de color informan al consumidor de la calidad y frescura en pescados. Las etiquetas pueden ser aplicadas en forma de tejido, por recubrimiento de fibras, filmes o películas.
Otro aspecto innovador con respecto a otras tecnologías es que pueden presentarse en diferentes formatos en función de las necesidades permitiendo el recubrimiento de otro tipo de materiales poliméricos y no poliméricos por métodos convencionales, mediante impresión, u otros procedimientos conocidos.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Determinación de la calidad y frescura de pescado envasado a través de una escala de color sencilla
- Fabricación del material polimérico de forma sencilla y muy económica
- Versatilidad de fabricación en diferentes formas y tamaños
Características técnicas
Material polimérico que comprende un polímero con grupos trinitrobenceno, y uso de éste como sensor colorimétrico para aminas.
Este material sensor se puede obtener o transformar en diferentes formatos, como membranas, filmes, fibras o recubrimientos mediante la preparación del material polimérico y la modificación química de grupos aromáticos presentes en los polímeros de partida que contienen restos aromáticos, en particular grupos fenilo. El material polimérico cambia de color ante compuestos químicos que contienen grupos amino, tanto primarios como secundarios o terciarios, tanto en disolución como en fase gaseosa; siendo este cambio de color claramente perceptible a simple vista.
La aplicación de estos sensores puede ser tanto en la solución y en fase gaseosa.
Aplicaciones
- Calidad y seguridad alimentaria: Determinación de la calidad del pescado a través de los cambios de color de las etiquetas incorporadas en el propio envase.
- Fabricación de textiles inteligentes capaces de determinar aminas biógenas en ambientes de trabajo facilitando la prevención de riesgos laborales.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegido por patente P201400595
Estado actual de desarrollo
En uso, resultados de pruebas disponibles
Relación deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Social and Economics concerns (8)
Resumen de la tecnología
Es una aplicación para dispositivos móviles que permite al personal sanitario evaluar las asistencias domiciliarias.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Es una aplicación para dispositivos móviles que mejora la calidad de las valoraciones, la eficiencia y eficacia del personal sanitario y moderniza el sistema de recogida de información en la asistencia domiciliaria.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Uso práctico y sencillo: olvídate del papel, todos los test de evaluación en una sola aplicación y para cualquier dispositivo móvil.
- Facilita el trabajo de los profesionales sanitarios en sus visitas domiciliarias
- Mejora la eficiencia y eficacia del personal sanitario: se obtiene el resultado del test al momento. Permite revisar el historial del paciente antes de la visita
- Moderniza el sistema de recogida de información del personal sanitario en la asistencia domiciliaria
- Mejora la valoración al paciente: permite crear anotaciones sobre la visita y comparar con resultados anteriores.
Características técnicas
La aplicación permite aglutinar todos los test de los diferentes pacientes en un mismo lugar ahorrando tiempo y dinero y haciendo que la asistencia domiciliaria sea más eficaz. Esta aplicación mejora la eficacia y eficiencia del personal sanitario ya que permite obtener los resultados de los diferentes test realizados al momento, además, permite revisar el historial del paciente antes de la visita. Y UBUnurse también permite mejorar la valoración del paciente ya que permite crear anotaciones sobre la visita y comparar con resultados anteriores.
Aplicaciones
Las posibles aplicaciones son en el entorno de enfermería domiciliaria y en centros socio-sanitarios.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante Registro propiedad intelectual BU-102-17
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización. Esta aplicación cuenta con una página web oficial. También existe una cuenta de YouTube donde se encuentran vídeos explicativos (cómo instalar la aplicación y cómo registrarse en la app).
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente concedida
BU-102-17
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Se trata de un dispositivo para mejorar el proceso de rehabilitación de las personas que adolecen de “mano en garra”.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
En la actualidad, los dispositivos destinados a la rehabilitación de “mano en garra” no son capaces de rehabilitar de forma autónoma, previa programación, los dedos de la mano dañada, ni existe en la actualidad ningún dispositivo motorizado para realizar tal función. Además, los procesos de rehabilitación con los sistemas actuales no se acercan a lo que debe ser una rehabilitación pasiva adecuada, que consiste, fundamentalmente en realizar repeticiones sucesivas, manteniendo el estiramiento durante un breve periodo de tiempo. Por tal motivo el tratamiento de rehabilitación, en la actualidad, lo realiza el terapeuta con sus propias manos durante sesiones de tiempo prefijadas por lo que los dispositivos existentes en la actualidad sólo se pueden considerar un complemento al tratamiento realizado por el fisioterapeuta.
El dispositivo descrito es autónomo y se encarga de realizar los esfuerzos mediante motores, gobernados por ordenador. El dispositivo permite un mejor control del esfuerzo realizado sobre los tendones de cada articulación de la mano de cada paciente, así como de las cargas y magnitudes alcanzadas en cada sesión de rehabilitación. Además esta invención permite que el fisioterapeuta pueda hacer terapia con varios pacientes a la vez, ya que el dispositivo es autónomo y funciona obedeciendo el ciclo individual marcado.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
• Dispositivo autónomo
• Permite que el fisioterapeuta pueda hacer terapia con varios pacientes a la vez
• El fisioterapeuta programa los ejercicios que el dispositivo va a realizar durante cada sesión de tratamiento de rehabilitación.
Características técnicas
El dispositivo para la rehabilitación de pacientes con la patología de “mano en garra” consta de una férula rígida de polímero termoestable donde el paciente debe introducir el antebrazo y la mano que debe ser rehabilitada.
El dispositivo dispone de cinco motores, paso a paso programables.
El dispositivo realiza de forma repetitiva el número de ciclos a la tensión estipulada por el terapeuta, en cada uno de los dedos de la mano a rehabilitar.
Aplicaciones
Las posibles aplicaciones son la rehabilitación de personas que padecen "mano en garra"
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante patente de invención P201300328
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo en etapa conceptual
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Se trata de un CD-Rom que recoge la creación y desarrollo de un Programa de actividades físicas y psico-socio-estimulativas (PESASMI) que proporcionan beneficios sobre la autonomía personal y la función física de las personas mayores institucionalizadas.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Se trata de un CD-Rom que recoge la creación y desarrollo de un Programa de actividades físicas y psico-socio-estimulativas (PESASMI) dirigido a personas mayores institucionalizadas. La participación continuada en un programa de actividades físicas y psico-socio-estimulativas produce beneficios en los participantes en su capacidad funcional (para desarrollar actividades básicas e instrumentales de la vida diaria), cognitiva, en su autoestima y en sus relaciones sociales.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Beneficios para los participantes en su capacidad funcional (para desarrollar actividades básicas e instrumentales de la vida diaria), cognitiva, en su autoestima y en sus relaciones sociales.
- Autonomía en la vida diaria
- Desarrollo personal
- Envejecimiento saludable y activo
Características técnicas
Se trata de un CD-Rom que recoge la creación y desarrollo de un Programa de actividades físicas y psico-socio-estimulativas (PESAMI) dirigido a personas mayores institucionalizadas.
Aplicaciones
Los posibles lugares de aplicación son centros socio-sanitarios como residencias para mayores, centros de día, clínicas especializadas, asociaciones y hospitales.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante: ISBN 978-84-92681-00-6
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo desarrollado y validado para su industrialización.
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente concedida
ISBN 978-84-92681-00-6
https://www.ubu.es/catalogo-de-publicaciones/programa-de-envejecimiento-saludable-activo-y-satisfactorio-con-mayores-institucionalizados-pesasmi
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
ARQuiz es un juego educativo personalizable para dispositivos móviles. ARQuiz es una aplicación diseñada con el fin de aprender y cuyas posibilidades de uso son ilimitadas.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
- Nuevas plataformas como Android
- Nuevas tecnologías como Realidad Aumentada
- Ámbito educativo: niños, mayores, discapacitados
- Interacción con las figuras a la hora de selección de las mismas
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Sencillez de uso de la herramienta
- Puede ser utilizada por niños, personas mayores y personas con discapacidad
Características técnicas
El juego muestra varios objetos (representados mediante el uso de la realidad aumentada en cualquier lugar de la pantalla del dispositivo móvil) y el objetivo del usuario es localizar aquellos que las pistas le vayan indicando.
Se dispone inicialmente de diversas categorías por defecto (figuras geométricas, animales, objetos de cocina, de baño…) y niveles de dificultad, pudiendo variar desde simplemente buscar un cubo hasta encontrar la forma en 3 dimensiones que tenga 30 aristas.
El usuario puede crear sus propias categorías, preguntas, niveles, y añadir sus diseños 3D desde el almacenamiento interno con sencillos menús, ofreciéndole la posibilidad de crear un juego a medida.
El software aplica la realidad aumentada en Smartphones y Tablets que cuenten con un sistema operativo Android y la correspondiente cámara.
Aplicaciones
Sector educativo. Formación de niños, personas discapacitadas y apoyo al envejecimiento. Hace hincapié en el aprendizaje de formas, colores, palabras, conceptos, idiomas, etc.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante registro propiedad intelectual BU-146-13
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo disponible para comercialización
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente concedida
BU-146-13
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Se trata de una aplicación informática útil para personas que necesiten realizar sesiones de rehabilitación mediante la repetición de ejercicios. Ayuda en el diseño y la gestión de los resultados de los protocolos de seguimiento aplicados en la recuperación de lesiones o en los ejercicios de mantenimiento.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
El objetivo perseguido es fundamentalmente cubrir una necesidad detectada en el seguimiento de los tratamientos de rehabilitación mediante la implantación de tecnologías actuales que permita:
- Realizar un seguimiento de paciente. Partiendo de la situación inicial del paciente antes de someterse al tratamiento, el objetivo final es la emisión de un informe con la evolución conseguida mediante las distintas sesiones planificadas por el personal facultativo.
- Diseñar los ejercicios de forma personalizada adaptados a la necesidad de cada paciente
- Captar la atención del paciente con temáticas interesantes acordes con su edad, a través de cambios de función especificados en el programa informático.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
La sencillez de uso de la herramienta, permite a cualquier usuario con conocimientos básicos de informática poder utilizarla de forma autónoma e intuitiva.
Características técnicas
La tecnología de Realidad Aumentada consiste en el posicionamiento de marcas – códigos de barras bidimensionales- mediante el uso de cámara web y la posterior representación en pantalla. Con el reconocimiento de las marcas por parte de la Webcams se busca capturar coordenadas del movimiento de personas para guardar posteriormente esos datos y visualizar la evolución del paciente.
Aplicaciones
- Esta herramienta es adecuada para uso en hospitales y centros de rehabilitación.
- Uso individual en pacientes con largas sesiones de rehabilitación que les permita seguir el tratamiento en su domicilio.
- Mejora en los resultados de los programas de envejecimiento activo.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante registro propiedad intelectual BU-8-12
Estado actual de desarrollo
Prototipo de trabajo o muestras listas para pruebas
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente concedida
BU-8-12
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Aplicación para facilitar el uso de la consola Wii de Nintendo para el acceso a redes sociales y correo electrónico. Destinado a personas mayores con dificultades de acceso a las tecnologías de la información.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Proporciona una interfaz sencilla, gráfica y dinámica. Uso de tecnología de videojuegos de bajo coste para uso asistivo. No necesita inversión extra en hardware. Independencia del PC.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Resulta una forma sencilla de acceder a las tecnologías de la información sin necesidad de un gran esfuerzo de aprendizaje. Proporciona un acceso inmediato a las herramientas de comunicación sin necesidad de conocimientos de informática.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
Resulta una forma sencilla de acceder a las tecnologías de la información sin necesidad de un gran esfuerzo de aprendizaje. Proporciona un acceso inmediato a las herramientas de comunicación sin necesidad de conocimientos de informática.
Aplicaciones
Ayuda al envejecimiento activo y a la comunicación entre personas mayores y con el resto de la sociedad.
Propiedad Intelectual
Programa de Ordenador con Copyright - BU-159-12
Estado actual de desarrollo
Prototipo de trabajo o muestras listas para pruebas
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente concedida
BU-159-12
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
HADA (Herramienta de Asistencia para Discapacitados Auditivos) es una herramienta preparada para las personas con problemas auditivos, que facilita la comunicación rompiendo las barreras presentes en la sociedad con dichas deficiencias.
Interfaz de usuario, sencilla e intuitiva, con la posibilidad de elección y configuración de las distintas modalidades (recepción de texto, vídeo, vídeo subtitulado).
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Por medio de un componente de transcripción del habla, nuestra aplicación recoge el texto y lo emite a los clientes conectados a nuestro servidor en tiempo real.
Además del texto recopilado, podemos emitir el vídeo capturado desde nuestra WebCam, un archivo de vídeo, de texto, que tengamos en nuestro propio ordenador.
Presenta amplia funcionalidad. Además de la transmisión de datos, HADA permite tratar archivos de subtitulado, grabación, reproducción, etc.
Tiene una interfaz sencilla e intuitiva, pantalla de aplicación simple, con botones de acceso descriptivos, acorde a sus funcionalidades. Distintos modos de visualización, en función de la elección del usuario, se ofrecen distintas interfaces (recepción de texto, vídeo subtitulado, etc.)
Las opciones de configuración son múltiples, la aplicación es completamente configurable, a las necesidades del usuario.
Presenta privacidad de uso, cerrada al grupo de usuarios conectados.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Ayuda a entender la información del entorno a personas con discapacidades auditivas y cuya información no pueden captar en situaciones donde la comunicación es principalmente oral.
- Una forma de eliminar las barreras de comunicación que sufre la comunidad con discapacidad auditiva, es la desarrollada con nuestro software HADA, que mediante la transmisión en tiempo real del texto capturado (como resultado de la transcripción procedente del audio recibido desde nuestro micrófono) acaba con dichos problemas.
Características técnicas
Software basado en ordenador de sobremesa con reconocimiento de voz. Su uso configurable como cliente y como servidor.
Aplicaciones
Especialmente útil para personas con deficiencias auditivas en situaciones de ámbito laboral, conferencias, presentaciones y reuniones, comunidad docente (colegios, institutos, universidades), ocio, uso doméstico.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante registro propiedad intelectual BU-39-11
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo en etapa conceptual
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Patente concedida
BU-39-11
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Resumen de la tecnología
Nuevo método de enseñanza/aprendizaje que permite que las personas ciegas o con dificultades visuales tengan acceso al aprendizaje del chino. Dado que la esencia del chino se encuentra en su escritura y en sus caracteres, se ha ideado un sistema para que las personas invidentes puedan aprender y reconocer fácilmente los caracteres y escribirlos.
Description of the technology
Aspectos nuevos e innovadores
Se propone el desarrollo de un dispositivo para un sistema de aprendizaje de un idioma basado en el uso de piezas, para personas ciegas o con discapacidad visual. El dispositivo representa una estructura innovadora de características estructurales y constitutivas desconocidas hasta el momento. Este permite el aprendizaje de chino a través del Sistema de braille occidental (seis puntos). Además, el método incluye un libro en braille, un diccionario táctil y un soporte para escribir los caracteres.
Principales ventajas derivadas de su utilización
- Permite aplicar un método de aprendizaje de chino para personas ciegas o con dificultades visuales.
- Potencia los sentidos del tacto y del oído.
- El uso de piezas como sistema facilita el aprendizaje de chino.
- El método está escrito en el sistema de braille occidental, por lo que no es necesario que los usuarios aprendan el sistema de braille oriental.
Características técnicas
El dispositivo para un sistema de aprendizaje de un idioma basado en el uso de una pluralidad de piezas, para personas ciegas o con discapacidad visual, comprende una pluralidad de paneles agrupados entre sí. cada uno de los paneles, está configurado para ubicar una pluralidad de piezas dispuestas en filas y columnas. Adicionalmente, puede incluirse una cobertura extraíble situada en la parte superior.
Cada uno de los paneles incluye inscripciones gráficas a modo de número y/o letras del alfabeto, generando unas coordenadas alfanuméricas, de modo que puede facilitar al usuario la implementación del método de aprendizaje.
Aplicaciones
- Dispositivo que permite aplicar un método de aprendizaje para personas ciegas o con dificultades visuales para aprender chino de forma sencilla.
- El usuario puede traducir frases del braille occidental a chino mandarín.
Propiedad Intelectual
Protegida mediante modelo de utilidad U202130050
Estado actual de desarrollo
Dispositivo en fase conceptual
Relación comercial deseada
Acuerdo comercial, Acuerdo de licencia, Cooperación técnica: un mayor desarrollo, Cooperación Técnica: testar nuevas aplicaciones; Cooperación Técnica: adaptación a necesidades específicas.
Intellectual property status
Información adicional (documentos adjuntos)
Sobre Universidad de Burgos
El objetivo de la Oficina de Transferencia de Conocimiento (OTRI) de la Universidad de Burgos es promover la Innovación tecnológica a través de la transferencia de resultados de investigación y las conexiones entre la Universidad y los nuevos requerimientos y realidades de la sociedad - somos el vínculo entre la Universidad y la Industria. Persona de Contacto: José Manuel López (jmllopez@ubu.es)
Start collaborating Now!
We are currently seeking best-in-class collaboration partners for the postings listed below. You can respond to current opportunities by browsing the listed entries. We do want to invite you to cooperate with us so please contact us through the available template and we will get in contact with you. Please provide as much detailed information as possible in order to facilitate the engagement process.
Contact Person

SUSANA CÁMARA DECIMAVILLA
Universidad de Burgos